Abstract
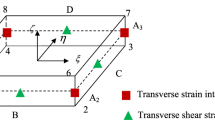
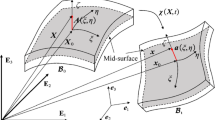
This paper investigates the numerical modeling of low velocity impact of composite multilayered plates using the smoothed particle hydrodynamics (SPH) method. Recently the authors developed a shell-based SPH (SSPH) model for the modeling of large deformations of composite multilayered structures, has been extended to the impact modeling. The proposed new shell-based SPH formulation is based on the Mindlin–Reissner theory which accounts for transverse shearing stresses. In the present investigation, the impact modeling solution is estimated using the explicit dynamics integration scheme, together with the Hertzian contact theory, for the fast estimation of contact forces. The predictive capability of the present SSPH model is demonstrated by comparison of the results with reference solutions for the impact response of composite multilayered plates.













Similar content being viewed by others
References
General Union Environment, Action Programme to 2020: living well, within the limits of our planet (2014). ISBN 978-92-79-34724-5. doi:10.2779/66315. Publications Office of the European Union
Panciroli R, Abrate S, Castani B, Rajapakse YDS (2013) Dynamic failure of composite and sandwich structures. Solid Mechanics and Its Applications 192. Springer, Netherlands. ISBN:978-94-007-5329-7
Yang SH, Sun CT (1982) Indentation law for composite laminates. ASTM STP 787:425–429
Tan TM, Sun CT (1985) Use of static indentation laws in the impact analysis of laminated composite plates. J Appl Mech 52:6–12
Aslan Z, Karakuzu R, Okutan B (2003) The response of laminated composite plates under low-velocity impact loading. Compos Struct 59:119–127
Abrate S (1998) Impact on composite structures. Cambridge University Press, Cambridge. ISBN-100-521-01832-3
Suemasu H, Herth S, Maier M (1994) Indentation of spherical head indentors on transversely isotropic composite plates. J Compos Mater 28(17):1723–1739
Wu E, Yen CS (1994) The contact behavior between laminated composite plates and rigid spheres. J Appl Mech 61:60–66
Choi IH, Lim CH (2004) Low-velocity impact analysis of composite laminates using linearized contact law. Compos Struct 66:125–132
Setoodeh AR, Malekzadeh P, Nikibin K (2009) Low velocity impact analysis of laminated composite plates using a 3D elasticity based layerwise FEM. Mater Des 30:3795–3801
Abrate S (2011) Impact engineering of composite structures. Series: CISM courses and lectures, vol 526. Springer, Wien. ISBN 978-3-7091-0523-8
Reddy JN (2004) Mechanics of laminated composite plates and shells: theory and analysis, 2nd edn. CRC Press, Boca Raton. ISBN 9780849315923
Zhang YX, Yang CH (2009) Recent developments in finite element analysis for laminated composite plates. Compos Struct 88:147–157
Yousefi P, Hosseini-Hashemi Sh, Kargarnovin MH (2012) Force vibration of laminated plates with various shapes subjected to low-velocity impact. J Mater Sci Res 1(3):106–116
Khalili MHA, Ardali A (2013) Low-velocity impact response of doubly curved symmetric cross-ply laminated panel with embedded SMA wires. Compos Struct 105:216–226
Ghasemi FA, Raissi S, Malekzadehfard K (2013) Analytical and mathematical modeling and optimization of fiber metal laminates (FMLs) subjected to low-velocity impact via combined response surface regression and zero-one programming. Lat Am J Solids Struct 10(2):391–408
Wang ZX, Xu J, Qiao P (2014) Nonlinear low-velocity impact analysis of temperature-dependent nanotube-reinforced composite plates. Compos Struct 108:423–434
Belytschko T, Kam Liu W, Moran B, Elkhodary K (2013) Nonlinear finite elements for continua and structures, 2nd edn. Wiley, Hoboken. ISBN: 978-1-118-63270-3
Li S, Liu WK (2004) Meshfree particle methods. Springer, Berlin. ISBN-10: 3540222561
Liu GR, Gu YT (2005) An introduction to meshfree methods and their programming. Springer, Amsterdam. ISBN-10 1-4020-3228-5
Ferreira AJM, Kansa EJ, Fasshauer GE (2009) Progress on meshless methods. Edition Springer, Amsterdam. ISBN-10: 9048179971
Lucy LB (1977) A numerical approach to the testing of the fission hypothesis. Astron J 82:1013–1024
Gingold RA, Monaghan JJ (1977) Smoothed particle hydrodynamics: theory and application to non-spherical stars. Mon Not R Astron Soc 181:375–389
Belytschko T, Lu YY, Gu L (1994) Element-free Galerkin methods. Int J Numer Methods Eng 37:229–256
Atluri SN, Zhu T (1998) A new Meshless Local Petrov-Galerkin (MLPG) approach in computational mechanics. Comput Mech 22:117–127
Liew KM, Zhao X, Ferreira AJM (2011) A review of meshless methods for laminated and functionally graded plates and shells. Compos Struct 93:2031–2041
Xiao JR, Gilhooley DF, Batra RC, Gillespie JW Jr, McCarthy MA (2008) Analysis of thick composite laminates using a higher-order shear and normal deformable plate theory (HOSNDPT) and a meshless method. Compos Part B Eng 39:414–427
Krysl P, Belytschko T (1996) Analysis of thin plates by the element-free Galerkin method. Comput Mech 17:26–35
Guiamatsia I, Falzon BG, Davies GAO, Iannucci L (2009) Element-free Galerkin modelling of composite damage. Compos Sci Technol 69:2640–2648
Zhang A, Ming F, Cao X (2014) Analysis of thin plates by the element-free Galerkin method. Comput Mech 225(1):253–275
Lin J, Naceur H, Coutellier D, Laksimi A (2014) Geometrically nonlinear analysis of thin-walled structures using efficient shell-based SPH method. Comput Mater Sci 85:127–133
Lin J, Naceur H, Laksimi A, Coutellier D (2014) On the implementation of a nonlinear shell-based SPH method for thin multilayered structures. Compos Struct 108:905–914
Belytschko T, Guo Y, Liu WK, Xiao SP (2000) A unified stability analysis of meshless particle methods. Int J Numer Methods Eng 48:1359–1400
Hertz H (1881) Uber die berührung fester elastischer körper. Journal für die reine und angewandte Mathematik 92:156–171
Johnson KL (2003) Contact mechanics. Cambridge University Press, Cambridge. ISBN: 0-521-34796-3
Sun CT (1977) An analytical method for evaluation of impact damage energy of laminated composites. ASTM Spec Tech Publ 617:427–440
Karas K (1939) Platten Unter Seitlichen Stoss. Ing Arch 10(4):237–250
Mahajana P, Dutta A (1999) Adaptive computation of impact force under low velocity impact. Comput Struct 70:229–241
Wu HYT, Chang FK (1989) Transient dynamic analysis of laminated composite plates subjected to transverse impact. Comput Struct 31(3):453–466
LS-DYNA Keyword User’s manual, vol I, Ls-dyna R7.1 (revision: 5471). Edition: Livermore Software Technology Corporation (LSTC), Livermore, California, 26 May 2014
Qian Y, Swanson SR (1990) A comparison of solution techniques for impact response of composite plates. Comput Struct 14:177–192
Abrate S (2001) Modeling of impacts on composite structures. Comput Struct 51:129–138
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Lin, J., Naceur, H., Coutellier, D. et al. Numerical modeling of the low-velocity impact of composite plates using a shell-based SPH method. Meccanica 50, 2649–2660 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11012-015-0243-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11012-015-0243-8