Abstract
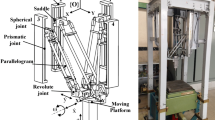
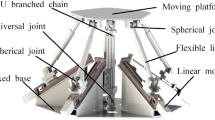
This paper carries out the elasto-dynamic analysis of a novel 2 degrees-of-freedom (DoF) rotational parallel mechanism (RPM) with an articulated travelling platform by means of kineto-elasto dynamic method. The architecture of the proposed 2-DoF RPM is firstly described, and then its kinematic analysis is carried out by closed-loop vector method. On the basis of finite element analysis, the elasto-dynamic models of movable components are established before assembling to formulate the elasto-dynamic equations of the whole mechanism in the light of deformation compatibility conditions. The free vibration equation is then achieved to evaluate the natural frequency of the novel 2-DoF RPM. Finally, an example is illustrated and the results are verified by finite element software. It shows that the relatively high natural frequencies and good dynamic performance make the novel 2-DoF RPM a promising solution for pose-adjusting module of 5-DoF machine centre.









Similar content being viewed by others
References
Li YG, Liu HT, Zhao XM, Huang T, Chetwynd DG (2010) Design of a 3-DOF PKM module for large structural component machining. Mech Mach Theory 45(6):941–954
Neumann KE (2002) Tricept applications. In: Proceedings of the 3rd Chemnitz parallel kinematics seminar, Zwickau, Germany, pp 547–551
Bruno S (1999) The Tricept robot: inverse kinematics, manipulability analysis and closed-loop direct kinematics algorithm. Robotica 17(4):437–445
Sun T, Song YM, Li YG, Zhang J (2010) Workspace decomposition based dimensional synthesis of a novel hybrid reconfigurable robot. ASME J Mech Robot 2(3):031009
Song YM, Lian BB, Sun T, Dong G, Qi Y (2014) A novel 5-DoF fully parallel manipulator and its kinematic optimization. ASME J Mech Robot 6(4):041008
Palpacelli M, Palmieri G, Carbonari L, Callegari M (2014) Experimental identification of the static model of the HPKM Tricept industrial robot. Adv Robot 28(19):1291–1304
Kong XW (2011) Forward displacement analysis and singularity analysis of a special 2-DOF 5R spherical parallel manipulator. ASME J Mech Robot 3(2):024501
Wu C, Liu XJ, Wang LP, Wang JS (2010) Optimal design of spherical 5R parallel manipulators considering the motion/force transmissibility. ASME J Mech Des 132(3):031002
Wu C, Liu XJ, Wang JS (2009) Force transmission analysis of spherical 5R parallel manipulators. In: Proceedings of the international conference on reconfigurable mechanisms and robots, London, England: 331-336
Baumann R, Maeder W, Glauser D (1997) The PantoScope: a spherical remote-center-of-motion parallel manipulator for force reflection. In: Proceedings of the 1997 IEEE international conference on robotics and automation, Albuquerque, New Mexico
Gosselin C, Caron F (1999) Two degree-of-freedom spherical orienting device. US Patent 5,966,991
Rosheim ME, Sauter GF (2002) New high-angulation omni-directional sensor mount. In: International symposium on optical science and technology. International society for optics and photonics, pp 163–174
Sofka J, Skormin V, Nikulin V, Nicholson DJ (2006) Omni-Wrist III-a new generation of pointing devices. Part I. Laser beam steering devices-mathematical modeling. IEEE T Aero Elec Sys 42(2):718–725
Chen B, Zong GH, Yu JJ, Dong X (2013) Dynamic modeling and analysis of 2-DOF quasi-sphere parallel platform. Chin J Mech Eng-En 49(13):24–31
Liu XJ, Wang JS, Xie FG (2008) A decoupled parallel spindle structure. CN Patent 101,269,465
Song YM, Dong G, Sun T, Zhao XM, Wang PF (2012) A novel parallel mechanism with two rotational degrees-of-freedom. CN Patent 2,012,105,131,575
Zhang C, Huang YQ, Wang ZL, Chen SX (1997) Analysis and design of the elastic linkages, 2nd edn. China Machine Press, Beijing
Bhatti MA (2005) Fundamental finite element analysis and applications. Wiley, Canada
Palmieri G, Martarelli M, Palpacelli MC, Carbonari L (2014) Configuration-dependent modal analysis of a cartesian parallel kinematics manipulator: numerical modeling and experimental validation. Meccanica 49(4):961–972
Acknowledgments
This research work was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant No. 51205278, 51475321), Ph.D. Programs Foundation of Ministry of Education of China (Grant No. 2012003211003, 2012003212003), and Tianjin Research Program of Application Foundation and Advanced Technology (Grant No. 13JCQNJC04600).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Song, Y., Dong, G., Sun, T. et al. Elasto-dynamic analysis of a novel 2-DoF rotational parallel mechanism with an articulated travelling platform. Meccanica 51, 1547–1557 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11012-014-0099-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11012-014-0099-3