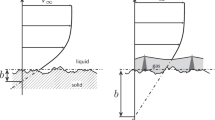
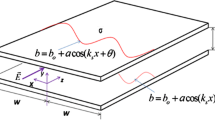
Abstract
Structured hydrophobic surfaces may present high wall slippage due to the microscopic details of wetting. This behavior can be exploited for reducing wall slippage in micro- and nanofluidic devices. In this work we focus on the influence of meniscus curvature and pressure on the slip length. We use realistic atomistic potentials in order to simulate liquid water (TIP4P/2005) flowing on a smooth/patterned silane (OTS) coated hydrophobic surface. Results confirm that even at the nanoscale the form of the meniscus has a strong influence on slippage. Continuum Navier-Stokes simulations show good agreement with the atomistic picture only if the shape of the meniscus and position of the triple line are correctly prescribed.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Squires T, Quake S (2005) Rev Mod Phys 77(3):977
Chinappi M, Melchionna S, Casiola C, Succi S (2008) J Chem Phys 129:124717
Li Z (2009) Phys Rev E 80(6):061204
Li H, Yoda M (2010) J Fluid Mech 662:269–287
Zhu L, Neto C, Attard P (2012) Langmuir 28(20):7768
Bouzigues C, Tabeling P, Bocquet L (2008) Phys Rev Lett 101(11):114503
Tsai P, Peters A, Pirat C, Wessling M, Lammertink R, Lohse D (2009) Phys Fluids 21:112002
Zhang H, Zhang Z, Ye H (2012) Microfluid Nanofluid 12:107–115
Lauga E, Brenner M, Stone H (2005) Microfluidics: The no-slip boundary condition. In: Handbook of experimental fluid dynamics (Chap. 15). Springer, Berlin
Chinappi M, Casciola C (2010) Phys Fluids 22:042003
Maali A, Bhushan B (2012) Philos Trans R Soc, Math Phys Eng Sci 370(1967):2304
Joseph P, Tabeling P (2005) Phys Rev E 71(3):035303
Cottin-Bizonne C, Steinberger A, Cross B, Raccurt O, Charlaix E (2008) Langmuir 24(4):1165
Lee C, Kim C (2011) In: Langmuir: the ACS journal of surfaces and colloids 27(7), p 4243
Ming Z, Jian L, Chunxia W, Xiaokang Z, Lan C (2011) Soft Matter 7(9):4391
Ybert C, Barentin C, Cottin-Bizonne C, Joseph P, Bocquet L (2007) Phys Fluids 19:123601
Ng C, Wang C (2010) Microfluid Nanofluid 8(3):361
Sbragaglia M, Prosperetti A (2007) Phys Fluids 19:043603
Benzi R, Biferale L, Sbragaglia M, Succi S, Toschi F (2006) Europhys Lett 74:651
Teo C, Khoo B (2010) Microfluid Nanofluid 9(2):499
Lauga E, Stone H (2003) J Fluid Mech 489(1):55
Cottin-Bizonne C, Barrat J, Bocquet L, Charlaix E (2003) Nat Mater 2(4):237
Cottin-Bizonne C, Cross B, Steinberger A, Charlaix E (2005) Phys Rev Lett 94:056102
Steinberger A, Cottin-Bizonne C, Kleimann P, Charlaix E (2007) Nat Mater 6(9):665
Thompson P, Troian S (1997) Nature 389(6649):360
Huang D, Sendner C, Horinek D, Netz R, Bocquet L (2008) Phys Rev Lett 101(22):226101
Cassie A, Baxter S (1944) Trans Faraday Soc 40:546
Lafuma A Quéré D et al. (2003) Nat Mater 2(7):457
Palumbo F, Di Mundo R, Cappelluti D, d’Agostino R (2011) Plasma Process Polym 8(2):118
Wenzel R (1936) Ind Eng Chem 28(8):988
Afferrante L, Carbone G (2010) J Phys Condens Matter 22:325107
Giacomello A, Chinappi M, Meloni S, Casciola CM (2012) Phys Rev Lett 109(22):226102
Savoy ES, Escobedo FA (2012) Langmuir 28:3412
Giacomello A, Meloni S, Chinappi M, Casciola C (2012) Langmuir 28(29):10764
Bolognesi G, Pirat C, Cottin-Bizonne E, Guene M, Teisseire J (2013) Soft Matter 9:2239
Hyväluoma J, Kunert C, Harting J (2011) J Phys Condens Matter 23:184106
Humphrey W, Dalke A, Schulten K et al. (1996) J Mol Graph 14(1):33
Abascal J, Vega C (2005) J Chem Phys 123:234505
Chinappi M, Gala F, Zollo G, Casciola C (2011) Philos Trans R Soc, Math Phys Eng Sci 369(1945):2537
Vega C, de Miguel E (2007) J Chem Phys 126(15):4707
Gala F, Zollo G (2011) Phys Rev B 84(19):195323
Phillips J, Braun R, Wang W, Gumbart J, Tajkhorshid E, Villa E, Chipot C, Skeel R, Kale L, Schulten K (2005) J Comput Chem 26(16):1781
Tuteja A, Choi W, Ma M, Mabry JM, Mazzella SA, Rutledge GC, McKinley GH, Cohen RE (2007) Science 318(5856):1618
Kell G, Whalley E (1975) J Chem Phys 62(9):3496
An T, Cho S, Choi W, Kim J, Lim S, Lim G (2011) Soft Matter 7(21):9867
Brown P, Talbot E, Wood T, Bain C, Badyal J (2012) Langmuir 28(38):13712–13719
Davis A, Lauga E (2009) Phys Fluids 21:011701
Acknowledgements
Part of the computing resources were made available by CASPUR (HPC grants 2011 and 2012).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Gentili, D., Chinappi, M., Bolognesi, G. et al. Water slippage on hydrophobic nanostructured surfaces: molecular dynamics results for different filling levels. Meccanica 48, 1853–1861 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11012-013-9717-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11012-013-9717-8