Abstract
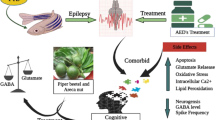
Epilepsy, a chronic neurological condition, impacts millions of individuals globally and remains a significant contributor to both illness and mortality. Available antiepileptic drugs have serious side effects which warrants to explore different medicinal plants used for the management of epilepsy reported in Traditional Indian Medicinal System (TIMS). Therefore, we explored the antiepileptic potential of the Grewia tiliaefolia (Tiliaeceae) which is known for its neuroprotective properties. Aerial parts of G. tiliaefolia were subjected to extraction with increasing order of polarity viz. hexane, chloroform and methanol. Antioxidant potential of hexane, chloroform and methanol extracts of G. tiliaefolia was evaluated by 2,2-diphenyl-1-picryl-hydrazyl-hydrate (DPPH) assay, total antioxidant capacity (TAC) assay, reducing power assay (RPA) and DNA nicking assay. Additionally, quantitative antioxidant assays were also conducted to quantify total phenolic (TPC) and total flavonoid content (TFC). As revealed by in vitro assays, methanol extract was found to contain more phenolic content. Hence, the methanol extract was further explored for its anticonvulsant potential in pentylenetetrazole (PTZ) induced acute seizures in mice. The methanol extract (400 mg/kg) significantly increased the latency to occurrence of myoclonic jerks and generalized tonic clonic seizures (GTCS). Additionally, it also reduced duration and seizure severity score associated with GTCS. The Grewia tiliaefolia methanol extract was further screened by Ultra High-Performance Liquid Chromatography (UHPLC) for presence of polyphenolic compounds, among which gallic acid and kaempferol were present in higher amount and were further analysed by in silico study to predict their possible binding sites and type of interactions these compounds show with gamma amino butyric acid (GABA) receptor and glutamate α amino-3- hydroxyl-5-methyl-4-isoxazolepropionic acid (Glu-AMPA) receptor. It was revealed that gallic acid and kaempferol had shown agonistic interaction for GABA receptor and antagonistic interaction for Glu-AMPA receptor. We concluded that G. tiliaefolia showed anticonvulsant potential possibly because of gallic acid and kaempferol possibly mediated through GABA and Glu-AMPA receptor.
Graphical abstract











Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
The datasets used or analyzed during the current study will be available from the corresponding author on reasonable request.
Code availability
Not applicable.
References
Adebiyi OE, Olopade FE, Olopade JO, Olayemi FO (2016a) Behavioural studies on the ethanol leaf extract of Grewia carpinifolia in Wistar rats. Afr Health Sci 16(1):339–346
Adebiyi OE, Olopade JO, Olayemi FO (2016b) Neuroprotective effect of Grewia carpinifolia extract against vanadium induced behavioral impairment. Folia Vet Lat 60(4):5–13
Aguiar CC, Almeida AB, Araújo PV, Abreu RN, Chaves EM, Vale OC, Macêdo DS, Woods DJ, Fonteles MM, Vasconcelos SM (2012) Oxidative stress and epilepsy: literature review. Oxid Med Cellular longev 2012:1–12
Alatorre A, Oviedo-Chávez A, Villalobos N, Ríos A, Barrientos R, Querejeta E (2015) The local application of a flavonoid, (−)-epicatechin, increases the spiking of globus pallidus neurons in a dose-dependent manner and diminishes the catalepsy induced by haloperidol. Behav Pharmacol 26(1 and 2-Special Issue):117–24
Aseervatham GS, Suryakala U, Sundaram S, Bose PC, Sivasudha T (2016) Expression pattern of NMDA receptors reveals antiepileptic potential of apigenin 8-C-glucoside and chlorogenic acid in pilocarpine induced epileptic mice. Biomed Pharmacother 82:54–64
Attri S, Kaur P, Singh D, Kaur H, Rashid F, Kumar A, Singh B, Bedi N, Arora S (2021) Induction of apoptosis in A431 cells via ROS generation and p53-mediated pathway by chloroform fraction of Argemone mexicana (Pepaveraceae). E S P R 1–20
Benzie IF, Strain JJ (1996) The ferric reducing ability of plasma (FRAP) as a measure of “antioxidant power”: the FRAP assay. Anal Biochem 239(1):70–76
Berghuis B, Hulst J, Sonsma A, McCormack M, de Haan GJ, Sander JW, Lindhout D, Koeleman BP (2021) Symptomatology of carbamazepine-and oxcarbazepine-induced hyponatremia in people with epilepsy. Epilepsia 62(3):778–784
Blume WT, Lüders HO, Mizrahi E, Tassinari C, van Emde Boas W, Engel Jr, Ex-officio J (2001) Glossary of descriptive terminology for ictal semiology: Report of the ILAE task force on classification and terminology. Epilepsia 42(9):1212–8
Cárdenas-Rodríguez N, González-Trujano ME, Aguirre-Hernández E, Ruíz-García M, Sampieri A, Coballase-Urrutia E, Carmona-Aparicio L (2014) Anticonvulsant and antioxidant effects of Tilia americana var. mexicana and flavonoids constituents in the pentylenetetrazole-induced seizures. Oxid Med Cell Longev 2014:1–10
Carton L, Auger F, Laloux C, Durieux N, Kyheng M, Potey C, Bergeron S, Rolland B, Deguil J, Bordet R (2022) Effects of acute ethanol and/or diazepam exposure on immediate and delayed hippocampal metabolite levels in rats anesthetized with isoflurane. Fundament Clinic Pharmacol 36(4):687–698
Chen J, Ye H, Zhang J, Li A, Ni Y (2022) Pathogenesis of seizures and epilepsy after stroke. Acta Epileptologica 1:1–6
Coelho VR, Vieira CG, de Souza LP, Moysés F, Basso C, Papke DK, Pires TR, Siqueira IR, Picada JN, Pereira P (2015) Antiepileptogenic, antioxidant and genotoxic evaluation of rosmarinic acid and its metabolite caffeic acid in mice. Life Sci 122:65–71
Dassault Systèmes BIOVIA Discovery Studio Modeling Environment, Release 2020 Dassault Systèmes, San Diego (2020)
Dev R, Kannan V, Kumar MS, Dayal D, Patel R (2019) Grewia Species: Diversity, Distribution, Traditional Knowledge and Utilization. Composition, Nutritional Value and Products, Wild Fruits, pp 395–426
Dhingra D, Jangra A (2014) Antiepileptic activity of ellagic acid, a naturally occurring polyphenolic compound, in mice. J Funct Foods 10:364–9
Dhir A (2020) Natural polyphenols in preclinical models of epilepsy. Phytother Res 34(6):1268–1281
Dicson SM, Samuthirapandi M, Govindaraju A, Kasi PD (2015) Evaluation of in vitro and in vivo safety profile of the Indian traditional medicinal plant Grewia tiliaefolia. Regul Toxicol Pharm 73(1):241–247
Eastman CL, D’Ambrosio R, Ganesh T (2020) Modulating neuroinflammation and oxidative stress to prevent epilepsy and improve outcomes after traumatic brain injury. Neuropharmacol 172:107907
Ferreira A, Rodrigues M, Fortuna A, Falcão A, Alves G (2018) Flavonoid compounds as reversing agents of the P-glycoprotein-mediated multidrug resistance: An in vitro evaluation with focus on antiepileptic drugs. Food Res Int 103:110–120
Fisher RS, Acevedo C, Arzimanoglou A, Bogacz A, Cross JH, Elger CE, Engel J Jr, Forsgren L, French JA, Glynn M, Hesdorffer DC (2014) ILAE official report: a practical clinical definition of epilepsy. Epilepsia 55(4):475–482
Geronzi U, Lotti F, Grosso S (2018) Oxidative stress in epilepsy. Expert Rev Neurother 18(5):427–434
Green JL, Dos Santos WF, Fontana AC (2021) Role of glutamate excitotoxicity and glutamate transporter EAAT2 in epilepsy: Opportunities for novel therapeutics development. Biochem Pharmacol 193:114786
Han Y, Chen JZ (2012) Oxidative stress induces mitochondrial DNA damage and cytotoxicity through independent mechanisms in human cancer cells. BioMed Res Int 2013:1-8
Hotz AL, Jamali A, Rieser NN, Niklaus S, Aydin E, Myren-Svelstad S, Lalla L, Jurisch-Yaksi N, Yaksi E, Neuhauss SC (2022) Loss of glutamate transporter eaat2a leads to aberrant neuronal excitability, recurrent epileptic seizures, and basal hypoactivity. Glia 70(1):196–214
Ishola IO, Akinleye MO, Afolayan OO, Okonkwo HE, Animashaun OT, Agbaje EO (2022) Anticonvulsant activity of Nymphaea lotus Linn. extract in mice: The role of GABAergic-glutamatergic neurotransmission and antioxidant defence mechanisms. Epilepsy Res 181:106871.
Jain S, Agarwal NB, Mediratta PK, Sharma KK (2012) Evaluation of anticonvulsant and nootropic effect of ondansetron in mice. Hum Exp Toxicol 31(9):905–912
Jastrzembski B, Locke J, Wan MJ (2020) Clinical implications and cost of electroretinography screening for vigabatrin toxicity. Can J Ophthalmol 55(3):e98-100
Jeavons PM, Clark JE (1974) Sodium valproate in treatment of epilepsy. Br Med J 2(5919):584–6
Jebin R, Molla MI, Chowdhury SM, Rafe MR (2019) Antidepressant and sedative-hypnotic activities of methanolic extract of Grewia asiatica Linn. leaves in mice. Bangladesh J Pharmacol 22(2):185–91
Kim DO, Jeong SW, Lee CY (2003) Antioxidant capacity of phenolic phytochemicals from various cultivars of plums. Food Chem 81(3):321–326
Kumar N, Singh A, Gulati HK, Bhagat K, Kaur K, Kaur J, Dudhal S, Duggal A, Gulati P, Singh H, Singh JV (2021) Phytoconstituents from ten natural herbs as potent inhibitors of main protease enzyme of SARS-COV-2: in silico study. Phytomed Plus 1(4):100083
Kumar Prasad SA, Subrahmanyam EV, Shabaraya AR (2014) Design and biological screening of some novel formazan derivatives from schiff bases of gallic acid. World J Pharm Res 3(2):2741–2752
Lee JC, Kim HR, Kim J, Jang YS (2002) Antioxidant property of an ethanol extract of the stem of Opuntia ficus-indica var. saboten. J Agric Food Chem 50(22):6490–6
Lin TK, Chen SD, Lin KJ, Chuang YC (2020) Seizure-induced oxidative stress in status epilepticus: is antioxidant beneficial? Antioxidants 9(11):1029
Loshali A, Joshi BC, Sundriyal A, Uniyal S (2021) Antiepileptic effects of antioxidant potent extract from Urtica dioica Linn. root on pentylenetetrazole and maximal electroshock induced seizure models. Heliyon 7(2):e06195
Łukawski K, Czuczwar SJ (2023) Oxidative Stress and Neurodegeneration in Animal Models of Seizures and Epilepsy. Antioxidants 12(5):1049
Madireddy S, Madireddy S (2023) Therapeutic strategies to ameliorate neuronal damage in epilepsy by regulating oxidative stress, mitochondrial dysfunction, and neuroinflammation. Brain Sci 13(5):784
Maier CM, Chan PH (2002) Book review: role of superoxide dismutases in oxidative damage and neurodegenerative disorders. Neuroscientist 8(4):323–334
Mary SJ, Merina AJ (2021) Studies on total antioxidant activity of the extract of Nyctasnthes arbortristis flower extract by DPPH radical-scavenging activity and superoxide anion scavenging activity assay. J Med Plants 9(2):160–164
Meinardi H, Scott RA, Reis R, On Behalf Of The ILAE Commission on the Developing World Sanders J W A S (2001) The treatment gap in epilepsy: the current situation and ways forward. Epilepsia 42(1):136–49
Mishra P, Mittal AK, Rajput SK, Sinha JK (2021) Cognition and memory impairment attenuation via reduction of oxidative stress in acute and chronic mice models of epilepsy using antiepileptogenic Nux vomica. J Ethnopharmacol 267:113509
Nieoczym D, Socała K, Raszewski G, Wlaź P (2014) Effect of quercetin and rutin in some acute seizure models in mice. Prog Neuropsychopharmacol Biol 54:50–58
Ojong LJ, Abdou JP, KavayeKandeda A, Yaya AJ, Tchamgoue AD, Tchokouaha LR, Nkantchoua NG, Agbor G, Agbor RS, Ngo EB (2016) Anticonvulsant and in vitro antioxidant activities of Momordica cissoides L.(Cucurbitaceae). J Appl Pharm Sci 6(04):117–23
Olowe R, Sandouka S, Saadi A, Shekh-Ahmad T (2020) Approaches for reactive oxygen species and oxidative stress quantification in epilepsy. Antioxidants 9(10):990
Park YS, Jung ST, Kang SG, Heo BG, Arancibia-Avila P, Toledo F, Drzewiecki J, Namiesnik J, Gorinstein S (2008) Antioxidants and proteins in ethylene-treated kiwifruits. Food Chem 107(2):640–648
Parsons AL, Bucknor E, Castroflorio E, Soares TR, Oliver PL, Rial D (2022) The interconnected mechanisms of oxidative stress and neuroinflammation in epilepsy. Antioxidants 11(1):157
Prieto P, Pineda M, Aguilar M (1999) Spectrophotometric quantitation of antioxidant capacity through the formation of a phosphomolybdenum complex: specific application to the determination of vitamin E. Anal Biochem 269(2):337–341
Qneibi M, Hanania M, Jaradat N, Emwas N, Radwan S (2021) Inula viscosa (L.) Greuter, phytochemical composition, antioxidant, total phenolic content, total flavonoids content and neuroprotective effects. Eur J Integr Med 42:101291
Rajput A, Sharma P, Kumar N, Kaur S, Arora S (2023a) Neuroprotective activity of novel phenanthrene derivative from Grewia tiliaefolia by in vitro and in silico studies. Sci Rep 13(1):2444
Rajput A, Sharma P, Singh H, Singh B, Kaur S, Arora S (2023b) Health Promoting Properties of Grewia asiatica and Grewia tenax Berries: A Potential Role in Cancer, Diabetes, and Liver Diseases Prevention. Bioactive Phytochemicals from Himalayas: A Phytotherapeutic Approach 41–48
Redfern J, Kinninmonth M, Burdass D, Verran J (2014) Using soxhlet ethanol extraction to produce and test plant material (essential oils) for their antimicrobial properties. J Microbiol Biol Educ 15(1):45–46
Rogawski MA, Löscher W (2004) The neurobiology of antiepileptic drugs. Nat Rev Neurosci 5(7):553–564
Salem M, El-Bardissy A (2021) Lamotrigine-induced neutropenia after high-dose concomitant initiation with phenytoin. Clin Case Rep 9(11):e05136
Shamoun MI, Mohamed AH, El-Hadiyah TM (2014) Anticonvulsant and anxiolytic properties of the roots of Grewia bicolor in rats. SJMS 9(3):137–143
Sharma J, Bhardwaj VK, Singh R, Rajendran V, Purohit R, Kumar S (2021) An in-silico evaluation of different bioactive molecules of tea for their inhibition potency against non-structural protein-15 of SARS-CoV-2. Food Chem 346:128933
Silva dos Santos J, Goncalves Cirino JP, de Oliveira CP, Ortega MM (2021) The pharmacological action of kaempferol in central nervous system diseases: A review. Front Pharmacol 11:2143
Singh T, Bagga N, Kaur A, Kaur N, Gawande DY, Goel RK (2017) Agmatine for combined treatment of epilepsy, depression and cognitive impairment in chronic epileptic animals. Biomed Pharmacother 92:720–725
Singh T, Mishra A, Goel RK (2021) PTZ kindling model for epileptogenesis, refractory epilepsy, and associated comorbidities: relevance and reliability. Metab Brain Dis 36(7):1573–1590
Tamboli AM, Rub RA, Ghosh P, Bodhankar SL (2012) Antiepileptic activity of lobeline isolated from the leaf of Lobelia nicotianaefolia and its effect on brain GABA level in mice. Asian Pac J Trop Biomed 2(7):537–542
Ullah W, Uddin G, Siddiqui BS (2012) Ethnic uses, pharmacological and phytochemical profile of genus Grewia. J Asian Natural Products Res 14(2):186–95
Watanabe Y, Kaida Y, Fukuhara S, Takechi K, Uehara T, Kamei C (2011) Participation of metabotropic glutamate receptors in pentetrazol-induced kindled seizure. Epilepsia 52(1):140–150
Zhu F, Li XX, Yang SY, Chen YZ (2018) Clinical success of drug targets prospectively predicted by in silico study. Trends Pharmacol Sci 39(3):229–231
Acknowledgements
Authors are very grateful to Guru Nanak Dev University for providing the necessary facilities for conducting research work.
Funding
Authors are thankful to Indian Council of Medical Research (ICMR-SRF) for fellowship to Ms. Ankita Rajput.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Ankita Rajput performed the experiment and wrote the original manuscript; Palvi Sharma, Nitish Kumar and Sharabjit Singh helped in the experiment work; Hasandeep Singh guided in the experiment work and edited the original manuscript writing; Tanveer Singh guided for the in vivo PTZ experiment; Gave suggestion and edited manuscript. Sarabjit Kaur and Saroj Arora perceived the idea and gave suggestions in the manuscript.
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Ethical approval
Studies were conducted as per the protocol approved by the institutional animal ethical committee (IAEC) of Guru Nanak Dev University, India with protocol number 226/CPCSEA-2019/30.
Consent to participate
Not Applicable.
Consent to publication
Not Applicable.
Competing interests
The authors have no relevant financial or non-financial interests to disclose.
Additional information
Publisher's note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Rajput, A., Sharma, P., Kumar, N. et al. Anticonvulsant potential of Grewia tiliaefolia in pentylenetetrazole induced epilepsy: insights from in vivo and in silico studies. Metab Brain Dis 38, 2355–2367 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11011-023-01252-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11011-023-01252-0