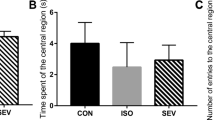
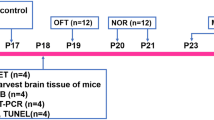
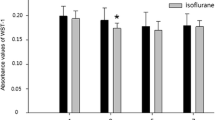
Abstract
Anesthetics such as sevoflurane are commonly administered to infants and children. However, the possible neurotoxicity caused by prolonged or repetitive exposure to it should be a concern. The neuroprotective effects of metformin are observed in many models of neurological disorders. In this study, we investigated whether metformin could reduce the developmental neurotoxicity induced by sevoflurane exposure in neonatal rats and the potential mechanism. Postnatal day 7 (PND 7) Sprague-Dawley rats and neural stem cells (NSCs) were treated with normal saline or metformin before sevoflurane exposure. The Morris water maze (MWM) was used to observe spatial memory and learning at PND 35–42. Immunofluorescence staining was used to detect neurogenesis in the subventricular zone (SVZ) of the lateral ventricle and the subgranular zone (SGZ) of the dentate gyrus at PND 14. MTT assays, immunofluorescence staining, and TUNEL staining were used to assess the viability, proliferation, differentiation, and apoptosis of NSCs. Western blotting and ELISA were used to assess the protein expression of cleaved caspase-3, nuclear factor erythroid 2-related factor 2 (Nrf2), and glucose-6-phosphate dehydrogenase (G6PD) pathway-related molecules. Exposure to sevoflurane resulted in late cognitive defects, impaired neurogenesis in both the SVZ and SGZ, reduced NSC viability and proliferation, increased NSC apoptosis, and decreased protein expression of G6PD in vitro. Metformin pretreatment attenuated sevoflurane-induced cognitive functional decline and neurogenesis inhibition. Metformin pretreatment also increased the protein expression of Nrf2 and G6PD. However, treatment with the Nrf2 inhibitor, ML385 or the G6PD inhibitor, dehydroepiandrosterone (DHEA) reversed the protective effect of metformin on sevoflurane-induced NSC damage in vitro. Our findings suggested that metformin could reduce sevoflurane-induced neurogenesis damage and neurocognitive defects in the developing rat brain by influencing the Nrf2/G6PD signaling pathways.










Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
The analyzed data sets generated during the present study are available from the corresponding author on reasonable request.
Abbreviations
- PND 7:
-
Postnatal day 7
- SD:
-
Sprague-Dawley
- NSCs:
-
Neural stem cells
- MWM:
-
Morris water maze
- SVZ:
-
Subventricular zone
- SGZ:
-
Subgranular zone
- MTT:
-
3-(4,5)-Dimethylthiahiazo (-z-y1)-3,5-di- phenytetrazoliumromide
- TUNEL:
-
Terminal dUTP nick-end labeling
- ELISA:
-
Enzyme-Linked Immunosorbent Assay
- Nrf2:
-
Nuclear factor erythroid 2-related factor 2
- G6PD:
-
Glucose-6-phosphate dehydrogenase
- DHEA:
-
Dehydroepiandrosterone
- AMPK:
-
AMP-activated protein kinase
- PPP:
-
Pentose phosphate pathway
- NADPH:
-
Nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide phosphate
- Ctrl:
-
Control
- Sev:
-
Sevoflurane
- Met:
-
Metformin
- CO2 :
-
Carbon dioxide
- O2 :
-
Oxygen
- BrdU:
-
5-Bromo-2´-deoxyuridine
- PBS:
-
Phosphate buffered saline
- DMEM/F12:
-
Dulbecco’s Modified Eagle Medium/Nutrient Mixture F-12
- EGF:
-
Epidermal growth factor
- bFGF:
-
Basic fibroblast growth factor
- FBS:
-
Fetal bovine serum
- GSH:
-
Glutathione
- HO-1:
-
Heme oxygenase-1
- MCAO:
-
Middle cerebral artery occlusion
References
Almeida AS, Soares NL, Sequeira CO, Pereira SA, Sonnewald U, Vieira HLA (2018) Improvement of neuronal differentiation by carbon monoxide: role of pentose phosphate pathway. Redox Biol 17:338–347
Altman J, Das GD (1965) Autoradiographic and histological evidence of postnatal hippocampal neurogenesis in rats. J Comp Neurol 124:319–335
Boorman E, Killick R, Aarsland D, Zunszain P, Mann GE (2022) NRF2: an emerging role in neural stem cell regulation and neurogenesis. Free Radic Biol Med 193:437–446
Boren J, Ramos-Montoya A, Bosch KS, Vreeling H, Jonker A, Centelles JJ, Cascante M, Frederiks WM (2006) In situ localization of transketolase activity in epithelial cells of different rat tissues and subcellularly in liver parenchymal cells. J Histochem Cytochem 54:191–199
Chen X, Shen WB, Yang P, Dong D, Sun W, Yang P (2018) High glucose inhibits neural stem cell differentiation through oxidative stress and endoplasmic reticulum stress. Stem Cells Dev 27:745–755
Deshpande SS, Malik SC, Conforti P, Lin JD, Chu YH, Nath S, Greulich F, Dumbach MA, Uhlenhaut NH, Schachtrup C (2022) P75 neurotrophin receptor controls subventricular zone neural stem cell migration after stroke. Cell Tissue Res 387:415–431
DiTacchio KA, Heinemann SF, Dziewczapolski G (2015) Metformin treatment alters memory function in a mouse model of Alzheimer’s disease. J Alzheimers Dis 44:43–48
Emsley JG, Mitchell BD, Kempermann G, Macklis JD (2005) Adult neurogenesis and repair of the adult CNS with neural progenitors, precursors, and stem cells. Prog Neurobiol 75:321–341
Fang F, Xue Z, Cang J (2012) Sevoflurane exposure in 7-day-old rats affects neurogenesis, neurodegeneration and neurocognitive function. Neurosci Bull 28:499–508
Farr SA, Roesler E, Niehoff ML, Roby DA, McKee A, Morley JE (2019) Metformin improves Learning and Memory in the SAMP8 mouse model of Alzheimer’s Disease. J Alzheimers Dis 68:1699–1710
Gao J, Luo A, Yan J, Fang X, Tang X, Zhao Y, Li S (2018) Mdivi-1 pretreatment mitigates isoflurane-induced cognitive deficits in developmental rats. Am J Transl Res 10:432–443
Hu LH, Yang JH, Zhang DT, Zhang S, Wang L, Cai PC, Zheng JF, Huang JS (2007) The TKTL1 gene influences total transketolase activity and cell proliferation in human colon cancer LoVo cells. Anticancer Drugs 18:427–433
Imayoshi I, Sakamoto M, Ohtsuka T, Takao K, Miyakawa T, Yamaguchi M, Mori K, Ikeda T, Itohara S, Kageyama R (2008) Roles of continuous neurogenesis in the structural and functional integrity of the adult forebrain. Nat Neurosci 11:1153–1161
Jinpiao Z, Zongze Z, Qiuyue Y, Peng F, Qi Z, Yanlin W, Chang C (2020) Metformin attenuates sevoflurane-induced neurocognitive impairment through AMPK-ULK1-dependent autophagy in aged mice. Brain Res Bull 157:18–25
Kahroba H, Ramezani B, Maadi H, Sadeghi MR, Jaberie H, Ramezani F (2021) The role of Nrf2 in neural stem/progenitors cells: from maintaining stemness and self-renewal to promoting differentiation capability and facilitating therapeutic application in neurodegenerative disease. Ageing Res Rev 65:101211
Kong F, Xu L, He D, Zhang X, Lu H (2011) Effects of gestational isoflurane exposure on postnatal memory and learning in rats. Eur J Pharmacol 670:168–174
Li H, Wang Y, Hu X, Ma B, Zhang H (2019) Thymosin beta 4 attenuates oxidative stress-induced injury of spinal cord-derived neural stem/progenitor cells through the TLR4/MyD88 pathway. Gene 707:136–142
Li W, Lu P, Lu Y, Wei H, Niu X, Xu J, Wang K, Zhang H, Li R, Qiu Z, Wang N, Jia P, Zhang Y, Zhang S, Lu H, Chen X, Liu Y, Zhang P (2020) 17β-Estradiol protects neural Stem/Progenitor cells against Ketamine-Induced Injury through Estrogen receptor β pathway. Front Neurosci 14:576813
Lin EP, Lee JR, Lee CS, Deng M, Loepke AW (2017) Do anesthetics harm the developing human brain? An integrative analysis of animal and human studies. Neurotoxicol Teratol 60:117–128
Liu B, Bai W, Ou G, Zhang J (2019) Cdh1-Mediated metabolic switch from Pentose phosphate pathway to Glycolysis contributes to Sevoflurane-Induced neuronal apoptosis in developing brain. ACS Chem Neurosci 10:2332–2344
Liu C, Zhang D, Lu Z, Man J, Zhang Z, Fu X, Cui K, Wang J (2022) Metformin protects against pericyte apoptosis and promotes neurogenesis through suppressing JNK p38 MAPK signalling activation in ischemia/reperfusion injury. Neurosci Lett 783:136708
Lu Y, Lei S, Wang N, Lu P, Li W, Zheng J, Giri PK, Lu H, Chen X, Zuo Z, Liu Y, Zhang P (2016) Protective effect of Minocycline against Ketamine-Induced Injury in neural stem cell: involvement of PI3K/Akt and Gsk-3 Beta pathway. Front Mol Neurosci 9:135
Mao FX, Li WJ, Chen HJ, Qian LH, Buzby JS (2013) White matter and SVZ serve as endogenous sources of glial progenitor cells for self-repair in neonatal rats with ischemic PVL. Brain Res 1535:38–51
Ming GL, Song H (2005) Adult neurogenesis in the mammalian central nervous system. Annu Rev Neurosci 28:223–250
Ming GL, Song H (2011) Adult neurogenesis in the mammalian brain: significant answers and significant questions. Neuron 70:687–702
Muramatsu R, Ikegaya Y, Matsuki N, Koyama R (2007) Neonatally born granule cells numerically dominate adult mice dentate gyrus. Neuroscience 148:593–598
Neag MA, Mitre AO, Catinean A, Mitre CI (2020) An overview on the Mechanisms of Neuroprotection and neurotoxicity of isoflurane and sevoflurane in experimental studies. Brain Res Bull 165:281–289
Nie Y, Li S, Yan T, Ma Y, Ni C, Wang H, Zheng H (2020) Propofol attenuates Isoflurane-Induced neurotoxicity and cognitive impairment in fetal and offspring mice. Anesth Analg 131:1616–1625
Ortega JA, Memi F, Radonjic N, Filipovic R, Bagasrawala I, Zecevic N, Jakovcevski I (2018) The Subventricular Zone: A Key Player in Human Neocortical Development. Neuroscientist 24:156–70
Pontén E, Viberg H, Gordh T, Eriksson P, Fredriksson A (2012) Clonidine abolishes the adverse effects on apoptosis and behaviour after neonatal ketamine exposure in mice. Acta Anaesthesiol Scand 56:1058–1065
Ramage TM, Chang FL, Shih J, Alvi RS, Quitoriano GR, Rau V, Barbour KC, Elphick SA, Kong CL, Tantoco NK, Ben-Tzur D, Kang H, McCreery MS, Huang P, Park A, Uy J, Rossi MJ, Zhao C, Di Geronimo RT, Stratmann G, Sall JW (2013) Distinct long-term neurocognitive outcomes after equipotent sevoflurane or isoflurane anaesthesia in immature rats. Br J Anaesth 110(Suppl 1):i39-46
Shen X, Dong Y, Xu Z, Wang H, Miao C, Soriano SG, Sun D, Baxter MG, Zhang Y, Xie Z (2013) Selective anesthesia-induced neuroinflammation in developing mouse brain and cognitive impairment. Anesthesiology 118:502–515
Shi Y, Zhao X, Hsieh J, Wichterle H, Impey S, Banerjee S, Neveu P, Kosik KS (2010) MicroRNA regulation of neural stem cells and neurogenesis. J Neurosci 30:14931–6
Shors TJ, Townsend DA, Zhao M, Kozorovitskiy Y, Gould E (2002) Neurogenesis may relate to some but not all types of hippocampal-dependent learning. Hippocampus 12:578–584
Slikker W Jr, Zou X, Hotchkiss CE, Divine RL, Sadovova N, Twaddle NC, Doerge DR, Scallet AC, Patterson TA, Hanig JP, Paule MG, Wang C (2007) Ketamine-induced neuronal cell death in the perinatal rhesus monkey. Toxicol Sci 98:145–158
Snyder JS, Hong NS, McDonald RJ, Wojtowicz JM (2005) A role for adult neurogenesis in spatial long-term memory. Neuroscience 130:843–52
Song R, Ling X, Peng M, Xue Z, Cang J, Fang F (2017) Maternal sevoflurane exposure causes abnormal development of fetal prefrontal cortex and induces cognitive dysfunction in offspring. Stem Cells Int 2017:6158468
Song R, Wang R, Shen Z, Chu H (2022) Sevoflurane diminishes neurogenesis and promotes ferroptosis in embryonic prefrontal cortex via inhibiting nuclear factor-erythroid 2-related factor 2 expression. Neuroreport 33:252–58
Sritawan N, Prajit R, Chaisawang P, Sirichoat A, Pannangrong W, Wigmore P, Welbat JU (2020) Metformin alleviates memory and hippocampal neurogenesis decline induced by methotrexate chemotherapy in a rat model. Biomed Pharmacother 131:110651
Sun LS, Li G, Dimaggio C, Byrne M, Rauh V, Brooks-Gunn J, Kakavouli A, Wood A (2008) Anesthesia and neurodevelopment in children: time for an answer? Anesthesiology 109:757–61
Tchouagué M, Grondin M, Glory A, Averill-Bates D (2019) Heat shock induces the cellular antioxidant defenses peroxiredoxin, glutathione and glucose 6-phosphate dehydrogenase through Nrf2. Chem Biol Interact 310:108717
Tokuda K, Baron B, Yamashiro C, Kuramitsu Y, Kitagawa T, Kobayashi M, Sonoda KH, Kimura K (2019) Up-regulation of the pentose phosphate pathway and HIF-1α expression during neural progenitor cell induction following glutamate treatment in rat ex vivo retina. Cell Biol Int 44:137–144
Vutskits L, Davidson A (2017) Update on developmental anesthesia neurotoxicity. Curr Opin Anaesthesiol 30:337–342
Walters JL, Paule MG (2017) Review of preclinical studies on pediatric general anesthesia-induced developmental neurotoxicity. Neurotoxicol Teratol 60:2–23
Wang J, Xiao B, Han F, Shi Y (2017) Metformin alleviated the neuronal oxidative stress in Hippocampus of rats under single prolonged stress. J Mol Neurosci 63:28–35
Xia Y, Sun X, Luo Y, Stary CM (2018) Ferroptosis contributes to isoflurane neurotoxicity. Front Mol Neurosci 11:486
Xu Z, You Y, Tang Q, Zeng H, Zhao T, Wang J, Li F (2022) Echinatin mitigates sevoflurane-induced hippocampal neurotoxicity and cognitive deficits through mitigation of iron overload and oxidative stress. Pharm Biol 60:1915–1924
Yan YH, Li SH, Li HY, Lin Y, Yang JX (2017) Osthole protects bone marrow-derived neural stem cells from oxidative damage through PI3K/Akt-1 pathway. Neurochem Res 42:398–405
Yang HC, Wu YH, Liu HY, Stern A, Chiu DT (2016) What has passed is prolog: new cellular and physiological roles of G6PD. Free Radic Res 50:1047–1064
Yu J, Wang WN, Matei N, Li X, Pang JW, Mo J, Chen SP, Tang JP, Yan M, Zhang JH (2020) Ezetimibe attenuates oxidative stress and neuroinflammation via the AMPK/Nrf2/TXNIP pathway after MCAO in rats. Oxid Med Cell Longev 2020:4717258
Yue T, Shanbin G, Ling M, Yuan W, Ying X, Ping Z (2015) Sevoflurane aggregates cognitive dysfunction and hippocampal oxidative stress induced by β-amyloid in rats. Life Sci 143:194–201
Yufune S, Satoh Y, Akai R, Yoshinaga Y, Kobayashi Y, Endo S, Kazama T (2016) Suppression of ERK phosphorylation through oxidative stress is involved in the mechanism underlying sevoflurane-induced toxicity in the developing brain. Sci Rep 6:21859
Zhang HS, Zhang ZG, Du GY, Sun HL, Liu HY, Zhou Z, Gou XM, Wu XH, Yu XY, Huang YH (2019) Nrf2 promotes breast cancer cell migration via up-regulation of G6PD/HIF-1α/Notch1 axis. J Cell Mol Med 23:3451–3463
Zhang Y, Zhao Y, Ran Y, Guo J, Cui H, Liu S (2020) Notoginsenoside R1 attenuates sevoflurane-induced neurotoxicity. Transl Neurosci 11:215–226
Zhang Y, Kuai S, Zhang Y, Xue H, Wu Z, Zhao P (2022a) Maternal sevoflurane exposure affects neural stem cell differentiation in offspring rats through NRF2 signaling. Neurotoxicology 93:348–54
Zhang Y, Li H, Zhang X, Wang S, Wang D, Wang J, Tong T, Zhang Z, Yang Q, Dong H (2020b) Estrogen receptor-a in medial preoptic area contributes to sex difference of mice in response to sevoflurane anesthesia. Neurosci Bull 38:703–719
Zhao C, Deng W, Gage FH (2008) Mechanisms and functional implications of adult neurogenesis. Cell 132:645–60
Zuo Y, Chang Y, Thirupathi A, Zhou C, Shi Z (2021) Prenatal sevoflurane exposure: Effects of iron metabolic dysfunction on offspring cognition and potential mechanism. Int J Dev Neurosci 81:1–9
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by the National Key Research and Development Program of China (2019YFE0115300), the National Natural Science Foundation of China (82071482), and the Key Research and Development Program of Shaanxi Province (2021KWZ-27).
Funding
This work was supported by the National Key Research and Development Program of China (2019YFE0115300), the National Natural Science Foundation of China (82071482), and the Key Research and Development Program of Shaanxi Province (2021KWZ-27).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
All authors contributed to the study conception and design. Material preparation, data collection and analysis were performed by Pei Fan and Yuying Lu. The first draft of the manuscript was written by Pei Fan and all authors commented on previous versions of the manuscript. All authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors have no relevant financial interests to disclose.
Ethics approval
All applicable international and national guidelines for the care and use of animals were followed. All procedures performed in the study involving animals were approved by the Xi’an Jiaotong University Animal Care Committee (2020-14), in accordance with the ethical standards of Xi’an Jiaotong University.
Consent to participate
Informed consent was obtained from all individual participants included in the study.
Consent to publish
All authors of the study consent to publish this paper.
Additional information
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Fan, P., Lu, Y., Wei, H. et al. Metformin attenuates sevoflurane-induced neurogenesis damage and cognitive impairment: involvement of the Nrf2/G6PD pathway. Metab Brain Dis 38, 2037–2053 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11011-023-01218-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11011-023-01218-2