Abstract
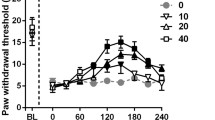
Background: Neuropathic pain is a subtype of chronic pain characterized by a primary lesion or dysfunction of the peripheral or central nervous system. The current pain management of neuropathic pain is inadequate and needs new medications. Aim: We studied the effects of 14 days of intraperitoneal ellagic acid (EA) and gabapentin administration in a rat model of neuropathic pain induced by chronic constriction injury (CCI) of the right sciatic nerve. Methods: Rats were divided into six groups: (1) control, (2) CCI, (3) CCI + EA (50 mg/kg), 4) CCI + EA (100 mg/kg), 5) CCI + gabapentin (100 mg/kg), and 6) CCI + EA (100 mg/kg) + gabapentin (100 mg/kg). Behavioral tests, including mechanical allodynia, cold allodynia, and thermal hyperalgesia, were conducted on days − 1(pre-operation), 7, and 14 post-CCI. In addition, at day 14 post-CCI, spinal cord segments were collected to measure the expression of inflammatory markers, including tumor necrosis factor-alpha (TNF-α), nitric oxide (NO), and oxidative stress markers, including malondialdehyde (MDA) and thiol. Results: CCI increased mechanical allodynia, cold allodynia, and thermal hyperalgesia in rats which were reduced by treatment with EA (50 or 100 mg/kg), gabapentin, or their combination. CCI increased TNF-α, NO, and MDA levels and decreased thiol content in the spinal cord, which all were reverted by administration of EA (50 or 100 mg/kg), gabapentin, or their combination. Conclusion: This is the first report on ellagic acid’s ameliorative effect in rats’ CCI-induced neuropathic pain. This effect can be attributed to its anti-oxidative and anti-inflammatory, thus making it potentially useful as an adjuvant to conventional treatment.







Similar content being viewed by others
Data Availability
The datasets used for analysis in this study are available upon request from the corresponding author.
Code Availability
Not applicable.
References
Ahmad N et al (2021) A novel gabapentin analogue assuages neuropathic pain response in chronic sciatic nerve constriction model in rats. Behav Brain Res 405:113190
Andrade P, Hoogland G, Del Rosario JS, Steinbusch HW, Visser-Vandewalle V, Daemen MA (2014) Tumor necrosis factor‐α inhibitors alleviation of experimentally induced neuropathic pain is associated with modulation of TNF receptor expression. J Neurosci Res 92:1490–1498
Asgharzade S, Khorrami MB, Forouzanfar F (2021) Neuroprotective effect of herniarin following transient focal cerebral ischemia in rats. Metab Brain Dis 36:2505–2510
Assaran AH et al (2022) Ellagic acid prevents oxidative stress and memory deficits in a rat model of scopolamine-induced Alzheimer’s Disease Central Nervous System Agents in Medicinal Chemistry (formerly current Medicinal Chemistry-Central Nervous. Syst Agents) 22:214–227
Bennett GJ, Xie Y-K (1988) A peripheral mononeuropathy in rat that produces disorders of pain sensation like those seen. in man Pain 33:87–107
Cavalli E, Mammana S, Nicoletti F, Bramanti P, Mazzon E (2019) The neuropathic pain: an overview of the current treatment and future therapeutic approaches. Int J ImmunoPathol Pharmacol 33:2058738419838383
Chao P-c, Hsu C-c, Yin M-cJN, metabolism (2009) Anti-inflammatory and anti-coagulatory activities of caffeic acid and ellagic acid in cardiac tissue. Diabet mice 6:1–8
Cornélio Favarin D et al (2013) Anti-inflammatory effects of ellagic acid on acute lung injury induced by acid in mice 2013
de Oliveira MR (2016) The effects of ellagic acid upon brain cells: a mechanistic view and future directions. Neurochem Res 41:1219–1228
de Souza Tavares W, Pena GR, Martin-Pastor M, de Sousa FFO (2021) Design and characterization of ellagic acid-loaded zein nanoparticles and their effect on the antioxidant and antibacterial activities. J Mol Liq 341:116915
Dolatshahi M, Farbood Y, Sarkaki A, Mansouri SMT, Khodadadi A (2015) Ellagic acid improves hyperalgesia and cognitive deficiency in 6-hydroxidopamine induced rat model of Parkinson’s disease. Iran J basic Med Sci 18:38
Ellman GL (1959) Tissue sulfhydryl groups Archives of biochemistry and biophysics 82:70–77
Finnerup NB, Kuner R, Jensen TS (2021) Neuropathic pain: from mechanisms to treatment. Physiol Rev 101:259–301
Forouzanfar F, Hosseinzadeh H, Khorrami MB, Asgharzade S, Rakhshandeh H (2019) Attenuating effect of Portulaca oleracea extract on chronic constriction injury induced neuropathic pain in rats: an evidence of anti-oxidative and anti-inflammatory effects CNS & neurological Disorders-Drug targets (formerly current drug Targets-CNS &. Neurol Disorders) 18:342–349
Gupta A, Kumar R, Ganguly R, Singh AK, Rana HK, Pandey AK (2021a) Antioxidant, anti-inflammatory and hepatoprotective activities of Terminalia bellirica and its bioactive component ellagic acid against diclofenac induced oxidative stress and hepatotoxicity. Toxicol Rep 8:44–52
Gupta A, Singh AK, Kumar R, Jamieson S, Pandey AK, Bishayee A (2021b) Neuroprotective potential of ellagic acid: a critical review advances. in Nutrition 12:1211–1238
Huh Y, Ji R-R, Chen GJFiI (2017) Neuroinflammation, bone marrow stem cells. and chronic pain 8:1014
Jain V, Pareek A, Bhardwaj YR, Sinha SK, Gupta MM, Singh NJNN (2021) Punicalagin and ellagic acid containing Punica granatum L. fruit rind extract prevents vincristine-induced neuropathic pain in rats: an in silico and in vivo evidence of GABAergic action and cytokine inhibition:1–18
Ji R-R, Chamessian A, Zhang Y-QJS (2016) Pain regulation by non-neuronal. cells and inflammation 354:572–577
Kaur R, Mehan S, Khanna D, Kalra SJIJoNR (2015) Polyphenol Ellagic Acid–Targeting To Brain: A Hidden Treasure 1:141–152
Krämer HH et al (2011) TNF-alpha in CRPS and ‘normal’trauma–. Signif differences between tissue serum 152:285–290
Levy D, Zochodne DW (2004) NO pain: potential roles of nitric oxide in neuropathic pain Pain practice: the. official J World Inst Pain 4:11–18. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1533-2500.2004.04002.x
Li Q-Y, Xu H-Y, Yang H-J (2017) Effect of proinflammatory factors TNF-α, IL-1β, IL-6 on neuropathic pain Zhongguo Zhong yao za zhi = Zhongguo zhongyao zazhi = China. J Chin materia Med 42:3709–3712
Liang F, Liu M, Fu X, Zhou X, Chen P, Han F (2017) Dexmedetomidine attenuates neuropathic pain in chronic constriction injury by suppressing NR2B, NF-κB, and iNOS activation saudi. Pharm J 25:649–654
Lubos E, Handy DE, Loscalzo J (2008) Role of oxidative stress and nitric oxide in atherothrombosis. Front Biosci 13:5323–5344. https://doi.org/10.2741/3084
Mansouri MT, Naghizadeh B, Ghorbanzadeh B (2015) Ellagic acid enhances the antinociceptive action of venlafaxine in mouse acetic acid-induced pain. isobolographic Anal Pharmacol Rep 67:473–477
Mansouri MT, Naghizadeh B, Ghorbanzadeh B, Farbood YJEjop (2013) Central and peripheral antinociceptive effects of ellagic acid in different animal. models of pain 707:46–53
Mansouri MT, Naghizadeh B, Ghorbanzadeh BJPB, Behavior (2014) Involvement of opioid receptors in the systemic and peripheral antinociceptive actions of ellagic acid in the rat formalin test 120:43–49
Marchand F, Perretti M, McMahon SB (2005) Role of the immune system in chronic pain. Nat Rev Neurosci 6:521–532
Mittal M, Siddiqui MR, Tran K, Reddy SP, Malik AB (2014) Reactive oxygen species in inflammation and tissue injury. Antioxid Redox Signal 20:1126–1167. https://doi.org/10.1089/ars.2012.5149
Naghizadeh B, Mansouri MT, Ghorbanzadeh B (2016) Ellagic acid enhances the antinociceptive action of carbamazepine in the acetic acid writhing test with mice. Pharm Biol 54:157–161
Park SW, Kwon MJ, Yoo JY, Choi H-J, Ahn Y-J (2014) Antiviral activity and possible mode of action of ellagic acid identified in Lagerstroemia speciosa leaves toward human rhinoviruses. BMC Complement Altern Med 14:1–8
Phaniendra A, Jestadi DB, Periyasamy L (2015) Free radicals: properties, sources, targets, and their implication in various diseases. Indian J Clin Biochem 30:11–26. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12291-014-0446-0
Rakhshandeh H, Asgharzade S, Khorrami MB, Forouzanfar F (2021a) Protective effect of capparis spinosa extract against focal cerebral ischemia-reperfusion injury in rats Central Nervous System Agents in Medicinal Chemistry (formerly current Medicinal Chemistry-Central Nervous. Syst Agents) 21:148–153
Rakhshandeh H, Ghorbanzadeh A, Negah SS, Akaberi M, Rashidi R, Forouzanfar F (2021b) Pain-relieving effects of Lawsonia inermis on neuropathic pain induced by chronic constriction injury. Metab Brain Dis 36:1709–1716
Rakhshandeh H, Pourbagher-Shahri AM, Hasanpour M, Iranshahi M, Forouzanfar F (2022) Effects of Capparis Spinosa extract on the neuropathic pain induced by chronic constriction injury in ratsMetabolic Brain Disease:1–14
Sandkuhler JJPr (2009) Models and mechanisms of hyperalgesia and allodynia 89:707–758
Shahidi S, Komaki A, Raoufi S, Salehi I, Zarei M, Mahdian M (2021) The anti-nociceptive effect of Ellagic Acid in Streptozotocin-induced hyperglycemic rats by oxidative stress involvement Basic and clinical neuroscience. 12:861–872. https://doi.org/10.32598/bcn.2021.2413.1
Sharma JN, Al-Omran A, Parvathy SS (2007) Role of nitric oxide in. Inflamm Dis Inflammopharmacology 15:252–259. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10787-007-0013-x
Uzar E, Alp H, Cevik MU, Fırat U, Evliyaoglu O, Tufek A, Altun YJNS (2012) Ellagic acid attenuates oxidative stress on brain and sciatic nerve and improves histopathology of brain in streptozotocin. -induced Diabet rats 33:567–574
Vanderwall AG, Milligan ED (2019) Cytokines in pain: harnessing endogenous anti-inflammatory signaling for improved pain management. Front Immunol 10:3009
Zhang H-M, Zhao L, Li H, Xu H, Chen W-W, Tao L (2014) Research progress on the anticarcinogenic actions and mechanisms of ellagic acid Cancer biology & medicine 11:92
Zhao K, Huang Z, Lu H, Zhou J, Wei T (2010) Induction of inducible nitric oxide synthase increases the production of reactive oxygen species in RAW264.7 macrophages Bioscience reports 30:233–241 doi:https://doi.org/10.1042/bsr20090048
Acknowledgements
This paper is based on the results from the thesis of two Medical Doctorate candidates. Two separate research grants supported this study (IDs: 992112 and 4000244). The Vice-Chancellor for Research and Technology, Mashhad University of Medical Sciences (MUMS), Mashhad, Iran, provided the grants.
Funding
Two separate research grants supported this study (IDs: 992112 and 4000244). The Vice-Chancellor for Research and Technology, Mashhad University of Medical Sciences (MUMS), Mashhad, Iran, provided the grants.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Fatemeh Forouzanfar and Hamed Ghazavi designed the experiment. Fatemeh Forouzanfar, Hamed Ghazavi, Nima Khalili Tanha, Ali Mohammad Pourbagher-Shahri, Saeide mahdianpour, and Mahdiyeh Esmaeili did the experiments. Fatemeh Forouzanfar, Ali Mohammad Pourbagher-Shahri, and Hamed Ghazavi wrote the paper. Fatemeh Forouzanfar and Hamed Ghazavi prepared the final draft of the paper.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflicts of interest/Competing interests
The authors have no conflicts of interest to disclose in this study.
Ethics approval
The Ethical Committee of MUMS approved the study (992112; ethics approval code: IR.MUMS.MEDICAL.REC.1400.103, 4000244; IR.MUMS.MEDICAL.REC.1400.410).
Consent to participate
Not applicable.
Consent for publication
Not applicable.
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Forouzanfar, F., Tanha, N.K., Pourbagher-Shahri, A.M. et al. Synergistic effect of ellagic acid and gabapentin in a rat model of neuropathic pain. Metab Brain Dis 38, 1421–1432 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11011-023-01190-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11011-023-01190-x