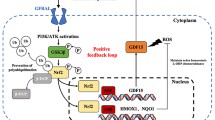
Abstract
Glioma is the most common malignant tumor of the central nervous system. The urea cycle (UC) is an essential pathway to convert excess nitrogen and ammonia into the less toxic urea in humans. However, less is known about the functional significance of the urea cycle in glioma. p53 functions as a tumor suppressor and modulates several cellular functions and disease processes. In the present study, we aimed to explore whether p53 influences glioma progression by regulating the urea cycle. Here, we demonstrated the inhibitory impact of p53 on the expression of urea cycle enzymes and urea genesis in glioma cells. The level of polyamine, a urea cycle metabolite, was also regulated by p53 in glioma cells. Carbamoyl phosphate synthetase-1 (CPS1) is the first key enzyme involved in the urea cycle. Functionally, we demonstrated that CPS1 knockdown suppressed glioma cell proliferation, migration and invasion. Mechanistically, we demonstrated that the expression of ornithine decarboxylase (ODC), which determines the generation of polyamine, was regulated by CPS1. In addition, the impacts of p53 knockdown on ODC expression, glioma cell growth and aggressive phenotypes were significantly reversed by CPS1 inhibition. In conclusion, these results demonstrated that p53 inhibits polyamine metabolism by suppressing the urea cycle, which inhibits glioma progression.






Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
The data that support the findings of this study are available from the corresponding author upon reasonable request.
References
Batash R, Asna N, Schaffer P, Francis N, Schaffer M (2017) Glioblastoma Multiforme, diagnosis and treatment; recent literature review. Curr Med Chem 24:3002–3009. https://doi.org/10.2174/0929867324666170516123206
Bieging KT, Mello SS, Attardi LD (2014) Unravelling mechanisms of p53-mediated tumour suppression. Nat Rev Cancer 14:359–370. https://doi.org/10.1038/nrc3711
Brazdova M, Quante T, Toegel L, Walter K, Loscher C, Tichy V, Cincarova L, Deppert W, Tolstonog GV (2009) Modulation of gene expression in U251 glioblastoma cells by binding of mutant p53 R273H to intronic and intergenic sequences. Nucleic Acids Res 37:1486–1500. https://doi.org/10.1093/nar/gkn1085
Casero RA Jr, Marton LJ (2007) Targeting polyamine metabolism and function in cancer and other hyperproliferative diseases. Nat Rev Drug Discovery 6:373–390. https://doi.org/10.1038/nrd2243
Chen CL, Hsu SC, Ann DK, Yen Y, Kung HJ (2021) Arginine Signaling and Cancer Metabolism. Cancers (Basel) 13:3541. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers13143541
de Oliveira EF, Guerreiro JR, Silva CA, Benedetti GFD, Lebrun I, Ulrich H, Lameu C, Camargo ACM (2010) Enhancement of the citrulline-nitric oxide cycle in astroglioma cells by the proline-rich peptide-10c from Bothrops jararaca venom. Brain Res 1363:11–19. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.brainres.2010.09.067
DeBerardinis RJ, Chandel NS (2016) Fundamentals of cancer metabolism. Sci Adv 2:e1600200. https://doi.org/10.1126/sciadv.1600200
Diaz RJ, Golbourn B, Shekarforoush M, Smith CA, Rutka JT (2012) Aurora kinase B/C inhibition impairs malignant glioma growth in vivo. J Neurooncol 108:349–360. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11060-012-0835-2
Duffy MJ, Synnott NC, Crown J (2017) Mutant p53 as a target for cancer treatment. Eur J Cancer 83:258–265. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ejca.2017.06.023
Ernestus RI, Rohn G, Schroder R, Els T, Lee JY, Klug N, Paschen W (1996) Polyamine metabolism in gliomas. J Neurooncol 29:167–174
Floter J, Kaymak I, Schulze A (2017) Regulation of metabolic activity by p53. Metabolites 7:21. https://doi.org/10.3390/metabo7020021
Franko A, Shao Y, Heni M, Hennenlotter J, Hoene M, Hu C, Liu X, Zhao X, Wang Q, Birkenfeld AL, Todenhoefer T, Stenzl A, Peter A, Haering H-U, Lehmann R, Xu G, Lutz SZ (2020) Human prostate Cancer is characterized by an increase in Urea Cycle Metabolites. Cancers (Basel) 12:1814. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers12071814
Gerner EW, Meyskens FL (2004) Polyamines and cancer: old molecules, new understanding. Nat Rev Cancer 4:781–792. https://doi.org/10.1038/nrc1454
Gnanapradeepan K, Basu S, Barnoud T, Budina-Kolomets A, Kung C-P, Murphy ME (2018) The p53 tumor suppressor in the control of metabolism and ferroptosis. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne) 9:124. https://doi.org/10.3389/fendo.2018.00124
Greene JM, Feugang JM, Pfeiffer KE, Stokes JV, Bowers SD, Ryan PL (2013) L-arginine enhances cell proliferation and reduces apoptosis in human endometrial RL95-2 cells. Reprod Biol Endocrinol 11:15. https://doi.org/10.1186/1477-7827-11-15
Guan F, Kang Z, Zhang J-T, Xue N-N, Yin H, Wang L, Mao B-B, Peng W-C, Zhang B-L, Liang X, Hu Z-Q (2019) KLF7 promotes polyamine biosynthesis and glioma development through transcriptionally activating ASL. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 514:51–57. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bbrc.2019.04.120
Haines RJ, Pendleton LC, Eichler DC (2011) Argininosuccinate synthase: at the center of arginine metabolism. Int J Biochem Mol Biol 2:8–23
Hajaj E, Sciacovelli M, Frezza C, Erez A (2021) The context-specific roles of urea cycle enzymes in tumorigenesis. Mol Cell 81:3749–3759. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.molcel.2021.08.005
Huang H-L, Hsu H-P, Shieh S-C, Chang Y-S, Chen W-C, Cho C-Y, Teng C-F, Su I-J, Hung W-C, Lai M-D (2013) Attenuation of Argininosuccinate Lyase inhibits Cancer Growth via Cyclin A2 and nitric oxide. Mol Cancer Ther 12:2505–2516. https://doi.org/10.1158/1535-7163.Mct-12-0863
Keshet R, Szlosarek P, Carracedo A, Erez A (2018) Rewiring urea cycle metabolism in cancer to support anabolism. Nat Rev Cancer 18:634–645. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41568-018-0054-z
Khare S, Kim LC, Lobel G, Doulias PT, Ischiropoulos H, Nissim I, Keith B, Simon MC (2021) ASS1 and ASL suppress growth in clear cell renal cell carcinoma via altered nitrogen metabolism. Cancer & Metabolism 9:40. https://doi.org/10.1186/s40170-021-00271-8
Kim J, Hu Z, Cai L, Li K, Choi E, Faubert B, Bezwada D, Rodriguez-Canales J, Villalobos P, Lin Y-F, Ni M, Huffman KE, Girard L, Byers LA, Unsal-Kacmaz K, Pena CG, Heymach JV, Wauters E, Vansteenkiste J, Castrillon DH, Chen BPC, Wistuba I, Lambrechts D, Xu J, Minna JD, DeBerardinis RJ (2017) CPS1 maintains pyrimidine pools and DNA synthesis in KRAS/LKB1-mutant lung cancer cells. Nature 546:168–. https://doi.org/10.1038/nature22359
Lanpher BC, Gropman A, Chapman KA, Lichter-Konecki U, Summar ML (1993) Urea Cycle Disorders Overview. GeneReviews™
Lee JS, Adler L, Karathia H, Carmel N, Rabinovich S, Auslander N, Keshet R, Stettner N, Silberman A, Agemy L, Helbling D, Eilam R, Sun Q, Brandis A, Malitsky S, Itkin M, Weiss H, Pinto S, Kalaora S, Levy R, Barnea E, Admon A, Dimmock D, Stern-Ginossar N, Scherz A, Nagamani SCS, Unda M, Wilson DM III, Elhasid R, Carracedo A, Samuels Y, Hannenhalli S, Ruppin E, Erez A (2018) Urea cycle Dysregulation generates clinically relevant genomic and biochemical signatures. Cell 174:1559–. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cell.2018.07.019
Li JJ, Meng Y, Wu XL, Sun YX (2020) Polyamines and related signaling pathways in cancer. Cancer Cell Int 20:539. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12935-020-01545-9
Li L, Mao Y, Zhao L, Li L, Wu J, Zhao M, Du W, Yu L, Jiang P (2019) p53 regulation of ammonia metabolism through urea cycle controls polyamine biosynthesis. Nature 567:253–. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41586-019-0996-7
Liu J, Zhang C, Hu WW, Feng ZH (2019a) Tumor suppressor p53 and metabolism. J Mol Cell Biol 11:284–292. https://doi.org/10.1093/jmcb/mjy070
Liu X, Zhang XT, Bi JB, Li ZH, Zhang Z, Kong CZ (2019b) Caspase recruitment domain family member 10 regulates carbamoyl phosphate synthase 1 and promotes cancer growth in bladder cancer cells. J Cell Mol Med 23:8128–8138. https://doi.org/10.1111/jcmm.14683
Liu Z, Chen Y, Gao H, Xu W, Zhang C, Lai J, Liu X, Sun Y, Huang H (2020) Berberine inhibits cell proliferation by interfering with wild-type and mutant P53 in human glioma cells. Onco Targets Ther 13:12151–12162. https://doi.org/10.2147/ott.S279002
Matos A, Carvalho M, Bicho M, Ribeiro R (2021) Arginine and Arginases modulate metabolism, tumor microenvironment and prostate Cancer progression. Nutrients 13:4503. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu13124503
Menendez D, Inga A, Resnick MA (2006) The biological impact of the human master regulator p53 can be altered by mutations that change the spectrum and expression of its target genes. Mol Cell Biol 26:2297–2308. https://doi.org/10.1128/mcb.26.6.2297-2308.2006
Moren L, Wibom C, Bergstrom P, Johansson M, Antti H, Bergenheim AT (2016) Characterization of the serum metabolome following radiation treatment in patients with high-grade gliomas. Radiat Oncol 11:51. https://doi.org/10.1186/s13014-016-0626-6
Morris SM (2002) Regulation of enzymes of the urea cycle and arginine metabolism. Annu Rev Nutr 22:87–105. https://doi.org/10.1146/annurev.nutr.22.110801.140547
Muthukumaran S, Jaidev J, Umashankar V, Sulochana KN (2017) Ornithine and its role in metabolic diseases: an appraisal. Biomed Pharmacother 86:185–194. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biopha.2016.12.024
Norouzi M, Yathindranath V, Thliveris JA, Kopec BM, Siahaan TJ, Miller DW (2020) Doxorubicin-loaded iron oxide nanoparticles for glioblastoma therapy: a combinational approach for enhanced delivery of nanoparticles. Sci Rep 10:11292. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-020-68017-y
Ochocki JD, Khare S, Hess M, Ackerman D, Qiu B, Daisak JI, Worth AJ, Lin N, Lee P, Xie H, Li B, Wubbenhorst B, Maguire TG, Nathanson KL, Alwine JC, Blair IA, Nissim I, Keith B, Simon MC (2018) Arginase 2 suppresses renal carcinoma progression via Biosynthetic Cofactor Pyridoxal phosphate depletion and increased polyamine toxicity. Cell Metab 27:1263–. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cmet.2018.04.009
Ohgaki H (2005) Genetic pathways to glioblastomas. Neuropathology 25:1–7. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1440-1789.2004.00600.x
Ohgaki H, Kleihues P (2007) Genetic pathways to primary and secondary glioblastoma. Am J Pathol 170:1445–1453. https://doi.org/10.2353/ajpath.2007.070011
Pan CY, Li B, Simon MC (2020) Moonlighting functions of metabolic enzymes and metabolites in cancer. Mol Cell 81:3760–3774. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.molcel.2021.08.031
Park CM, Park MJ, Kwak HJ, Moon SI, Yoo DH, Lee HC, Park IC, Rhee CH, Hong SI (2006) Induction of p53-mediated apoptosis and recovery of chemosensitivity through p53 transduction in human glioblastoma cells by cisplatin. Int J Oncol 28:119–125
Patil MD, Bhaumik J, Babykutty S, Banerjee UC, Fukumura D (2016) Arginine dependence of tumor cells: targeting a chink in cancer’s armor. Oncogene 35:4957–4972. https://doi.org/10.1038/onc.2016.37
Rabinovich S, Adler L, Yizhak K, Sarver A, Silberman A, Agron S, Stettner N, Sun Q, Brandis A, Helbling D, Korman S, Itzkovitz S, Dimmock D, Ulitsky I, Nagamani SCS, Ruppin E, Erez A (2015) Diversion of aspartate in ASS1-deficient tumours fosters de novo pyrimidine synthesis. Nature 527:379–. https://doi.org/10.1038/nature15529
Reardon DA, Mitchell DA (2017) The development of dendritic cell vaccine-based immunotherapies for glioblastoma. Semin Immunopathol 39:225–239. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00281-016-0616-7
Ridder DA, Schindeldecker M, Weinmann A, Berndt K, Urbansky L, Witzel HR, Heinrich S, Roth W, Straub BK (2021) Key enzymes in Pyrimidine Synthesis, CAD and CPS1, predict prognosis in Hepatocellular Carcinoma. Cancers (Basel) 13:744. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers13040744
Shechter KR, Kafkia E, Zirngibl K, Gawrzak S, Alladin A, Machado D, Luchtenborg C, Sevin DC, Brugger B, Patil KR, Jechlinger M (2021) Metabolic memory underlying minimal residual disease in breast cancer. Mol Syst Biol 17:e10141. https://doi.org/10.15252/msb.202010141
Shen L, Sun X, Fu Z, Yang G, Li J, Yao L (2012) The fundamental role of the p53 pathway in Tumor Metabolism and its implication in Tumor Therapy. Clin Cancer Res 18:1561–1567. https://doi.org/10.1158/1078-0432.Ccr-11-3040
Sheng J, He X, Yu W, Chen Y, Long Y, Wang K, Zhu S, Liu Q (2021) p53-targeted lncRNA ST7-AS1 acts as a tumour suppressor by interacting with PTBP1 to suppress the Wnt/β-catenin signalling pathway in glioma. Cancer Lett 503:54–68. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.canlet.2020.12.039
Shergalis A, Bankhead A III, Luesakul U, Muangsin N, Neamati N (2018) Current Challenges and Opportunities in Treating Glioblastoma. Pharmacol Rev 70:412–445. https://doi.org/10.1124/pr.117.014944
Shu KX, Li B, Liang YL, Xie YF, Zhang JC, Wei JM (2006) Effects of exogenous p53 transfection on the gene expression in the human brain glioma cell line U251. Colloids and Surfaces B-Biointerfaces 47:126–131. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.colsurfb.2005.12.005
Stindt MH, Muller PAJ, Ludwig RL, Kehrloesser S, Dotsch V, Vousden KH (2015) Functional interplay between MDM2, p63/p73 and mutant p53. Oncogene 34:4300–4310. https://doi.org/10.1038/onc.2014.359
Syed N, Langer J, Janczar K, Singh P, Lo Nigro C, Lattanzio L, Coley HM, Hatzimichael E, Bomalaski J, Szlosarek P, Awad M, O’Neil K, Roncaroli F, Crook T (2013) Epigenetic status of argininosuccinate synthetase and argininosuccinate lyase modulates autophagy and cell death in glioblastoma. Cell Death Dis 4:e458. https://doi.org/10.1038/cddis.2012.197
Vander Heiden MG, DeBerardinis RJ (2017) Understanding the Intersections between Metabolism and Cancer Biology. Cell 168:657–669. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cell.2016.12.039
Vousden KH, Prives C (2009) Blinded by the light: the growing complexity of p53. Cell 137:413–431. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cell.2009.04.037
Wong KB, DeDecker BS, Freund SMV, Proctor MR, Bycroft M, Fersht AR (1999) Hot-spot mutants of p53 core domain evince characteristic local structural changes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 96:8438–8442. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.96.15.8438
Wu GT, Yan YL, Zhou YY, Wang X, Wei J, Chen X, Lin W, Qu CL, Zhou JH, Xu ZJ (2019) Expression and clinical significance of CPS1 in glioblastoma multiforme. Curr Res Translational Med 67:123–128. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.retram.2019.08.003
Zhang T, Hu L, Tang JF, Xu H, Tian K, Wu MN, Huang SY, Du YM, Zhou P, Lu RJ, He S, Xu JM, Si JJ, Li J, Chen DL, Ran JH (2021) Metformin Inhibits the Urea Cycle and Reduces Putrescine Generation in Colorectal Cancer Cell Lines. Molecules 26:1990. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules26071990
Zhang XD, Qin ZH, Wang J (2010) The role of p53 in cell metabolism. Acta Pharmacol Sin 31:1208–1212. https://doi.org/10.1038/aps.2010.151
Statements & Declarations
Funding
This work was supported by the Natural Science Foundation of Chongqing Science and Technology Bureau (Grant/award No: #cstc2020jcyj-msxmX0387), Yuzhong Science and Technology Bureau of Chongqing (Grant/award No: #2020115).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
In our research, Yuhong Zhao conducted the experiments and wrote the paper. Yingxi Chen and Ling Wei assisted with the experiments and data analysis. Jianhua Ran, Kejian Wang, Shujuan Zhu gave advice for experimental design. Qian Liu designed the experiments and revised the manuscript. All authors approved the final manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
All authors declare no conflict of interest.
Ethical approval
Not applicable.
Consent to participate
Not applicable.
Consent for publication
Not applicable.
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Zhao, Y., Chen, Y., Wei, L. et al. p53 inhibits the Urea cycle and represses polyamine biosynthesis in glioma cell lines. Metab Brain Dis 38, 1143–1153 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11011-023-01173-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11011-023-01173-y