Abstract
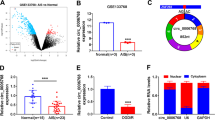
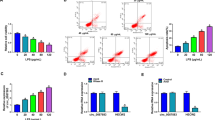
Circular RNAs (circRNAs) exert regulatory roles in cerebrovascular disease. Human brain microvascular endothelial cells (HBMECs) participated in brain vascular dysfunction in ischemic stroke. Herein, the functions of circ_0000566 in oxygen–glucose deprivation and reoxygenation (OGD/R)-induced HBMECs were investigated. The expression of circ_0000566, miR-18a-5p, and Activin receptor type 2B (ACVR2B) was measured via quantitative real-time PCR (qRT-PCR). Cell Counting Kit-8 (CCK-8) and flow cytometry assays were utilized to detect cell viability and cell apoptosis. Western blot assay was employed to measure the levels of apoptotic-related proteins and ACVR2B. The secretion of IL-1β, IL-6, and TNF-α was detected via corresponding kits. The relationship between miR-18a-5p and circ_0000566 or ACVR2B was examined via dual-luciferase reporter assay and RNA immunoprecipitation (RIP) assay. Circ_0000566 and ACVR2B were highly expressed, while miR-18a-5p was down-regulated in OGD/R-treated HBMECs. OGD/R treatment promoted HBMECs apoptosis and inflammation and suppressed cell viability, which could be attenuated by silencing of circ_0000566. Circ_0000566 acted as a miR-18a-5p sponge to contribute to OGD/R-induced HBMECs injury. ACVR2B served as a direct target of miR-18a-5p, and ACVR2B overexpression might abolish the inhibitory role of miR-18a-5p on OGD/R-treated HBMEC injury. Circ_0000566 sponged miR-18a-5p to regulate OGD/R-induced HBMECs injury via regulating ACVR2B expression.
Highlights
• The expression of circ_0000566 was elevated in OGD/R-induced human brain microvascular endothelial cell injury.
• Knockdown of circ_0000566 attenuated OGD/R-induced human brain microvascular endothelial cells injury via sponging miR-18a-5p.
• MiR-18a-5p regulated ACVR2B expression to alleviate OGD/R-induced human brain microvascular endothelial cell injury.
• Circ_0000566 regulated OGD/R-induced human brain microvascular endothelial cell injury via targeting the miR-18a-5p/ACVR2B.







Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
The analyzed data sets generated during the present study are available from the corresponding author on reasonable request.
References
Campbell BC, Mitchell PJ, Kleinig TJ, Dewey HM, Churilov L, Yassi N, Yan B, Dowling RJ, Parsons MW, Oxley TJ, Wu TY, Brooks M, Simpson MA, Miteff F, Levi CR, Krause M, Harrington TJ, Faulder KC, Steinfort BS, Priglinger M, Ang T, Scroop R, Barber PA, McGuinness B, Wijeratne T, Phan TG, Chong W, Chandra RV, Bladin CF, Badve M, Rice H, de Villiers L, Ma H, Desmond PM, Donnan GA, Davis SM, Investigators E-I (2015) Endovascular therapy for ischemic stroke with perfusion-imaging selection. N Engl J Med 372:1009–1018
Feng B, Meng L, Luan L, Fang Z, Zhao P, Zhao G (2020) Upregulation of extracellular vesicles-encapsulated miR-132 released from mesenchymal stem cells attenuates ischemic neuronal injury by inhibiting Smad2/c-jun pathway via Acvr2b suppression. Front Cell Dev Biol 8:568304
Guo T, Liu Y, Ren X, Wang W, Liu H (2020) Promoting role of long non-coding RNA small nucleolar RNA host gene 15 (SNHG15) in neuronal injury following ischemic stroke via the MicroRNA-18a/CXC Chemokine Ligand 13 (CXCL13)/ERK/MEK axis. Med Sci Monit 26:e923610
Kristensen LS, Andersen MS, Stagsted LVW, Ebbesen KK, Hansen TB, Kjems J (2019) The biogenesis, biology and characterization of circular RNAs. Nat Rev Genet 20:675–691
Lakhan SE, Kirchgessner A, Hofer M (2009) Inflammatory mechanisms in ischemic stroke: therapeutic approaches. J Transl Med 7:97
Lee ECS, Elhassan SAM, Lim GPL, Kok WH, Tan SW, Leong EN, Tan SH, Chan EWL, Bhattamisra SK, Rajendran R, Candasamy M (2019) The roles of circular RNAs in human development and diseases. Biomed Pharmacother 111:198–208
Li G, Morris-Blanco KC, Lopez MS, Yang T, Zhao H, Vemuganti R, Luo Y (2018) Impact of microRNAs on ischemic stroke: from pre- to post-disease. Prog Neurobiol 163–164:59–78
Li J, Wang J, Wang Z (2021) Circ_0006768 upregulation attenuates oxygen-glucose deprivation/reoxygenation-induced human brain microvascular endothelial cell injuries by upregulating VEZF1 via miR-222-3p inhibition. Metab Brain Dis 36:2521–2534
Liu H, Wei X, Kong L, Liu X, Cheng L, Yan S, Zhang X, Chen L (2015) NOD2 is involved in the inflammatory response after cerebral ischemia-reperfusion injury and triggers NADPH oxidase 2-derived reactive oxygen species. Int J Biol Sci 11:525–535
Lu YY, Ma XJ, Yang YN (2020) MicroRNA-18a-5p mitigates oxygen-glucose-deprivation/reoxygenation-induced injury through suppression of TLRs/NF-kappaB signaling by targeting TLR8 in PC12 cells. Biosci Biotechnol Biochem 84:2476–2483
Lyu D, Huang S (2017) The emerging role and clinical implication of human exonic circular RNA. RNA Biol 14:1000–1006
Magga J, Vainio L, Kilpio T, Hulmi JJ, Taponen S, Lin R, Rasanen M, Szabo Z, Gao E, Rahtu-Korpela L, Alakoski T, Ulvila J, Laitinen M, Pasternack A, Koch WJ, Alitalo K, Kivela R, Ritvos O, Kerkela R (2019) Systemic blockade of ACVR2B ligands protects myocardium from acute ischemia-reperfusion injury. Mol Ther 27:600–610
Mandalaneni K, Rayi A, Jillella DV (2021) Stroke reperfusion injury. In: StatPearls. Treasure Island (FL)
Manning NW, Campbell BC, Oxley TJ, Chapot R (2014) Acute ischemic stroke: time, penumbra, and reperfusion. Stroke 45:640–644
Min X, Liu DL, Xiong XD (2021) Circular RNAs as competing endogenous RNAs in cardiovascular and cerebrovascular diseases: molecular mechanisms and clinical implications. Front Cardiovasc Med 8:682357
Panda AC (2018) Circular RNAs act as miRNA sponges. Adv Exp Med Biol 1087:67–79
Sayed D, Abdellatif M (2011) MicroRNAs in development and disease. Physiol Rev 91:827–887
Tang C, Ou J, Kou L, Deng J, Luo S (2020) Circ_016719 plays a critical role in neuron cell apoptosis induced by I/R via targeting miR-29c/Map2k6. Mol Cell Probes 49:101478
Wang X, Xu Q, Wang S (2021) Overexpression of miR-149–5p attenuates cerebral Ischemia/Reperfusion (I/R) injury by targeting notch2. Neuromol Med 24:279–289
Wilczynska A, Bushell M (2015) The complexity of miRNA-mediated repression. Cell Death Differ 22:22–33
Xu X, Wu Z, Qiu H, Wu J (2021) Circular RNA circPHC3 promotes cell death and apoptosis in human BMECs after oxygen glucose deprivation via miR-455-5p/TRAF3 axis in vitro. Neuropsychiatr Dis Treat 17:147–156
Yan H, Huang W, Rao J, Yuan J (2021) miR-21 regulates ischemic neuronal injury via the p53/Bcl-2/Bax signaling pathway. Aging (Albany NY) 13:22242–22255
Yang J, Chen M, Cao RY, Li Q, Zhu F (2018) The role of circular RNAs in cerebral ischemic diseases: ischemic stroke and cerebral ischemia/reperfusion injury. Adv Exp Med Biol 1087:309–325
Yang X, Li X, Zhong C, Peng J, Pang J, Peng T, Wan W, Li X (2021a) Circular RNA circPHKA2 relieves OGD-induced human brain microvascular endothelial cell injuries through competitively binding miR-574-5p to modulate SOD2. Oxid Med Cell Longev 2021:3823122
Yang Z, Huang C, Wen X, Liu W, Huang X, Li Y, Zang J, Weng Z, Lu D, Tsang CK, Li K, Xu A (2021b) Circular RNA circ-FoxO3 attenuates blood-brain barrier damage by inducing autophagy during ischemia/reperfusion. Mol Ther 30(3):1275–1287
Funding
This work was funded by the Education Department of Heilongjiang Province Number: 12541760.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Conceptualization and Methodology: Haitao Xiao and Jinxing Liu; Formal analysis and Data curation: Yixin Zhang, Jialiang Li and Tingyu Zhang; Validation and Investigation: Dan Liu and Honglin Chen; Writing—original draft preparation and Writing—review and editing: Dan Liu, Haitao Xiao, and Jinxing Liu who were also the major contributors in writing the manuscript. All authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethics approval and consent to participate
The present study was approved by the ethical review committee of First Affiliated Hospital,Heilongjiang University of Chinese Medicine. Written informed consent was obtained from all enrolled patients.
Consent for publication
Patients agree to participate in this work.
Competing interests
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher's note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Dan Liu and Haitao Xiao contributed equally to this work as co-first authors.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary

Supplementary Figure 1.
The cell images under normoxia and OGD conditions. (PNG 533 kb)

Supplementary Figure 2.
ACVR2B regulated OGD/R-stimulated HBMEC damage. A ACVR2B protein expression was detected by Western blot in HBMECs transfected with si-NC or si-ACVR2B (n = 3). B-M Cells were differently treated as the following groups: control, OGD/R, OGD/R + si-NC, OGD/R + si-ACVR2B (n = 3). B The expression of ACVR2B was detected by qRT-PCR. C Cell viability was determined using CCK-8 assay. D LDH release was measured by LDH Cytotoxicity Assay Kit. E Flow cytometry was used to detect cell apoptosis. F-J Western blot was used to examine the protein level of Bcl-2, Bax, c-caspase 3, and c-caspase 9. K-M ELISA was employed to assess the levels of IL-1β, IL-6, and TNF-α via corresponding detection kits. **P < 0.01, ***P < 0.001. (PNG 788 kb)
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Liu, D., Xiao, H., Liu, J. et al. Circ_0000566 contributes oxygen–glucose deprivation and reoxygenation (OGD/R)-induced human brain microvascular endothelial cell injury via regulating miR-18a-5p/ACVR2B axis. Metab Brain Dis 38, 1273–1284 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11011-023-01166-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11011-023-01166-x