Abstract
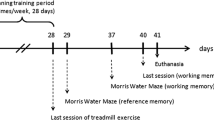
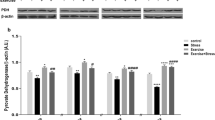
Neuroinflammation plays an essential role in the pathogenesis of Alzheimer’s disease. The preventive effect of physical exercise on attenuating neuroinflammation has not been completely defined. Levisticum officinale is known as a medicinal plant with antioxidant and anti-inflammatory properties. The current study was designed to investigate the neuroprotective impacts of treadmill running and Levisticum officinale on lipopolysaccharide (LPS)-induced learning and memory impairments and neuroinflammation in rats. Male Wistar rats ran on a treadmill and/or were pretreated with Levisticum officinale extract at a dose of 100 mg/kg for a week. Then, rats received intraperitoneal injection of LPS at a dose of 1 mg/kg. Treadmill running and/or treatment of extract lasted three more weeks. Behavioral, molecular, biochemical and immunohistochemical assessments were carried out after the end of the experiment. LPS administration resulted in spatial learning and memory impairments along with increased mRNA expression of interleukin-6 and malondialdehyde levels, as well as decreased superoxide dismutase activity and neurogenesis in the hippocampus. Moreover, treadmill running for four weeks, alone and in combination with Levisticum officinale extract attenuated spatial learning and memory deficits, decreased the mRNA expression of interleukin-6 and malondialdehyde levels, and enhanced superoxide dismutase activity and neurogenesis in the hippocampus. In conclusion, the advantageous effects of running exercise and Levisticum officinale extract on LPS-induced memory impairments are possibly due to the antioxidant and anti-inflammatory activity and enhancing neurogenesis.






Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
On request from the corresponding author.
References
Aebi H (1984) Catalase in vitro. Methods Enzymol 105:121–126
Afarnegan H, Shahraki A, Shahraki J (2017) The hepatoprotective effects of aquatic extract of Levisticum officinale against paraquat hepatocyte toxicity. Pak J Pharm Sci 30:2363–2368
Ahmadi M, Rajaei Z, Hadjzadeh MA, Nemati H, Hosseini M (2017) Crocin improves spatial learning and memory deficits in the Morris water maze via attenuating cortical oxidative damage in diabetic rats. Neurosci Lett 642:1–6
Ali MR, Abo-Youssef AM, Messiha BA, Khattab MM (2016) Tempol and perindopril protect against lipopolysaccharide-induced cognition impairment and amyloidogenesis by modulating brain-derived neurotropic factor, neuroinflammation and oxido-nitrosative stress. NaunynSchmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol 389:637–656
Amooheydari Z, Rajaei Z, Alaei H, Esmaeil N (2022) Supplementation of carvacrol attenuates hippocampal tumor necrosis factor–alpha level, oxidative stress, and learning and memory dysfunction in lipopolysaccharide–exposed rats. Adv Biomed Res 11:33
Amraie I, Pouraboli I, Rajaei Z (2020) Neuroprotective effects of Levisticum officinale on LPS-induced spatial learning and memory impairments through neurotrophic, anti-inflammatory, and antioxidant properties. Food Funct 11:6608–6621
Babcock KR, Page JS, Fallon JR, Webb AE (2021) Adult hippocampal neurogenesis in aging and AD. Stem cell reports 16:681–693
Bai K, Xu W, Zhang J, Kou T, Niu Y, Wan X, Zhang L, Wang C, Wang T (2016) Assessment of free radical scavenging activity of dimethylglycine sodium salt and its role in providing protection against lipopolysaccharide-induced oxidative stress in mice. PLoS ONE 11:e0155393
Barnham KJ, Masters CL, Bush AI (2004) Neurodegenerative diseases and oxidative stress. Nat Rev Drug Discov 3:205–214
Batista CRA, Gomes GF, Candelario-Jalil E, Fiebich BL, de Oliveira ACP (2019) Lipopolysaccharide-induced neuroinflammation as a bridge to understand neurodegeneration. Int J Mol Sci 20:2293
Beheshti F, Hashemzehi M, Sabeti N, Hashemi Sadr S, Hosseini M (2019) The effects of aminoguanidine on hippocampal cytokines, amyloid beta, brain-derived neurotrophic factor, memory and oxidative stress status in chronically lipopolysaccharide-treated rats. Cytokine 113:347–355
Borsini A, Zunszain PA, Thuret S, Pariante CM (2015) The role of inflammatory cytokines as key modulators of neurogenesis. Trends Neurosci 38:145–157
Bossù P, Cutuli D, Palladino I, Caporali P, Angelucci F, Laricchiuta D, Gelfo F, De Bartolo P, Caltagirone C, Petrosini L (2012) A single intraperitoneal injection of endotoxin in rats induces long-lasting modifications in behavior and brain protein levels of TNF-α and IL-18. J Neuroinflammation 9:101
Bouzid MA, Filaire E, Matran R, Robin S, Fabre C (2018) Lifelong voluntary exercise modulates age-related changes in oxidative stress. Int J Sport Med 39:21–28
Bradford MM (1976) A rapid and sensitive method for the quantitation of microgram quantities of protein utilizing the principle of protein-dye binding. Anal Biochem 72:248–254
Brown GC (2019) The endotoxin hypothesis of Neurodegeneration. J Neuroinflammation 16:180
Castellani RJ, Rolston RK, SmithMA (2011) Alzheimer disease. Dis Mon 56:484–546
Cechetti F, Worm PV, Elsner VR, Bertoldi K, Sanches E, Ben J, Siqueira IR, Netto CA (2012) Forced treadmill exercise prevents oxidative stress and memory deficits following chronic cerebral hypoperfusion in the rat. Neurobiol Learn Mem 97:90–96
Chen J, Buchanan JB, Sparkman NL, Godbout JP, Freund GG, Johnson RW (2008) Neuroinflammation and disruption in working memory in aged mice after acute stimulation of the peripheral innate immune system. Brain Behav Immun 22:301–311
Chowdhury AA, Gawali NB, Shinde P, Munshi R, Juvekar AR (2018) Imperatorin ameliorates lipopolysaccharide induced memory deficit by mitigating proinflammatory cytokines, oxidative stress and modulating brain-derived neurotropic factor. Cytokine 110:78–86
Dementia WHO Newsletter; 2 September 2021
Devi SA, Kiran TR (2004) Regional responses in antioxidant system to exercise training and dietary vitamin E in aging rat brain. Neurobiol Aging 25:501–508
Donev R (2017) Advances in protein chemistry and structural biology, stress and inflammation in disorders. Academic Press
Downie S, Plunkett G, Watson M, Spalik K, Katz-Downie D, Valiejo-Roman C, Terentieva E, Troitsky A, Lee B, Lahham J, El-oqlah A (2001) Tribes and clades within Apiaceae subfamily Apioideae: the contribution of molecular data. Edinb J of Bot 58:301–330
Dugan LL, Ali SS, Shekhtman G, Roberts, Lucero J, Quick KL, Behrens MM (2009) IL-6 mediated degeneration of forebrain GABAergic interneurons and cognitive impairment in aged mice through activation of neuronal NADPH oxidase. PLoS ONE 4:e5518
Ekdahl CT, Claasen JH, Bonde S, Kokaia Z, Lindvall O (2003) Inflammation is detrimental for neurogenesis in adult brain. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 100:13632–13637
Farmer J, Zhao X, van Praag H, Wodtke K, Gage FH, Christie BR (2004) Effects of voluntary exercise on synaptic plasticity and gene expression in the dentate gyrus of adult male sprague–dawley rats in vivo. Neuroscience 124:71–79
Garcı´a-Mesa Y, Lo´pez-Ramos JC, Gime´nez-Llort L, Revilla S, Guerra R, Gruart A, LaFerla FM, Cristo`fol R, Delgado-Garcı´a JM, Sanfeliu C (2011) Physical exercise protects against Alzheimer’s disease in 3xTg-AD mice. J Alzheimer Dis 24:421–454
Ghaedi N, Pouraboli I, Askari N (2019) Antidiabetic properties of hydroalcoholic leaf and stem extract of Levisticum officinale: an implication for α-amylase inhibitory activity of extract ingredients through molecular docking. Iran J Pharm Res 19:231–250
Giannopolitis CN, Ries S (1977) Superoxide dismutases. I. occurrence in higher plants. Plant Physiol 59:309–314
Hosseini M, Salmani H, Baghcheghi Y (2021) Losartan improved hippocampal long-term potentiation impairment induced by repeated LPS injection in rats. Physiol Rep 9:e14874
Hou Y, Xie G, Miao F, Ding L, Mou Y, Wang L, Su G, Chen G, Yang J, Wu C (2014) Pterostilbene attenuates lipopolysaccharide-induced learning and memory impairment possibly via inhibiting microglia activation and protecting neuronal injury inmice. Prog Neuropsychopharmacol Biol Psychiatr 54:92–102
Houdek HM, Larson J, Watt JA, Rosenberger TA (2014) Bacterial lipopolysaccharide induces a dose-dependent activation of neuroglia and loss of basal forebrain cholinergic cells in the rat brain. Inflamm Cell Signal 1:e47
Ighodaro O, Akinloye O (2018) First line defence antioxidants-superoxide dismutase (SOD), catalase (CAT) and glutathione peroxidase (GPX): their fundamental role in the entire antioxidant defence grid. Alex J Med 54:287–293
Jakubczyk A, Złotek U, Szymanowska U, Rybczyńska-Tkaczyk K, Jęderka K, Lewicki S (2020) In vitro antioxidant, anti-inflammatory, anti-metabolic syndrome, antimicrobial, and anticancer effect of phenolic acids isolated from fresh lovage leaves [Levisticum officinale Koch] elicited with jasmonicacid and yeast extract. Antioxid (Basel) 9:554
Kelly AM (2018) Exercise-induced modulation of neuroinflammation in models of Alzheimer’s disease. Brain Plast 4:81–94
Kurtel H, Granger DN, Tso P, Grisham MB (1992) Vulnerability of intestinal interstitial fluid to oxidant stress. Am J Physiol 263:G573–G578
Lee JW, Lee YK, Yuk DY, Choi DY, Ban SB, Oh KW, Hong JT (2008) Neuro-inflammation induced by lipopolysaccharide causes cognitive impairment through enhancement of beta-amyloid generation. J Neuroinflammation 29:5–37
Leem YH, Lee YL, Son HJ, Lee SH (2011) Chronic exercise ameliorates the neuroinflammation in mice carrying NSE/htau23. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 406:359–365
Lin TW, Chen SJ, Huang TY, Chang CY, Chuang JI, Wu FS, Kuo YM, Jen CJ (2012) Different types of exercise induce differential effects on neuronal adaptations and memory performance. Neurobiol Learn Mem 97:140–147
Littlefield AM, Setti SE, Priester C, Kohman RA (2015) Voluntary exercise attenuates LPS-induced reductions in neurogenesis and increases microglia expression of a proneurogenic phenotype in aged mice. J Neuroinflammation 12:138
Liu HL, Zhao G, Cai K, Zhao HH, Shi LD (2011) Treadmill exercise prevents decline in spatial learning and memory in APP/PS1 transgenic mice through improvement of hippocampal long-term potentiation. Behav Brain Res 218:308–314
Livak KJ, Schmittgen TD (2001) Analysis of relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and the 2 – ∆∆CT method. Methods 25:402–408
Lonnemann N, Hosseini S, Ohm M, Geffers R, Hiller K, Dinarello CA, Korte M (2022) IL-37 expression reduces acute and chronic neuroinflammation and rescues cognitive impairment in an Alzheimer’s disease mouse model. eLife 11:e75889
Lovatel GA, Elsner VR, Bertoldi K, Vanzella A, Spindler C, Cechinel LR, Netto CA, Moutri AR, Siqueira IR (2013) Treadmill exercise induces age-related changes in aversive memory, neuroinflammatory and epigenetic processes in the rat hippocampus. Neurobiol Learn Mem 101:94–102
Ming Z, Sawicki G, Bekar LK (2015) Acute systemic LPS mediated inflammation induces lasting changes in mouse cortical neuromodulation and behavior. Neurosci Lett 590:96–100
Mollashahee-Kohkan F, Saravani R, Khalili T, Galavi H, Sargazi S (2019) Levisticum Officinale extract triggers apoptosis and down-regulates ZNF703 gene expression in breast cancer cell lines. Rep Biochem Mol Biol 8:119–125
Monje ML, Toda H, Palmer TD (2003) Inflammatory blockade restores adult hippocampal neurogenesis. Science 302:1760–1765
Mota BC, Kelly ÁM (2020) Exercise alters LPS-induced glial activation in the mouse brain. Neuronal Signal 4:NS20200003
Mu L, Cai J, Gu B, Yu L, Li C, Liu QS, Zhao L (2022) Treadmill exercise prevents decline in spatial learning and memory in 3×Tg-AD mice through enhancement of structural synaptic plasticity of the hippocampus and prefrontal cortex. Cells 11:244
Murphy MP, LeVine H 3rd (2010) Alzheimer’s disease and the amyloid-beta peptide. J Alzheimers Dis 19:311–323
Ohkawa H, Ohishi N, Yagi K (1979) Assay for lipid peroxides in animal tissues by thiobarbituric acid reaction. Anal Biochem 95:351–358
Ormerod BK, Hanft SJ, Asokan A, Haditsch U, Lee SW, Palmer TD (2013) PPARγ activation prevents impairments in spatial memory and neurogenesis following transient illness. Brain Behav Immun 29:28–38
Rovio S, Kareholt I, Helkala EL, Viitanen M, Winblad B, TuomilehtoJ, Soininen H, Nissinen A, Kivipelto M (2005) Leisure-time physical activity at midlife and the risk of dementia and Alzheimer’s disease. Lancet Neurol 4:705–711
Ryan SM, Nolan YM (2016) Neuroinflammation negatively affects adult hippocampal neurogenesis and cognition: can exercise compensate? Neurosci Biobehav Rev 61:121–131
Shahidani S, Rajaei Z, Alaei H, Mohammadzadeh S (2022) The impact of sesamol and exercise on striatal TNF-α level, behavioral deficits and oxidative stress status in the rat model of Parkinson’s disease. Physiol Pharmacol 26:30–38
Sung PS, Lin PY, Liu CH, Su HC, Tsai KJ (2020) Neuroinflammation and neurogenesis in Alzheimer’s disease and potential therapeutic approaches. Int J Mol Sci 21:701
Suwannakot K, Sritawan N, Naewla S, Aranarochana A, Sirichoat A, Pannangrong W, Wigmore P, Welbat JU (2022) Melatonin attenuates methotrexate-induced reduction of antioxidant activity related to decreases of neurogenesis in adult rat hippocampus and prefrontal cortex. Oxid Med Cell Longev 2022:1596362
Tsai S-F, Ku N-W, Wang T-F, Yang Y-H, Shih Y-H, Wu S-Y, Lee C-W, Yu M, Yang T-T, Kuo Y-M (2018) Long-term moderate exercise rescues age-related decline in hippocampal neuronal complexity and memory. Gerontology 64:551–561
Um HS, Kang EB, Koo JH, Kim HT, Lee J, Kim EJ, Yang CH, An GY, Cho IH, Cho JY (2011) Treadmill exercise represses neuronal cell death in an aged transgenic mouse model of Alzheimer’s disease. Neurosci Res 69:161–173
Valero J, Mastrella G, Neiva I, Sanchez S, Malva JO (2014) Long term effects of an acute and systemic administration of LPS on adult neurogenesis and spatial memory. Front Neurosci 8:83
Vallieres L, Campbell IL, Gage FH, Sawchenko PE (2002) Reduced hippocampal neurogenesis in adult transgenic mice with chronic astrocytic production ofinterleukin-6. J Neurosci 22:486–492
van Praag H, Christie BR, Sejnowski TJ, Gage FH (1999) Running enhances neurogenesis, learning, and long-term potentiation in mice. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 96:13427–13431
van Praag H, Shubert T, Zhao C, Gage FH (2005) Exercise enhances learning and hippocampal neurogenesis in aged mice. J Neurosci 25:8680–8685
Vanzella C, Neves JD, Vizuete AF, Aristimunha D, Kolling J, Longoni A, Gonçalves CAS, Wyse ATS, Netto CA (2017) Treadmill running prevents age-related memory deficit and alters neurotrophic factors and oxidative damage in the hippocampus of Wistar rats. Behave Brain Res 334:78–85
Veerhuis R (2011) Histological and direct evidence for the role of complement in the neuroinflammation of AD. Curr Alzheimer Res 8:34–58
Wu CW, Chen YC, Yu L, Chen HI, Jen CJ, Huang AM, Tsai HJ, Chang YT, Kuo YM (2007) Treadmill exercise counteracts the suppressive effects of peripheral lipopolysaccharide on hippocampal neurogenesis and learning and memory. J Neurochem 103:2471–2481
Zakaria R, Wan Yaacob WM, Othman Z, Long I, Ahmad AH, Al-Rahbi B (2017) Lipopolysaccharide-induced memory impairment in rats: a model of Alzheimer’s disease. Physiol Res 66:553–565
Zarei S, Mohammadi P, Bakhtiari A, Moridi H, Janmohammadi E, Kaki A, Gholamhoseinian A, Sharifi-far F, Hatami M, Hosseini-Zijoud SM, Moradi MN (2013) Identification of anticholinesterase compounds from Berberis integerrima, Rheum ribes and Levisticum officinale. Ann Biol Res 4:138–142
Zhao J, Bi W, Xiao S, Lan X, Cheng X, Zhang J, Lu D, Wei W, Wang Y, Li H, Fu Y, Zhu L (2019) Neuroinflammation induced by lipopolysaccharide causes cognitive impairment in mice. Sci Rep 9:5790
Zhang Q, Zhang J, Yan Y, Zhang P, Zhang W, Xia R (2017) Proinflammatory cytokines correlate with early exercise attenuating anxiety-like behaviour after cerebral ischemia. Brain Behav 7:e00854
Zhang L, Liu Y, Wang X, Wang D, Wu H, Chen H, Chen J, Liu Y (2022) Treadmill exercise improve recognition memory by TREM2 pathway to inhibit hippocampal microglial activation and neuroinflammation in Alzheimer’s disease model. Physiol Behav 251:113820
Zheng C, Zhou XW, Wang JZ (2016) The dual roles of cytokines in Alzheimer’s disease: update on interleukins, TNF-α, TGF-β and IFN-γ. Transl Neurodegener 5:7
Zhu J, Ge F, Zeng Y, Qu Y, Chen W, Yang H, Yang L, Fang F, Song H (2022) Physical and mental activity, disease susceptibility, and risk of dementia: a prospective cohort study based on UK Biobank. Neurology 99:e799–e813
Złotek U, Szymanowska U, Pecio U, Kozachok S, Jakubczyk A (2019) Antioxidative and potentially anti-inflammatory activity of phenolics from Lovage leaves Levisticum officinale Koch elicited with jasmonic acid and yeast extract. Molecules 24:1441
Funding
This study was supported by grants from the Council of Research, Isfahan University of Medical Sciences, and the Council of Research, Shahid Bahonar University of Kerman.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
ZR, IP designed the study; EA acquired data; ZR, IP, HS, EA analyzed and interpreted the data; ZR prepared the draft of the paper; ZR, IP, HS critically revised the article. All authors approved final version of the article.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethical approval and consent to participate
The maintenance and treatment of animals were carried out in accordance with the National Institute of Health Guide for the Care and Use of Laboratory Animals (NIH Publication, 8th edition, 2011). The Ethic Committee for Animal Experiments at Isfahan University of Medical Sciences approved the study (Ethical code: IR.MUI.REC.1396.1.067).
Consent for publication
Not applicable.
Competing interests
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Amraie, E., Pouraboli, I., Salehi, H. et al. Treadmill running and Levisticum Officinale extract protect against LPS-induced memory deficits by modulating neurogenesis, neuroinflammation and oxidative stress. Metab Brain Dis 38, 999–1011 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11011-022-01140-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11011-022-01140-z