Abstract
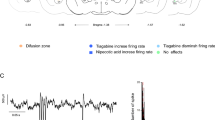
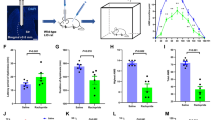
The globus pallidus has emerged as a crucial node in the basal ganglia motor control circuit under both healthy and parkinsonian states. Previous studies have shown that angiotensin II (Ang II) and angiotensin subtype 1 receptor (AT1R) are closely related to Parkinson’s disease (PD). Recent morphological study revealed the expression of AT1R in the globus pallidus of mice. To investigate the functions of Ang II/AT1R on the globus pallidus neurons of both normal and parkinsonian rats, electrophysiological recordings and behavioral tests were performed in the present study. Electrophysiological recordings showed that exogenous and endogenous Ang II mainly excited the globus pallidus neurons through AT1R. Behavioral tests further demonstrated that unilateral microinjection of Ang II into the globus pallidus induced significantly contralateral-biased swing in elevated body swing test (EBST), and bilateral microinjection of Ang II into the globus pallidus alleviated catalepsy and akinesia caused by haloperidol. AT1R was involved in Ang II-induced behavioral effects. Immunostaining showed that AT1R was expressed in the globus pallidus of rats. On the basis of the present findings, we concluded that pallidal Ang II/AT1R alleviated parkinsonian motor deficits through activating globus pallidus neurons, which will provide a rationale for further investigations into the potential of Ang II in the treatment of motor disorders originating from the basal ganglia.








Similar content being viewed by others
Data Availability
All data were included in the submitted manuscript.
References
Baluchnejadmojarad, T, Roghani, M (2004) Evaluation of functional asymmetry in rats with dose-dependent lesions of dopaminergic nigrostriatal system using elevated body swing test. Physiol Behav 82(2–3): 369–373. https://doi:10.1016/j.physbeh.2004.04.005
Borlongan, C V, Randall, T S, Cahill, D W, Sanberg, P R (1995) Asymmetrical motor behavior in rats with unilateral striatal excitotoxic lesions as revealed by the elevated body swing test. Brain Res 676(1): 231–234. https://doi:10.1016/0006-8993(95)00150-o
Brown, T M, McLachlan, E, Piggins, H D (2008) Angiotensin II regulates the activity of mouse suprachiasmatic nuclei neurons. Neuroscience 154(2): 839–847. https://doi:10.1016/j.neuroscience.2008.03.068
Chen, K, Sun, D, Qu, S, Chen, Y, Wang, J, Zhou, L, Jose, P A, Yang, Y, Zeng, C (2019) Prenatal cold exposure causes hypertension in offspring by hyperactivity of the sympathetic nervous system. Clin Sci (Lond) 133(9): 1097–1113. https://doi:10.1042/CS20190254
Chen, Q, Pan, H L (2007) Signaling mechanisms of angiotensin II-induced attenuation of GABAergic input to hypothalamic presympathetic neurons. J Neurophysiol 97(5): 3279–3287. https://doi:10.1152/jn.01329.2006
Chen, X Y, Xue, Y, Chen, H, Chen, L (2020) The globus pallidus as a target for neuropeptides and endocannabinoids participating in central activities. Peptides 124: 170210. https://doi:10.1016/j.peptides.2019.170210
Cosarderelioglu, C, Nidadavolu, L S, George, C J, Oh, E S, Bennett, D A, Walston, J D, Abadir, P M (2020) Brain Renin-Angiotensin System at the Intersect of Physical and Cognitive Frailty. Front Neurosci 14: 586314. https://doi:10.3389/fnins.2020.586314
de Gasparo, M, Catt, K J, Inagami, T, Wright, J W, Unger, T (2000) International union of pharmacology. XXIII. The angiotensin II receptors. Pharmacol Rev 52(3): 415–472.
Diaz-Ruiz, C, Villar-Cheda, B, Dominguez-Meijide, A, Garrido-Gil, P, Guerra, M J, Labandeira-Garcia, J L (2020) Aging-Related Overactivity of the Angiotensin/AT1 Axis Decreases Sirtuin 3 Levels in the Substantia Nigra, Which Induces Vulnerability to Oxidative Stress and Neurodegeneration. J Gerontol A Biol Sci Med Sci 75(3): 416–424. https://doi:10.1093/gerona/gly259
Dietz, N, Neimat, J (2019) Neuromodulation: Deep Brain Stimulation for Treatment of Dystonia. Neurosurg Clin N Am 30(2): 161–168. https://doi:10.1016/j.nec.2018.12.001
Dodson, P D, Larvin, J T, Duffell, J M, Garas, F N, Doig, N M, Kessaris, N, Duguid, I C, Bogacz, R, Butt, S J, Magill, P J (2015) Distinct developmental origins manifest in the specialized encoding of movement by adult neurons of the external globus pallidus. Neuron 86(2): 501–513. https://doi:10.1016/j.neuron.2015.03.007
Eid, L, Parent, M (2016) Chemical anatomy of pallidal afferents in primates. Brain Struct Funct 221(9): 4291–4317. https://doi:10.1007/s00429-016-1216-y
Ellens, D J, Leventhal, D K (2013) Review: electrophysiology of basal ganglia and cortex in models of Parkinson disease. J Parkinsons Dis 3(3): 241–254. https://doi:10.3233/JPD-130204
Emanuelli, T, Prauchner, C A, Dacanal, J, Zeni, A, Reis, E C, de Mello, C F, de Souza, D O (2000) Intrastriatal administration of 5-aminolevulinic acid induces convulsions and body asymmetry through glutamatergic mechanisms. Brain Res 868(1): 88–94. https://doi:10.1016/s0006-8993(00)02327-1
Forrester, S J, Booz, G W, Sigmund, C D, Coffman, T M, Kawai, T, Rizzo, V, Scalia, R, Eguchi, S (2018) Angiotensin II Signal Transduction: An Update on Mechanisms of Physiology and Pathophysiology. Physiol Rev 98(3): 1627–1738. https://doi:10.1152/physrev.00038.2017
Ge, J, Barnes, N M (1996) Alterations in angiotensin AT1 and AT2 receptor subtype levels in brain regions from patients with neurodegenerative disorders. Eur J Pharmacol 297(3): 299–306. https://doi:10.1016/0014-2999(95)00762-8
Grammatopoulos, T N, Jones, S M, Ahmadi, F A, Hoover, B R, Snell, L D, Skoch, J, Jhaveri, V V, Poczobutt, A M, Weyhenmeyer, J A, Zawada, W M (2007) Angiotensin type 1 receptor antagonist losartan, reduces MPTP-induced degeneration of dopaminergic neurons in substantia nigra. Mol Neurodegener 2: 1. https://doi:10.1186/1750-1326-2-1
Grobe, J L, Xu, D, Sigmund, C D (2008) An intracellular renin-angiotensin system in neurons: fact, hypothesis, or fantasy. Physiology (Bethesda) 23: 187–193. https://doi:10.1152/physiol.00002.2008
Hagiwara, Y, Kubo, T (2004) Tonic angiotensinergic inputs to neurons in the anterior hypothalamic area of rats. Brain Res 1006(2): 207–214. https://doi:10.1016/j.brainres.2004.02.007
Hagiwara, Y, Kubo, T (2007) Intracerebroventricular injection of losartan inhibits angiotensin II-sensitive neurons via GABA inputs in the anterior hypothalamic area of rats. Neurosci Lett 416(2): 150–154. https://doi:10.1016/j.neulet.2007.01.059
Henry, M, Grob, M, Mouginot, D (2009) Endogenous angiotensin II facilitates GABAergic neurotransmission afferent to the Na+-responsive neurons of the rat median preoptic nucleus. Am J Physiol Regul Integr Comp Physiol 297(3): R783-792. https://doi:10.1152/ajpregu.00226.2009
Hu, B, Qiao, H, Cao, T, Sun, B, Luo, X, Jia, R, Fan, Y, Wang, N, Lu, Y, Yan, J (2018) Angiotensin II facilitates GABAergic neurotransmission at postsynaptic sites in rat amygdala neurons. Neuropharmacology 133: 334–344. https://doi:10.1016/j.neuropharm.2018.02.009
Ingberg, E, Gudjonsdottir, J, Theodorsson, E, Theodorsson, A, Ström, J O (2015) Elevated body swing test after focal cerebral ischemia in rodents: methodological considerations. BMC Neurosci 16: 50. https://doi:10.1186/s12868-015-0189-8
Joglar, B, Rodriguez-Pallares, J, Rodriguez-Perez, A I, Rey, P, Guerra, M J, Labandeira-Garcia, J L (2009) The inflammatory response in the MPTP model of Parkinson’s disease is mediated by brain angiotensin: relevance to progression of the disease. J Neurochem 109(2): 656–669. https://doi:10.1111/j.1471-4159.2009.05999.x
Kawajiri, M, Mogi, M, Higaki, N, Tateishi, T, Ohyagi, Y, Horiuchi, M, Miki, T, Kira, J I (2009) Reduced angiotensin II levels in the cerebrospinal fluid of patients with amyotrophic lateral sclerosis. Acta Neurol Scand 119(5): 341–344. https://doi:10.1111/j.1600-0404.2008.01099.x
Kawajiri, M, Mogi, M, Osoegawa, M, Matsuoka, T, Tsukuda, K, Kohara, K, Horiuchi, M, Miki, T, Kira, J I (2008) Reduction of angiotensin II in the cerebrospinal fluid of patients with multiple sclerosis. Mult Scler 14(4): 557–560. https://doi:10.1177/1352458507085760
Kehoe, P G, Al Mulhim, N, Zetterberg, H, Blennow, K, Miners, J S (2019) Cerebrospinal Fluid Changes in the Renin-Angiotensin System in Alzheimer’s Disease. J Alzheimers Dis 72(2): 525–535. https://doi:10.3233/jad-190721
Kehoe, P G, Hibbs, E, Palmer, L E, Miners, J S (2017) Angiotensin-III is Increased in Alzheimer’s Disease in Association with Amyloid-β and Tau Pathology. J Alzheimers Dis 58(1): 203–214. https://doi:10.3233/jad-161265
Kelland, M D, Soltis, R P, Anderson, L A, Bergstrom, D A, Walters, J R (1995) In vivo characterization of two cell types in the rat globus pallidus which have opposite responses to dopamine receptor stimulation: comparison of electrophysiological properties and responses to apomorphine, dizocilpine, and ketamine anesthesia. Synapse 20(4): 338–350. https://doi:10.1002/syn.890200407
Ketzef, M, Silberberg, G (2021) Differential Synaptic Input to External Globus Pallidus Neuronal Subpopulations In Vivo. Neuron 109(3): 516–529.e514. https://doi:10.1016/j.neuron.2020.11.006
Kita, H, Kita, T (2001) Number, origins, and chemical types of rat pallidostriatal projection neurons. J Comp Neurol 437(4): 438–448. https://doi:10.1002/cne.1294
Kurosaki, R, Muramatsu, Y, Kato, H, Watanabe, Y, Imai, Y, Itoyama, Y, Araki, T (2005) Effect of angiotensin-converting enzyme inhibitor perindopril on interneurons in MPTP-treated mice. Eur Neuropsychopharmacol 15(1): 57–67. https://doi:10.1016/j.euroneuro.2004.05.007
Labandeira-Garcia, J L, Valenzuela, R, Costa-Besada, M A, Villar-Cheda, B, Rodriguez-Perez, A I (2021) The intracellular renin-angiotensin system: Friend or foe. Some light from the dopaminergic neurons. Prog Neurobiol 199: 101919. https://doi:10.1016/j.pneurobio.2020.101919
Li, D P, Chen, S R, Pan, H L (2003) Angiotensin II stimulates spinally projecting paraventricular neurons through presynaptic disinhibition. J Neurosci 23(12): 5041–5049. https://doi:10.1523/jneurosci.23-12-05041.2003
Li, D P, Pan, H L (2005) Angiotensin II attenuates synaptic GABA release and excites paraventricular-rostral ventrolateral medulla output neurons. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 313(3): 1035–1045. https://doi:10.1124/jpet.104.082495
Lilascharoen, V, Wang, E H, Do, N, Pate, S C, Tran, A N, Yoon, C D, Choi, J H, Wang, X Y, Pribiag, H, Park, Y G, Chung, K, Lim, B K (2021) Divergent pallidal pathways underlying distinct Parkinsonian behavioral deficits. Nat Neurosci 24(4): 504–515. https://doi:10.1038/s41593-021-00810-y
Liu, C, Xue, Y, Liu, M F, Wang, Y, Liu, Z R, Diao, H L, Chen, L (2018) Orexins increase the firing activity of nigral dopaminergic neurons and participate in motor control in rats. J Neurochem 147(3): 380–394. https://doi:10.1111/jnc.14568
Lopez-Real, A, Rey, P, Soto-Otero, R, Mendez-Alvarez, E, Labandeira-Garcia, J L (2005) Angiotensin-converting enzyme inhibition reduces oxidative stress and protects dopaminergic neurons in a 6-hydroxydopamine rat model of Parkinsonism. J Neurosci Res 81(6): 865–873. https://doi:10.1002/jnr.20598
Lorenc-Koci, E, Wolfarth, S, Ossowska, K (1996) Haloperidol-increased muscle tone in rats as a model of parkinsonian rigidity. Exp Brain Res 109(2): 268–276. https://doi:10.1007/bf00231786
Magnin, M, Morel, A, Jeanmonod, D (2000) Single-unit analysis of the pallidum, thalamus and subthalamic nucleus in parkinsonian patients. Neuroscience 96(3): 549–564. https://doi:10.1016/s0306-4522(99)00583-7
Marino, M J, Valenti, O, Conn, P J (2003) Glutamate receptors and Parkinson’s disease: opportunities for intervention. Drugs Aging 20(5): 377–397. https://doi:10.2165/00002512-200320050-00006
Ni, Z, Bouali-Benazzouz, R, Gao, D, Benabid, A L, Benazzouz, A (2000) Changes in the firing pattern of globus pallidus neurons after the degeneration of nigrostriatal pathway are mediated by the subthalamic nucleus in the rat. Eur J Neurosci 12(12): 4338–4344.
Parent, A, Sato, F, Wu, Y, Gauthier, J, Lévesque, M, Parent, M (2000) Organization of the basal ganglia: the importance of axonal collateralization. Trends Neurosci 23(10 Suppl): S20-27. https://doi:10.1016/s1471-1931(00)00022-7
Parrish, J N, Bertholomey, M L, Pang, H W, Speth, R C, Torregrossa, M M (2019) Estradiol modulation of the renin-angiotensin system and the regulation of fear extinction. Transl Psychiatry 9(1): 36. https://doi:10.1038/s41398-019-0374-0
Pascale, E, Purcaro, C, Passarelli, E, Guglielmi, R, Vestri, A R, Passarelli, F, Meco, G (2009) Genetic polymorphism of Angiotensin-Converting Enzyme is not associated with the development of Parkinson’s disease and of L-dopa-induced adverse effects. J Neurol Sci 276(1–2): 18–21. https://doi:10.1016/j.jns.2008.08.017
Plenz, D, Kital, S T (1999) A basal ganglia pacemaker formed by the subthalamic nucleus and external globus pallidus. Nature 400(6745): 677–682. https://doi:10.1038/23281
Qiu, Y, Zheng, F, Ye, C, Chen, A D, Wang, J J, Chen, Q, Li, Y H, Kang, Y M, Zhu, G Q (2020) Angiotensin Type 1 Receptors and Superoxide Anion Production in Hypothalamic Paraventricular Nucleus Contribute to Capsaicin-Induced Excitatory Renal Reflex and Sympathetic Activation. Neurosci Bull 36(5): 463–474. https://doi:10.1007/s12264-019-00460-y
Raz, A, Vaadia, E, Bergman, H (2000) Firing patterns and correlations of spontaneous discharge of pallidal neurons in the normal and the tremulous 1-methyl-4-phenyl-1,2,3,6-tetrahydropyridine vervet model of parkinsonism. J Neurosci 20(22): 8559–8571. https://doi:10.1523/jneurosci.20-22-08559.2000
Ruskin, D N, Rawji, S S, Walters, J R (1998) Effects of full D1 dopamine receptor agonists on firing rates in the globus pallidus and substantia nigra pars compacta in vivo: tests for D1 receptor selectivity and comparisons to the partial agonist SKF 38393. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 286(1): 272–281.
Savaskan, E, Hock, C, Olivieri, G, Bruttel, S, Rosenberg, C, Hulette, C, Müller-Spahn, F (2001) Cortical alterations of angiotensin converting enzyme, angiotensin II and AT1 receptor in Alzheimer’s dementia. Neurobiol Aging 22(4): 541–546. https://doi:10.1016/s0197-4580(00)00259-1
Su, G, Dou, H, Zhao, L, Wang, H, Liu, G, Huang, B, Peng, B (2015) The angiotensin-converting enzyme (ACE) I/D polymorphism in Parkinson’s disease. J Renin Angiotensin Aldosterone Syst 16(2): 428–433. https://doi:10.1177/1470320313494432
Sumners, C, Alleyne, A, Rodriguez, V, Pioquinto, D J, Ludin, J A, Kar, S, Winder, Z, Ortiz, Y, Liu, M, Krause, E G, de Kloet, A D (2020) Brain angiotensin type-1 and type-2 receptors: cellular locations under normal and hypertensive conditions. Hypertens Res 43(4): 281–295. https://doi:10.1038/s41440-019-0374-8
Sun, G C, Wong, T Y, Chen, H H, Ho, C Y, Yeh, T C, Ho, W Y, Tseng, C J, Cheng, P W (2019) Angiotensin II inhibits DDAH1-nNOS signaling via AT1R and muOR dimerization to modulate blood pressure control in the central nervous system. Clin Sci (Lond) 133(23): 2401–2413. https://doi:10.1042/CS20191005
Tabuse, M, Yaguchi, M, Ohta, S, Kawase, T, Toda, M (2010) A simple behavioral test for locomotor function after brain injury in mice. J Clin Neurosci 17(11): 1412–1416. https://doi:10.1016/j.jocn.2010.01.056
Villar-Cheda, B, Dominguez-Meijide, A, Joglar, B, Rodriguez-Perez, A I, Guerra, M J, Labandeira-Garcia, J L (2012) Involvement of microglial RhoA/Rho-kinase pathway activation in the dopaminergic neuron death. Role of angiotensin via angiotensin type 1 receptors. Neurobiol Dis 47(2): 268–279. https://doi:10.1016/j.nbd.2012.04.010
Villar-Cheda, B, Rodríguez-Pallares, J, Valenzuela, R, Muñoz, A, Guerra, M J, Baltatu, O C, Labandeira-Garcia, J L (2010) Nigral and striatal regulation of angiotensin receptor expression by dopamine and angiotensin in rodents: implications for progression of Parkinson’s disease. Eur J Neurosci 32(10): 1695–1706. https://doi:10.1111/j.1460-9568.2010.07448.x
Villar-Cheda, B, Valenzuela, R, Rodriguez-Perez, A I, Guerra, M J, Labandeira-Garcia, J L (2012) Aging-related changes in the nigral angiotensin system enhances proinflammatory and pro-oxidative markers and 6-OHDA-induced dopaminergic degeneration. Neurobiol Aging 33(1): 204.e201-211. https://doi:10.1016/j.neurobiolaging.2010.08.006
Wang, H, Chen, X Y, Chen, W F, Xue, Y, Wei, L, Chen, L (2013) Anticataleptic effects of 5-HT(1B) receptors in the globus pallidus. Neurosci Res 77(3): 162–169. https://doi:10.1016/j.neures.2013.09.002
Wichmann, T (2019) Changing views of the pathophysiology of Parkinsonism. Mov Disord 34(8): 1130–1143. https://doi:10.1002/mds.27741
Xing, J, Lu, J, Li, J (2009) Angiotensin II inhibits GABAergic synaptic transmission in dorsolateral periaqueductal gray neurons. Neurosci Lett 455(1): 8–13. https://doi:10.1016/j.neulet.2009.03.063
Xue, Y, Bai, B, Yung, W H, Chen, L (2009) Electrophysiological effects of neurotensin on globus pallidus neurons of 6-hydroxydopamine-lesioned rats. Neurosignals 17(2): 153–161. https://doi:10.1159/000199047
Zawada, W M, Mrak, R E, Biedermann, J, Palmer, Q D, Gentleman, S M, Aboud, O, Griffin, W S (2015) Loss of angiotensin II receptor expression in dopamine neurons in Parkinson’s disease correlates with pathological progression and is accompanied by increases in Nox4- and 8-OH guanosine-related nucleic acid oxidation and caspase-3 activation. Acta Neuropathol Commun 3: 9. https://doi:10.1186/s40478-015-0189-z
Zhou, X, Yang, H, Song, X, Wang, J, Shen, L, Wang, J (2019) Central blockade of the AT1 receptor attenuates pressor effects via reduction of glutamate release and downregulation of NMDA/AMPA receptors in the rostral ventrolateral medulla of rats with stress-induced hypertension. Hypertens Res 42(8): 1142–1151. https://doi:10.1038/s41440-019-0242-6
Zold, C L, Ballion, B, Riquelme, L A, Gonon, F, Murer, M G (2007) Nigrostriatal lesion induces D2-modulated phase-locked activity in the basal ganglia of rats. Eur J Neurosci 25(7): 2131–2144. https://doi:10.1111/j.1460-9568.2007.05475.x
Zubenko, G S, Volicer, L, Direnfeld, L K, Freeman, M, Langlais, P J, Nixon, R A (1985) Cerebrospinal fluid levels of angiotensin-converting enzyme in Alzheimer’s disease, Parkinson’s disease and progressive supranuclear palsy. Brain Res 328(2): 215–221. https://doi:10.1016/0006-8993(85)91032-7
Funding
This work was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (grant number 31671076 and 32200939).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
HongXia Liu performed the experiment, analyzed the data and drafted the manuscript. Lei Chen and Yan Xue designed the research and revised the manuscript. All authors contributed to manuscript revision, read, and approved the submitted version.
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Consent to participate
Not applicable.
Consent for publication
Not applicable.
Competing interests
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Ethics approval
The animal study was reviewed and approved by the Research Ethics Board of Qingdao University.
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Liu, H., Xue, Y. & Chen, L. Angiotensin II increases the firing activity of pallidal neurons and participates in motor control in rats. Metab Brain Dis 38, 573–587 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11011-022-01127-w
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11011-022-01127-w