Abstract
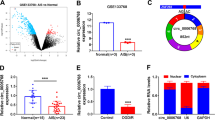
The effect of Celastrol on cerebral ischemia-reperfusion remains unknown. The study aims to explore the role of circular RNA DLGAP4 (circDLGAP4) in cerebral ischemia-reperfusion and the underlying mechanism. Ischemia-reperfusion (I/R) injury of human brain microvascular endothelial cells (HBMECs) was induced by oxygen-glucose deprivation and reoxygenation (OGD/R). Reverse transcription quantitative real-time PCR (RT-qPCR) and western blotting analysis were performed to detect the expression of circDLGAP4, microRNA-6085 (miR-6085), growth differentiation factor 11 (GDF11), B-cell lymphoma-2 (BCL2) and BCL2-associated x protein (BAX). Cell viability, proliferation, and apoptosis were analyzed by cell counting kit-8, 5-Ethynyl-2’-deoxyuridine and flow cytometry analysis. Oxidative stress was analyzed by evaluating the levels of Malondialdehyde (MDA) and Reactive Oxygen Species (ROS) and the activity of Superoxide Dismutase (SOD). The associations among circDLGAP4, miR-6085 and GDF11 were identified by dual-luciferase reporter, RNA immunoprecipitation (RIP) and RNA pull-down assays. Celastrol reduced OGD/R-induced inhibition of circDLGAP4 expression in HBMECs. Celastrol treatment protected HBMECs from OGD/R-induced cell proliferation inhibition and apoptosis and oxidative stress promotion; however, circDLGAP4 depletion attenuated these effects. CircDLGAP4 acted as a sponge for miR-6085, and miR-6085 mimics restored circDLGAP4-mediated effects in OGD/R-stimulated HBMECs. In addition, GDF11 was identified as a targte of miR-6085, and participated in the regulation of miR-6085 to OGD/R-induced HBMEC damage. Further, circDLGAP4 absence inhibited GDF11 expression by interacting with miR-6085 under Celastrol treatment. Celastrol ameliorated OGD/R-induced HBMEC apoptosis and oxidative stress by circDLGAP4/miR-6085/GDF11 pathway, supporting the use of Celastrol as a therapeutic agent for cerebral infarction.







Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
The analyzed data sets generated during the present study are available from the corresponding author on reasonable request.
References
Abu Bakar MH, Sarmidi MR, Tan JS, Mohamad Rosdi MN (2017) Celastrol attenuates mitochondrial dysfunction and inflammation in palmitate-mediated insulin resistance in C3A hepatocytes. Eur J Pharmacol 799:73–83. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ejphar.2017.01.043
Alkabie S, Basivireddy J, Zhou L, Roskams J, Rieckmann P, Quandt JA (2016) SPARC expression by cerebral microvascular endothelial cells in vitro and its influence on blood-brain barrier properties. J Neuroinflammation 13:225. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12974-016-0657-9
Bai Y, Zhang Y, Han B, Yang L, Chen X, Huang R, Wu F, Chao J, Liu P, Hu G, Zhang JH, Yao H (2018) Circular RNA DLGAP4 Ameliorates Ischemic Stroke Outcomes by Targeting miR-143 to Regulate Endothelial-Mesenchymal Transition Associated with Blood-Brain Barrier Integrity. J Neurosci 38:32–50. https://doi.org/10.1523/JNEUROSCI.1348-17.2017
Che F, Du H, Wei J, Zhang W, Cheng Z, Tong Y (2019) MicroRNA-323 suppresses nerve cell toxicity in cerebral infarction via the transforming growth factor-β1/SMAD3 signaling pathway. Int J Mol Med 43:993–1002. https://doi.org/10.3892/ijmm.2018.4020
Chen M, Liu M, Luo Y, Cao J, Zeng F, Yang L, Yang J, Tao T, Jiang Y (2022) Celastrol Protects against Cerebral Ischemia/Reperfusion Injury in Mice by Inhibiting Glycolysis through Targeting HIF-1α/PDK1 Axis. Oxid Med Cell Longev 2022:7420507. https://doi.org/10.1155/2022/7420507
Chen W, Wang H, Feng J, Chen L (2020) Overexpression of circRNA circUCK2 Attenuates Cell Apoptosis in Cerebral Ischemia-Reperfusion Injury via miR-125b-5p/GDF11 Signaling. Mol Ther Nucleic Acids 22:673–683. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.omtn.2020.09.032
Deane CA, Brown IR (2016) Induction of heat shock proteins in differentiated human neuronal cells following co-application of celastrol and arimoclomol. Cell Stress Chaperones 21:837–848. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12192-016-0708-2
Fan Z-X, Yang J (2015) The role of microRNAs in regulating myocardial ischemia reperfusion injury. Saudi Med J 36:787–793. https://doi.org/10.15537/smj.2015.7.11089
Guo J, Mei Y, Li K, Huang X, Yang H (2016) Downregulation of miR-17-92a cluster promotes autophagy induction in response to celastrol treatment in prostate cancer cells. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 478:804–810. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bbrc.2016.08.029
Guo Z, Zhang G, Xu B, Zhang C, Tao A, He M, He X (2021) Circ_0062166 aggravates cerebral ischemia-reperfusion injury through targeting miR-526b-5p/BCL2L13 axis. Brain Inj 35:1245–1253. https://doi.org/10.1080/02699052.2021.1972143
Han B, Chao J, Yao H (2018) Circular RNA and its mechanisms in disease: From the bench to the clinic. Pharmacol Ther 187:31–44. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.pharmthera.2018.01.010
Hu Y, Deng H, Xu S, Zhang J (2015) MicroRNAs Regulate Mitochondrial Function in Cerebral Ischemia-Reperfusion Injury. Int J Mol Sci 16:24895–24917. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms161024895
Hudobenko J, Ganesh BP, Jiang J, Mohan EC, Lee S, Sheth S, Morales D, Zhu L, Kofler JK, Pautler RG, McCullough LD, Chauhan A (2020) Growth differentiation factor-11 supplementation improves survival and promotes recovery after ischemic stroke in aged mice. Aging (Albany NY) 12:8049–8066. https://doi.org/10.18632/aging.103122
Jaquet V, Marcoux J, Forest E, Leidal KG, McCormick S, Westermaier Y, Perozzo R, Plastre O, Fioraso-Cartier L, Diebold B, Scapozza L, Nauseef WM, Fieschi F, Krause KH, Bedard K (2011) NADPH oxidase (NOX) isoforms are inhibited by celastrol with a dual mode of action. Br J Pharmacol 164:507–520. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1476-5381.2011.01439.x
Jiang M, Liu X, Zhang D, Wang Y, Hu X, Xu F, Jin M, Cao F, Xu L (2018) Celastrol treatment protects against acute ischemic stroke-induced brain injury by promoting an IL-33/ST2 axis-mediated microglia/macrophage M2 polarization. J Neuroinflammation 15:78. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12974-018-1124-6
Kristensen LS, Andersen MS, Stagsted LVW, Ebbesen KK, Hansen TB, Kjems J (2019) The biogenesis, biology and characterization of circular RNAs. Nat Rev Genet 20:675–691. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41576-019-0158-7
Lasda E, Parker R (2014) Circular RNAs: diversity of form and function. RNA 20:1829–1842. https://doi.org/10.1261/rna.047126.114
Li W, Chen Z, Yan M, He P, Chen Z, Dai H (2016) The protective role of isorhamnetin on human brain microvascular endothelial cells from cytotoxicity induced by methylglyoxal and oxygen-glucose deprivation. J Neurochem 136:651–659. https://doi.org/10.1111/jnc.13436
Li Y, He D, Zhang X, Liu Z, Zhang X, Dong L, Xing Y, Wang C, Qiao H, Zhu C, Chen Y (2012) Protective effect of celastrol in rat cerebral ischemia model: down-regulating p-JNK, p-c-Jun and NF-κB. Brain Res 1464:8–13. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.brainres.2012.04.054
Li Z, Li J, Tang N (2017) Long noncoding RNA Malat1 is a potent autophagy inducer protecting brain microvascular endothelial cells against oxygen-glucose deprivation/reoxygenation-induced injury by sponging miR-26b and upregulating ULK2 expression. Neuroscience 354:1–10. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neuroscience.2017.04.017
Liang J, Wang Q, Li JQ, Guo T, Yu D (2020) Long non-coding RNA MEG3 promotes cerebral ischemia-reperfusion injury through increasing pyroptosis by targeting miR-485/AIM2 axis. Exp Neurol 325:113139. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.expneurol.2019.113139
Liu P, Wang M, Tang W, Li G, Gong N (2020) Circ_SATB2 Attenuates the Anti-Tumor Role of Celastrol in Non-Small-Cell Lung Carcinoma Through Targeting miR-33a-5p/E2F7 Axis. Onco Targets Ther 13:11899–11912. https://doi.org/10.2147/ott.S279434
Miller JB, Merck LH, Wira CR, Meurer WJ, Schrock JW, Nomura JT, Siket MS, Madsen TE, Wright DW, Panagos PD, Lewandowski C (2017) The Advanced Reperfusion Era: Implications for Emergency Systems of Ischemic Stroke Care. Ann Emerg Med 69:192–201. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.annemergmed.2016.06.042
Nakashima M, Toyono T, Akamine A, Joyner A (1999) Expression of growth/differentiation factor 11, a new member of the BMP/TGFbeta superfamily during mouse embryogenesis. Mech Dev 80:185–189. https://doi.org/10.1016/s0925-4773(98)00205-6
Ohshiro K, Chen J, Srivastav J, Mishra L, Mishra B (2020) Alterations in TGF-β signaling leads to high HMGA2 levels potentially through modulation of PJA1/SMAD3 in HCC cells. Genes Cancer 11:43–52. https://doi.org/10.18632/genesandcancer.199
Orellana-Urzúa S, Rojas I, Líbano L, Rodrigo R (2020) Pathophysiology of Ischemic Stroke: Role of Oxidative Stress. Curr Pharm Des 26:4246–4260. https://doi.org/10.2174/1381612826666200708133912
Peng L, Yin J, Wang S, Ge M, Han Z, Wang Y, Zhang M, Xie L, Li Y (2019) TGF-β2/Smad3 Signaling Pathway Activation Through Enhancing VEGF and CD34 Ameliorates Cerebral Ischemia/Reperfusion Injury After Isoflurane Post-conditioning in Rats. Neurochem Res 44:2606–2618. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11064-019-02880-8
Peng Q-S, Cheng Y-N, Zhang W-B, Fan H, Mao Q-H, Xu P (2020) circRNA_0000140 suppresses oral squamous cell carcinoma growth and metastasis by targeting miR-31 to inhibit Hippo signaling pathway. Cell Death Dis 11:112–112. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41419-020-2273-y
Qiu L, He J, Chen H, Xu X, Tao Y (2021) CircDLGAP4 overexpression relieves oxygen-glucose deprivation-induced neuronal injury by elevating NEGR1 through sponging miR-503-3p. J Mol Histol. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10735-021-10036-8
Rybak-Wolf A, Stottmeister C, Glažar P, Jens M, Pino N, Giusti S, Hanan M, Behm M, Bartok O, Ashwal-Fluss R, Herzog M, Schreyer L, Papavasileiou P, Ivanov A, Öhman M, Refojo D, Kadener S, Rajewsky N (2015) Circular RNAs in the Mammalian Brain Are Highly Abundant, Conserved, and Dynamically Expressed. Mol Cell 58:870–885. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.molcel.2015.03.027
Salminen A, Lehtonen M, Paimela T, Kaarniranta K (2010) Celastrol: Molecular targets of Thunder God Vine. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 394:439–442. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bbrc.2010.03.050
Schiavone S, Morgese M, Tucci P, Trabace L (2021) The Therapeutic Potential of Celastrol in Central Nervous System Disorders: Highlights from In Vitro and In Vivo Approaches. Molecules (Basel, Switzerland) 26. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules26154700
Song X, Zhang Y, Dai E, Du H, Wang L (2019) Mechanism of action of celastrol against rheumatoid arthritis: A network pharmacology analysis. Int Immunopharmacol 74:105725. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.intimp.2019.105725
Suzuki HI, Miyazono K (2011) Emerging complexity of microRNA generation cascades. J Biochem 149:15–25. https://doi.org/10.1093/jb/mvq113
Teng H, Li M, Qian L, Yang H, Pang M (2020) Long non-coding RNA SNHG16 inhibits the oxygen-glucose deprivation and reoxygenation-induced apoptosis in human brain microvascular endothelial cells by regulating miR-15a-5p/bcl-2. Mol Med Rep 22:2685–2694. https://doi.org/10.3892/mmr.2020.11385
Wang H, Zheng X, Jin J, Zheng L, Guan T, Huo Y, Xie S, Wu Y, Chen W (2020) LncRNA MALAT1 silencing protects against cerebral ischemia-reperfusion injury through miR-145 to regulate AQP4. J Biomed Sci 27:40. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12929-020-00635-0
Yang J, Chen M, Cao RY, Li Q, Zhu F (2018) The Role of Circular RNAs in Cerebral Ischemic Diseases: Ischemic Stroke and Cerebral Ischemia/Reperfusion Injury. Adv Exp Med Biol 1087:309–325. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-981-13-1426-1_25
Yang Z, Huang C, Wen X, Liu W, Huang X, Li Y, Zang J, Weng Z, Lu D, Tsang CK, Li K, Xu A (2021) Circular RNA circ-FoxO3 attenuates blood-brain barrier damage by inducing autophagy during ischemia/reperfusion. Mol Ther. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ymthe.2021.11.004
Yu X, Ruan X, Zhang J, Zhao Q (2016) Celastrol Induces Cell Apoptosis and Inhibits the Expression of the AML1-ETO/C-KIT Oncoprotein in t(8;21) Leukemia. Molecules 21. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules21050574
Zhang B, Zhong Q, Chen X, Wu X, Sha R, Song G, Zhang C, Chen X (2020) Neuroprotective Effects of Celastrol on Transient Global Cerebral Ischemia Rats via Regulating HMGB1/NF-κB Signaling Pathway. Front Neurosci 14:847. https://doi.org/10.3389/fnins.2020.00847
Zhang T, Zhao Q, Xiao X, Yang R, Hu D, Zhu X, Gonzalez FJ, Li F (2019) Modulation of Lipid Metabolism by Celastrol. J Proteome Res 18:1133–1144. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.jproteome.8b00797
Zhang W, Chen Y, Liu P, Chen J, Song L, Tang Y, Wang Y, Liu J, Hu FB, Hui R (2012) Variants on chromosome 9p21.3 correlated with ANRIL expression contribute to stroke risk and recurrence in a large prospective stroke population. Stroke 43:14–21. https://doi.org/10.1161/strokeaha.111.625442
Zhu X, Ding J, Wang B, Wang J, Xu M (2019) Circular RNA DLGAP4 is down-regulated and negatively correlates with severity, inflammatory cytokine expression and pro-inflammatory gene miR-143 expression in acute ischemic stroke patients. Int J Clin Exp Pathol 12:941–948
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Conceptualization and Methodology: Jiahui Gu and Yingli Yu; Formal analysis and Data curation: Chunhong Liu and Yingli Yu; Validation and Investigation: Chunhong Liu and Jiahui Gu; Writing - original draft preparation and Writing - review and editing: Chunhong Liu, Jiahui Gu and Yingli Yu; Approval of final manuscript: all authors
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethics approval and consent to participate
The present study was approved by the ethical review committee of Yantai Hospital of Traditional Chinese Medicine. Written informed consent was obtained from all enrolled patients.
Consent for publication
Patients agree to participate in this work
Competing interests
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Highlights
1. Celastrol attenuated OGD/R-induced inhibition of circDLGAP4 expression
2. Celastrol protected HBMECs from OGD/R-induced damage by regulating circDLGAP4.
3. CircDLGAP4 acted as a miR-6085 sponge.
4. MiR-6085 targeted GDF11.
5. CircDLGAP4 regulated GDF11 expression by interacting with miR-6085.
Supplementary information

Fig. S1
Celastrol assuaged OGD/R-induced cell apoptosis and oxidative stress through circDLGAP4. (A-J) HBMECs were divided into control+si-con, control+si-circDLGAP4, OGD/R+si-con, OGD/R+si-circDLGAP4, OGD/R+Cel+si-con, OGD/R+Cel+ si-circDLGAP4. (A) CircDLGAP4 expression was examined by RT-qPCR. (B and C) Cell proliferation was analyzed by EdU assay. (D and E) Cell apoptosis was assessed by flow cytometry analysis. (F and G) The protein expression of BCL2 and BAX was detected by Western blotting analysis. (H) MDA level was detected by lipid peroxidation MDA assay kit. (I) ROS level was examined by Cellular ROS Assay kit. (J) SOD activity was analyzed by Superoxide Dismutase Activity Assay kit. NS: no significant difference; aP<0.05, bP<0.05, cP<0.05, dP<0.05, #P<0.05, &P<0.05. Statistical analysis in (A-B), (D) and (H-J) was conducted using one-way analysis of variance and in (G) using two-way analysis of variance (PNG 3733 kb)

Fig. S2
The proportion of viable, early apoptotic, late apoptotic and necrotic cells in related apoptosis assays in this study. NS: no significant difference; aP<0.05, bP<0.05, cP<0.05, dP<0.05, #P<0.05, &P<0.05 (PNG 575 kb)
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Liu, C., Gu, J. & Yu, Y. Celastrol assuages oxygen-glucose deprivation and reoxygenation-induced damage in human brain microvascular endothelial cells through the circDLGAP4/miR-6085/GDF11 pathway. Metab Brain Dis 38, 255–267 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11011-022-01106-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11011-022-01106-1