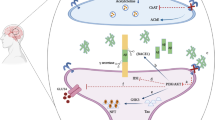
Abstract
The prevalence of both Alzheimer's disease (AD) and diabetes mellitus is increasing with the societies' aging and has become an essential social concern worldwide. Accumulation of amyloid plaques and neurofibrillary tangles (NFTs) of tau proteins in the brain are hallmarks of AD. Diabetes is an underlying risk factor for AD. Insulin resistance has been proposed to be involved in amyloid-beta (Aβ) aggregation in the brain. It seems that diabetic conditions can result in AD pathology by setting off a cascade of processes, including inflammation, mitochondrial dysfunction, and ROS and advanced glycation end products (AGEs) synthesis. Due to the several side effects of chemical drugs and their high cost, using herbal medicine has recently attracted attention for the treatment of diabetes and AD. Saffron and its active ingredients have been used for its anti-inflammatory, anti-oxidant, anti-diabetic, and anti-AD properties. Therefore, in the present review paper, we take account of the clinical, in vivo and in vitro evidence regarding the anti-diabetic and anti-AD effects of saffron and discuss the preventive or postponing properties of saffron or its components on AD development via its anti-diabetic effects.


Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
Not applicable.
Abbreviations
- AD :
-
Alzheimer's disease
- NFTs :
-
Neurofibrillary tangles
- Aβ :
-
Amyloid-beta
- AGEs :
-
Advanced glycation end products
- APP :
-
Amyloid precursor protein
- BACE1 :
-
Beta-secretase 1
- DM :
-
Diabetes mellitus
- SIRT1 :
-
Silent information regulator T1
- ROS :
-
Reactive oxygen species
- BBB :
-
Blood–brain barrier
- LRP1 :
-
Low-density lipoprotein receptor-related protein 1
- ABC :
-
ATP Binding Cassette transporter
- IDE :
-
Insulin-degrading enzyme
- IGF :
-
Insulin-like growth factor
- IRS-1 :
-
Insulin receptor substrate 1
- GSK-3β :
-
Glycogen synthase kinase 3 beta
- CAT :
-
Catalase
- SOD :
-
Superoxide dismutase
- GSH :
-
Glutathione
- MDA :
-
Malondialdehyde
- GPx :
-
Glutathione peroxidase
References
Abbaszadeh-Mashkani S, Hoque SS, Banafshe HR, Ghaderi A (2020) The effect of crocin (the main active saffron constituent) on the cognitive functions, craving, and withdrawal syndrome in opioid patients under methadone maintenance treatment. Phytother Res 35(3):1486–1494. https://doi.org/10.1002/ptr.6913
Abedimanesh N, Motlagh B, Abedimanesh S, Bathaie SZ, Separham A, Ostadrahimi A (2020) Effects of crocin and saffron aqueous extract on gene expression of SIRT1, AMPK, LOX1, NF-κB, and MCP-1 in patients with coronary artery disease: A randomized placebo-controlled clinical trial. Phytothe Res 34(5):1114–1122. https://doi.org/10.1002/ptr.6580
Abinaya R, Peter SJ, Shalini M, Sabina EP (2020) Prevalence of Diabetes mellitus and herbal medication. J Pharm Sci Res 12(5):720–729
Abou-Hany HO, Atef H, Said E, Elkashef HA, Salem HA (2018) Crocin mediated amelioration of oxidative burden and inflammatory cascade suppresses diabetic nephropathy progression in diabetic rats. Chem-Biol Interact 284:90–100. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cbi.2018.02.001
Agostinho P, Cunha RA, Oliveira C (2010) Neuroinflammation, oxidative stress and the pathogenesis of Alzheimer’s disease. Curr Pharm Des 16(25):2766–2778. https://doi.org/10.2174/138161210793176572
Ahmadi M, Rajaei Z, Hadjzadeh M, Nemati H, Hosseini M (2017) Crocin improves spatial learning and memory deficits in the Morris water maze via attenuating cortical oxidative damage in diabetic rats. Neurosci Lett 642:1–6. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neulet.2017.01.049
Akhondzadeh S, Sabet MS, Harirchian MH, Togha M, Cheraghmakani H, Razeghi S, Hejazi SSh, Yousefi MH, Alimardani R, Jamshidi A, Rezazadeh Sh A, Yousefi A, Zare F, Moradi A, Vossoughi A (2010a) A 22-week, multicenter, randomized, double-blind controlled trial of Crocus sativus in the treatment of mild-to-moderate Alzheimer’s disease. Psychopharmacology 207(4):637–643. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00213-009-1706-1
Akhondzadeh S, Sabet MS, Harirchian M, Togha M, Cheraghmakani H, Razeghi S, Hejazi SSh, Yousefi MH, Alimardani R, Jamshidi A, Zare F, Moradi A (2010b) Saffron in the treatment of patients with mild to moderate Alzheimer’s disease: a 16‐week, randomized and placebo‐controlled trial. J Clin Pharm Ther 35(5):581–8. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1365-2710.2009.01133.x
Akhter F, Chen D, Yan SF, Yan S (2017) Mitochondrial perturbation in alzheimer’s disease and diabetes. Prog Mol Biol Transl Sci 146:341–361. https://doi.org/10.1016/bs.pmbts.2016.12.019
Alavizadeh SH, Hosseinzadeh H (2014) Bioactivity assessment and toxicity of crocin: a comprehensive review. Food Chem Toxicol 64:65–80. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.fct.2013.11.016
Alexiou P, Chatzopoulou M, Pegklidou K, Demopoulos V (2010) RAGE: a multi-ligand receptor unveiling novel insights in health and disease. Curr Med Chem 17(21):2232–2252. https://doi.org/10.2174/092986710791331086
Alford S, Patel D, Perakakis N, Mantzoros C (2018) Obesity as a risk factor for Alzheimer’s disease: weighing the evidence. Obes Rev 19(2):269–280. https://doi.org/10.1111/obr.12629
Altinoz E, Oner Z, Elbe H, Cigremis Y, Turkoz Y (2015) Protective effects of saffron (its active constituent, crocin) on nephropathy in streptozotocin-induced diabetic rats. Hum Exp Toxicol 34(2):127–134. https://doi.org/10.1177/0960327114538989
Andalib S, Divani AA, Michel TM, Høilund-Carlsen PF, Vafaee MS, Gjedde A (2017) Pandora's Box: mitochondrial defects in ischaemic heart disease and stroke. Expert Rev Mol Med 19. https://doi.org/10.1017/erm.2017.5
Andalib S, Ghayeghran A, Moadabi Y, Asadi K, Mohammadpour M, Ghorbani-Shirkouhi S (2019) Association of Diabetes Mellitus Type 2 and Alzheimer’s Disease. Caspian J Health Res 4(4):86–89. https://doi.org/10.29252/cjhr.4.4.86
Andalib S, Vaseghi A, Vaseghi G, Naeini AM (2011) Sedative and hypnotic effects of Iranian traditional medicinal herbs used for treatment of insomnia. EXCLI J 10:192
Andrade-Cetto A, Heinrich M (2005) Mexican plants with hypoglycaemic effect used in the treatment of diabetes. J Ethnopharmacol 99(3):325–348. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jep.2005.04.019
Arrieta-Cruz I, Gutiérrez-Juárez R (2016) The role of insulin resistance and glucose metabolism dysregulation in the development of Alzheimer s disease. Rev Invest Clin 68(2):53–58
Asadi F, Jamshidi AH, Khodagholi F, Yans A, Azimi L, Faizi M, Vali L, Abdollahi M, Ghahremani MH, Sharifzadeh M (2015) Reversal effects of crocin on amyloid β-induced memory deficit: Modification of autophagy or apoptosis markers. Pharmacol Biochem Behav 139:47–58. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.pbb.2015.10.011
Ashrafi M, Afsar Z, Erjaee H, Nazifi S (2018) The effects of saffron (crocus sativus) aqueous extract on TNF-α levels in liver, kidney, and lens tissues of diabetic rats. Turkish J Endocrinol Metab 22(4):217. https://doi.org/10.25179/tjem.2018-59710
Alzheimer's Association (2012) 2012 Alzheimer’s disease facts and figures. Alzheimers Dement 8(2):131–168. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jalz.2012.02.001
Avgerinos KI, Vrysis C, Chaitidis N, Kolotsiou K, Myserlis PG, Kapogiannis D (2020) Effects of saffron (Crocus sativus L.) on cognitive function. A systematic review of RCTs. Neurol Sci 41:2747–2754. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10072-020-04427-0
Azmand MJ, Rajaei Z (2021) Effects of crocin on spatial or aversive learning and memory impairments induced by lipopolysaccharide in rats. Avicenna J Phytomedicine 11(1):79
Baghishani F, Mohammadipour A, Hosseinzadeh H, Hosseini M, Ebrahimzadeh-Bideskan A (2018) The effects of tramadol administration on hippocampal cell apoptosis, learning and memory in adult rats and neuroprotective effects of crocin. Metab Brain Dis 33(3):907–916. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11011-018-0194-6
Baglietto-Vargas D, Shi J, Yaeger DM, Ager R, LaFerla FM (2016) Diabetes and Alzheimer’s disease crosstalk. Neurosci Biobehav Rev 64:272–287. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neubiorev.2016.03.005
Bajerska J, Mildner-Szkudlarz S, Podgórski T, Oszmatek-Pruszyńska E (2013) Saffron (Crocus sativus L.) powder as an ingredient of rye bread: an anti-diabetic evaluation. J Med Food 16(9):847–856. https://doi.org/10.1089/jmf.2012.0168
Baluchnejadmojarad T, Mohamadi-Zarch S-M, Roghani M (2019) Safranal, an active ingredient of saffron, attenuates cognitive deficits in amyloid β-induced rat model of Alzheimer’s disease: underlying mechanisms. Metab Brain Dis 34(6):1747–1759. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11011-019-00481-6
Batarseh YS, Bharate SS, Kumar V, Kumar A, Vishwakarma RA, Bharate SB, Kaddoumi A (2017) Crocus sativus extract tightens the blood-brain barrier, reduces amyloid β load and related toxicity in 5XFAD mice. ACS Chem Neurosci 8(8):1756–1766. https://doi.org/10.1021/acschemneuro.7b00101
Bathaie SZ, Hoshyar R, Miri H, Sadeghizadeh M (2013a) Anticancer effects of crocetin in both human adenocarcinoma gastric cancer cells and rat model of gastric cancer. Biochem Cell Biol 91(6):397–403
Bathaie SZ, Miri H, Mohagheghi M-A, Mokhtari-Dizaji M, Shahbazfar A-A, Hasanzadeh H (2013b) Saffron aqueous extract inhibits the chemically-induced gastric cancer progression in the Wistar albino rat. Iran J Basic Med Sci 16(1):27
Baune BT (2015) Inflammation and neurodegenerative disorders: is there still hope for therapeutic intervention? Curr Opin Psychiatry 28(2):148–154. https://doi.org/10.1097/YCO.0000000000000140
Beeri MS, Moshier E, Schmeidler J, Godbold J, Uribarri J, Reddy S, Sano M, Grossman HT, Cai W, Vlassara H (2011) Serum concentration of an inflammatory glycotoxin, methylglyoxal, is associated with increased cognitive decline in elderly individuals. Mech Ageing Dev 132(11–12):583–587. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.mad.2011.10.007
Benjamin B, Burns A (2007) Donepezil for Alzheimer’s disease. Expert Rev Neurother 7(10):1243–1249. https://doi.org/10.1586/14737175.7.10.1243
Bezprozvanny I, Mattson MP (2008) Neuronal calcium mishandling and the pathogenesis of Alzheimer’s disease. Trends Neurosci 31(9):454–463. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tins.2008.06.005
Bharate SS, Kumar V, Singh G, Singh A, Gupta M, Singh D, Kumar A, Vishwakarma RA, Bharate SB (2018) Preclinical development of Crocus sativus-based botanical lead IIIM-141 for Alzheimer’s disease: Chemical standardization, efficacy, formulation development, pharmacokinetics, and safety pharmacology. ACS Omega 3(8):9572–9585. https://doi.org/10.1021/acsomega.8b00841
Bhutada P, Mundhada Y, Bansod K, Bhutada C, Tawari S, Dixit P, Mundhada D (2010) Ameliorative effect of quercetin on memory dysfunction in streptozotocin-induced diabetic rats. Neurobiol Learn Mem 94(3):293–302
Blázquez E, Velázquez E, Hurtado-Carneiro V, Ruiz-Albusac JM (2014) Insulin in the brain: its pathophysiological implications for States related with central insulin resistance, type 2 diabetes and Alzheimer’s disease. Front Endocrinol (lausanne) 5:161. https://doi.org/10.3389/fendo.2014.00161
Bourne KZ, Ferrari DC, Lange-Dohna C, Roßner S, Wood TG, Perez-Polo JR (2007) Differential regulation of BACE1 promoter activity by nuclear factor-κB in neurons and glia upon exposure to β-amyloid peptides. J Neurosci Res 85(6):1194–1204. https://doi.org/10.1002/jnr.21252
Bukhari SI, Manzoor M, Dhar M (2018) A comprehensive review of the pharmacological potential of Crocus sativus and its bioactive apocarotenoids. Biomed Pharmacother 98:733–745. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biopha.2017.12.090
Butterfield DA, Swomley AM, Sultana R (2013) Amyloid β-peptide (1–42)-induced oxidative stress in Alzheimer disease: importance in disease pathogenesis and progression. Antioxid Redox Signal 19(8):823–835
Caccamo A, Majumder S, Richardson A, Strong R, Oddo S (2010) Molecular interplay between mammalian target of rapamycin (mTOR), amyloid-beta, and Tau: effects on cognitive impairments. J Biol Chem 285(17):13107–13120. https://doi.org/10.1074/jbc.M110.100420
Cao W, Cui J, Li S, Zhang D, Guo Y, Li Q, Luan Y, Liu X (2017) Crocetin restores diabetic endothelial progenitor cell dysfunction by enhancing NO bioavailability via regulation of PI3K/AKT-eNOS and ROS pathways. Life Sci 181:9–16. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.lfs.2017.05.021
Cardoso S, Santos RX, Correia SC, Carvalho C, Santos MS, Baldeiras I, Oliveira CR, Moreira PI (2013) Insulin-induced recurrent hypoglycemia exacerbates diabetic brain mitochondrial dysfunction and oxidative imbalance. Neurobiol Dis 49:1–12
Carlsson CM (2010) Type 2 diabetes mellitus, dyslipidemia, and Alzheimer’s disease. J Alzheimer’s Dis 20(3):711–722. https://doi.org/10.3233/JAD-2010-100012
Carvalho C, Cardoso S (2021) Diabetes–Alzheimer’s Disease Link: Targeting Mitochondrial Dysfunction and Redox Imbalance. Antioxid Redox Signal 34(8):631–649
Chalatsa I, Arvanitis DA, Koulakiotis NS, Giagini A, Skaltsounis AL, Papadopoulou-Daifoti Z, Tsarbopoulos A, Sanoudou D (2019) The Crocus sativus compounds trans-crocin 4 and trans-crocetin modulate the amyloidogenic pathway and tau misprocessing in Alzheimer disease neuronal cell culture models. Front Neurosci 13:249. https://doi.org/10.3389/fnins.2019.00249
Chatterjee S, Ambegaokar S, Jackson GR, Mudher A (2019) Insulin-mediated changes in tau hyperphosphorylation and autophagy in a Drosophila model of tauopathy and neuroblastoma cells. Front Neurosci 13:801. https://doi.org/10.3389/fnins.2019.00801
Chen Z, Zhong C (2014) Oxidative stress in Alzheimer’s disease. Neurosci Bull 30(2):271–281. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12264-013-1423-y
Chiu SL, Chen CM, Cline HT (2008) Insulin receptor signaling regulates synapse number, dendritic plasticity, and circuit function in vivo. Neuron 58(5):708–719. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neuron.2008.04.014
Christodoulou E, Kadoglou N, Stasinopoulou M, Konstandi O, Kenoutis C, Kakazanis Z, Rizakou A, Kostomitsopoulos N, Valsami G (2018) Crocus sativus L. aqueous extract reduces atherogenesis, increases atherosclerotic plaque stability and improves glucose control in diabetic atherosclerotic animals. Atherosclerosis 268:207–214. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.atherosclerosis.2017.10.032
Christodoulou E, Kadoglou NP, Kostomitsopoulos N, Valsami G (2015) Saffron: a natural product with potential pharmaceutical applications. J Pharm Pharmacol 67(12):1634–1649. https://doi.org/10.1111/jphp.12456
Craft S (2012) Insulin resistance and AD—Extending the translational path. Nat Rev Neurol 8(7):360–362. https://doi.org/10.1038/nrneurol.2012.112
Dashti-r M, Zeinali F, Anvari M, Hosseini S (2012) Saffron (Crocus sativus L) extract prevents and improves D-galactose and NaNO2 induced memory impairment in mice. EXCLI J 11:328
De Felice FG, Ferreira ST (2014) Inflammation, defective insulin signaling, and mitochondrial dysfunction as common molecular denominators connecting type 2 diabetes to Alzheimer disease. Diabetes 63(7):2262–2272. https://doi.org/10.2337/db13-1954
De Felice FG, Vieira MN, Bomfim TR, Decker H, Velasco PT, Lambert MP, Viola KL, Zhao W-Q, Ferreira ST, Klein WL (2009) Protection of synapses against Alzheimer’s-linked toxins: insulin signaling prevents the pathogenic binding of Aβ oligomers. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 106(6):1971–1976. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.0809158106
Deane R, Du Yan S, Submamaryan RK, LaRue B, Jovanovic S, Hogg E, Welch D, Manness L, Lin C, Yu J (2003) RAGE mediates amyloid-β peptide transport across the blood-brain barrier and accumulation in brain. Nat Med 9(7):907–913. https://doi.org/10.1038/nm890
Delkhosh-Kasmaie F, Farshid AA, Tamaddonfard E, Imani M (2018) The effects of safranal, a constitute of saffron, and metformin on spatial learning and memory impairments in type-1 diabetic rats: behavioral and hippocampal histopathological and biochemical evaluations. Biomed Pharmacother 107:203–211. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biopha.2018.07.165
Diniz Pereira J, Gomes Fraga V, Morais Santos AL, Carvalho MDG, Caramelli P, Braga Gomes K (2021) Alzheimer’s disease and type 2 diabetes mellitus: A systematic review of proteomic studies. J Neurochem 156(6):753–776. https://doi.org/10.1111/jnc.15166
Ebrahimi F, Sahebkar A, Aryaeian N, Pahlavani N, Fallah S, Moradi N, Abbasi D, Hosseini AF (2019) Effects of saffron supplementation on inflammation and metabolic responses in type 2 diabetic patients: A randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial. Diabetes Metab Syndr Obes 12:2107. https://doi.org/10.2147/DMSO.S216666
Ebrahimpour S, Zakeri M, Esmaeili A (2020) Crosstalk between obesity, diabetes, and alzheimer’s disease: Introducing quercetin as an effective triple herbal medicine. Ageing Res Rev 62:101095. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.arr.2020.101095
Eckman E, Eckman C (2005) Aβ-degrading enzymes: modulators of Alzheimer’s disease pathogenesis and targets for therapeutic intervention. Biochem Soc Trans 33(5):1101–1105. https://doi.org/10.1042/BST20051101
Faridi S, Delirezh N, Froushani SMA (2019) Beneficial effects of hydroalcoholic extract of saffron in alleviating experimental autoimmune diabetes in C57bl/6 mice. Iran J Allergy Asthma Immunol 18(1):38–47
Farokhnia M, Shafiee Sabet M, Iranpour N, Gougol A, Yekehtaz H, Alimardani R, Farsad F, Kamalipour M, Akhondzadeh S (2014) Comparing the efficacy and safety of Crocus sativus L. with memantine in patients with moderate to severe Alzheimer's disease: a double‐blind randomized clinical trial. Hum Psychopharmacol 29(4):351–9. https://doi.org/10.1002/hup.2412
Farris W, Mansourian S, Chang Y, Lindsley L, Eckman EA, Frosch MP, Eckman CB, Tanzi RE, Selkoe DJ, Guénette S (2003) Insulin-degrading enzyme regulates the levels of insulin, amyloid β-protein, and the β-amyloid precursor protein intracellular domain in vivo. Proc Natl Acad Sci 100(7):4162–4167. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.0230450100
Farshid AA, Tamaddonfard E, Moradi-Arzeloo M, Mirzakhani N (2016) The effects of crocin, insulin and their co-administration on the heart function and pathology in streptozotocin-induced diabetic rats. Avicenna J Phytomedicine 6(6):658–570
Feidantsis K, Mellidis K, Galatou E, Sinakos Z, Lazou A (2018) Treatment with crocin improves cardiac dysfunction by normalizing autophagy and inhibiting apoptosis in STZ-induced diabetic cardiomyopathy. Nutr Metab Cardiovasc Dis 28(9):952–961. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.numecd.2018.06.005
Feng J, Xing W, Xie L (2016) Regulatory roles of microRNAs in diabetes. Int J Mol Sci 17(10):1729. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms17101729
Ghadami MR, Pourmotabbed A (2009) The effect of Crocin on scopolamine induced spatial learning and memory deficits in rats. Physiol Pharmacol 12(4):287–295. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bbr.2007.06.001
Ghadrdoost B, Vafaei AA, Rashidy-Pour A, Hajisoltani R, Bandegi AR, Motamedi F, Haghighi S, Sameni HR, Pahlvan S (2011) Protective effects of saffron extract and its active constituent crocin against oxidative stress and spatial learning and memory deficits induced by chronic stress in rats. Eur J Pharmacol 667(1–3):222–229. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ejphar.2011.05.012
Ghaffari S, Hatami H, Dehghan G (2015) Saffron ethanolic extract attenuates oxidative stress, spatial learning, and memory impairments induced by local injection of ethidium bromide. Res Pharm Sci 10(3):222
Ghaffari S, Roshanravan N (2019) Saffron; An updated review on biological properties with special focus on cardiovascular effects. Biomed Pharmacother 109:21–27. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biopha.2018.10.031
Ghodrat M, Sahraei H, Razjouyan J, Meftahi G (2014) Effects of a saffron alcoholic extract on visual short-term memory in humans: a psychophysical study. Neurophysiology 46(3):247–253. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11062-014-9436-3
Ghorbanzadeh V, Mohammadi M, Mohaddes G, Darishnejad H, Chodari L (2017) Effect of crocin and voluntary exercise on P53 protein in pancreas of type2 diabetic rats. Pharm Sci 23(3):182–188. https://doi.org/10.15171/PS.2017.27
Guzik TJ, Mussa S, Gastaldi D, Sadowski J, Ratnatunga C, Pillai R, Channon KM (2002) Mechanisms of increased vascular superoxide production in human diabetes mellitus: role of NAD (P) H oxidase and endothelial nitric oxide synthase. Circulation 105(14):1656–1662. https://doi.org/10.1161/01.CIR.0000012748.58444.08
Hadipour M, Kaka G, Bahrami F, Meftahi GH, Pirzad Jahromi G, Mohammadi A, Sahraei H (2018) Crocin improved amyloid beta induced long-term potentiation and memory deficits in the hippocampal CA1 neurons in freely moving rats. Synapse 72(5):e22026. https://doi.org/10.1002/syn.22026
Hadipour M, Meftahi GH, Afarinesh MR, Jahromi GP, Hatef B (2021) Crocin attenuates the granular cells damages on the dentate gyrus and pyramidal neurons in the CA3 regions of the hippocampus and frontal cortex in the rat model of Alzheimer’s disease. J Chem Neuroanat 113:101837. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jchemneu.2020.101837
Haghighizad H, Pourmotabbed A, Sahraei H, Ghadami MR, Ghadami S, Kamalinejad M (2008) Protective effect of Saffron extract on morphine–induced inhibition of spatial learning and memory in rat. Pharmacol Pharm 12(3):170–179
Hanson AJ, Rubinow KB (2021) Optimizing clinical phenotyping to better delineate the complex relationship between type 2 diabetes and Alzheimer’s disease. Clin Transl Sci. https://doi.org/10.1111/cts.13024
Hara Y, Yuk F, Puri R, Janssen WG, Rapp PR, Morrison JH (2014) Presynaptic mitochondrial morphology in monkey prefrontal cortex correlates with working memory and is improved with estrogen treatment. Natl Acad Sci U S A 111(1):486–491. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.1311310110
Hasanpour M, Ashrafi M, Erjaee H, Nazifi S (2018) The effect of saffron aqueous extract on oxidative stress parameters and important biochemical enzymes in the testis of streptozotocin-induced diabetic rats. Physiol Pharmacol 22(1):28–37
Harrington LS, Findlay GM, Gray A, Tolkacheva T, Wigfield S, Rebholz H, Barnett J, Leslie NR, Cheng S, Shepherd PR, Gout I, Downes CP, Lamb RF (2004) The TSC1-2 tumor suppressor controls insulin–PI3K signaling via regulation of IRS proteins. J Cell Biol 166(2):213–223. https://doi.org/10.1083/jcb.200403069
Hazman Ö, Ovalı S (2015) Investigation of the anti-inflammatory effects of safranal on high-fat diet and multiple low-dose streptozotocin induced type 2 diabetes rat model. Inflammation 38(3):1012–1019. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10753-014-0065-1
Heidari S, Mehri S, Hosseinzadeh H (2017) Memory enhancement and protective effects of crocin against D-galactose aging model in the hippocampus of Wistar rats. Iran J Basic Med Sci 20(11):1250. https://doi.org/10.22038/IJBMS.2017.9541
Hildreth KL, Van Pelt RE, Schwartz RS (2012) Obesity, insulin resistance, and Alzheimer’s disease. Obesity (Silver Spring, Md.) 20(8):1549. https://doi.org/10.1038/oby.2012.19
Hoshyar R, Bathaie SZ, Sadeghizadeh M (2013) Crocin triggers the apoptosis through increasing the Bax/Bcl-2 ratio and caspase activation in human gastric adenocarcinoma, AGS, cells. DNA Cell Biol 32(2):50–57. https://doi.org/10.1089/dna.2012.1866
Hosseinzadeh H, Sadeghnia HR, Ghaeni FA, Motamedshariaty VS, Mohajeri SA (2012) Effects of saffron (Crocus sativus L.) and its active constituent, crocin, on recognition and spatial memory after chronic cerebral hypoperfusion in rats. Phytother Res 26(3):381–386. https://doi.org/10.1002/ptr.3566
Hosseinzadeh H, Ziaei T (2006) Effects of Crocus sativus stigma extract and its constituents, crocin and safranal, on intact memory and scopolamine-induced learning deficits in rats performing the Morris water maze task. J Med Plants 3(19):40–50
Ikram M, Muhammad T, Rehman SU, Khan A, Jo MG, Ali T, Kim MO (2019) Hesperetin confers neuroprotection by regulating Nrf2/TLR4/NF-κB signaling in an Aβ mouse model. Mol Neurobiol 56(9):6293–6309. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12035-019-1512-7
Imenshahidi M, Hosseinzadeh H, Javadpour Y (2010) Hypotensive effect of aqueous saffron extract (Crocus sativus L) and its constituents, safranal and crocin, in normotensive and hypertensive rats. Phytother Res 24(7):990–994. https://doi.org/10.1002/ptr.3044
Jagadeeswaran R, Thirunavukkarasu C, Gunasekaran P, Ramamurty N, Sakthisekaran D (2000) In vitro studies on the selective cytotoxic effect of crocetin and quercetin. Fitoterapia 71(4):395–399. https://doi.org/10.1016/s0367-326x(00)00138-6
Jarald E, Joshi SB, Jain DC (2008) Diabetes and herbal medicines. Iran J Pharmacol Ther 7(1):97–106
Jash K, Gondaliya P, Kirave P, Kulkarni B, Sunkaria A, Kalia K (2020) Cognitive dysfunction: A growing link between diabetes and Alzheimer’s disease. Drug Dev Res 81(2):144–164. https://doi.org/10.1002/ddr.21579
Jayaraj RL, Azimullah S, Beiram R (2020) Diabetes as a risk factor for Alzheimer’s disease in the Middle East and its shared pathological mediators. Saudi J Biol Sci 27(2):736–750. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.sjbs.2019.12.028
Kakouri E, Agalou A, Kanakis C, Beis D, Tarantilis PA (2020) Crocins from Crocus sativus L. in the Management of Hyperglycemia. In Vivo Evidence from Zebrafish. Molecules 25(22):5223. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules25225223
Kamalipour M, Akhondzadeh S (2011) Cardiovascular effects of saffron: An evidence-based review. J Tehran Heart Cent 6(2):59–61
Kang C, Lee H, Jung E-S, Seyedian R, Jo M, Kim J, Kim J-S, Kim E (2012) Saffron (Crocus sativus L.) increases glucose uptake and insulin sensitivity in muscle cells via multipathway mechanisms. Food Chem 135(4):2350–2358. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.foodchem.2012.06.092
Karakani AM, Riazi G, Ghaffari SM, Ahmadian S, Mokhtari F, Firuzi MJ, Bathaie SZ (2015) Inhibitory effect of corcin on aggregation of 1N/4R human tau protein in vitro. Iran J Basic Med Sci 18(5):485
Karimi-Nazari E, Nadjarzadeh A, Masoumi R, Marzban A, Mohajeri SA, Ramezani-Jolfaie N, Salehi-Abargouei A (2019) Effect of saffron (Crocus sativus L.) on lipid profile, glycemic indices and antioxidant status among overweight/obese prediabetic individuals: A double-blinded, randomized controlled trial. Clinical Nutrition ESPEN 34:130–136. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.clnesp.2019.07.012
Karkoula E, Dagla I-V, Baira E, Kokras N, Dalla C, Skaltsounis A-L, Gikas E, Tsarbopoulos A (2020) A novel UHPLC-HRMS-based metabolomics strategy enables the discovery of potential neuroactive metabolites in mice plasma, following ip administration of the main Crocus sativus L. bioactive component. J Pharm Biomed Anal 177:112878. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jpba.2019.112878
Khalili M, Hamzeh F (2010) Effects of active constituents of Crocus sativus L., crocin on streptozocin-induced model of sporadic Alzheimer’s disease in male rats. Iran Biomed J 14(1–2):59–65
Khalili M, Kiasalari Z, Rahmati B, Narenjkar J (2010) Behavioral and histological analysis of Crocus sativus effect in intracerebroventricular streptozotocin model of Alzheimer disease in rats. Iran J Pathol 5(1):27–33
Khalili M, Roghani M, Ekhlasi M (2009) The effect of aqueous crocus sativus L. extract on intracerebroventricular streptozotocin-induced cognitive deficits in rat: a behavioral analysis. Iran J Pharm Res 8(3):185–191
Kianbakht S (2008) A systematic review on pharmacology of saffron and its active constituents. J Medicinal Plants 7(28):1–27
Kianbakht S, Hajiaghaee R (2011) Anti-hyperglycemic effects of saffron and its active constituents, crocin and safranal, in alloxan-induced diabetic rats. J Med Plants 3(39):82–89
Kianbakht S, Mozafari K (2009) Effects of saffron and its active constituents, crocin and safranal, on prevention of indomethacin induced gastric ulcers in diabetic and nondiabetic rats. J Med Plants 8(29):30–38
Killick R, Scales G, Leroy K, Causevic M, Hooper C, Irvine EE, Choudhury AI, Drinkwater L, Kerr F, Al-Qassab H (2009) Deletion of Irs2 reduces amyloid deposition and rescues behavioural deficits in APP transgenic mice. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 386(1):257–262. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bbrc.2009.06.032
Kiritoshi S, Nishikawa T, Sonoda K, Kukidome D, Senokuchi T, Matsuo T, Matsumura T, Tokunaga H, Brownlee M, Araki E (2003) Reactive oxygen species from mitochondria induce cyclooxygenase-2 gene expression in human mesangial cells: potential role in diabetic nephropathy. Diabetes 52(10):2570–2577. https://doi.org/10.2337/diabetes.52.10.2570
Kong Y, Kong L-P, Luo T, Li G-W, Jiang W, Li S, Zhou Y, Wang H-Q (2014) The protective effects of crocetin on Aβ1-42-induced toxicity in HT22 cells. CNS Neurol Disord Drug Targets 13(9):1627–32. https://doi.org/10.2174/1871527313666140806125410
Konstantopoulos P, Doulamis IP, Tzani A, Korou ML, Agapitos E, Vlachos IS, Pergialiotis V, Verikokos C, Mastorakos G, Katsilambros NL, Perrea DN (2017) Metabolic effects of Crocus sativus and protective action against non-alcoholic fatty liver disease in diabetic rats. Biomed Rep 6(5):513–518. https://doi.org/10.3892/br.2017.884
Koyama A, O’Brien J, Weuve J, Blacker D, Metti AL, Yaffe K (2013) The role of peripheral inflammatory markers in dementia and Alzheimer’s disease: a meta-analysis. J Gerontol A Biol Sci Med Sci 68(4):433–440. https://doi.org/10.1093/gerona/gls187
Lahmass I, Sabouni A, Berraouan A, Zoheir K, Belakbir S, Elyoubi M, Benabbes R, Himri I, Mokhtari S, Mekhfi H (2018) Treatment with saffron extract of the diabetogenic rats induced by the food colorant Tartrazine. Indian J Physiol Pharmacol 62:249–258
Lahmass I, Sabouni A, Elyoubi M, Benabbes R, Mokhtari S, Saalaoui E (2017) Anti-diabetic effect of aqueous extract Crocus sativus L. in tartrazine induced diabetic male rats. Physiol Pharmacol 21(4):312–321
Lavan BE, Fantin VR, Chang ET, Lane WS, Keller SR, Lienhard GE (1997) A novel 160-kDa phosphotyrosine protein in insulin-treated embryonic kidney cells is a new member of the insulin receptor substrate family. J Biol Chem 272(34):21403–21407. https://doi.org/10.1074/jbc.272.34.21403
Li X-H, Lv B-L, Xie J-Z, Liu J, Zhou X-W, Wang J-Z (2012) AGEs induce Alzheimer-like tau pathology and memory deficit via RAGE-mediated GSK-3 activation. Neurobiol Aging 33(7):1400–1410. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neurobiolaging.2011.02.003
Liang H, Nie J, Van Skike CE, Valentine JM, Orr ME (2019) Mammalian target of rapamycin at the crossroad between Alzheimer’s disease and diabetes. Adv Exp Med Biol 185-225. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-981-13-3540-2_10
Lin C-Y, Sheu J-J, Tsai I-S, Wang S-T, Yang L-Y, Hsu I-U, Chang H-W, Lee H-M, Kao S-H, Lee C-K (2018) Elevated IgM against Nε-(Carboxyethyl) lysine-modified Apolipoprotein A1 peptide 141–147 in Taiwanese with Alzheimer’s disease. Clin Biochem 56:75–82. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.clinbiochem.2018.04.009
Linardaki ZI, Lamari FN, Margarity M (2017) Saffron (Crocus sativus L.) tea intake prevents learning/memory defects and neurobiochemical alterations induced by aflatoxin B 1 exposure in adult mice. Neurochem Res 42(10):2743–2754. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11064-017-2283-z
Linardaki ZI, Orkoula MG, Kokkosis AG, Lamari FN, Margarity M (2013) Investigation of the neuroprotective action of saffron (Crocus sativus L.) in aluminum-exposed adult mice through behavioral and neurobiochemical assessment. Food Chem Toxicol 52:163–170. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.fct.2012.11.016
Lovestone S, Smith U (2014) Advanced glycation end products, dementia, and diabetes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 111(13):4743–4744. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.1402277111
Lüth H-J, Ogunlade V, Kuhla B, Kientsch-Engel R, Stahl P, Webster J, Arendt T, Münch G (2005) Age-and stage-dependent accumulation of advanced glycation end products in intracellular deposits in normal and Alzheimer’s disease brains. Cereb Cortex 15(2):211–220. https://doi.org/10.1093/cercor/bhh123
Macauley SL, Stanley M, Caesar EE, Yamada SA, Raichle ME, Perez R, Mahan TE, Sutphen CL, Holtzman DM (2015) Hyperglycemia modulates extracellular amyloid-β concentrations and neuronal activity in vivo. J Clin Invest 125(6):2463–2467. https://doi.org/10.1172/JCI79742
Maciejczyk M, Żebrowska E, Chabowski A (2019) Insulin resistance and oxidative stress in the brain: what’s new? Int J Mol Sci 20(4):874. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms20040874
Maeda A, Kai K, Ishii M, Ishii T, Akagawa M (2014) Safranal, a novel protein tyrosine phosphatase 1 B inhibitor, activates insulin signaling in C 2 C 12 myotubes and improves glucose tolerance in diabetic KK-Ay mice. Mol Nutr Food Res 58(6):1177–1189. https://doi.org/10.1002/mnfr.201300675
Manczak M, Park BS, Jung Y, Reddy PH (2004) Differential expression of oxidative phosphorylation genes in patients with Alzheimer’s disease. Neuromolecular Med 5(2):147–162. https://doi.org/10.1385/NMM:5:2:147
Margaritis I, Angelopoulou K, Lavrentiadou S, Mavrovouniotis IC, Tsantarliotou M, Taitzoglou I, Theodoridis A, Veskoukis A, Kerasioti E, Kouretas D (2020) Effect of crocin on antioxidant gene expression, fibrinolytic parameters, redox status and blood biochemistry in nicotinamide-streptozotocin-induced diabetic rats. J Biol Res (thessalon) 27(1):1–15. https://doi.org/10.1186/s40709-020-00114-5
Martin-Jiménez CA, Gaitán-Vaca DM, Echeverria V, González J, Barreto GE (2017) Relationship between obesity, Alzheimer’s disease, and Parkinson’s disease: an astrocentric view. Mol Neurobiol 54(9):7096–7115. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12035-016-0193-8
Martins IJ (2015) Overnutrition Determines LPS Regulation of Mycotoxin Induced Neurotoxicity in Neurodegenerative Diseases. Int J Mol Sci 16(12):29554–29573. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms161226190
Martins IJ (2016) Anti-Aging Genes Improve Appetite Regulation and Reverse Cell Senescence and Apoptosis in Global Populations. Adv Aging Res 5(1):9–26. https://doi.org/10.4236/aar.2016.51002
Mattson M, Meffert M (2006) Roles for NF-κB in nerve cell survival, plasticity, and disease. Cell Death Differ 13(5):852–860. https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.cdd.4401837
McGeer EG, McGeer PL (2010) Neuroinflammation in Alzheimer’s disease and mild cognitive impairment: a field in its infancy. J Alzheimer’s Dis 19(1):355–361. https://doi.org/10.3233/JAD-2010-1219
Meng L, Cui L (2008) Inhibitory effects of crocetin on high glucose-induced apoptosis in cultured human umbilical vein endothelial cells and its mechanism. Arch Pharm Res 31(3):357–363. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12272-001-1164-y
Metz CN, Pavlov VA (2021) Treating disorders across the lifespan by modulating cholinergic signaling with galantamine. J Neurochem 158(6):1359–1380. https://doi.org/10.1111/jnc.15243
Milajerdi A, Jazayeri S, Hashemzadeh N, Shirzadi E, Derakhshan Z, Djazayeri A, Akhondzadeh S (2018) The effect of saffron (Crocus sativus L.) hydroalcoholic extract on metabolic control in type 2 diabetes mellitus: A triple-blinded randomized clinical trial. J Res Med Sci 23. https://doi.org/10.4103/jrms.JRMS_286_17
Mobasseri M, Ostadrahimi A, Tajaddini A, Asghari S, Barati M, Akbarzadeh M, Nikpayam O, Houshyar J, Roshanravan N, Alamdari NM (2020) Effects of saffron supplementation on glycemia and inflammation in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus: A randomized double-blind, placebo-controlled clinical trial study. Diabetes Metab Syndr 14(4):527–534. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.dsx.2020.04.031
Mohajeri D, Mousavi G, Doustar Y (2009) Antihyperglycemic and pancreas-protective effects of crocus sativus l. (saffron) stigma ethanolic extract on rats with alloxan-induced diabetes. J Biol Sci 9(4):302–310. https://doi.org/10.3923/jbs.2009.302.310
MoravejAleali A, Amani R, Shahbazian H, Namjooyan F, Latifi SM, Cheraghian B (2019) The effect of hydroalcoholic Saffron (Crocus sativus L.) extract on fasting plasma glucose, HbA1c, lipid profile, liver, and renal function tests in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus: A randomized double-blind clinical trial. Phytother Res 33(6):1648–1657. https://doi.org/10.1002/ptr.6351
Morris JK, Vidoni ED, Honea RA, Burns JM, Initiative A, s D N, (2014) Impaired glycemia increases disease progression in mild cognitive impairment. Neurobiol Aging 35(3):585–589. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neurobiolaging.2013.09.033
Mousavi SH, Tayarani N, Parsaee H (2010) Protective effect of saffron extract and crocin on reactive oxygen species-mediated high glucose-induced toxicity in PC12 cells. Cell Mol Neurobiol 30(2):185–191. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10571-009-9441-z
Naghibi SM, Hosseini M, Khani F, Rahimi M, Vafaee F, Rakhshandeh H, Aghaie A (2012) Effect of aqueous extract of Crocus sativus L. on morphine-induced memory impairment. Adv Pharmacol Sci 2012. https://doi.org/10.1155/2012/494367
Naghizadeh B, Mansouri M, Ghorbanzadeh B, Farbood Y, Sarkaki A (2013) Protective effects of oral crocin against intracerebroventricular streptozotocin-induced spatial memory deficit and oxidative stress in rats. Phytomedicine 20(6):537–542. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.phymed.2012.12.019
Nam KN, Park Y-M, Jung H-J, Lee JY, Min BD, Park S-U, Jung W-S, Cho K-H, Park J-H, Kang I (2010) Anti-inflammatory effects of crocin and crocetin in rat brain microglial cells. Eur J Pharmacol 648(1–3):110–116. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ejphar.2010.09.003
Nikbakht-Jam I, Khademi M, Nosrati M, Eslami S, Foroutan-Tanha M, Sahebkar A, Tavalaie S, Ghayour-Mobarhan M, Ferns GA, Hadizadeh F (2016) Effect of crocin extracted from saffron on pro-oxidant–anti-oxidant balance in subjects with metabolic syndrome: a randomized, placebo-controlled clinical trial. Eur J Integr Med 8(3):307–312. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.eujim.2015.12.008
Ochiai T, Ohno S, Soeda S, Tanaka H, Shoyama Y, Shimeno H (2004) Crocin prevents the death of rat pheochromyctoma (PC-12) cells by its antioxidant effects stronger than those of α-tocopherol. Neurosci Lett 362(1):61–64. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neulet.2004.02.067
Ochiai T, Shimeno H, Mishima K-i, Iwasaki K, Fujiwara M, Tanaka H, Shoyama Y, Toda A, Eyanagi R, Soeda S (2007) Protective effects of carotenoids from saffron on neuronal injury in vitro and in vivo. Biochim Biophys Acta 1770(4):578–584. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bbagen.2006.11.012
Oliver D, Reddy PH (2019) Dynamics of dynamin-related protein 1 in Alzheimer’s disease and other neurodegenerative diseases. Cells 8(9):961. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells8090961
Organization WH (2016) Global report on diabetes. 2016. Geneva. World Health Organization available from http://apps.whoint/iris/bitstream/10665/204871/1/9789241565257_eng.pdf. https://apps.who.int/iris/bitstream/handle/10665/204871/9?sequence=1
Ouahhoud S, Lahmass I, Bouhrim M, Khoulati A, Sabouni A, Benabbes R, Asehraou A, Choukri M, Bnouham M, Saalaoui E (2019) Antidiabetic effect of hydroethanolic extract of Crocus sativus stigmas, tepals and leaves in streptozotocin-induced diabetic rats. Physiol Pharmacol 23(1):9–20
Papandreou MA, Kanakis CD, Polissiou MG, Efthimiopoulos S, Cordopatis P, Margarity M, Lamari FN (2006) Inhibitory activity on amyloid-β aggregation and antioxidant properties of Crocus sativus stigmas extract and its crocin constituents. J Agric Food Chem 54(23):8762–8768. https://doi.org/10.1021/jf061932a
Papandreou MA, Tsachaki M, Efthimiopoulos S, Cordopatis P, Lamari FN, Margarity M, (2011) Memory enhancing effects of saffron in aged mice are correlated with antioxidant protection. Behav Brain Res 219(2):197–204. https://doi.org/10.1111/10.1016/j.bbr.2011.01.007
Patel PH, Gupta V (2021) Rivastigmine. StatPearls [Internet].
Paul S, Saha D, Binukumar B (2021) Mitochondrial Dysfunction and Mitophagy Closely Cooperate in Neurological Deficits Associated with Alzheimer’s Disease and Type 2 Diabetes. Mol Neurobiol: 1-15. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12035-021-02365-2
Peraldi P, Xu M, Spiegelman BM (1997) Thiazolidinediones block tumor necrosis factor-alpha-induced inhibition of insulin signaling. J Clin Invest 100(7):1863–1869. https://doi.org/10.1172/JCI119715
Perry G, Zhu X, Smith MA (2013) Alzheimer’s disease: advances for a new century. J Alzheimers Dis 33(Suppl 1):S1
Picone P, Giacomazza D, Vetri V, Carrotta R, Militello V, Biagio PLS, Di Carlo M (2011) Insulin-activated Akt rescues Aβ oxidative stress-induced cell death by orchestrating molecular trafficking. Aging Cell 10(5):832–843. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1474-9726.2011.00724.x
Pitsikas N, Sakellaridis N (2006) Crocus sativus L. extracts antagonize memory impairments in different behavioural tasks in the rat. Behav Brain Res 173(1):112–115. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bbr.2006.06.005
Prince M, Guerchet M, Ali G (2015) Alzheimer’s Disease International: World Alzheimer Report 2015: The Global Impact of Dementia. Published by Alzheimer’s Disease International (ADI), London: 1–92
Pugazhenthi S, Qin L, Reddy PH (2017) Common neurodegenerative pathways in obesity, diabetes, and Alzheimer’s disease. Biochim Biophys Acta Mol Basis Dis 1863(5):1037–1045. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bbadis.2016.04.017
Qiu Y, Jiang X, Liu D, Deng Z, Hu W, Li Z, Li Y (2020) The hypoglycemic and renal protection properties of crocin via oxidative stress-regulated NF-κB Signaling in db/db Mice. Front Pharmacol 11:541. https://doi.org/10.3389/fphar.2020.00541
Querfurth HW, LaFerla FM (2010) Mechanisms of disease. N Engl J Med 362(4):329–344
Rafieipour F, Hadipour E, Emami SA, Asili J, Tayarani-Najaran Z (2019) Safranal protects against beta-amyloid peptide-induced cell toxicity in PC12 cells via MAPK and PI3 K pathways. Metab Brain Dis 34(1):165–72. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11011-018-0329-9
Rajaei Z, Hadjzadeh M-A-R, Nemati H, Hosseini M, Ahmadi M, Shafiee S (2013) Antihyperglycemic and antioxidant activity of crocin in streptozotocin-induced diabetic rats. J Med Food 16(3):206–210. https://doi.org/10.1089/jmf.2012.2407
Ramirez A, Wolfsgruber S, Lange C, Kaduszkiewicz H, Weyerer S, Werle J, Pentzek M, Fuchs A, Riedel-Heller SG, Luck T (2015) Elevated HbA 1c is associated with increased risk of incident dementia in primary care patients. J Alzheimer’s Dis 44(4):1203–1212. https://doi.org/10.3233/JAD-141521
Rashedinia M, Lari P, Abnous K, Hosseinzadeh H (2015) Protective effect of crocin on acrolein-induced tau phosphorylation in the rat brain. Acta Neurobiol Exp 75(2):208–219
Rönnemaa E, Zethelius B, Sundelöf J, Sundström J, Degerman-Gunnarsson M, Berne C, Lannfelt L, Kilander L (2008) Impaired insulin secretion increases the risk of Alzheimer disease. Neurology 71(14):1065–1071. https://doi.org/10.1212/01.wnl.0000310646.32212.3a
Sadeghnia HR, Kamkar M, Assadpour E, Boroushaki MT, Ghorbani A (2013) Protective effect of safranal, a constituent of Crocus sativus, on quinolinic acid-induced oxidative damage in rat hippocampus. Iran J Basic Med Sci 16(1):73
Salkovic-Petrisic M, Tribl F, Schmidt M, Hoyer S, Riederer P (2006) Alzheimer-like changes in protein kinase B and glycogen synthase kinase-3 in rat frontal cortex and hippocampus after damage to the insulin signalling pathway. J Neurochem 96(4):1005–1015. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1471-4159.2005.03637.x
Samarghandian S, Azimi-Nezhad M, Farkhondeh T (2017) Immunomodulatory and antioxidant effects of saffron aqueous extract (Crocus sativus L.) on streptozotocin-induced diabetes in rats. Indian Heart J 69(2):151–159. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ihj.2016.09.008
Samarghandian S, Azimi-Nezhad M, Samini F (2014) Ameliorative effect of saffron aqueous extract on hyperglycemia, hyperlipidemia, and oxidative stress on diabetic encephalopathy in streptozotocin induced experimental diabetes mellitus. Biomed Res Int. 2014. https://doi.org/10.1155/2014/920857
Samarghandian S, Borji A (2014) Anticarcinogenic effect of saffron (Crocus sativus L.) and its ingredients. Pharmacognosy Res 6(2):99. https://doi.org/10.4103/0974-8490.128963
Sasaki N, Toki S, Chowei H, Saito T, Nakano N, Hayashi Y, Takeuchi M, Makita Z (2001) Immunohistochemical distribution of the receptor for advanced glycation end products in neurons and astrocytes in Alzheimer’s disease. Brain Res 888(2):256–262. https://doi.org/10.1016/s0006-8993(00)03075-4
Shaheen MJ, Bekdash AM, Itani HA, Borjac JM (2021) Saffron extract attenuates neuroinflammation in rmTBI mouse model by suppressing NLRP3 inflammasome activation via SIRT1. PLoS ONE 16(9):e0257211. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0257211
Shati A, Elsaid F, Hafez E (2011) Biochemical and molecular aspects of aluminium chloride-induced neurotoxicity in mice and the protective role of Crocus sativus L. extraction and honey syrup. Neuroscience 175:66–74. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neuroscience.2010.11.043
Shieh JC, Huang PT, Lin YF (2020) Alzheimer’s Disease and Diabetes: Insulin Signaling as the Bridge Linking Two Pathologies. Mol Neurobiol 57(4):1966–1977. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12035-019-01858-5
Shoffner JM (1997) Oxidative phosphorylation defects and Alzheimer’s disease. Neurogenetics 1(1):13–19. https://doi.org/10.1007/s100480050002
Sims-Robinson C, Kim B, Rosko A, Feldman EL (2010) How does diabetes accelerate Alzheimer disease pathology? Nat Rev Neurol 6(10):551–559. https://doi.org/10.1038/nrneurol.2010.130
Skourtis G, Krontira A, Ntaoula S, Ferlemi AV, Zeliou K, Georgakopoulos C, Margarity GM, Lamari NF, Pharmakakis N (2020) Protective antioxidant effects of saffron extract on retinas of streptozotocin-induced diabetic rats. Rom J Ophthalmol 64(4):394. https://doi.org/10.22336/rjo.2020.61
Soeda S, Ochiai T, Paopong L, Tanaka H, Shoyama Y, Shimeno H (2001) Crocin suppresses tumor necrosis factor-α-induced cell death of neuronally differentiated PC-12 cells. Life Sci 69(24):2887–2898. https://doi.org/10.1016/s0024-3205(01)01357-1
Srikanth V, Westcott B, Forbes J, Phan TG, Beare R, Venn A, Pearson S, Greenaway T, Parameswaran V, Münch G (2013) Methylglyoxal, cognitive function and cerebral atrophy in older people. J Gerontol A Biol Sci Med Sci 68(1):68–73. https://doi.org/10.1093/gerona/gls100
Srivastava R, Ahmed H, Dixit R (2010) Crocus sativus L: a comprehensive review. Pharmacogn Rev 4(8):200. https://doi.org/10.4103/0973-7847.70919
Steen E, Terry BM, Rivera EJ, Cannon JL, Neely TR, Tavares R, Xu XJ, Wands JR, de la Monte SM (2005) Impaired insulin and insulin-like growth factor expression and signaling mechanisms in Alzheimer’s disease–is this type 3 diabetes? J Alzheimer’s Dis 7(1):63–80. https://doi.org/10.3233/jad-2005-7107
Sun Y, Ma C, Sun H, Wang H, Peng W, Zhou Z, Wang H, Pi C, Shi Y, He X (2020) Metabolism: a novel shared link between diabetes mellitus and alzheimer’s disease. J Diabetes Res 2020. https://doi.org/10.1155/2020/4981814
Takeda S, Sato N, Rakugi H, Morishita R (2011) Molecular mechanisms linking diabetes mellitus and Alzheimer disease: beta-amyloid peptide, insulin signaling, and neuronal function. Mol Biosyst 7(6):1822–1827. https://doi.org/10.1039/c0mb00302f
Tamaddonfard E, Farshid AA, Asri-Rezaee S, Javadi S, Khosravi V, Rahman B, Mirfakhraee Z (2013) Crocin improved learning and memory impairments in streptozotocin-induced diabetic rats. Iran J Basic Med Sci 16(1):91
Tiribuzi R, Crispoltoni L, Chiurchiù V, Casella A, Montecchiani C, Del Pino AM, Maccarrone M, Palmerini CA, Caltagirone C, Kawarai T (2017) Trans-crocetin improves amyloid-β degradation in monocytes from Alzheimer’s Disease patients. J Neurol Sci 372:408–412. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jns.2016.11.004
Tsolaki M, Karathanasi E, Lazarou I, Dovas K, Verykouki E, Karakostas A, Georgiadis K, Tsolaki A, Adam K, Kompatsiaris I (2016) Efficacy and safety of Crocus sativus L. in patients with mild cognitive impairment: one year single-blind randomized, with parallel groups, clinical trial. J Alzheimer’s Dis 54(1):129–133. https://doi.org/10.3233/JAD-160304
Uemura E, Greenlee HW (2006) Insulin regulates neuronal glucose uptake by promoting translocation of glucose transporter GLUT3. Exp Neurol 198(1):48–53. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.expneurol.2005.10.035
Valente T, Gella A, Fernàndez-Busquets X, Unzeta M, Durany N (2010) Immunohistochemical analysis of human brain suggests pathological synergism of Alzheimer’s disease and diabetes mellitus. Neurobiol Dis 37(1):67–76. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.nbd.2009.09.008
Valle Garcia-Rodriguez M, Serrano-Diaz J, Tarantilis PA, Lopez-Corcoles H, Carmona M, Alonso GL (2014) Determination of saffron quality by high-performance liquid chromatography. J Agric Food Chem 62(32):8068–8074. https://doi.org/10.1021/jf5019356
Vandal M, Bourassa P, Calon F (2015) Can insulin signaling pathways be targeted to transport Aβ out of the brain? Front Aging Neurosci 7:114. https://doi.org/10.3389/fnagi.2015.00114
Wang C, Cai X, Hu W, Li Z, Kong F, Chen X, Wang D (2019a) Investigation of the neuroprotective effects of crocin via antioxidant activities in HT22 cells and in mice with Alzheimer’s disease. Int J Mol Med 43(2):956–966. https://doi.org/10.3892/ijmm.2018.4032
Wang D-M, Li S-Q, Wu W-L, Zhu X-Y, Wang Y, Yuan H-Y (2014) Effects of long-term treatment with quercetin on cognition and mitochondrial function in a mouse model of Alzheimer’s disease. Neurochem Res 39(8):1533–1543. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11064-014-1343-x
Wang X, Yuan B, Cheng B, Liu Y, Zhang B, Wang X, ... Gong G (2019b) Crocin Alleviates Myocardial Ischemia/Reperfusion-Induced Endoplasmic Reticulum Stress via Regulation of miR-34a/Sirt1/Nrf2 Pathway. Shock 51(1), 123-130. https://doi.org/10.1097/shk.0000000000001116
Wani A, Al Rihani SB, Sharma A, Weadick B, Govindarajan R, Khan SU, Sharma PR, Dogra A, Nandi U, Reddy CN (2021) Crocetin promotes clearance of amyloid-β by inducing autophagy via the STK11/LKB1-mediated AMPK pathway. Autophagy. https://doi.org/10.1080/15548627.2021.1872187
Wolfe MS (2008) Inhibition and modulation of γ-secretase for Alzheimer’s disease. Neurotherapeutics 5(3):391–398. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.nurt.2008.05.010
Xi L, Qian Z, Du P, Fu J (2007) Pharmacokinetic properties of crocin (crocetin digentiobiose ester) following oral administration in rats. Phytomedicine 14(9):633–636. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.phymed.2006.11.028
Yaribeygi H, Noroozadeh A, Mohammadi MT, Johnston TP, Sahebkar A (2019) Crocin improves oxidative stress by potentiating intrinsic anti-oxidant defense systems in pancreatic cells during uncontrolled hyperglycemia. J Pharmacopuncture 22(2):83. https://doi.org/10.3831/KPI.2019.22.010
Ying L, Chaudhry MT, Xiao F, Mao Y, Wang M, Wang B, Wang S, Li Y (2020) The effects and mechanism of quercetin dietary supplementation in streptozotocin-induced hyperglycemic arbor acre broilers. Oxid Med Cell Longev 2020. https://doi.org/10.1155/2020/9585047
Yoshino Y, Ishisaka M, Umigai N, Shimazawa M, Tsuruma K, Hara H (2014) Crocetin prevents amyloid β 1-42-induced cell death in murine hippocampal cells. Pharmacol Pharm 2014. https://doi.org/10.4236/pp.2014.51007
Zarezadeh M, Vazifeshenas-Darmiyan K, Afshar M, Valavi M, Serki E, Hosseini M (2017) Effects of extract of Crocus sativus petal on renal function in diabetic rats. Journal of Mazandaran University of Medical Sciences 27(147):11–24
Zhang X-y, Zhang X-j, Xv J, Jia W, Pu X-y, Wang H-y, Liang H, Lu D-x (2018) Crocin attenuates acute hypobaric hypoxia-induced cognitive deficits of rats. Eur J Pharmacol 818:300–305. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ejphar.2017.10.042
Zhang Y, Shoyama Y, Sugiura M, Saito H (1994) Effects of Crocus sativus L. on the ethanol-induced impairment of passive avoidance performances in mice. Biol Pharm Bull 17(2):217–221. https://doi.org/10.1248/bpb.17.217
Zhao WQ, De Felice FG, Fernandez S, Chen H, Lambert MP, Quon MJ, Krafft GA, Klein WL (2008) Amyloid beta oligomers induce impairment of neuronal insulin receptors. FASEB Jl 22(1):246–260. https://doi.org/10.1096/fj.06-7703com
Zheng B-W, Yang L, Dai X-L, Jiang Z-F, Huang H-C (2016) Roles of O-GlcNAcylation on amyloid-β precursor protein processing, tau phosphorylation, and hippocampal synapses dysfunction in Alzheimer’s disease. Neurol Res 38(2):177–186. https://doi.org/10.1080/01616412.2015.1133485
Zhong K, Wang R-X, Qian X-D, Yu P, Zhu X-Y, Zhang Q, Ye Y-L (2020) Neuroprotective effects of saffron on the late cerebral ischemia injury through inhibiting astrogliosis and glial scar formation in rats. Biomed Pharmacother 126:110041. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biopha.2020.110041
Zilaee M, Soukhtanloo M, Ghayour-Mobarhan M, Shemshian M, Salehi M, Ferns GA (2018) Effect of saffron on serum leptin levels in patients with metabolic syndrome, a double-blind, randomized and placebo-controlled trial study. Prog Nutr 20:140–144
Acknowledgements
We are grateful to the office of the Vice-Chancellor for Research and Technology at Tabriz University of Medical Sciences for supporting further research.
Funding
This research did not receive any specific grant from funding agencies in the public, commercial, or not-for-profit sectors.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Sarvin Sanaie: Conceptualization, Data interpretation; Saba Nikanfar: Writing- Original draft preparation, Data analysis; Zahra Yousefi Kalekhane: Investigation, Data search and extraction; Akbar Azizi-Zeinalhajlou: Data analysis; Saeed Sadigh-Eteghad: literature search; Mostafa Araj-Khodaei and Mohammad Hossein Ayati: Supervision, Project administration; Sasan Andalib; Writing—Review & Editing. All the authors have read and approved the final manuscript.
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Ethics approval and consent to participate
Not applicable.
Consent for publication
Not applicable.
Competing interests
The authors declare no conflict of interest with respect to the present paper.
Additional information
Publisher's note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Sanaie, S., Nikanfar, S., Kalekhane, Z.Y. et al. Saffron as a promising therapy for diabetes and Alzheimer's disease: mechanistic insights. Metab Brain Dis 38, 137–162 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11011-022-01059-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11011-022-01059-5