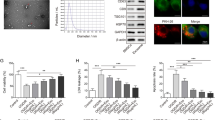
Abstract
Background/aim
Bone marrow mesenchymal stem cell (BMSC)-derived exosomes can prevent oxidative stress and inflammation in cerebral ischemia-reperfusion injury. This study intended to assess influences of BMSC-released exosomes on oxidative stress and inflammation following ischemic stroke.
Methods
In vitro and in vivo models were developed using oxygen-glucose deprivation/reperfusion (OGD/R) and middle cerebral artery occlusion (MCAO), respectively. After exosome isolation, co-culture experiments of BMSCs or BMSC-derived exosomes and OGD/R-treated BV-2 cells were implemented to evaluate the impacts of BMSCs or BMSC-secreted exosomes on proliferation, inflammation, oxidative stress, and apoptosis. The gain-of-function experiments of ZFAS1 or microRNA (miR)-15a-5p were conducted to investigate the associated mechanisms. Besides, MCAO mice were injected with exosomes from BMSCs overexpressing ZFAS1 for in vivo verification. The binding of ZFAS1 to miR-15a-5p was assessed through dual-luciferase reporter gene assay.
Results
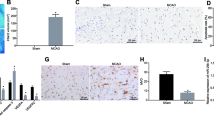
Co-culture with BMSCs accelerated proliferation and downregulated IL-1β, IL-6, and TNF-α in OGD/R-exposed BV-2 cells, accompanied by increased SOD level and decreased MDA level and apoptosis, all of which were nullified by inhibiting exosome secretion. Mechanistically, ZFAS1 bound to miR-15a-5p to negatively orchestrate its expression. In addition, BMSC-released exosomes or BMSC-secreted exosomal ZFAS1 augmented proliferation but reduced oxidative stress, apoptosis, and inflammation in OGD/R-exposed BV-2 cells, whereas these impacts of BMSC-released exosomal ZFAS1 were nullified by overexpressing miR-15a-5p. Moreover, BMSC-derived exosomal ZFAS1 diminished MCAO-induced oxidative stress, cerebral infarction, and inflammation in mice.
Conclusions
Conclusively, BMSC-released exosomes might carry long noncoding RNA ZFAS1 to curb oxidative stress and inflammation related to ischemic stroke, which was possibly realized through miR-15a-5p inhibition.






Similar content being viewed by others
Availability of supporting data
Not applicable.
References
Ai Z, Cheng C, Zhou L, Yin S, Wang L, Liu Y (2021) Bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells-derived extracellular vesicles carrying microRNA-221-3p protect against ischemic stroke via ATF3. Brain Res Bull 172:220–228
An L, Yang T, Zhong Y, Yin Y, Li W, Gao H (2021) Molecular pathways in sepsis-induced cardiomyocyte pyroptosis: Novel finding on long non-coding RNA ZFAS1/miR-138-5p/SESN2 axis. Immunol Lett 238:47–56
Campbell BCV, De Silva DA, Macleod MR, Coutts SB, Schwamm LH, Davis SM, Donnan GA (2019) Ischaemic stroke. Nat Rev Dis Primers 5:70
Chehaibi K, Trabelsi I, Mahdouani K, Slimane MN (2016) Correlation of Oxidative Stress Parameters and Inflammatory Markers in Ischemic Stroke Patients. J Stroke Cerebrovasc Dis 25:2585–2593
Chen J, Chopp M (2018) Exosome Therapy for Stroke. Stroke 49:1083–1090
Deng Y, Chen D, Gao F, Lv H, Zhang G, Sun X, Liu L, Mo D, Ma N, Song L, Huo X, Yan T, Zhang J, Miao Z (2019) Exosomes derived from microRNA-138-5p-overexpressing bone marrow-derived mesenchymal stem cells confer neuroprotection to astrocytes following ischemic stroke via inhibition of LCN2. J Biol Eng 13:71
Dichgans M, Pulit SL, Rosand J (2019) Stroke genetics: discovery, biology, and clinical applications. Lancet Neurol 18:587–599
Dziedzic T (2015) Systemic inflammation as a therapeutic target in acute ischemic stroke. Expert Rev Neurother 15:523–531
George PM, Steinberg GK (2015) Novel Stroke Therapeutics: Unraveling Stroke Pathophysiology and Its Impact on Clinical Treatments. Neuron 87:297–309
Gong J, Meng HB, Hua J, Song ZS, He ZG, Zhou B, Qian MP (2014) The SDF-1/CXCR4 axis regulates migration of transplanted bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells towards the pancreas in rats with acute pancreatitis. Mol Med Rep 9:1575–1582
Guo RB, Dong YF, Yin Z, Cai ZY, Yang J, Ji J, Sun YQ, Huang XX, Xue TF, Cheng H, Zhou XQ, Sun XL (2021) Iptakalim improves cerebral microcirculation in mice after ischemic stroke by inhibiting pericyte contraction. Acta Pharmacol Sin
He J, Xie P, Ouyang J (2021) Circ_0122396 Protects Human Lens Epithelial Cells from Hydrogen Peroxide-induced Injury by Binding to miR-15a-5p to Stimulate FGF1 Expression.Curr Eye Res1–10
Jiang Y, Zhang W (2021) LncRNA ZFAS1 plays a role in regulating the inflammatory responses in sepsis-induced acute lung injury via mediating miR-193a-3p. Infect Genet Evol 92:104860
Kalluri R, LeBleu VS (2020) The biology, function, and biomedical applications of exosomes.Science367
Khan H, Pan JJ, Li Y, Zhang Z, Yang GY (2021) Native and Bioengineered Exosomes for Ischemic Stroke Therapy. Front Cell Dev Biol 9:619565
Kim M, Lee Y, Lee M (2021) Hypoxia-specific anti-RAGE exosomes for nose-to-brain delivery of anti-miR-181a oligonucleotide in an ischemic stroke model. Nanoscale 13:14166–14178
Lan XY, Sun ZW, Xu GL, Chu CY, Qin HM, Li S, Geng X, Gao P, Boltze J, Li S (2021) Bone Marrow Mesenchymal Stem Cells Exert Protective Effects After Ischemic Stroke Through Upregulation of Glutathione. Stem Cell Rev Rep
Li P, Stetler RA, Leak RK, Shi Y, Li Y, Yu W, Bennett MVL, Chen J (2018) Oxidative stress and DNA damage after cerebral ischemia: Potential therapeutic targets to repair the genome and improve stroke recovery. Neuropharmacology 134:208–217
Li H, Wang Y, Wang B, Li M, Liu J, Yang H, Shi Y (2021) Baicalin and Geniposide Inhibit Polarization and Inflammatory Injury of OGD/R-Treated Microglia by Suppressing the 5-LOX/LTB4 Pathway. Neurochem Res 46:1844–1858
Liu X, Zhang M, Liu H, Zhu R, He H, Zhou Y, Zhang Y, Li C, Liang D, Zeng Q, Huang G (2021) Bone marrow mesenchymal stem cell-derived exosomes attenuate cerebral ischemia-reperfusion injury-induced neuroinflammation and pyroptosis by modulating microglia M1/M2 phenotypes. Exp Neurol 341:113700
Lou Y, Huang Z (2020) microRNA-15a-5p participates in sepsis by regulating the inflammatory response of macrophages and targeting TNIP2. Exp Ther Med 19:3060–3068
Ma F, Sun P, Zhang X, Hamblin MH, Yin KJ (2020) Endothelium-targeted deletion of the miR-15a/16 – 1 cluster ameliorates blood-brain barrier dysfunction in ischemic stroke.Sci Signal13
Min W, Wu Y, Fang Y, Hong B, Dai D, Zhou Y, Liu J, Li Q (2022) Bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells-derived exosomal microRNA-124-3p attenuates hypoxic-ischemic brain damage through depressing tumor necrosis factor receptor associated factor 6 in newborn rats. Bioengineered 13:3194–3206
Osier N, Motamedi V, Edwards K, Puccio A, Diaz-Arrastia R, Kenney K, Gill J (2018) Exosomes in Acquired Neurological Disorders: New Insights into Pathophysiology and Treatment. Mol Neurobiol 55:9280–9293
Pegtel DM, Gould SJ (2019) Exosomes. Annu Rev Biochem 88:487–514
Pradeep H, Diya JB, Shashikumar S, Rajanikant GK (2012) Oxidative stress–assassin behind the ischemic stroke. Folia Neuropathol 50:219–230
Shekhar S, Cunningham MW, Pabbidi MR, Wang S, Booz GW, Fan F (2018) Targeting vascular inflammation in ischemic stroke: Recent developments on novel immunomodulatory approaches. Eur J Pharmacol 833:531–544
Sun M, Yamashita T, Shang J, Liu N, Deguchi K, Feng J, Abe K (2015) Time-dependent profiles of microRNA expression induced by ischemic preconditioning in the gerbil hippocampus. Cell Transpl 24:367–376
Venkat P, Chopp M, Chen J (2018) Cell-Based and Exosome Therapy in Diabetic Stroke. Stem Cells Transl Med 7:451–455
Wang W, Li Z, Feng J (2018) The potential role of exosomes in the diagnosis and therapy of ischemic diseases. Cytotherapy 20:1204–1219
Wang J, Ruan J, Zhu M, Yang J, Du S, Xu P, Zhang Z, Wang P, Yang W, Yu M (2019) Predictive value of long noncoding RNA ZFAS1 in patients with ischemic stroke. Clin Exp Hypertens 41:615–621
Wang G, Zhou Y, Zhong T, Song A, Xue Q (2022) The role of blood lnc-ZFAS1 in acute ischemic stroke: correlation with neurological impairment, inflammation, and survival profiles. J Clin Lab Anal 36:e24219
Wu J, Du K, Lu X (2015) Elevated expressions of serum miR-15a, miR-16, and miR-17-5p are associated with acute ischemic stroke. Int J Clin Exp Med 8:21071–21079
Yao B, Ye L, Chen J, Zhuo S, Lin H (2021) LINC00473 protects against cerebral ischemia reperfusion injury via sponging miR-15b-5p and miR-15a-5p to regulate SRPK1 expression. Brain Inj 35:1462–1471
Yong KW, Choi JR, Mohammadi M, Mitha AP, Sanati-Nezhad A, Sen A (2018) Mesenchymal Stem Cell Therapy for Ischemic Tissues. Stem Cells Int 2018:8179075
Zhang ZG, Buller B, Chopp M (2019) Exosomes - beyond stem cells for restorative therapy in stroke and neurological injury. Nat Rev Neurol 15:193–203
Zhang Y, Zhang Y (2020) lncRNA ZFAS1 Improves Neuronal Injury and Inhibits Inflammation, Oxidative Stress, and Apoptosis by Sponging miR-582 and Upregulating NOS3 Expression in Cerebral Ischemia/Reperfusion Injury. Inflammation 43:1337–1350
Zhang S, Song S, Zhuang Y, Hu J, Cui W, Wang X, Zhao Z, Liu X, Sun Z (2021) Role of microRNA-15a-5p/Sox9/NF-kappaB axis in inflammatory factors and apoptosis of murine nucleus pulposus cells in intervertebral disc degeneration. Life Sci 277:119408
Zhao H, Han Z, Ji X, Luo Y (2016) Epigenetic Regulation of Oxidative Stress in Ischemic Stroke. Aging Dis 7:295–306
Zhong Y, Luo L (2021) Exosomes from Human Umbilical Vein Endothelial Cells Ameliorate Ischemic Injuries by Suppressing the RNA Component of Mitochondrial RNA-processing Endoribonuclease via the Induction of miR-206/miR-1-3p Levels. Neuroscience 476:34–44
Acknowledgements
Thanks for all authors’ contribution.
Funding
Not applicable.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
JCC conceived the ideas. JCC designed the experiments. HTY analyzed the data. JCC provided critical materials. JCC and HTY wrote the manuscript. JCC supervised the study. All the authors have read and approved the final version for publication.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors report no relationships that could be construed as a conflict of interest.
Ethical approval and consent to participate
Not applicable.
Consent for publication
I represent all my co-authors who have approved the publication of the article.
Additional information
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Yang, H., Chen, J. Bone marrow mesenchymal stem cell-derived exosomes carrying long noncoding RNA ZFAS1 alleviate oxidative stress and inflammation in ischemic stroke by inhibiting microRNA-15a-5p. Metab Brain Dis 37, 2545–2557 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11011-022-00997-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11011-022-00997-4