Abstract
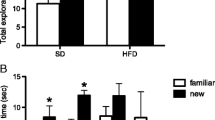
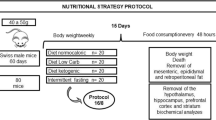
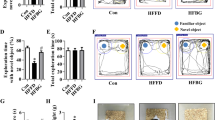
The excessive production of pro-inflammatory mediators, characteristic of obesity, leads to neuroinflammation. Zinc (Zn) and the branched-chain amino acids (BCAA) are supplements known for their immunomodulatory properties. Our goal was to evaluate if Zn or BCAA supplementation can affect long-term recognition memory and neuroinflammatory parameters of obese rats after a high-fat diet (HFD). Three-month-old Wistar rats were divided into six groups: Standard diet (SD) + vehicle; SD + Zn; SD + BCAA; High-fat diet (HFD) + vehicle; HFD + Zn; and HFD + BCAA. Diets were administrated for 19 weeks, Zn (1,2 mg/kg/day) or BCAA (750 mg/kg/day) supplementation was conducted in the last 4 weeks. Long-term recognition memory was evaluated by the novel object recognition test. IL-1β immunoreactivity in the cortex and hippocampus, and IL-6 levels in the cortex tissue were assessed. Astrogliosis were evaluated through GFAP + cell count and morphological analysis (Sholl Method). Zn supplementation improved object recognition memory in HFD-fed rats, which was not observed following BCAA supplementation. The levels of IL-6 in the cerebral cortex were higher after HFD, which was not diminished after neither supplementation. Obesity also led to increased IL-1β immunoreactivity in the cerebral cortex and hippocampus, which was reduced by Zn. BCAA supplementation also diminished IL-1β immunoreactivity, but only in the hippocampus. We also showed that astrocyte reactivity caused by HFD is area-dependent, being the cerebral cortex more susceptible to the diet. Even though BCAA and Zn can affect IL-1β immunoreactivity and astrocyte morphology, only Zn improved memory. Future studies are needed to clarify the pathways by which Zn improves cognition in obesity.
Graphical abstract







Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
The datasets generated during the current study are available from the corresponding author on reasonable request.
References
Abdollahi S, Toupchian O, Jayedi A, Meyre D, Tam V, Soltani S (2020) Zinc supplementation and body weight: a systematic review and dose-response meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials. Adv Nutr 11(2):398–411
Beilharz JE, Maniam J, Morris MJ (2016) Short-term exposure to a diet high in fat and sugar, or liquid sugar, selectively impairs hippocampal-dependent memory, with differential impacts on inflammation. Behav Brain Res 306:1–7
Bifari F, Nisoli E (2017) Branched-chain amino acids differently modulate catabolic and anabolic states in mammals: a pharmacological point of view. Br J Pharmacol 174(11):1366–1377
Buckman LB, Thompson MM, Moreno HN, Ellacott KL (2013) Regional astrogliosis in the mouse hypothalamus in response to obesity. J Comp Neurol 521(6):1322–1333
Clausen BH, Wirenfeldt M, Høgedal SS, Frich LH, Nielsen HH, Schrøder HD, Østergaard K, Finsen B, Kristensen BW, Lambertsen KL (2020) Characterization of the TNF and IL-1 systems in human brain and blood after ischemic stroke. Acta Neuropathol Commun 8(1):81
Cope EC, Morris DR, Scrimgeour AG, VanLandingham JW, Levenson CW (2011) Zinc supplementation provides behavioral resiliency in a rat model of traumatic brain injury. Physiol Behav 104(5):942–947
Coppola A, Wenner BR, Ilkayeva O, Stevens RD, Maggioni M, Slotkin TA, Levin ED, Newgard CB (2013) Branched-chain amino acids alter neurobehavioral function in rats. Am J Physiol Endocrinol Metab 304(4):E405-413
Cordner ZA, Tamashiro KL (2015) Effects of high-fat diet exposure on learning & memory. Physiol Behav 152(Pt B):363–371
Costarelli L, Muti E, Malavolta M, Cipriano C, Giacconi R, Tesei S, Piacenza F, Pierpaoli S, Gasparini N, Faloia E, Tirabassi G, Boscaro M, Polito A, Mauro B, Maiani F, Raguzzini A, Marcellini F, Giuli C, Papa R, Emanuelli M, Lattanzio F, Mocchegiani E (2010) Distinctive modulation of inflammatory and metabolic parameters in relation to zinc nutritional status in adult overweight/obese subjects. J Nutr Biochem 21(5):432–437
Cruz KJ, Morais JB, de Oliveira AR, Severo JS, Marreiro DD (2017) The effect of zinc supplementation on insulin resistance in obese subjects: a systematic review. Biol Trace Elem Res 176(2):239–243
Dall’Oglio A, Gehlen G, Achaval M, Rasia-Filho AA (2008) Dendritic branching features of Golgi-impregnated neurons from the “ventral” medial amygdala subnuclei of adult male and female rats. Neurosci Lett 439(3):287–292
de Andrade AM, Fernandes MDC, de Fraga LS, Porawski M, Giovenardi M, Guedes RP (2017) Omega-3 fatty acids revert high-fat diet-induced neuroinflammation but not recognition memory impairment in rats. Metab Brain Dis 32(6):1871–1881
de Moura AC, Lazzari VM, Becker RO, Gil MS, Ruthschilling CA, Agnes G, Almeida S, da Veiga AB, Lucion AB, Giovenardi M (2015) Gene expression in the CNS of lactating rats with different patterns of maternal behavior. Neurosci Res 99:8–15
de Oliveira S, Feijó GDS, Neto J, Jantsch J, Braga MF, Castro L, Giovenardi M, Porawski M, Guedes RP (2021) Zinc supplementation decreases obesity-related neuroinflammation and improves metabolic function and memory in rats. Obesity (Silver Spring) 29(1):116–124
De Simone R, Vissicchio F, Mingarelli C, De Nuccio C, Visentin S, Ajmone-Cat MA, Minghetti L (2013) Branched-chain amino acids influence the immune properties of microglial cells and their responsiveness to pro-inflammatory signals. Biochim Biophys Acta 1832(5):650–659
Ellulu MS, Patimah I, Khaza’ai H, Rahmat A, Abed Y (2017) Obesity and inflammation: the linking mechanism and the complications. Arch Med Sci 13(4):851–863
Ennaceur A, Delacour J (1988) A new one-trial test for neurobiological studies of memory in rats. 1: behavioral data. Behav Brain Res 31(1):47–59
Faber C, Gabriel P, Ibs KH, Rink L (2004) Zinc in pharmacological doses suppresses allogeneic reaction without affecting the antigenic response. Bone Marrow Transplant 33(12):1241–1246
Fischer A, Sananbenesi F, Wang X, Dobbin M, Tsai LH (2007) Recovery of learning and memory is associated with chromatin remodelling. Nature 447(7141):178–182
Frazzini V, Granzotto A, Bomba M, Massetti N, Castelli V, d’Aurora M, Punzi M, Iorio M, Mosca A, Delli Pizzi S, Gatta V, Cimini A, Sensi SL (2018) The pharmacological perturbation of brain zinc impairs BDNF-related signaling and the cognitive performances of young mice. Sci Rep 8(1):9768
Gregor MF, Hotamisligil GS (2011) Inflammatory mechanisms in obesity. Annu Rev Immunol 29:415–445
Guillemot-Legris O, Muccioli GG (2017) Obesity-induced neuroinflammation: beyond the hypothalamus. Trends Neurosci 40(4):237–253
Gunstad J, Paul RH, Cohen RA, Tate DF, Spitznagel MB, Grieve S, Gordon E (2008) Relationship between body mass index and brain volume in healthy adults. Int J Neurosci 118(11):1582–1593
Gzielo K, Kielbinski M, Ploszaj J, Janeczko K, Gazdzinski SP, Setkowicz Z (2017) Long-term consumption of high-fat diet in rats: effects on microglial and astrocytic morphology and neuronal nitric oxide synthase expression. Cell Mol Neurobiol 37(5):783–789
Gómez-Apo E, Mondragón-Maya A, Ferrari-Díaz M, Silva-Pereyra J (2021) Structural brain changes associated with overweight and obesity. J Obes 2021:6613385
Heyward FD, Gilliam D, Coleman MA, Gavin CF, Wang J, Kaas G, Trieu R, Lewis J, Moulden J, Sweatt JD (2016) Obesity weighs down memory through a mechanism involving the neuroepigenetic dysregulation of sirt1. J Neurosci 36(4):1324–1335
Kelly B, Pearce EL (2020) Amino assets: how amino acids support immunity. Cell Metab 32(2):154–175
Kwon HS, Koh SH (2020) Neuroinflammation in neurodegenerative disorders: the roles of microglia and astrocytes. Transl Neurodegener 9(1):42
Leigh SJ, Morris MJ (2020) Diet, inflammation and the gut microbiome: mechanisms for obesity-associated cognitive impairment. Biochim Biophys Acta Mol Basis Dis 1866(6):165767
Lizarbe B, Soares AF, Larsson S, Duarte JMN (2018) Neurochemical modifications in the hippocampus, cortex and hypothalamus of mice exposed to long-term high-fat diet. Front Neurosci 12:985
Malik VS, Willett WC, Hu FB (2013) Global obesity: trends, risk factors and policy implications. Nat Rev Endocrinol 9(1):13–27
Neal M, Richardson JR (2018) Epigenetic regulation of astrocyte function in neuroinflammation and neurodegeneration. Biochim Biophys Acta Mol Basis Dis 1864(2):432–443
Nguyen JC, Killcross AS, Jenkins TA (2014) Obesity and cognitive decline: role of inflammation and vascular changes. Front Neurosci 8:375
Olesen RH, Hyde TM, Kleinman JE, Smidt K, Rungby J, Larsen A (2016) Obesity and age-related alterations in the gene expression of zinc-transporter proteins in the human brain. Transl Psychiatry 6(6):e838
Pekny M, Pekna M (2014) Astrocyte reactivity and reactive astrogliosis: costs and benefits. Physiol Rev 94(4):1077–1098
Plum LM, Rink L, Haase H (2010) The essential toxin: impact of zinc on human health. Int J Environ Res Public Health 7(4):1342–1365
Portbury SD, Adlard PA (2017) Zinc signal in brain diseases. Int J Mol Sci 18(12):2506
Raji CA, Ho AJ, Parikshak NN, Becker JT, Lopez OL, Kuller LH, Hua X, Leow AD, Toga AW, Thompson PM (2010) Brain structure and obesity. Hum Brain Mapp 31(3):353–364
Rhea EM, Salameh TS, Logsdon AF, Hanson AJ, Erickson MA, Banks WA (2017) Blood-brain barriers in obesity. Aaps j 19(4):921–930
Rios-Lugo MJ, Madrigal-Arellano C, Gaytán-Hernández D, Hernández-Mendoza H, Romero-Guzmán ET (2020) Association of serum zinc levels in overweight and obesity. Biol Trace Elem Res 198(1):51–57
Rosa L, Scaini G, Furlanetto CB, Galant LS, Vuolo F, Dall’Igna DM, Schuck PF, Ferreira GC, Dal-Pizzol F, Streck EL (2016) Administration of branched-chain amino acids alters the balance between pro-inflammatory and anti-inflammatory cytokines. Int J Dev Neurosci 48:24–30
Samara A, Murphy T, Strain J, Rutlin J, Sun P, Neyman O, Sreevalsan N, Shimony JS, Ances BM, Song SK, Hershey T, Eisenstein SA (2019) Neuroinflammation and white matter alterations in obesity assessed by diffusion basis spectrum imaging. Front Hum Neurosci 13:464
Scaini G, Jeremias GC, Furlanetto CB, Dominguini D, Comim CM, Quevedo J, Schuck PF, Ferreira GC, Streck EL (2014) Behavioral responses in rats submitted to chronic administration of branched-chain amino acids. JIMD Rep 13:159–167
Schneider CA, Rasband WS, Eliceiri KW (2012) NIH Image to ImageJ: 25 years of image analysis. Nat Methods 9(7):671–675
Sholl DA (1953) Dendritic organization in the neurons of the visual and motor cortices of the cat. J Anat 87(4):387–406
Skalny AV, Aschner M, Tinkov AA (2021) Zinc. Adv Food Nutr Res 96:251–310
Sofroniew MV (2014) Astrogliosis. Cold Spring Harb Perspect Biol 7(2):a020420
Solati Z, Jazayeri S, Tehrani-Doost M, Mahmoodianfard S, Gohari MR (2015) Zinc monotherapy increases serum brain-derived neurotrophic factor (BDNF) levels and decreases depressive symptoms in overweight or obese subjects: a double-blind, randomized, placebo-controlled trial. Nutr Neurosci 18(4):162–168
Tamano H, Koike Y, Nakada H, Shakushi Y, Takeda A (2016) Significance of synaptic Zn(2+) signaling in zincergic and non-zincergic synapses in the hippocampus in cognition. J Trace Elem Med Biol 38:93–98
Tamano H, Minamino T, Fujii H, Takada S, Nakamura M, Ando M, Takeda A (2015) Blockade of intracellular Zn2+ signaling in the dentate gyrus erases recognition memory via impairment of maintained LTP. Hippocampus 25(8):952–962
Thoen RU, Barther NN, Schemitt E, Bona S, Fernandes S, Coral G, Marroni NP, Tovo C, Guedes RP, Porawski M (2019) Zinc supplementation reduces diet-induced obesity and improves insulin sensitivity in rats. Appl Physiol Nutr Metab 44(6):580–586
Tomassoni D, Nwankwo IE, Gabrielli MG, Bhatt S, Muhammad AB, Lokhandwala MF, Tayebati SK, Amenta F (2013) Astrogliosis in the brain of obese Zucker rat: a model of metabolic syndrome. Neurosci Lett 543:136–141
Tournissac M, Vandal M, Tremblay C, Bourassa P, Vancassel S, Emond V, Gangloff A, Calon F (2018) Dietary intake of branched-chain amino acids in a mouse model of Alzheimer’s disease: Effects on survival, behavior, and neuropathology. Alzheimers Dement (NY) 4:677–687
Tsai SF, Wu HT, Chen PC, Chen YW, Yu M, Wang TF, Wu SY, Tzeng SF, Kuo YM (2018) High-fat diet suppresses the astrocytic process arborization and downregulates the glial glutamate transporters in the hippocampus of mice. Brain Res 1700:66–77
Wang X, Wu W, Zheng W, Fang X, Chen L, Rink L, Min J, Wang F (2019) Zinc supplementation improves glycemic control for diabetes prevention and management: a systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials. Am J Clin Nutr 110(1):76–90
WHO, W. H. O (2018) Obesity and Overweight
Yosaee S, Soltani S, Esteghamati A, Motevalian SA, Tehrani-Doost M, Clark CCT, Jazayeri S (2020) Effects of zinc, vitamin D, and their co-supplementation on mood, serum cortisol, and brain-derived neurotrophic factor in patients with obesity and mild to moderate depressive symptoms: A phase II, 12-wk, 2 × 2 factorial design, double-blind, randomized, placebo-controlled trial. Nutrition 71:110601
Zhang S, Zeng X, Ren M, Mao X, Qiao S (2017) Novel metabolic and physiological functions of branched chain amino acids: a review. J Anim Sci Biotechnol 8:10
Funding
This study was supported by the Brazilian funding agencies: Conselho Nacional de Desenvolvimento Científico e Tecnológico (CNPq), Coordenação de Aperfeiçoamento de Pessoal de Nível Superior (CAPES), Fundação de Amparo à Pesquisa do Estado do Rio Grande do Sul (FAPERGS); G.S. Feijó and J. Jantsch were recipients of FAPERGS and CNPq fellowships, respectivelly. L.L. Correia and S.Eller were recipients of UFCSPA fellowships.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Renata Padilha Guedes and Marilene Porawski conceived the presented idea. Grace dos Santos Feijó, Jeferson Jantsch, Lidia Luz Correia, Sarah Eller, and Orlando Vieira Furtado Filho carried out the experiments. Grace dos Santos Feijó, Renata Padilha Guedes, Elizandra Braganhol and Márcia Giovenardi contributed to the interpretation of the results. Grace dos Santos Feijó and Jeferson Jantsch wrote the manuscript in consultation with Renata Padilha Guedes and Elizandra Braganhol. All authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethics approval
All procedures were approved by the Institutional Animal Care and Use Committee (UFCSPA, Brazil, protocol No. 359/16).
Competing interests
The authors have no relevant financial or non-financial interests to disclose.
Additional information
Publisher's note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Feijó, G.d., Jantsch, J., Correia, L.L. et al. Neuroinflammatory responses following zinc or branched-chain amino acids supplementation in obese rats. Metab Brain Dis 37, 1875–1886 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11011-022-00996-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11011-022-00996-5