Abstract
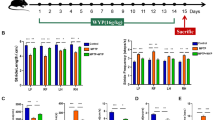
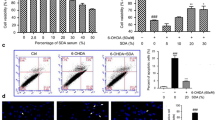
Wuzi Yanzong Pill (WYP) was found to play a protective role on nerve cells and neurological diseases, however the molecular mechanism is unclear. To understand the molecular mechanisms that underly the neuroprotective effect of WYP on dopaminergic neurons in Parkinson’s disease (PD). PD mouse model was induced by the 1-methyl-4-phenyl-1,2,3,6-tetrahydropyridine (MPTP). Gait and hanging tests were used to assess motor behavioral function. Immunofluorescence assay was used to determine TH-positive neurons in substantia nigra (SN). Apoptosis, dopamine and neurotrophic factors as well as expression of PI3K/Akt pathway were detected by TUNEL staining, ELISA and western blotting, respectively. First, it was observed that WYP intervention improved abnormal motor function in MPTP-induced PD model, alleviated the loss of TH+ neurons in SN, and increased dopamine content in brain, revealing a potential protective effect. Second, network pharmacology was used to analyze the possible targets and pathways of WYP action in the treatment of PD. A total of 126 active components related to PD were screened in WYP, and the related core targets included ALB, GAPDH, Akt1, TP53, IL6 and TNF. Particularly, the effect of WYP on PD may be medicate through PI3K/Akt signaling pathway and apoptotic regulation. The WYP treated PD mice had higher expression of p-PI3K, p-Akt and Bcl-2 but lower expression of Bax and cleaved caspase-3 than the non-WYP treated PD mice. Secretion of brain-derived neurotrophic factor (BDNF) and cerebral dopamine neurotrophic factor (CDNF) were also increased in the treated mice. WYP may inhibit apoptosis and increase the secretion of neurotrophic factor via activating PI3K/ Akt signaling pathway, thus protecting the loss of dopamine neurons in MPTP-induced PD mice.
Highlights
-
Network pharmacology approach combined with experimental verification to clarify the mechanism.
-
Wuzi Yanzong Pill ameliorated MPTP-induced PD mice by activating PI3K/Akt signaling pathway.
-
Wuzi Yanzong Pill inhibited apoptosis of dopaminergic neurons in MPTP-induced PD mice.











Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
Data are available from the corresponding author upon request.
References
Afentou N, Jarl J, Gerdtham UG et al (2019) Economic evaluation of interventions in Parkinson’s Disease: A systematic literature review. Mov Disord Clin Pract 6(04):282–290. https://doi.org/10.1002/mdc3.12755
Amberger JS, Bocchini CA, Schiettecatte F et al (2015) OMIM.org: Online Mendelian Inheritance in Man (OMIM®), an online catalog of human genes and genetic disorders. Nucleic Acids Res 43(Database issue):D789-98. https://doi.org/10.1093/nar/gku1205
Balakrishnan R, Vijayraja D, Mohankumar T et al (2021) Isolongifolene mitigates rotenone-induced dopamine depletion and motor deficits through anti-oxidative and anti-apoptotic effects in a rat model of Parkinson’s disease. J Chem Neuroanat 112:101890. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jchemneu.2020.101890
Blandini F, Cosentino M, Mangiagalli A et al (2004) Modifications of apoptosis-related protein levels in lymphocytes of patients with Parkinson’s disease. The effect of dopaminergic treatment[J]. J Neural Transm 111(8):1017–1030. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00702-004-0123-1
Chen H, Zhang Z, He J et al (2017) Traditional Chinese Medicine symptom pattern analysis for Parkinson’s disease. J Tradit Chin Med 37(5):688–694
Connolly BS, Lang AE (2014) Pharmacological treatment of Parkinson disease: a review. JAMA 311(16):1670–1683. https://doi.org/10.1001/jama.2014.3654
Cousins KR (2011) Computer review of ChemDraw Ultra 12.0. J Am Chem Soc 133(21):8388. https://doi.org/10.1021/ja204075s
da Huang W, Sherman BT, Lempicki RA (2009) Systematic and integrative analysis of large gene lists using DAVID bioinformatics resources. Nat Protoc 4(1):44–57. https://doi.org/10.1038/nprot.2008.211
Dockx K, Bekkers EM, Van den Bergh V et al (2016) Virtual reality for rehabilitation in Parkinson’s disease. Cochrane Database Syst Rev 12(12):CD010760. https://doi.org/10.1002/14651858
Duan Y, Zhu CC, Yuan WC et al (2015) Advances in research on pharmacological effects and clinical application of Wuzi Yanzong Pill [J]. Liaoning J Tradit Chin Med 42(09):1814–1816. https://doi.org/10.13192/j.issn.1000-1719.2015.09.085 (in Chinese)
Dwivedi PSR, Patil VS, Khanal P et al (2022) System biology-based investigation of Silymarin to trace hepatoprotective effect. Comput Biol Med 142:105223. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.compbiomed.2022.105223
Faust K, Vajkoczy P, Xi B et al (2021) The effects of deep brain stimulation of the subthalamic nucleus on vascular endothelial growth factor, brain-derived neurotrophic factor, and glial cell line-derived neurotrophic factor in a rat model of Parkinson’s disease. Stereotact Funct Neurosurg 99(3):256–266. https://doi.org/10.1159/000511121
Feng YS, Yang SD, Tan ZX et al (2020) The benefits and mechanisms of exercise training for Parkinson’s disease. Life Sci 245:117345. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.lfs.2020.117345
Filomeni G, Graziani I, De Zio D et al (2012) Neuroprotection of kaempferol by autophagy in models of rotenone-mediated acute toxicity: possible implications for Parkinson’s disease. Neurobiol Aging 33(4):767–785. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neurobiolaging.2010.05.021
Ge Q, Chen L, Tang M et al (2018) Analysis of mulberry leaf components in the treatment of diabetes using network pharmacology. Eur J Pharmacol 833:50–62. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ejphar.2018.05.021
Guo C, Hao LJ, Yang ZH et al (2016) Deferoxamine-mediated up-regulation of HIF-1α prevents dopaminergic neuronal death via the activation of MAPK family proteins in MPTP-treated mice. Exp Neurol 280:13–23. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.expneurol.2016.03.016
Hopkins AL (2008) Network pharmacology: the next paradigm in drug discovery. Nat Chem Biol 4(11):682–690. https://doi.org/10.1038/nchembio.118
Hu M, Li F, Wang W (2018) Vitexin protects dopaminergic neurons in MPTP-induced Parkinson’s disease through PI3K/Akt signaling pathway. Drug Des Devel Ther 12:565–573. https://doi.org/10.2147/DDDT.S156920
Jiang D, Peng Y (2021) The protective effect of decoction of Rehmanniae via PI3K/Akt/mTOR pathway in MPP+-induced Parkinson’s disease model cells. J Recept Signal Transduct Res 41(1):74–84. https://doi.org/10.1080/10799893.2020.1787445
Kandil EA, Sayed RH, Ahmed LA et al (2019) Hypoxia-inducible factor 1 alpha and nuclear-related receptor 1 as targets for neuroprotection by albendazole in a rat rotenone model of Parkinson’s disease. Clin Exp Pharmacol Physiol 46(12):1141–1150. https://doi.org/10.1111/1440-1681.13162
Li M, Zhou F, Xu T et al (2018) Acteoside protects against 6-OHDA-induced dopaminergic neuron damage via Nrf2-ARE signaling pathway. Food Chem Toxicol 119:6–13. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.fct.2018.06.018
Li RX, Fan HJ, Chai Z et al (2019a) Effects of Wuzi Yanzong Pills on the apoptotic pathway of neural tube defects cell model [J]. J Tradit Chin Med 60(13):1134–1141. https://doi.org/10.13288/j.11-2166/r.2019.13.012 (in Chinese)
Li GY, Chen YG, Zeng TC et al (2019b) Action mechanism of total flavonoids of diaphragma jugland is fructus in treating type 2 diabetes mellitus based on network pharmacology and cellular experimental validation of AKT/FoxO1 signaling pathway [J]. Drug Eval. Res. 42(01):30–40. https://doi.org/10.7501/j.issn.1674-6376.2019.01.005 (in Chinese)
Li YR, Fan HJ, Chai Z et al (2020a) Neuroprotective and anti-inflammatory effects of Wuzi Yanzong Pills on Parkinson’s disease mice [J]. China J Tradit Chin Med Pharm 35(07):3623–3626 ((in Chinese) CNKI: SUN: BXYY.0.2020-07-096)
Li YR, Fan HJ, Chai Z et al (2020b) Effects of Wuzi Yanzong Pills on behavior and oxidative stress in Parkinson’s disease mice [J]. China J Tradit Chin Med Pharm 35(06):2795–2799 ((in Chinese) CNKI: SUN: BXYY.0.2020-06-027)
Mehrabani M, Nematollahi MH, Tarzi ME et al (2020) Protective effect of hydralazine on a cellular model of Parkinson’s disease: a possible role of hypoxia-inducible factor (HIF)-1α. Biochem Cell Biol 98(3):405–414. https://doi.org/10.1139/bcb-2019-0117
Nataraj J, Manivasagam T, Thenmozhi AJ et al (2017) Neurotrophic effect of Asiatic acid, a triterpene of centella asiatica against chronic 1-methyl 4-phenyl 1, 2, 3, 6-tetrahydropyridine hydrochloride/probenecid mouse model of Parkinson’s disease: The role of MAPK, PI3K-Akt-GSK3β and mTOR signalling pathways. Neurochem Res 42(5):1354–1365. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11064-017-2183-2
Piñero J, Queralt-Rosinach N, Bravo À et al (2015) DisGeNET: a discovery platform for the dynamical exploration of human diseases and their genes. Database (Oxford) 2015:bav028. https://doi.org/10.1093/database/bav028
Ru J, Li P, Wang J, Zhou W et al (2014) TCMSP: a database of systems pharmacology for drug discovery from herbal medicines. J Cheminform 6:13. https://doi.org/10.1186/1758-2946-6-13
Safran M, Dalah I, Alexander J et al (2010) GeneCards Version 3: the human gene integrator. Database (Oxford) 2010:baq020. https://doi.org/10.1093/database/baq020
Salama RM, Abdel-Latif GA, Abbas SS et al (2020) Neuroprotective effect of crocin against rotenone-induced Parkinson’s disease in rats: Interplay between PI3K/Akt/mTOR signaling pathway and enhanced expression of miRNA-7 and miRNA-221. Neuropharmacology 164:107900. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neuropharm.2019.107900
Schober A (2004) Classic toxin-induced animal models of Parkinson’s disease: 6-OHDA and MPTP. Cell Tissue Res 318(1):215–224. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00441-004-0938-y
Shannon P, Markiel A, Ozier O et al (2003) Cytoscape: a software environment for integrated models of biomolecular interaction networks. Genome Res 13(11):2498–2504. https://doi.org/10.1101/gr.1239303
Szklarczyk D, Franceschini A, Wyder S et al (2015) STRING v10: protein-protein interaction networks, integrated over the tree of life. Nucleic Acids Res 43(Database issue):D447-52. https://doi.org/10.1093/nar/gku1003
The UniProt Consortium (2017) UniProt: the universal protein knowledgebase. Nucleic Acids Res 45(D1):D158–D169. https://doi.org/10.1093/nar/gkw1099
Tome D, Fonseca CP, Campos FL et al (2017) Role of Neurotrophic Factors in Parkinson’s Disease. Curr Pharm Des 23(5):809–838. https://doi.org/10.2174/1381612822666161208120422
Wang J, Zhao KH, Tang C et al (2017) Network pharmacology of tibetan medicine duoxuekang capsule in treatment of high-altitude polycythemia [J]. J Chin Med Mater 040(007):1687–1694. https://doi.org/10.13863/j.issn1001-4454.2017.07.041 (in Chinese)
Wang Y, Zhang S, Li F et al (2020) Therapeutic target database 2020: enriched resource for facilitating research and early development of targeted therapeutics. Nucleic Acids Res 48(D1):D1031–D1041. https://doi.org/10.1093/nar/gkz981
Wu D, Gao Y, Xiang H et al (2018) Exploration into mechanism of antidepressant of Bupleuri radix based on network pharmacology [J]. Acta Pharm Sin 53(02):210–219. https://doi.org/10.16438/j.0513-4870.2017-0914 (in Chinese)
Xue R, Fang Z, Zhang M et al (2013) TCMID: Traditional Chinese Medicine integrative database for herb molecular mechanism analysis. Nucleic Acids Res 41(Database issue):D1089-95. https://doi.org/10.1093/nar/gks1100
Yan T, Sun Y, Gong G et al (2019) The neuroprotective effect of schisandrol A on 6-OHDA-induced PD mice may be related to PI3K/AKT and IKK/IκBα/NF-κB pathway. Exp Gerontol 128:110743. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.exger.2019.110743
Yin H, Jiang Y, Zhang Y et al (2019) The inhibition of BDNF/TrkB/PI3K/Akt signal mediated by AG1601 promotes apoptosis in malignant glioma. J Cell Biochem 120(11):18771–18781. https://doi.org/10.1002/jcb.29190
Zeng BY (2017) Effect and mechanism of Chinese herbal medicine on Parkinson’s disease. Int Rev Neurobiol 135:57–76. https://doi.org/10.1016/bs.irn.2017.02.004
Zhang HH, Huang JP, Li W et al (2016) Clinical study on Wuzi Yanzong Tang for mild cognitive impairment in Parkinson disease of kidney deficiency and marrow depletion type [J]. Zhejiang J Integr Traditional Chin West Med 26(11):998–1001. https://doi.org/10.3969/j.issn.1005-4561.2016.11.008
Zhang RN, Chai Z, Fan HJ et al (2018) Preventive and therapeutic effect and its mechanism of Wuzi Yanzong Pills on EAE mouse [J]. China J Tradit Chin Med Pharm. 33(04):1316–1319 ((in Chinese) CNKI: SUN: BXYY.0.2018-04-032)
Zhang HR, Wang Y, Li MJ et al (2019) A preliminary network pharmacological analysis of Xiaobanxia decoction in treating vomiting [J]. J Precis Medi 34(05):427–432. https://doi.org/10.13362/j.jpmed.201905012 (in Chinese)
Zhong Y, Zhu Y, He T et al (2019) Brain-derived neurotrophic factor inhibits hyperglycemia-induced apoptosis and downregulation of synaptic plasticity-related proteins in hippocampal neurons via the PI3K/Akt pathway. Int J Mol Med 43(1):294–304. https://doi.org/10.3892/ijmm.2018.3933
Zhu B, Zhang W, Lu Y et al (2018) Network pharmacology-based identification of protective mechanism of panax notoginseng saponins on aspirin induced gastrointestinal injury. Biomed Pharmacother 105:159–166. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biopha.2018.04.054
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (No.81703978, 81102552), the Central Government Guided Local Funding Projects for Science and Technology Development(No.YDZX20201400001483), Outstanding Youth Talents Program of Shanxi Province(No.〔2019〕35), the Natural Science Foundation of Shanxi Province (No. 201901D111334), the Returned Chinese Scholars Technology Activities Preferred Project, Shanxi Province of China(No. 20200026), the Research Project supported by Shanxi Scholarship Council of China(No.2021-142), Shanxi university Science and technology innovation Project(No.2019L0724), the Key science and technology R&D project of Jinzhong (No.Y213004) , and the Young Scientist Cultivation Program Project, Shanxi University of Chinese Medicine (No.2021PY-QN-03).
Funding
This work was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (No.81703978, 81102552), the Central Government Guided Local Funding Projects for Science and Technology Development(No.YDZX20201400001483), Outstanding Youth Talents Program of Shanxi Province(No.〔2019〕35), the Natural Science Foundation of Shanxi Province (No. 201901D111334), the Returned Chinese Scholars Technology Activities Preferred Project, Shanxi Province of China(No. 20200026), the Research Project supported by Shanxi Scholarship Council of China(No.2021–142), Shanxi university Science and technology innovation Project(No.2019L0724), the Key science and technology R&D project of Jinzhong (No.Y213004), and the Young Scientist Cultivation Program Project, Shanxi University of Chinese Medicine (No.2021PY-QN-03).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Wei Hang, Hui-jie Fan, Yan-rong Li and Qi Xiao carried out the studies, participated in collecting data, and drafted the manuscript. Zhi Chai, Cun-gen Ma, Bao-guo Xiao and Xiao-ming Jin performed the statistical analysis and participated in its design. Lu Jia, Yao Gao, Jie-zhong Yu and Li-juan Song participated in acquisition, analysis, or interpretation of data. All authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Hang, W., Fan, Hj., Li, Yr. et al. Wuzi Yanzong pill attenuates MPTP-induced Parkinson’s Disease via PI3K/Akt signaling pathway. Metab Brain Dis 37, 1435–1450 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11011-022-00993-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11011-022-00993-8