Abstract
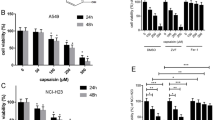
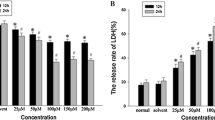
Glioblastoma is one of the deadliest malignant gliomas. Capsaicin is a homovanillic acid derivative that can show anti-cancer effects by regulating various signaling pathways. The aim of this study is to investigate the effects of capsaicin on cell proliferation via ferroptosis in human U87-MG and U251 glioblastoma cells. Firstly, effects of capsaicin treatment on cell viability were determined by MTT analysis. Next, cellular-proliferation and cytotoxicity assays were determined by analyzing bromodeoxyuridine (BrdU) and lactate dehydrogenase (LDH) activity, respectively. Following, acyl-CoA synthetase long chain family member 4 (ACSL4), glutathione peroxidase 4 (GPx4), 5-hydroxyeicosatetraenoic acid (5-HETE), total oxidant status (TOS), malondialdehyde (MDA), total antioxidant status (TAS) and reduced glutathione (GSH) levels were determined by ELISA. Additionally, ACSL4 and GPx4 mRNA and protein levels were analyzed. Capsaicin showed a concentration-dependent anti-proliferative effects in U87-MG and U251 cells. Cell viability was decreased in the both cell lines treated with capsaicin concentrations above 50 μM, while LDH activity increased. Treatment of 121.6, 188.5, and 237.2 μM capsaicin concentrations for 24 h indicated an increase in ACSL4, 5-HETE, TOS and MDA levels in U87-MG and U251 cells (p < 0.05). On the other hand, we found that capsaicin administration caused a decrease in BrdU, GPx4, TAS and GSH levels in U87-MG and U251 cells (p < 0.05). Besides, ACSL4 mRNA and protein levels were increased in the glioblastoma cells treated with capsaicin, whereas GPx4 mRNA and protein levels were decreased. Finally, capsaicin might be used as a potential anticancer agent with ferroptosis-induced anti-proliferative effects in the treatment of human glioblastoma.






Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
All data generated during this study are available from the corresponding author on reasonable request.
References
Barceloux DG (2009) Pepper and capsaicin (Capsicum and Piper species). Dis Mon 55(6):380–390. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.disamonth.2009.03.008
Bley K, Boorman G, Mohammad B, McKenzie D, Babbar S (2012) A comprehensive review of the carcinogenic and anticarcinogenic potential of capsaicin. Toxicol Pathol 40(6):847–873. https://doi.org/10.1177/0192623312444471
Brieger K, Schiavone S, Miller FJ Jr, Krause KH (2012) Reactive oxygen species: from health to disease. Swiss Med Wkly 142:w13659. https://doi.org/10.4414/smw.2012.13659
Bush NA, Chang SM, Berger MS (2017) Current and future strategies for treatment of glioma. Neurosurg Rev 40(1):1–14. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10143-016-0709-8
Cao JY, Dixon SJ (2016) Mechanisms of ferroptosis. Cell Mol Life Sci 73(11–12):2195–2209. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00018-016-2194-1
Chen X, Yu C, Kang R, Kroemer G, Tang D (2021 Apr) (2021). Cellular degradation systems in ferroptosis. Cell Death Differ 28(4):1135–1148. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41418-020-00728-1
Cheng J, Fan YQ, Liu BH, Zhou H, Wang JM, Chen QX (2020) ACSL4 suppresses glioma cells proliferation via activating ferroptosis. Oncol Rep 43(1):147–158. https://doi.org/10.3892/or.2019.7419
Clark R, Lee SH (2016) Anticancer properties of capsaicin against human cancer. Anticancer Res 36(3):837–843
Dixon SJ, Lemberg KM, Lamprecht MR, Skouta R, Zaitsev EM, Gleason CE, Patel DN, Bauer AJ, Cantley AM, Yang WS, Morrison B 3rd, Stockwell BR (2012) Ferroptosis: an iron-dependent form of nonapoptotic cell death. Cell 149(5):1060–1072. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cell.2012.03.042
Doll S, Conrad M (2017) Iron and ferroptosis: a still ill-defined liaison. IUBMB Life 69(6):423–434. https://doi.org/10.1002/iub.1616
Doll S, Proneth B, Tyurina YY et al (2017 Jan) (2017) ACSL4 dictates ferroptosis sensitivity by shaping cellular lipid composition. Nat Chem Biol 13(1):91–98. https://doi.org/10.1038/nchembio.2239
Ellis JM, Frahm JL, Li LO, Coleman RA (2010) Acyl-coenzyme a synthetases in metabolic control. Curr Opin Lipidol 21(3):212–217. https://doi.org/10.1097/mol.0b013e32833884bb
Friedmann Angeli JP, Schneider M, Proneth B et al (2014) Inactivation of the ferroptosis regulator Gpx4 triggers acute renal failure in mice. Nat Cell Biol 16(12):1180–1191. https://doi.org/10.1038/ncb3064
Guo M, Roman RJ, Falck JR, Edwards PA, Scicli AG (2005) Human U251 glioma cell proliferation is suppressed by HET0016 [N-hydroxy-N'-(4-butyl-2-methylphenyl)formamidine], a selective inhibitor of CYP4A. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 315(2):526–533. https://doi.org/10.1124/jpet.105.088567
Hacioglu C (2022) Capsaicin inhibits cell proliferation by enhancing oxidative stress and apoptosis through SIRT1/NOX4 signaling pathways in HepG2 and HL-7702 cells. J Biochem Mol Toxicol 36(3):e22974. https://doi.org/10.1002/jbt.22974
Hacioglu C, Kacar S, Kar F, Kanbak G, Sahinturk V (2020) Concentration-dependent effects of zinc sulfate on DU-145 human prostate Cancer cell line: oxidative, apoptotic, inflammatory, and morphological analyzes. Biol Trace Elem Res 195(2):436–444. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12011-019-01879-0
Imai H, Matsuoka M, Kumagai T, Sakamoto T, Koumura T (2017) Lipid peroxidation-dependent cell death regulated by GPx4 and Ferroptosis. Curr Top Microbiol Immunol 403:143–170. https://doi.org/10.1007/82_2016_508
Ingold I, Berndt C, Schmitt S et al (2018) Selenium utilization by GPX4 is required to prevent Hydroperoxide-induced Ferroptosis. Cell 172(3):409–422.e21. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cell.2017.11.048
Kagan VE, Mao G, Qu F et al (2017) Oxidized arachidonic and adrenic PEs navigate cells to ferroptosis. Nat Chem Biol 13(1):81–90. https://doi.org/10.1038/nchembio.2238
Kajarabille N, Latunde-Dada GO (2019) Programmed cell-death by Ferroptosis: antioxidants as Mitigators. Int J Mol Sci 20(19):4968. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms20194968
Latunde-Dada GO (2017) Ferroptosis: role of lipid peroxidation, iron and ferritinophagy. Biochim Biophys Acta Gen Subj 1861(8):1893–1900. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bbagen.2017.05.019
Lei P, Bai T, Sun Y (2019) Mechanisms of Ferroptosis and relations with regulated cell death: a review. Front Physiol 10:139. https://doi.org/10.3389/fphys.2019.00139
Li D, Li Y (2020) The interaction between ferroptosis and lipid metabolism in cancer. Signal Transduct Target Ther 5(1):108. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41392-020-00216-5
Li H, Lei B, Xiang W, Wang H, Feng W, Liu Y, Qi S (2017) Differences in protein expression between the U251 and U87 cell lines. Turk Neurosurg 27(6):894–903. https://doi.org/10.5137/1019-5149.JTN.17746-16.1
Li C, Deng X, Zhang W, Xie X, Conrad M, Liu Y, Angeli JPF, Lai L (2019) Novel allosteric activators for Ferroptosis regulator glutathione peroxidase 4. J Med Chem 62(1):266–275. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.jmedchem.8b00315
Lowry OH, Rosebrough NJ, Farr AL, Randall RJ (1951) Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem 193:265–275
Lu HF, Chen YL, Yang JS, Yang YY, Liu JY, Hsu SC, Lai KC, Chung JG (2010) Antitumor activity of capsaicin on human colon cancer cells in vitro and Colo 205 tumor xenografts in vivo. J Agric Food Chem 58(24):12999–13005. https://doi.org/10.1021/jf103335w
Lu B, Chen XB, Ying MD, He QJ, Cao J, Yang B (2018) The role of Ferroptosis in Cancer development and treatment response. Front Pharmacol 8:992. https://doi.org/10.3389/fphar.2017.00992
Moreno JJ (2009) New aspects of the role of hydroxyeicosatetraenoic acids in cell growth and cancer development. Biochem Pharmacol 77(1):1–10. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bcp.2008.07.033
Nabors LB, Ammirati M, Bierman PJ et al (2013) Central nervous system cancers. J Natl Compr Cancer Netw 11(9):1114–1151. https://doi.org/10.6004/jnccn.2013.0132
Ostrom QT, Bauchet L, Davis FG, Deltour I, Fisher JL, Langer CE, Pekmezci M, Schwartzbaum JA, Turner MC, Walsh KM, Wrensch MR, Barnholtz-Sloan JS (2014a) The epidemiology of glioma in adults: a "state of the science" review. Neuro-Oncology 16(7):896–913. https://doi.org/10.1093/neuonc/nou087
Ostrom QT, Gittleman H, Liao P, Rouse C, Chen Y, Dowling J, Wolinsky Y, Kruchko C, Barnholtz-Sloan J (2014b) CBTRUS statistical report: primary brain and central nervous system tumors diagnosed in the United States in 2007-2011. Neuro-Oncology 16(4):iv1–i63. https://doi.org/10.1093/neuonc/nou223
Radif Y, Ndiaye H, Kalantzi V, Jacobs R, Hall A, Minogue S, Waugh MG (2018) The endogenous subcellular localisations of the long chain fatty acid-activating enzymes ACSL3 and ACSL4 in sarcoma and breast cancer cells. Mol Cell Biochem 448(1–2):275–286. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11010-018-3332-x
Shah R, Shchepinov MS, Pratt DA (2018) Resolving the role of lipoxygenases in the initiation and execution of ferroptosis. ACS Cent Sci 4(3):387–396. https://doi.org/10.1021/acscentsci.7b00589
Song Y, Luo Q, Long H et al (2014) Alpha-enolase as a potential cancer prognostic marker promotes cell growth, migration, and invasion in glioma. Mol Cancer 13:65. https://doi.org/10.1186/1476-4598-13-65
Stockwell BR, Jiang X (2020) The chemistry and biology of Ferroptosis. Cell Chem Biol 27(4):365–375. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chembiol.2020.03.013
Stockwell BR, Friedmann Angeli JP, Bayir H et al (2017) Ferroptosis: a regulated cell death Nexus linking metabolism, redox biology, and disease. Cell 171(2):273–285. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cell.2017.09.021
Tan S, Hou X, Mei L (2020) Dihydrotanshinone I inhibits human glioma cell proliferation via the activation of ferroptosis. Oncol Lett 20(4):122. https://doi.org/10.3892/ol.2020.11980
Yang WS, Stockwell BR (2016) Ferroptosis: death by lipid peroxidation. Trends Cell Biol 26(3):165–176. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tcb.2015.10.014
Yang J, Li TZ, Xu GH, Luo BB, Chen YX, Zhang T (2013) Low-concentration capsaicin promotes colorectal cancer metastasis by triggering ROS production and modulating Akt/mTOR and STAT-3 pathways. Neoplasma 60(4):364–372. https://doi.org/10.4149/neo_2013_048
Yang WS, SriRamaratnam R, Welsch ME et al (2014) Regulation of ferroptotic cancer cell death by GPX4. Cell 156(1–2):317–331. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cell.2013.12.010
Yang WS, Kim KJ, Gaschler MM, Patel M, Shchepinov MS, Stockwell BR (2016) Peroxidation of polyunsaturated fatty acids by lipoxygenases drives ferroptosis. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 113(34):E4966–E4975. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.1603244113
Yuan H, Li X, Zhang X, Kang R, Tang D (2016) Identification of ACSL4 as a biomarker and contributor of ferroptosis. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 478(3):1338–1343. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bbrc.2016.08.124
Zhang R, Humphreys I, Sahu RP, Shi Y, Srivastava SK (2008) In vitro and in vivo induction of apoptosis by capsaicin in pancreatic cancer cells is mediated through ROS generation and mitochondrial death pathway. Apoptosis 13(12):1465–1478. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10495-008-0278-6
Zhang S, Wang D, Huang J, Hu Y, Xu Y (2020) Application of capsaicin as a potential new therapeutic drug in human cancers. J Clin Pharm Ther 45(1):16–28. https://doi.org/10.1111/jcpt.13039
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
The design of the study, the performing of the experiments, the evaluation of the results and the writing of the article were carried out by CH and FK. The authors critically reviewed the article and approved the final version.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethics approval
Since experimental procedures were performed on cell lines in this study, ethics committee permission was not needed.
Consent for publication
Not applicable.
Competing interests
The author declares that there is no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Hacioglu, C., Kar, F. Capsaicin induces redox imbalance and ferroptosis through ACSL4/GPx4 signaling pathways in U87-MG and U251 glioblastoma cells. Metab Brain Dis 38, 393–408 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11011-022-00983-w
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11011-022-00983-w