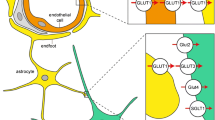
Abstract
Tissue exposure to high levels of tyrosine, which is characteristic of an inborn error of metabolism named Tyrosinemia, is related to severe symptoms, including neurological alterations. The clinical manifestations and pathogenesis of tyrosine neurotoxicity can be recapitulated in experimental models in vivo and in vitro. A widely used experimental model to study brain tyrosine damage is the chronic and acute administration of this amino acid in infant rats. Other research groups and we have extensively studied the pathogenic events in the brain structures of rats exposed to high tyrosine levels. Rats administered acutely and chronically with tyrosine presented decreased and inhibition of the essential metabolism enzymes, e.g., Krebs cycle enzymes and mitochondrial respiratory complexes in the brain structures. These alterations induced by tyrosine toxicity were associated with brain oxidative stress, astrocytes, and, ultimately, cognitive impairments. Notably, in vivo data were corroborated by in vitro studies using cerebral regions homogenates incubated with tyrosine excess. Considering metabolism’s importance to brain functioning, we hypothesized that mitochondrial and metabolic dysfunctions are closely related to neurological alterations induced by tyrosine neurotoxicity. Herein, we reviewed the main mechanisms associated with tyrosine neurotoxicity in experimental models, emphasizing the role of mitochondrial dysfunction.


Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
Data sharing not applicable to this article as no datasets were generated or analyzed during the current study. This article is a review of information content in previous works.
References
Alvarez F, Atkinson S, Bouchard M et al (2017) The Quebec NTBC study. Adv Exp Med Biol 959:187–195
Antonini R, Scaini G, Michels M et al (2020) Effects of omega-3 fatty acids supplementation on inflammatory parameters after chronic administration of L-tyrosine. Metab Brain Dis. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11011-019-00525-x
Ashrafi G, Ryan TA (2017) Glucose metabolism in nerve terminals. Curr Opin Neurobiol 45:156–161
Banay-Schwartz M, Palkovits M, Lajtha A (1993) Heterogeneous distribution of functionally important amino acids in brain areas of adult and aging humans. Neurochem Res 18(4):417–23
Baune BT, Konrad C, Grotegerd D et al (2012) Interleukin-6 gene (IL-6): A possible role in brain morphology in the healthy adult brain. J Neuroinflammation. https://doi.org/10.1186/1742-2094-9-125
Blokland A (1995) Acetylcholine: a neurotransmitter for learning and memory? Brain Res Rev 21(3):285–300
Boekema EJ, Braun HP (2007) Supramolecular structure of the mitochondrial oxidative phosphorylation system. J Biol Chem 282(1):1–4
Bongiovanni R, Yamamoto BK, Simpson C, Jaskiw GE (2003) Pharmacokinetics of systemically administered tyrosine: A comparison of serum, brain tissue and in vivo microdialysate levels in the rat. J Neurochem. https://doi.org/10.1046/j.1471-4159.2003.02007.x
Canadian Agency for Drugs and Technologies in Health (2018) Clinical review report: nitisinone (nitisinone tablets): (Cycle Pharmaceuticals Ltd.): indication: for the treatment of patients with hereditary tyrosinemia type 1 in combination with dietary restriction of tyrosine and phenylalanine. Appendix 4, Validity of Outcome Measures. Available from: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK539973
Carvalho-Silva M, Gomes LM, Scaini G et al (2017) Omega-3 fatty acid supplementation decreases DNA damage in brain of rats subjected to a chemically induced chronic model of Tyrosinemia type II. Metab Brain Dis. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11011-017-9994-3
Carvalho-Silva M, Gomes LM, Gomes ML et al (2019) Omega-3 fatty acid supplementation can prevent changes in mitochondrial energy metabolism and oxidative stress caused by chronic administration of L-tyrosine in the brain of rats. Metab Brain Dis. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11011-019-00411-6
Carvalho-Silva M, Gomes LM, de Prá SDT et al (2020) Evidence of hippocampal astrogliosis and antioxidant imbalance after L-tyrosine chronic administration in rats. Metab Brain Dis. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11011-019-00511-3
Chepelev NL, Bennitz JD, Wright JS et al (2009) Oxidative modification of citrate synthase by peroxyl radicals and protection with novel antioxidants. J Enzyme Inhib Med Chem. https://doi.org/10.3109/14756360902852586
Chinsky JM, Singh R, Ficicioglu C et al (2017) Diagnosis and treatment of tyrosinemia type I: a US and Canadian consensus group review and recommendations. Genet Med 19(12). https://doi.org/10.1038/gim.2017.101
Corrêa C, Amboni G, Assis LC et al (2007) Effects of lithium and valproate on hippocampus citrate synthase activity in an animal model of mania. Prog Neuro-Psychopharmacology Biol Psychiatry. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.pnpbp.2007.02.005
De Andrade RB, Gemelli T, Rojas DB et al (2011) Tyrosine inhibits creatine kinase activity in cerebral cortex of young rats. Metab Brain Dis. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11011-011-9255-9
De Andrade RB, Gemelli T, Rojas DB et al (2012) Tyrosine impairs enzymes of energy metabolism in cerebral cortex of rats. Mol Cell Biochem. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11010-012-1225-y
de Andrade RB, Gemelli T, Rojas DB et al (2015) Creatine and pyruvate prevent the alterations caused by tyrosine on parameters of oxidative stress and enzyme activities of phosphoryltransfer network in cerebral cortex of wistar rats. Mol Neurobiol. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12035-014-8791-9
De Braekeleer M, Larochelle J (1990) Genetic epidemiology of hereditary tyrosinemia in Quebec and Saguenay-Lac-St-Jean. Am J Hum Genet 47(2):302–7
De Prá SDT, Ferreira GK, Carvalho-Silva M et al (2014) L-Tyrosine induces DNA damage in brain and blood of rats. Neurochem Res. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11064-013-1207-9
Dzeja P, Terzic A (2009) Adenylate kinase and AMP signaling networks: metabolic monitoring, signal communication and body energy sensing. Int J Mol Sci 10(4):1729–72
Erta M, Quintana A, Hidalgo J (2012) Interleukin-6, a major cytokine in the central nervous system. Int J Biol Sci 8(9):1254–66
Fernie AR, Carrari F, Sweetlove LJ (2004) Respiratory metabolism: Glycolysis, the TCA cycle and mitochondrial electron transport. Curr Opin Plant Biol 7(3):254–61
Fernstrom JD, Fernstrom MH (2007) Tyrosine, phenylalanine, and catecholamine synthesis and function in the brain. J Nutr 137(6 Suppl 1):1539S–1547S
Ferreira GK, Carvalho-Silva M, Gonçalves CL et al (2012) L-Tyrosine administration increases acetylcholinesterase activity in rats. Neurochem Int. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neuint.2012.09.017
Ferreira GK, Jeremias IC, Scaini G et al (2013a) Effect of acute and chronic administration of l-tyrosine on nerve growth factor levels in rat brain. Neurochem Res. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11064-013-1078-0
Ferreira GK, Scaini G, Carvalho-Silva M et al (2013b) Effect of l-tyrosine in vitro and in vivo on energy metabolism parameters in brain and liver of young rats. Neurotox Res. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12640-012-9345-4
Ferreira GK, Carvalho-Silva M, Gomes LM et al (2014a) The characterization of neuroenergetic effects of chronic L-tyrosine administration in young rats: evidence for striatal susceptibility. Metab Brain Dis. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11011-014-9615-3
Ferreira GK, Scaini G, Jeremias IC et al (2014b) An evaluation of the effects of acute and chronic L-tyrosine administration on BDNF levels and bdnf mRNA expression in the rat brain. Mol Neurobiol. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12035-013-8552-1
Fodale V, Quattrone D, Trecroci C et al (2006) Alzheimer’s disease and anaesthesia: Implications for the central cholinergic system. Br J Anaesth 97(4):445–52
Garcia-Cazorla A, Quadros EV, Nascimento A et al (2008) Mitochondrial diseases associated with cerebral folate deficiency. Neurology. https://doi.org/10.1212/01.wnl.0000309223.98616.e4
Gomes LM, Scaini G, Carvalho-Silva M et al (2018) Antioxidants Reverse the Changes in the Cholinergic System Caused by L-Tyrosine Administration in Rats. Neurotox Res. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12640-018-9866-6
Gong Y, Chang L, Viola KL et al (2003) Alzheimer's disease-affected brain: presence of oligomeric A beta ligands (ADDLs) suggests a molecular basis for reversible memory loss. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 100(18):10417–22. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.1834302100
Grompe M (2016) Disorders of tyrosine metabolism. In: Post TW (ed). UpToDate [Internet]. Waltham (MA)
Gupta RC (2004) Brain regional heterogeneity and toxicological mechanisms of organophosphates and carbamates. Toxicol Mech Methods 14(3):103–43
Halliwell B (2011) Free radicals and antioxidants -. Quo vadis? Trends Pharmacol Sci 32(3):125–30
Held PK (2006) Disorders of tyrosine catabolism. Mol Genet Metab. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ymgme.2006.04.002
Horn D, Barrientos A (2008) Mitochondrial copper metabolism and delivery to cytochrome C oxidase. IUBMB Life 60(7):421–9
In ’T, Zandt HJA, Renema WKJ, Streijger F et al (2004) Cerebral creatine kinase deficiency influences metabolite levels and morphology in the mouse brain: A quantitative in vivo 1H and 31P magnetic resonance study. J Neurochem. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1471-4159.2004.02599.x
Jost CR, Van der Zee CEEM, In ’t Zandt HJA, et al (2002) Creatine kinase B-driven energy transfer in the brain is important for habituation and spatial learning behaviour, mossy fibre field size and determination of seizure susceptibility. Eur J Neurosci. https://doi.org/10.1046/j.1460-9568.2002.02001.x
Kany S, Vollrath JT, Relja B (2019) Cytokines in inflammatory disease. Int J Mol Sci 20(23):6008. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms20236008
Levi-Montalcini R (1987) The nerve growth factor 35 years later. Science 237(4819):1154–1162. https://doi.org/10.1126/science.3306916
Lurie DI (2018) An integrative approach to neuroinflammation in psychiatric disorders and neuropathic pain. J Exp Neurosci. https://doi.org/10.1177/1179069518793639
Macêdo LGRP, Carvalho-Silva M, Ferreira GK et al (2013) Effect of acute administration of l-tyrosine on oxidative stress parameters in brain of young rats. Neurochem Res. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11064-013-1180-3
Mitchell G, Larochelle J, Lambert M et al (1990) Neurologic Crises in Hereditary Tyrosinemia. N Engl J Med. https://doi.org/10.1056/NEJM199002153220704
Morre MC, Hefti F, Wurtman RJ (1980) Regional tyrosine levels in rat brain after tyrosine administration. J Neural Transm. https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01249188
Nakafuku M, Satoh T, Kaziro Y (1992) Differentiation factors, including nerve growth factor, fibroblast growth factor, and interleukin-6, induce an accumulation of an active Ras·GTP complex in rat pheochromocytoma PC12 cells. J Biol Chem 267(27):19448–19454
Picciotto MR, Higley MJ, Mineur YS (2012) Acetylcholine as a neuromodulator. Cholinergic signaling shapes nervous system function and behavior. Neuron 76(1):116–29
Poo M (2001) Neurotrophins as synaptic modulators. Nat Rev Neurosci. https://doi.org/10.1038/35049004
Ramos AC, Ferreira GK, Carvalho-Silva M et al (2013) Acute administration of l-tyrosine alters energetic metabolism of hippocampus and striatum of infant rats. Int J Dev Neurosci. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijdevneu.2013.03.005
Rutter J, Winge DR, Schiffman JD (2010) Succinate dehydrogenase - Assembly, regulation and role in human disease. Mitochondrion. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.mito.2010.03.001
Sarter M, Parikh V (2005) Choline transporters, cholinergic transmission and cognition. Nat Rev Neurosci 6(1):48–56
Sawa K, Uematsu T, Korenaga Y et al (2017) Krebs cycle intermediates protective against oxidative stress by modulating the level of reactive oxygen species in neuronal HT22 cells. Antioxidants. https://doi.org/10.3390/antiox6010021
Schurr A (2002) Energy metabolism, stress hormones and neural recovery from cerebral ischemia/hypoxia. Neurochem Int 41(1):1–8
Scott CR (2006) The genetic tyrosinemias. Am J Med Genet - Semin Med Genet. https://doi.org/10.1002/ajmg.c.30092
Sener RN (2005) Brain magnetic resonance imaging in tyrosinemia. Acta Radiol. https://doi.org/10.1080/02841850510021517
Sgaravatti ÂM, Vargas BA, Zandoná BR et al (2008) Tyrosine promotes oxidative stress in cerebral cortex of young rats. Int J Dev Neurosci. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijdevneu.2008.05.007
Sgaravatti ÂM, Magnusson AS, De Oliveira AS et al (2009) Tyrosine administration decreases glutathione and stimulates lipid and protein oxidation in rat cerebral cortex. Metab Brain Dis. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11011-009-9153-6
Soreq H (2001) Acetylcholinesterase — new roles for an old actor. Nat Rev Neurosci. https://doi.org/10.1038/35067589
Streck EL, De Prá SDT, Ferro PR et al (2017) Role of antioxidant treatment on DNA and lipid damage in the brain of rats subjected to a chemically induced chronic model of tyrosinemia type II. Mol Cell Biochem. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11010-017-3070-5
Strle K, Zhou JH, Shen WH et al (2001) Interleukin-10 in the brain. Crit Rev Immunol 21(5):427–49
Teodorak BP, Scaini G, Carvalho-Silva M et al (2017) Antioxidants reverse the changes in energy metabolism of rat brain after chronic administration of L.-tyrosine. Metab Brain Dis. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11011-016-9936-5
Uttara B, Singh A, Zamboni P, Mahajan R (2009) Oxidative stress and neurodegenerative diseases: a review of upstream and downstream antioxidant therapeutic options. Curr Neuropharmacol. https://doi.org/10.2174/157015909787602823
Wallimann T, Wyss M, Brdiczka D et al (1992) Intracellular compartmentation, structure and function of creatine kinase isoenzymes in tissues with high and fluctuating energy demands: The “phosphocreatine circuit” for cellular energy homeostasis. Biochem J 281(Pt 1):21–40
Funding
This research was supported by grants from Universidade do Extremo Sul Catarinense (UNESC), Coordenação de Aperfeiçoamento de Pessoal de Nível Superior (CAPES) and Conselho Nacional de Desenvolvimento Científico e Tecnológico (CNPq).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
All authors were involved in literature review, writing the manuscript, and figure preparation.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
de Oliveira, J., Farias, H.R. & Streck, E.L. Experimental evidence of tyrosine neurotoxicity: focus on mitochondrial dysfunction. Metab Brain Dis 36, 1673–1685 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11011-021-00781-w
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11011-021-00781-w