Abstract
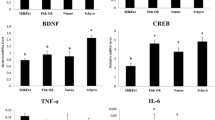
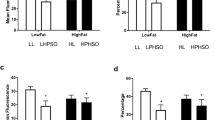
In this study, we elucidated the modulatory potentials of lipid-solubles from ginger and turmeric that may migrate to oils during heating on the brain antioxidant defense and cognitive response in rats. Male Wistar rats were fed with control diet [including native canola oil (N-CNO), and native sunflower oil (N-SFO)], or experimental diets [including heated canola oil (H-CNO), heated sunflower oil (H-SFO), heated canola oil with ginger (H-CNO + GI), heated canola oil with turmeric (H-CNO + TU), heated sunflower oil with ginger (H-SFO + GI), heated sunflower oil with turmeric (H-SFO + TU)] for 90 days. Memory parameters [Morris water maze, elevated plus maze, novel object recognition test, T-maze (spontaneous alteration)], locomotor skills (open field test and rotarod test), antioxidant defense enzymes, reactive oxygen species, NOS2, ICAM-1, and NRF-2 level in the brain were assessed. Compared to their respective controls, heated oil-fed rats, but not those fed oils heated with ginger or turmeric, showed significant (p < 0.05) reduction in the memory, motor coordination skills, antioxidant defense enzymes, and NRF-2 activation in the brain. Compared to their respective controls, the brain NOS-2 and ICAM-1 were significantly (p < 0.05) increased in heated oil-fed rats, but not those fed oils heated with ginger or turmeric. Chronic intake of repeatedly heated oil causes brain dysfunction by inducing oxidative stress through NRF-2 downregulation. Lipid-solubles from ginger and turmeric that may migrate to oil during heating prevent the oxidative stress and cognitive dysfunction triggered by heated oils in rats.










Similar content being viewed by others
References
Adam SK, Sulaiman NA, Top AM, Jaarin K (2007) Heating reduces vitamin E content in palm and soy oils. Malaysian J Biochem Mol Biol 15:76–79
Aebi H (1984) [13] Catalase in vitro. In: methods in enzymology, vol 105. Academic Press, pp 121–126. https://doi.org/10.1016/s0076-6879(84)05016-3
Anh NH, Kim SJ, Long NP, Min JE, Yoon YC, Lee EG, Kim M, Kim TJ, Yang YY, Son EY, Yoon SJ, Diem NC, Kim HM, Kwon SW (2020) Ginger on human health: a comprehensive systematic review of 109 randomized controlled trials. Nutrients 12:157. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu12010157
Aubele T, Kaufman R, Montalmant F, Kritzer M (2008) Effects of gonadectomy and hormone replacement on a spontaneous novel object recognition task in adult male rats. Horm Behav 54:244–252. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.yhbeh.2008.04.001
Barnard ND, Bunner AE, Agarwal U (2014) Saturated and trans fats and dementia: a systematic review. Neurobiol Aging 35:S65–S73
Bautista R, Carreón-Torres E, Luna-Luna M, Komera-Arenas Y, Franco M, Fragoso JM, López-Olmos V, Cruz-Robles D, Vargas-Barrón J, Vargas-Alarcón G, Pérez-Méndez O (2014) Early endothelial nitrosylation and increased abdominal adiposity in Wistar rats after long-term consumption of food fried in canola oil. Nutrition 30:1055–1060. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.nut.2014.01.010
Bromley-Brits K, Deng Y, Song W (2011) Morris water maze test for learning and memory deficits in Alzheimer's disease model mice. J Vis Exp 53:e2920. https://doi.org/10.3791/2920
Cao GY, Li M, Han L, Tayie F, Yao SS, Huang Z, Ai P, Liu YZ, Hu YH, Xu B (2019) Dietary fat intake and cognitive function among older populations: a systematic review and meta-analysis. J Prev Alzheimers Dis 6(3):204–211. https://doi.org/10.14283/jpad.2019.9
Devore EE, Stampfer MJ, Breteler MM, Rosner B, Kang JH, Okereke O, Hu FB, Grodstein F (2009) Dietary fat intake and cognitive decline in women with type 2 diabetes. Diabetes Care 32(4):635–640
Esatbeyoglu T, Ulbrich K, Rehberg C, Rohn S, Rimbach G (2015) Thermal stability, antioxidant, and anti-inflammatory activity of curcumin and its degradation product 4-vinyl guaiacol. Food Funct 6:887–893
Flohe L (1984) [10] Superoxide dismutase assays. In: Methods in enzymology, vol 105. Academic Press, pp 93–104. https://doi.org/10.1016/s0076-6879(84)05013-8
Gómez-Pinilla F (2008) Brain foods: the effects of nutrients on brain function. Nat Rev Neurosci 9:568–578. https://doi.org/10.1038/nrn2421
Green LC, Wagner DA, Glogowski J, Skipper PL, Wishnok JS, Tannenbaum SR (1982) Analysis of nitrate, nitrite, and [15N] nitrate in biological fluids. Anal Biochem 126:131–138. https://doi.org/10.1016/0003-2697(82)90118-x
Greenwood CE, Winocur G (2005) High-fat diets, insulin resistance and declining cognitive function. Neurobiol Aging 26:42–45. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neurobiolaging.2005.08.017
Habig WH, Pabst MJ, Jakoby WB (1974) Glutathione S-transferases the first enzymatic step in mercapturic acid formation. J Biol Chem 249:7130–7139
Itoh J, Nabeshima T, Kameyama T (1990) Utility of an elevated plus-maze for the evaluation of memory in mice: effects of nootropics, scopolamine and electroconvulsive shock. Psychopharmacology 101:27–33. https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02253713
Jafarian S, Ling KH, Hassan Z, Perimal‐Lewis L, Sulaiman MR, Perimal EK (2019) Effect of zerumbone on scopolamine‐induced memory impairment and anxiety‐like behaviours in rats. Alzheimers & Dementia: Trans Res Clin Interv 5:637–643. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.trci.2019.09.009
Jolad SD, Lantz RC, Chen GJ, Bates RB, Timmermann BN (2005) Commercially processed dry ginger (Zingiber officinale): composition and effects on LPS-stimulated PGE2 production. Phytochemistry 66:1614–1635
Jones B, Roberts D (1968) The quantitative measurement of motor inco-ordination in naive mice using an accelerating rotarod. J Pharm Pharmacol 20:302–304. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.2042-7158.1968.tb09743.x
Kahkhaie KR, Mirhosseini A, Aliabadi A, Mohammadi A, Mousavi MJ, Haftcheshmeh SM, Sathyapalan T, Sahebkar A (2019) Curcumin: a modulator of inflammatory signaling pathways in the immune system. Inflammopharmacology 27:885–900. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10787019-00607-3
Kocaadam B, Şanlier N (2017) Curcumin, an active component of turmeric (Curcuma longa), and its effects on health. Crit Rev Food Sci Nutr 57:2889–2895
Kornienko JS et al (2019) High doses of synthetic antioxidants induce premature senescence in cultivated mesenchymal stem cells. Sci Rep 9:1–13. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-018-37972-y
Li L, Wu X-H, Zhao X-J, Xu L, Pan C-L, Zhang Z-Y (2020) Zerumbone ameliorates behavioral impairments and neuropathology in transgenic APP/PS1 mice by suppressing MAPK signaling. J Neuroinflammation 17:1–20. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12974-020-01744-1
Lowry OH, Rosebrough NJ, Farr AL, Randall RJ (1951) Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem 193:265–275
Ma Q (2013) Role of nrf2 in oxidative stress and toxicity. Annu Rev Pharmacol Toxicol 53:401–426. https://doi.org/10.1146/annurev-pharmtox-011112-140320
Mao Q-Q, Xu X-Y, Cao S-Y, Gan R-Y, Corke H, Li H-B (2019) Bioactive compounds and bioactivities of ginger (Zingiber officinale roscoe). Foods 8:185. https://doi.org/10.3390/foods8060185
Mazza E, Fava A, Ferro Y, Rotundo S, Romeo S, Bosco D, Pujia A, Montalcini T (2018) Effect of the replacement of dietary vegetable oils with a low dose of extra virgin olive oil in the Mediterranean diet on cognitive functions in the elderly. J Transl Med 16:10. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12967-018-1386-x
Mesquita CS, Oliveira R, Bento F, Geraldo D, Rodrigues JV, Marcos JC (2014) Simplified 2, 4-dinitrophenylhydrazine spectrophotometric assay for quantification of carbonyls in oxidized proteins. Anal Biochem 458:69–71. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ab.2014.04.034
Miller DM, Aust SD (1989) Studies of ascorbate-dependent, iron-catalyzed lipid peroxidation. Arch Biochem Biophys 271:113–119. https://doi.org/10.1016/0003-9861(89)90261-0
Mishima K, Tanoue A, Tsuda M, Hasebe N, Fukue Y, Egashira N, Takano Y, Kamiya HO, Tsujimoto G, Iwasaki K, Fujiwara M (2004) Characteristics of behavioral abnormalities in α1d-adrenoceptors deficient mice. Behav Brain Res 152:365–373. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bbr.2003.10.038
Mouzon B, Chaytow H, Crynen G, Bachmeier C, Stewart J, Mullan M, Stewart W, Crawford F (2012) Repetitive mild traumatic brain injury in a mouse model produces learning and memory deficits accompanied by histological changes. J Neurotrauma 29:2761–2773. https://doi.org/10.1089/neu.2012.2498
Panahi Y, Ghanei M, Hajhashemi A, Sahebkar A (2016) Effects of curcuminoids-piperine combination on systemic oxidative stress, clinical symptoms and quality of life in subjects with chronic pulmonary complications due to sulfur mustard: a randomized controlled trial. J Dietary Suppl 13:93–105. https://doi.org/10.3109/19390211.2014.952865
Pistell PJ, Morrison CD, Gupta S, Knight AG, Keller JN, Ingram DK, Bruce-Keller AJ (2010) Cognitive impairment following high-fat diet consumption is associated with brain inflammation. J Neuroimmunol 219:25–32. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jneuroim.2009.11.010
Rainey-Smith SR, Brown BM, Sohrabi HR, Shah T, Goozee KG, Gupta VB, Martins RN (2016) Curcumin and cognition: a randomized, placebo-controlled, double-blind study of community-dwelling older adults. Br J Nutr 115:2106–2113. https://doi.org/10.1017/S0007114516001203
Rangel-Zuñiga OA, Haro C, Tormos C, Perez-Martinez P, Delgado-Lista J, Marin C, Quintana-Navarro GM, Cerdá C, Sáez GT, Lopez-Segura F, Lopez-Miranda J, Perez-Jimenez F, Camargo A (2017) Frying oils with high natural or added antioxidants content, which protect against postprandial oxidative stress, also protect against DNA oxidation damage. Eur J Nutr 56:1597–1607. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00394-016-1205-1
Reeves PG, Nielsen FH, Fahey GC Jr (1993) AIN-93 purified diets for laboratory rodents: final report of the American Institute of Nutrition ad hoc writing committee on the reformulation of the AIN-76A rodent diet. J Nutr 123:1939–1951. https://doi.org/10.1093/jn/123.11.1939
Sarath TS, Waghe P, Gupta P, Choudhury S, Kannan K, Pillai AH, Harikumar SK, Mishra SK, Sarkar SN (2014) Atorvastatin ameliorates arsenic-induced hypertension and enhancement of vascular redox signaling in rats. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol 280:443–454. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.taap.2014.08.032
Schwertner HA, Rios DC, Pascoe JE (2006) Variation in concentration and labelling of ginger root dietary supplements. Obstet Gynaecol 107:1337–1343
Sharma AC, Kulkarni SK (1992) Evaluation of learning and memory mechanisms employing elevated plus-maze in rats and mice. Progr Neuro-Psychopharmacol Biol Psychiatry 16:117–125. https://doi.org/10.1016/0278-5846(92)90014-6
Singh IN, Sullivan PG, Hall ED (2007) Peroxynitrite-mediated oxidative damage to brain mitochondria: protective effects of peroxynitrite scavengers. J Neurosci Res 85:2216–2223. https://doi.org/10.1002/jnr.21360
Tappel ME, Chaudiere J, Tappel AL (1982) Glutathione peroxidase activities of animal tissues. Comp Biochem Physiol Part B: Comp Biochem 73:945–949. https://doi.org/10.1016/0305-0491(82)90341-8
Tatem KS, Quinn JL, Phadke A, Yu Q, Gordish-Dressman H, Nagaraju K (2014) Behavioral and locomotor measurements using an open field activity monitoring system for skeletal muscle diseases. J Vis Exp 91:e51785. https://doi.org/10.3791/51785
Uppin V, Acharya P, Kempaiah BB, Talahalli RR (2020) Hyperlipidemia down-regulate brain antioxidant defense enzymes and neurotrophins in rats: assessment of the modulatory potential of EPA+ DHA and Zerumbone. Mol Nutr Food Res. https://doi.org/10.1002/mnfr.202000381
Valladolid-Acebes I, Stucchi P, Cano V, Fernández-Alfonso MS, Merino B, Gil-Ortega M, Fole A, Morales L, Ruiz-Gayo M, Del Olmo N (2011) High-fat diets impair spatial learning in the radial-arm maze in mice. Neurobiol Learn Mem 95(1):80–85
Venkata RP, Subramanyam R (2016) Evaluation of the deleterious health effects of consumption of repeatedly heated vegetable oil. Toxicol Rep 3:636–643. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.toxrep.2016.08.003
Zarei M, Acharya P, Talahalli RR (2020) Ginger and turmeric lipid-solubles attenuate heated oil-induced cardio-hepatic oxidative stress via the upregulation of NRF2 and decrease blood pressure in rats. Br J Nutr: 1–22. https://doi.org/10.1017/S0007114520003967
Zhang X, Dong F, Ren J, Driscoll MJ, Culver B (2005) High dietary fat induces NADPH oxidase-associated oxidative stress and inflammation in rat cerebral cortex. Exp Neurol 191:318–325. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.expneurol.2004.10.011
Acknowledgments
Mr. Mehrdad Zarei acknowledges ICCR, New Delhi, for Research Fellowship and CSIR-CFTRI, Mysore, India, for providing the research facilities.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Mehrdad Zarei conducted the animal experiments and data analysis, Pooja Acharya involved in enzyme assays and manuscript writing, Vinayak Uppin involved in behavioral studies, while Ramaprasad Talahalli designed the experiments and wrote the manuscript. All the listed authors have contributed to the writing and editing of the manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Ethical approval
The animal procedures were approved (CFT/IAEC/120/2018) and monitored by the Institutional Animal Care and Use Committee of CSIR-CFTRI, Mysore, India. All the experiments were performed according to the CPCSEA (Committee for Control and Supervision of Experiments on Animals) guidelines (CPCSEA Reg No: 49/ReBi/S/99/CPCSEA).
Additional information
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zarei, M., Uppin, V., Acharya, P. et al. Ginger and turmeric lipid-solubles attenuate heated oil-induced oxidative stress in the brain via the upregulation of NRF2 and improve cognitive function in rats. Metab Brain Dis 36, 225–238 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11011-020-00642-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11011-020-00642-y