Abstract
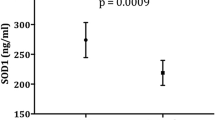
The role of malondialdehyde-modified low-density lipoprotein (MDA-LDL), an oxidized LDL, in the pathophysiology of autism spectrum disorder (ASD) is unclear. We studied association between MDA-LDL and behavioral symptoms in 11 individuals with ASD and 7 age -matched normal controls. Behavioral symptoms were assessed using the Aberrant Behavior Checklists (ABC). Because small sample size in this study, three measures were conducted: first, employment of adaptive Lasso for enhancing the accuracy of prediction and interpretability; second, calculation of coefficient of variation for an appropriate selection of plasma variables; and third, selection of good candidates of plasma variables. Plasma levels of MDA-LDL, eicosapentaenoic acid, docosahexaenoic acid (DHA) and DHA/arachidonic acid ratios were significantly higher, while plasma superoxide dismutase (SOD) levels were significantly lower in the ASD group than in the control group. The total ABC scores were significantly higher in the ASD group than in the control group. Multiple linear regression analysis and the adaptive Lasso revealed association of increased plasma DHA levels with the ABC total scores and increased plasma MDA-LDL levels. Such association between DHA and plasma MDA-LDL levels may contribute to behavior in individuals with ASD.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abdul-Razik Ismail E (2015) Behavior of lasso quantile regression with small sample sizes. J Multidiscip Eng Sci Technol 2:388–394 ISNN, 3159–0040
Albert A, Zhang L (2010) A novel definition of the multivariate coefficient of variation. Biom J 52:667–675. https://doi.org/10.1002/bimj.201000030
Al-Gadani Y, El-Ansary A, Attas O, Al-Ayadhi L (2009) Metabolic biomarkers related to oxidative stress and antioxidant status in Saudi autistic children. Clin Biochem 42:1032–1040. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.clinbiochem.2009.03.011
Altun H, Şahin N, Kurutaş EB, Karaaslan U, Sevgen FH, Fındıklı E (2018) Assessment of malondialdehyde levels, superoxide dismutase, and catalase activity in children with autism spectrum disorders. Psychiatry Clin Psychopharmacol 28:408–415. https://doi.org/10.1080/24750573.2018.1470360
Avramovic N, DragutinovicV KD, Colovic M, Trbovic A, de Luka S, Milovanovic I, Popovic T (2016) The effects of omega 3 fatty acid supplementation on brain tissue oxidative status in aged Wistar rats. Hippokratia 16(3):241–245
Ayala A, Muñoz MF, Argüelles S (2014) Lipid peroxidation: production, metabolism, and signaling mechanisms of malondialdehyde and 4-hydroxy-2-nonenal. Oxidative Med Cell Longev 2014:360438–360431. https://doi.org/10.1155/2014/360438
Cheng J, Wang F, Yu DF, Wu PF, Chen J (2011) The cytotoxic mechanism of malondialdehyde and protective effect of carnosine via protein cross-linking/mitochondrial dysfunction/reactive oxygen species/MAPK pathway in neurons. Eur J Pharmacol 650:650184–650194. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ejphar.2010.09.033
Curran-Everett D (2008) Explorations in statistics: standard deviations and standard errors. Adv Physiol Educ 32(3):203–208. https://doi.org/10.1152/advan.90123.2008
Dyall SC (2015) Long-chain omega-3 fatty acids and the brain: a review of the independent and shared effects of EPA, DPA and DHA. Front Aging Neurosci 7:52. https://doi.org/10.3389/fnagi.2015.00052
Dziobekm I, Gold SM, Wolf OT, Convit A (2007) Hypercholesterolemia in Asperger syndrome: independence from lifestyle, obsessive-compulsive behavior, and social anxiety. Psychiatry Res 149(1–3):321–324
Eldridge SM, Ashby D, Kerry S (2006) Sample size for cluster randomized trials: effect of coefficient of variation of cluster size and analysis method. Int J Epidemiol 35:1292–1300
Ghasemi Fard S, Wang F, Sinclair AJ, Elliott G, Turchini GM (2019) How does high DHA fish oil affect health? A systematic review of evidence. Crit Rev Food Sci Nutr 59:1684–1727. https://doi.org/10.1080/10408398.2018.1425978
González-Fraguela ME, Hung MD, Vera H, Maragoto C, Noris E, Blanco L, Galvizu R, Robindon M (2013) Oxidative stress markers in children with autism spectrum disorders. Br J Med Med Res 3:307–317
Horspool AM, Chang HC (2018) Neuron-specific regulation of superoxide dismutase amid pathogen-induced gut dysbiosis. Redox Biol 17:377–385. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.redox.2018.05.007
Itokawa M, Miyashita M, Arai M, DanT, Takahashi K, Tokunaga T et al (2018) Pyridoxamine: A novel treatment for schizophrenia with enhanced carbonyl stress. Psychiatry Clin Neurosci 72:35–44. https://doi.org/10.1111/pcn.12613
Jiménez-Fernández S, Gurpegui M, Díaz-Atienza F, Pérez-Costillas L, Gerstenberg M, Correll CU (2015) Oxidative stress and antioxidant parameters in patients with major depressive disorder compared to healthy controls before and after antidepressant treatment: results from a meta-analysis. J Clin Psychiatry 76:1658–1667. https://doi.org/10.4088/JCP.14r09179
Karabekiroglu K, Aman MG (2009) Validity of the aberrant behavior checklist in a clinical sample of toddlers. Child Psychiatry Hum Dev 40:99–110. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10578-008-0108-7
Kitano S, Kanno T, Maekawa M, Sakiurabayashi I, Kotani K, Hisatomi H (2004) Improved method for the immunological detection of malondialdehyde-modified low-density lipoproteins in human serum. Anal Chim Acta 509:229–235
Kubo T, Takahashi K, Furujo M, Hyodo Y, Tsuchiya H, Hattori M, Fujinaga S, Urayama K (2017) Usefulness of non-fasting lipid parameters in children. J Pediatr Endocrinol Metab 30:77–83. https://doi.org/10.1515/jpem-2016-0271
Lichou F, Orazio S, Dulucq S, Etienne G, Longy M, Hubert C, Groppi A, Monnereau A, Mahon FX, Turcq B (2019) Novel analytical methods to interpret large sequencing data from small sample sizes. Hum Genomics 13:41. https://doi.org/10.1186/s40246-019-0235-1
Luchi K, Ema M, Suzuki M, Yokoyama C, Hisatomi H (2018) Oxidized unsaturated fatty acids induce apoptotic cell death in cultured cells. Mol Med Rep 19:2767–2773. https://doi.org/10.3892/mmr.2019.9940
Meguid N, Dardir AA, Abdel-Raouf ER, Hashish A (2011) Evaluation of oxidative stress in autism: defective antioxidant enzymes and increased lipid peroxidation. Biol Trace Elem Res 143:58–65. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12011-010-8840-9
Morgan CJ (2017) Use of proper statistical techniques for research studies with small samples. Am J Phys Lung Cell Mol Phys 313:L873–L877. https://doi.org/10.1152/ajplung.00238.2017
Mousavinejad E, Ghaffari MA, Riahi F, Hajmohammadi M, Tiznobeyk Z, Mousavinejad M (2018) Coenzyme Q10 supplementation reduces oxidative stress and decreases antioxidant enzyme activity in children with autism spectrum disorders. Psychiatry Res 265:62–69. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.psychres.2018.03.061
Nordestgaard BG, Langsted A, Mora S, Kolovou G, Baum H, Bruckert E, Watts GF, Sypniewska G, Wiklund O, Borén J, Chapman MJ, Cobbaert C, Descamps OS, von Eckardstein A, Kamstrup PR, Pulkki K, Kronenberg F, Remaley AT, Rifai N, Ros E, Langlois M, European Atherosclerosis Society (EAS) and the European Federation of Clinical Chemistry and Laboratory Medicine (EFLM) Joint Consensus Initiative (2016) Fasting is not routinely required for determination of a lipid profile: clinical and laboratory implications including flagging at desirable concentration cutpoints-a joint consensus statement from the European atherosclerosis society and European Federation of Clinical Chemistry and Laboratory Medicine. Clin Chem 62:930–946. https://doi.org/10.1373/clinchem.2016.258897
Ogawa K, Tanaka T, Nagoshi T, Sekiyama H, Arase S, Minai K, Ogawa T, Yoshimura M (2015) Increase in the oxidised low-density lipoprotein level by smoking and the possible inhibitory effect of statin therapy in patients with cardiovascular disease: a retrospective study. BMJ Open. https://doi.org/10.1136/bmjopen-2014-005455
Packiasabapathy S, Prasad V, Rangasamy V, Popok D, Xu X, Novack V, Subramaniam B (2020) Cardiac surgical outcome prediction by blood pressure variability indices Poincaré plot and coefficient of variation: a retrospective study. BMC Anesthesiol 20:56. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12871-020-00972-5
Pongsuthana S, Tivatunsakul N (2016) Optimal fasting time before measurement of serum triglyceride levels in healthy volunteers. J Med Assoc Thail 99(Suppl 2):S42–S46
Roig-Pérez S, Guardiola F, Moretó M, Ferrer R (2014) Lipid peroxidation induced by DHA enrichment modifies paracellular permeability in Caco-2 cells: protective role of taurine. J Lipid Res 45(8):1418–1428
Sharma R, Rosenberg A, Bennett ER, Laskowitz DT, Acheson SK (2017) A blood-based biomarker panel to risk-stratify mild traumatic brain injury. PLoS One 12:e0173798. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0173798
Shortreed SM, Ertefaie A (2017) Outcome-adaptive lasso: variable selection for causal inference. Biometrics 73:1111–1122. https://doi.org/10.1111/biom.12679
Simundic AM, Cornes M, Grankvist K, Lippi G, Nybo M (2014) Standardization of collection requirements for fasting samples: for the Working Group on Preanalytical Phase (WG-PA) of the European Federation of Clinical Chemistry and Laboratory Medicine (EFLM). Clin Chim Acta 432:33–337. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cca.2013.11.008
Singh K, Connors SL, Macklin EA, Smith KD, Fahey JW, Talalay P, Zimmerman AW (2014) Sulforaphane treatment of autism spectrum disorder (ASD). Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 111:15550–11555. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.1416940111
Song X, Schenk JM, Diep P, Murphy RA, Harris TB, Eiriksdottir G, Gudnason V, Casper C, Lampe JW, Neuhouser ML (2016) Measurement of circulating phospholipid fatty acids: association between relative weight percentage and absolute concentrations. J Am Coll Nutr 35:647–656
Wahid A, Khan DM, Hussain I (2017) Robust adaptive lasso method for parameter's estimation and variable selection in high-dimensional sparse models. PLoS One 12(8):e0183518. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0183518 eCollection 2017
Yang B, Ren XL, Fu YQ, Gao JL, Li D (2014) Ratio of n-3/n-6 PUFAs and risk of breast cancer: a meta-analysis of 274135 adult females from 11 independent prospective studies. BMC Cancer 4:105. https://doi.org/10.1186/1471-2407-14-105
Yui K, Imataka G, Kawasak Y, Yamada H (2017) Increased ω-3 polyunsaturated fatty acid/arachidonic acid ratios and upregulation of signaling mediator in individuals with autism spectrum disorders. Life Sci 145:205–212. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.lfs.2015.12.039
Funding
This study was funded by a Grant-in-Aid for Scientific Research (C) (2014–2016; No 26461777) from the Ministry of Education, Culture, Sports, Science and Technology, Japan.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors have no conflict of interests concerning the materials or methods used in the present study or findings presented in this study.
Informed consent
Informed consent was obtained by all participants in this study. This study was performed with the approval of the Ethics Committee of the Fujimoto Medical Clinic in Kobe City, Japan. Written informed consent was obtained from the patients or their parents.
Ethical responsibilities of authors
-
The manuscript was not be submitted to more than one journal for simultaneous consideration.
-
The submitted work was original and should not have been published elsewhere in any form or language (partially or in full).
-
A single study was not be split up into several parts to increase the quantity of submissions and submitted to various journals or to one journal over time (i.e. ‘salami-slicing/publishing’).
-
Results were presented clearly, honestly, and without fabrication, falsification or inappropriate data manipulation (including image based manipulation). Authors adhered to discipline-specific rules for acquiring, selecting and processing data.
-
No data, text, or theories by others are presented as if they were the author’s own (‘plagiarism’).
-
This research do not misapply to pose a threat to public health or national security.
-
We avoided untrue statements about an entity (who can be an individual person or a company) or descriptions of their behavior or actions that could potentially be seen as personal attacks or allegations about that person.
-
Research that did not misapply to pose a threat to public health or national security.
-
The corresponding author, and the order of authors are all correct at submission. We understood that change to authorship cannot be made after acceptance of a manuscript.
Authorship clarified
All authors adhere to the guidelines for authorship that are applicable in their specific research field and the following guidelines:
-
1)
Kunio Yui developed the study project.
-
2)
All authors whose names appear on the submission.
-
3)
Kunio Yui, George Imataka and Hitomi Sasaki made substantial contributions to the conception, design of the work, the acquisition, analysis, or interpretation of data; Hitomi Sasaki and or Ryoichi Shiroki reviewed the paper. All authors drafted the work or revised it critically for important intellectual content and agree to be accountable for all aspects of the work in ensuring that questions related to the accuracy or integrity of any part of the work are appropriately investigated and resolved.
Data transparency
All authors made sure that all data and materials as well as software application or custom code support their published claims and comply with field standards. All authors have agreed that journals may have individual policies on (sharing) research data in concordance with disciplinary norms and expectations.
Additional information
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Yui, K., Imataka, G., Sasaki, H. et al. The role of lipid peroxidation in individuals with autism spectrum disorders. Metab Brain Dis 35, 1101–1108 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11011-020-00585-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11011-020-00585-4