Abstract
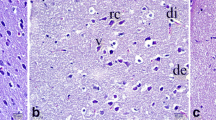
Ethanol is known as an effective agent against cerebral lesions after ischemia. Modafinil is a stimulant of the central nervous system (CNS) with antioxidant properties. We assessed the neuroprotective effect of modafinil in combination with ethanol after focal cerebral ischemia. Male wistar rats weighing 280–300 g were divided into nine groups (n = 12 each group): The groups consisted of the MCAO (middle cerebral artery occlusion) group (i.e. ischemia without treatment); the vehicle group(Dimethylsulfoxide); the modafinil group including three subgroups which pretreated with Modafinil (10, 30, 100 mg/kg), respectively, for seven days prior to the induction of MCAO; the ethanol group which received 1.5g/kg ethanol at the time of reperfusion; and modafinil+ethanol group which was divided into three subgroups that received three doses of modanifil (10, 30,100 mg/kg), respectively, for seven days prior to MCAO as well as ethanol at the time of reperfusion. Transient cerebral ischemia was induced by 60-min intraluminal occlusion of the right middle cerebral artery. Edema, infarct volume, glial scar formation (gliosis) and apoptosis were analyzed. The ethanol alone treatment (with a less significant effect), modafinil (in a dose-dependent way), and the combination of modafinil and ethanol significantly decreased the brain infarct volume, edema, apoptosis, and gliosis (P ≤ 0.05). Additionally, modafinil+ethanol mediated the restoration of aerobic metabolism and hyper-glycolysis suppress, thereby resulting in an increase in pyruvate dehydrogenase and a decrease in lactate dehydrogenase activity, respectively, which ultimately reduced oxidative reperfusion injury. These results demonstrate that pretreatment with modafinil (100 mg/kg) and modafinil+ethanol(1.5 g/kg) may prevent ischemic brain injuries.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Aguirre JA et al (1999) A stereological study on the neuroprotective actions of acute Modafinil treatment on 1-methyl-4-phenyl-1,2,3,6-tetrahydropyridine-induced nigral lesions of the male black mouse. Neurosci Lett 275:215–218. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0304-3940(99)00706-5
Aronowski J, Strong R, Shirzadi A, Grotta JC (2003) Ethanol plus caffeine (caffeinol) for treatment of ischemic stroke: preclinical experience. Stroke 34:1246–1251. https://doi.org/10.1161/01.str.0000068170.80517.b3
Barreto G, White RE, Ouyang Y, Xu L, Giffard RG (2011) Astrocytes: targets for neuroprotection in stroke. Cent Nerv Syst Agents Med Chem 11:164–173
Beraki S et al (2013) A pharmacological screening approach for discovery of neuroprotective compounds in ischemic stroke. PLoS One 8:e69233. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0069233
Bezu M, Shanmugasundaram B, Lubec G, Korz V (2016) Repeated application of Modafinil and levodopa reveals a drug-independent precise timing of spatial working memory modulation. Behav Brain Res 312:9–13. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bbr.2016.06.003
Bibani RH, Tench CR, George J, Manouchehrinia A, Palace J, Constantinescu CS (2012) Reduced EDSS progression in multiple sclerosis patients treated with modafinil for three years or more compared to matched untreated subjects. Mult Scler Relat Disord 1:131–135. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.msard.2012.03.004
Bivard A et al (2017) MIDAS (Modafinil in debilitating fatigue after stroke): a randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled, cross-over trial. Stroke 48:1293–1298. https://doi.org/10.1161/strokeaha.116.016293
Brandt MD, Ellwardt E, Storch A (2014) Short- and long-term treatment with modafinil differentially affects adult hippocampal neurogenesis. Neuroscience 278:267–275. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neuroscience.2014.08.014
Buga AM, Dunoiu C, Balseanu A, Popa-Wagner A (2008) Cellular and molecular mechanisms underlying neurorehabilitation after stroke in aged subjects. Rom J Morphol Embryo 49:279–302
Cai L et al (2016a) Adjuvant therapies using normobaric oxygen with hypothermia or ethanol for reducing hyperglycolysis in thromboembolic cerebral ischemia. Neuroscience 318:45–57. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neuroscience.2016.01.010
Cai L et al (2016b) Combination therapy of normobaric oxygen with hypothermia or ethanol modulates pyruvate dehydrogenase complex in thromboembolic cerebral ischemia. J Neurosci Res 94:749–758. https://doi.org/10.1002/jnr.23740
Carmichael ST (2005) Rodent models of focal stroke: size, mechanism, and purpose. NeuroRx: Neurotherapeutics 2:396–409. https://doi.org/10.1602/neurorx.2.3.396
Chamorro A, Vila N, Ascaso C, Elices E, Schonewille W, Blanc R (1998) Blood pressure and functional recovery in acute ischemic stroke. Stroke 29:1850–1853
Chandler LJ, Sumners C, Crews FT (1993) Ethanol inhibits NMDA receptor-mediated excitotoxicity in rat primary neuronal cultures. Alcohol Clin Exp Res 17:54–60
Chen W et al (2016) Pretreatment of rats with increased bioavailable berberine attenuates cerebral ischemia-reperfusion injury via down regulation of adenosine-5'monophosphate kinase activity. Eur J Pharmacol 779:80–90. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ejphar.2016.03.015
Davis S, Thomas A, Perry R, Oakley A, Kalaria RN, O'Brien JT (2002) Glial fibrillary acidic protein in late life major depressive disorder: an immunocytochemical study. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry 73:556–560
Dias VT, Vey LT, Rosa HZ, D'Avila LF, Barcelos RCS, Burger ME (2017) Could Modafinil prevent psychostimulant addiction?. An experimental study in rats. Basic Clin Pharmacol Toxicol 121:400–408. https://doi.org/10.1111/bcpt.12821
Doyle KP, Simon RP, Stenzel-Poore MP (2008) Mechanisms of ischemic brain damage. Neuropharmacology 55:310–318. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neuropharm.2008.01.005
Enayati A et al (2018) Cardioprotective and anti-apoptotic effects of Potentilla reptans L. root via Nrf2 pathway in an isolated rat heart ischemia/reperfusion model. Life Sci 215:216–226. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.lfs.2018.11.021
Florence G, Bonnier R, Plagnes D, Pierard C, Satabin P, Peres M, Lagarde D (2000) Effect of modafinil on cerebral blood flow of anaesthetised rats. Comparison with amphetamine. Exp Brain Res 135:552–556
Fuxe K et al (1992) Evidence for a protective action of the vigilance promoting drug Modafinil on the MPTP-induced degeneration of the nigrostriatal dopamine neurons in the black mouse: an immunocytochemical and biochemical analysis. Exp Brain Res 88:117–130. https://doi.org/10.1007/bf02259133
Gerrard P, Malcolm R (2007) Mechanisms of modafinil: a review of current research. Neuropsychiatr Dis Treat 3:349–364
Ghahari L, Safari M, Joghataei MT, Mehdizadeh M, Soleimani M (2014) Effect of combination therapy using hypothermia and granulocyte colony-stimulating factor in a rat transient middle cerebral artery occlusion model. Iran Biomed J 18:239–244
Hafeez A, Elmadhoun O, Peng C, Ding JY, Geng X, Guthikonda M, Ding Y (2014) Reduced apoptosis by ethanol and its association with PKC-delta and Akt signaling in ischemic stroke. Aging Dis 5:366–372. https://doi.org/10.14336/ad.2014.0500366
Jin R, Yang G, Li G (2010) Inflammatory mechanisms in ischemic stroke: role of inflammatory cells. J Leukoc Biol 87:779–789. https://doi.org/10.1189/jlb.1109766
Kanbak G, Kartkaya K, Ozcelik E, Guvenal AB, Kabay SC, Arslan G, Durmaz R (2013) The neuroprotective effect of acute moderate alcohol consumption on caspase-3 mediated neuroapoptosis in traumatic brain injury: the role of lysosomal cathepsin. L and nitric oxide. Gene 512:492–495. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.gene.2012.10.012
Kelly DF, Kozlowski DA, Haddad E, Echiverri A, Hovda DA, Lee SM (2000) Ethanol reduces metabolic uncoupling following experimental head injury. J Neurotrauma 17:261–272. https://doi.org/10.1089/neu.2000.17.261
Kim JS (1996) Cytokines and adhesion molecules in stroke and related diseases. J Neurol Sci 137:69–78
Kochanski R, Peng C, Higashida T, Geng X, Huttemann M, Guthikonda M, Ding Y (2013) Neuroprotection conferred by post-ischemia ethanol therapy in experimental stroke: an inhibitory effect on hyperglycolysis and NADPH oxidase activation. J Neurochem 126:113–121. https://doi.org/10.1111/jnc.12169
Lange R, Volkmer M, Heesen C, Liepert J (2009) Modafinil effects in multiple sclerosis patients with fatigue. J Neurol 256:645–650. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00415-009-0152-7
Lin JH et al (1998) Gap-junction-mediated propagation and amplification of cell injury. Nat Neurosci 1:494–500. https://doi.org/10.1038/2210
Liu D (2018) Effects of procyanidin on cardiomyocyte apoptosis after myocardial ischemia reperfusion in rats. BMC Cardiovasc Disord 18:35–35. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12872-018-0772-x
Lundgren J, Zhang H, Agardh CD, Smith ML, Evans PJ, Halliwell B, Siesjo BK (1991) Acidosis-induced ischemic brain damage: are free radicals involved?. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab 11:587–596. https://doi.org/10.1038/jcbfm.1991.108
Maleki SN, Aboutaleb N, Souri F (2018) Berberine confers neuroprotection in coping with focal cerebral ischemia by targeting inflammatory cytokines. J Chem Neuroanat 87:54–59. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jchemneu.2017.04.008
Martinez AD, Saez JC (2000) Regulation of astrocyte gap junctions by hypoxia-reoxygenation. Brain Res Brain Res Rev 32:250–258
McCarter KD et al (2017a) Effect of low-dose alcohol consumption on inflammation following transient focal cerebral ischemia in rats. Sci Rep 7:12547. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-017-12720-w
McCarter KD, Sun H, Li C (2017b) Neuroprotective effect of low dose alcohol consumption against transient focal cerebral ischemia. FASEB J 31:693.693–693.693. https://doi.org/10.1096/fasebj.31.1_supplement.693.3
Mokudai T, Ayoub IA, Sakakibara Y, Lee EJ, Ogilvy CS, Maynard KI (2000) Delayed treatment with nicotinamide (vitamin B(3)) improves neurological outcome and reduces infarct volume after transient focal cerebral ischemia in Wistar rats. Stroke 31:1679–1685
Murakami K, Kondo T, Chan PH (1997) Reperfusion following focal cerebral ischemia alters distribution of neuronal cells with DNA fragmentation in mice. Brain Res 751:160–164
Pradeep H, Diya JB, Shashikumar S, Rajanikant GK (2012) Oxidative stress--assassin behind the ischemic stroke. Folia Neuropathol 50:219–230
Raineri M, Peskin V, Goitia B, Taravini IR, Giorgeri S, Urbano FJ, Bisagno V (2011) Attenuated methamphetamine induced neurotoxicity by modafinil administration in mice. Synapse (New York, NY) 65:1087–1098. https://doi.org/10.1002/syn.20943
Raineri M et al (2012) Modafinil abrogates methamphetamine-induced Neuroinflammation and apoptotic effects in the mouse striatum. PLoS One 7:e46599. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0046599
Richards EM, Rosenthal RE, Kristian T, Fiskum G (2006) Postischemic hyperoxia reduces hippocampal pyruvate dehydrogenase activity. Free Radic Biol Med 40:1960–1970. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.freeradbiomed.2006.01.022
Rossignol F, Solares M, Balanza E, Coudert J, Clottes E (2003) Expression of lactate dehydrogenase a and B genes in different tissues of rats adapted to chronic hypobaric hypoxia. J Cell Biochem 89:67–79. https://doi.org/10.1002/jcb.10484
Sahu S, Kauser H, Ray K, Kishore K, Kumar S, Panjwani U (2013) Caffeine and modafinil promote adult neuronal cell proliferation during 48 h of total sleep deprivation in rat dentate gyrus. Exp Neurol 248:470–481. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.expneurol.2013.07.021
Sicard KM, Fisher M (2009) Animal models of focal brain ischemia. Exp Transl Stroke Med 1:7. https://doi.org/10.1186/2040-7378-1-7
Siesjo BK (1988) Acidosis and ischemic brain damage. Neurochem Pathol 9:31–88
Sofroniew MV (2000) Astrocyte failure as a cause of CNS dysfunction. Mol Psychiatry 5:230–232
Strong R, Grotta JC, Aronowski J (2000) Combination of low dose ethanol and caffeine protects brain from damage produced by focal ischemia in rats. Neuropharmacology 39:515–522
Su F et al (2017) Low-dose ethanol preconditioning protects against oxygen-glucose deprivation/Reoxygenation-induced neuronal injury by activating large conductance, ca(2+)-activated K(+) channels in vitro. Neurosci Bull 33:28–40. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12264-016-0080-3
Svandova E, Vesela B, Tucker AS, Matalova E (2018) Activation of pro-apoptotic caspases in non-apoptotic cells during Odontogenesis and related osteogenesis. Front Physiol 9:174. https://doi.org/10.3389/fphys.2018.00174
Tuttolomondo A, Di Raimondo D, di Sciacca R, Pinto A, Licata G (2008) Inflammatory cytokines in acute ischemic stroke. Curr Pharm Des 14:3574–3589
Ueki A et al (1993) Evidence for a preventive action of the vigilance-promoting drug modafinil against striatal ischemic injury induced by endothelin-1 in the rat. Exp Brain Res 96:89–99. https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00230442
van Vliet SA, Vanwersch RA, Jongsma MJ, van der Gugten J, Olivier B, Philippens IH (2006) Neuroprotective effects of modafinil in a marmoset Parkinson model: behavioral and neurochemical aspects. Behav Pharmacol 17:453–462
Volkow ND et al (1990) Acute effects of ethanol on regional brain glucose metabolism and transport. Psychiatry Res 35:39–48
Volkow ND et al (2006) Low doses of alcohol substantially decrease glucose metabolism in the human brain. NeuroImage 29:295–301. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neuroimage.2005.07.004
Wang W et al (2008) Rat focal cerebral ischemia induced astrocyte proliferation and delayed neuronal death are attenuated by cyclin-dependent kinase inhibition. J Clin Neurosci 15:278–285. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jocn.2007.02.004
Wang F et al (2012) Neuroprotective effect of acute ethanol administration in a rat with transient cerebral ischemia. Stroke 43:205–210. https://doi.org/10.1161/strokeaha.111.629576
Wang F et al (2014) A novel small-molecule activator of procaspase-3 induces apoptosis in cancer cells and reduces tumor growth in human breast, liver and gallbladder cancer xenografts. Mol Oncol 8:1640–1652. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.molonc.2014.06.015
Women’s Hospitals B (2009) Ischemic stroke: pathophysiology and principles of localization. Neurology 13:1
Xiao YL, Fu JM, Dong Z, Yang JQ, Zeng FX, Zhu LX, He BC (2004) Neuroprotective mechanism of modafinil on Parkinson disease induced by 1-methyl-4-phenyl-1,2,3,6-tetrahydropyridine. Acta Pharmacol Sin 25:301–305
Zager A et al (2018) The wake-promoting drug Modafinil prevents motor impairment in sickness behavior induced by LPS in mice: role for dopaminergic D1 receptor. Progress Neuro-Psychopharmacol Biol Psychiatry 81:468–476. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.pnpbp.2017.05.003
Zhang J et al (2015) Intravenous injections of human mesenchymal stromal cells modulated the redox state in a rat model of radiation myelopathy. Evid Based Complement Alternat Med 2015:6. https://doi.org/10.1155/2015/432369
Acknowledgements
This study was financially supported by a research grant from Iran University of Medical Sciences. Our thanks go to Sobhan Darou Pharmaceutical Company for providing us with the pure form of modafinil.
Funding
This study was financially supported by a research grant from Iran University of Medical Science (grant number:29298) for a Ph.D. student thesis.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflicts of interests
Conflict of interest the authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Ethical approval
All procedures performed in studies involving animals were in accordance with the ethical standards of ethics Committee of Iran University of Medical Sciences (ethical code: ir.iums.rec 1395.9221313204).
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Abbasi, Y., Shabani, R., Mousavizadeh, K. et al. Neuroprotective effect of ethanol and Modafinil on focal cerebral ischemia in rats. Metab Brain Dis 34, 805–819 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11011-018-0378-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11011-018-0378-0