Abstract
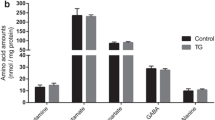
Alzheimer’s disease (AD) has been associated with the disturbance of brain glucose metabolism. The present study investigates brain glucose metabolism using 13C NMR metabolomics in combination with intravenous [1-13C]-glucose infusion in APP/PS1 transgenic mouse model of amyloid pathology at 10 months of age. We found that brain glucose was significantly accumulated in APP/PS1 mice relative to wild-type (WT) mice. Reductions in 13C fluxes into the specific carbon sites of tricarboxylic acid (TCA) intermediate (succinate) as well as neurotransmitters (glutamate, glutamine, γ-aminobutyric acid and aspartate) from [1-13C]-glucose were also detected in the brain of APP/PS1 mice. In addition, our results reveal that the 13C-enrichments of the C3 of alanine were significantly lower and the C3 of lactate have a tendency to be lower in the brain of APP/PS1 mice than WT mice. Taken together, the development of amyloid pathology could cause a reduction in glucose utilization and further result in decreases in energy and neurotransmitter metabolism as well as the lactate-alanine shuttle in the brain.



Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- AD:
-
Alzheimer’s disease
- Ala:
-
Alanine
- Asp:
-
Aspartate
- 13C-NMR:
-
13C nuclear magnetic resonance
- GABA:
-
γ-aminobutyric acid
- Glu:
-
Glutamate
- Gln:
-
Glutamine
- Lac:
-
Lactate
- MWM:
-
Morris water maze
- PC:
-
Pyruvate carboxylase
- PDH:
-
Pyruvate dehydrogenase
- Suc:
-
Succinate
- T1D:
-
Type 1 diabetes
- T2D:
-
Type 2 diabetes
- TCA:
-
Tricarboxylic acid
- WT:
-
Wild-type
References
Anandatheerthavarada HK, Biswas G, Robin MA, Avadhani NG (2003) Mitochondrial targeting and a novel transmembrane arrest of Alzheimer's amyloid precursor protein impairs mitochondrial function in neuronal cells. J Cell Biol 161(1):41–54
Ballarini T, Iaccarino L, Magnani G, Ayakta N, Miller BL, Jagust WJ, Gorno-Tempini ML, Rabinovici GD, Perani D (2016) Neuropsychiatric subsyndromes and brain metabolic network dysfunctions in early onset Alzheimer's disease. Hum Brain Mapp 37(12):4234–4247
Baxter LR, Schwartz JM, Phelps ME, Mazziotta JC, Guze BH, Selin CE, Gerner RH, Sumida RM (1989) Reduction of prefrontal cortex glucose metabolism common to three types of depression. Arch Gen Psychiatry 46(3):243–250
Bélanger M, Allaman I, Magistretti PJ (2011) Brain energy metabolism: focus on astrocyte-neuron metabolic cooperation. Cell Metab 14(6):724–738
Blennow K, de Leon MJ, Zetterberg H (2006) Alzheimer's disease. Lancet 368(9533):387–403
Cabezas-Opazo FA, Vergara-Pulgar K, Pérez MJ, Jara C, Osorio-Fuentealba C, Quintanilla RA (2015) Mitochondrial dysfunction contributes to the pathogenesis of Alzheimer’s disease. Oxid med cell Longev. 2015, Article ID 509654
Deelchand DK, Nelson C, Shestov AA, Ugurbil K, Henry PG (2009) Simultaneous measurement of neuronal and glial metabolism in rat brain in vivo using co-infusion of [1,6-13C2] glucose and [1,2-13C2] acetate. J Magn Reson 196(2):157–163
Ferri CP, Prince M, Brayne C, Brodaty H, Fratiglioni L, Ganguli M, Hall K, Hasegawa K, Hendrie H, Huang Y, Jorm A, Mathers C, Menezes PR, Rimmer E, Scazufca M (2005) Global prevalence of dementia: a Delphi consensus study. Lancet 366(9503):2112–2117
Haberg A, Qu H, Haraldseth O, Unsgard G, Sonnewald U (1998) In vivo injection of [1-13C] glucose and [1,2-13C] acetate combined with ex vivo 13C nuclear magnetic resonance spectroscopy: a novel approach to the study of middle cerebral artery occlusion in the rat. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab 18(11):1223–1232
Hardy J, Selkoe DJ (2002) The amyloid hypothesis of Alzheimer's disease: progress and problems on the road to therapeutics. Science 297(5580):353–356
Holtzman DM, Morris JC, Goate AM (2011) Alzheimer’s disease: the challenge of the second century. Sci Transl Med 3(77):77sr1
Hoyer S, Henneberg N, Knapp S, Lannert H, Martin E (1996) Brain glucose metabolism is controlled by amplification and desensitization of the neuronal insulin receptor. Ann N Y Acad Sci 777(1):374–379
Lauretti E, Li JG, Di Meco A, Praticò D (2017) Glucose deficit triggers tau pathology and synaptic dysfunction in a tauopathy mouse model. Transl Psychiatry 7(1):e1020
Li XY, Men WW, Zhu H, Lei JF, Zuo FX, Wang ZJ, Zhu ZH, Bao XJ, Wang RZ (2016) Age- and brain region-specific changes of glucose metabolic disorder, learning, and memory dysfunction in early Alzheimer’s disease assessed in APP/PS1 transgenic mice using 18F-FDG-PET. Int J Mol Sci 17(10):1707
Mergenthaler P, Lindauer U, Dienel GA, Meisel A (2013) Sugar for the brain: the role of glucose in physiological and pathological brain function. Trends Neurosci 36(10):587–597
Mosconi L (2005) Brain glucose metabolism in the early and specific diagnosis of Alzheimer’s disease. Eur J Nucl Med Mol Imaging 32(4):486–510
Norenberg MD, Martinez-Hernandez A (1979) Fine structural localization of glutamine synthetase in astrocytes of rat brain. Brain Res 161(2):303–310
Saint-Aubert L, Almkvist O, Chiotis K, Almeida R, Wall A, Nordberg A (2016) Regional tau deposition measured by [18F] THK5317 positron emission tomography is associated to cognition via glucose metabolism in Alzheimer’s disease. Alzheimers Res Ther 8(1):38
Schousboe A, Sonnewald U, Waagepetersen HS (2003) Differential roles of alanine in GABAergic and glutamatergic neurons. Neurochem Int 43(4):311–315
Shulman GI, Rothman DL, Jue T, Stein P, DeFronzo RA, Shulman RG (1990) Quantitation of muscle glycogen synthesis in normal subjects and subjects with non-insulin-dependent diabetes by 13C nuclear magnetic resonance spectroscopy. N Engl J Med 322(4):223–228
Sibson NR, Mason GF, Shen J, Cline GW, Herskovits AZ, Wall JE, Behar KL, Rothman DL, Shulman RG (2001) In vivo 13C NMR measurement of neurotransmitter glutamate cycling, anaplerosis and TCA cycle flux in rat brain during. J Neurochem 76(4):975–989
Suzanne M (2014) Type 3 diabetes is sporadic Alzheimer′ s disease: mini-review. Eur Neuropsychopharmacol 24(12):1954–1960
Videbech P (2000) PET measurements of brain glucose metabolism and blood flow in major depressive disorder: a critical review. Acta Psychiatr Scand 101(1):11–20
Waagepetersen HS, Sonnewald U, Larsson OM, Schousboe A (2000) A possible role of alanine for ammonia transfer between astrocytes and glutamatergic neurons. J Neurochem 75(2):471–479
Wang N, Zhao LC, Zheng YQ, Dong MJ, Su Y, Chen WJ, Hu ZL, Yang YJ, Gao HC (2015) Alteration of interaction between astrocytes and neurons in different stages of diabetes: a nuclear magnetic resonance study using [1-13C] glucose and [2-13C] acetate. Mol Neurobiol 51(3):843–852
Winkler EA, Nishida Y, Sagare AP, Rege SV, Bell RD, Perlmutter D, Sengillo JD, Hillman S, Kong P, Nelson AR, Sullivan JS, Zhao Z, Meiselman HJ, Wenby RB, Soto J, Abel ED, Makshanoff J, Zuniga E, De Vivo DC, Zlokovic BV (2015) GLUT1 reductions exacerbate Alzheimer's disease vasculo-neuronal dysfunction and degeneration. Nat Neurosci 18(4):521–530
Xie H, Guan J, Borrelli LA, Xu J, Serrano-Pozo A, Bacskai BJ (2013) Mitochondrial alterations near amyloid plaques in an Alzheimer's disease mouse model. J Neurosci 33(43):17042–17051
Zheng H, Zheng Y, Wang D, Cai A, Lin Q, Zhao L, Chen M, Deng M, Ye X, Gao H (2017) Analysis of neuron-astrocyte metabolic cooperation in the brain of db/db mice with cognitive decline using 13C NMR spectroscopy. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab 37(1):332–343
Zwingmann C, Richter-Landsberg C, Brand A, Leibfritz D (2000) NMR spectroscopic study on the metabolic fate of [3-13C] alanine in astrocytes, neurons and cocultures. Glia 32(3):286–303
Zwingmann C, Chatauret N, Leibfritz D, Butterworth RF (2003) Selective increase of brain lactate synthesis in experimental acute liver failure: results of a [1H-13C] nuclear magnetic resonance study. Hepatology 37(2):420–428
Acknowledgments
The Laboratory Animal Center of Wenzhou Medical University was appreciated for technical services.
Funding
This study was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Nos.: 21605115, 21575105) and the Public Welfare Technology Application Research Foundation of Zhejiang Province (No.: 2017C33066).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
HZ and HCG contributed to experimental design. QZ, CL and LCZ contributed to animal feeding and intravenous [1-13C]-glucose infusion, QZ, YD, CL and HHX contributed to sample collection and NMR metabolomic analysis. HZ and HCG contributed to data analysis, result interpretation and writing. All authors have read, revised and approved the final manuscript.
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflicting interests
The authors declare no conflict of interest in this study.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhou, Q., Zheng, H., Chen, J. et al. Metabolic fate of glucose in the brain of APP/PS1 transgenic mice at 10 months of age: a 13C NMR metabolomic study. Metab Brain Dis 33, 1661–1668 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11011-018-0274-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11011-018-0274-7