Abstract
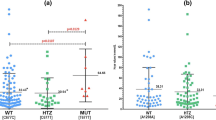
Methylenetetrahydrofolate reductase (MTHFR) polymorphism (C677T, A1298C) has been implicated in increased plasma homocysteine (Hcy) levels. The present study was designed to investigate the association between MTHFR polymorphism and increased Hcy levels in subarachnoid haemorrhage (SAH) patients. A total of 150 subjects from North India were included in the study, comprising of 100 SAH patients and 50 healthy controls. Plasma Hcy levels was determined and MTHFR polymorphism (C677T, A1298C) was screened by High resolution melting (HRM) analysis. Plasma Hcy levels were found to be significantly higher (p < 0.001) in SAH patients than in healthy controls. No significant difference in the genotype and allele frequency of MTHFR A1298C was observed. However, frequency of MTHFR C677T genotype, CT (53% vs. 20%; p < 0.001) and TT (15% vs. 2%; p < 0.05) was significantly higher in SAH group as compared to healthy controls. The frequency of T allele (41.5% vs. 12%; p < 0.001) was also found to be higher in SAH patients in comparison to healthy controls. Furthermore, Hcy levels were higher in SAH patients with TT genotype than in patients having CT genotype, whereas CC genotype had lower Hcy levels. The study suggests that higher frequency of MTHFR C677T allele may contribute to etiopathology of SAH through increase in Hcy levels.

Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- CAD:
-
Coronary artery diseases
- HRM:
-
High resolution melting
- Hcy:
-
Homocysteine
- HHcy:
-
Hyperhomocysteinemia
- MTHFR :
-
Methylenetetrahydrofolate reductase
- SNP:
-
Single nucleotide polymorphism
- SAH:
-
Subarachnoid haemorrhage
- SBD-F:
-
7-benzo-2-oxa-1,3-diazole-4-sulfonic acid
- TCEP:
-
Tris-(2-carboxyl-ethyl)-phosphine
References
Aggarwal A, Dhandapani S, Praneeth K et al (2018) Comparative evaluation of H&H and WFNS grading scales with modified H&H (sans systemic disease): A study on 1000 patients with subarachnoid hemorrhage. Neurosurg Rev 41:241–247. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10143-017-0843-y
Al-Allawi N, Avo A, Jubrael J (2009) Methylenetetrahydrofolate reductase C677T polymorphism in Iraqi patients with ischemic stroke. Neurol India 57:631. https://doi.org/10.4103/0028-3886.57821
Alluri RV, Mohan V, Komandur S et al (2005) MTHFR C677T gene mutation as a risk factor for arterial stroke: a hospital based study. Eur J Neurol 12:40–44. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1468-1331.2004.00938.x
Amouzou EK, Chabi NW, Adjalla CE et al (2004) High prevalence of hyperhomocysteinemia related to folate deficiency and the 677C>T mutation of the gene encoding methylenetetrahydrofolate reductase in coastal West Africa. Am J Clin Nutr 79:619–624
Angeline T, Jeyaraj N, Granito S, Tsongalis GJ (2004) Prevalence of MTHFR gene polymorphisms (C677T and A1298C) among Tamilians. Exp Mol Pathol 77:85–88. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.yexmp.2004.04.006
Banerjee I, Gupta V, Ganesh S (2007) Association of gene polymorphism with genetic susceptibility to stroke in Asian populations: a meta-analysis. J Hum Genet 52:205–219. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10038-006-0098-x
Bhagwati SN (1998) Incidence of subarachnoid hemorrhage from aneurysmal rupture in India. Neurol Med Chir 38(Suppl):128–130
Bhargava S, Parakh R, Manocha A et al (2007) Prevalence of Hyperhomocysteinemia in Vascular Disease: Comparative Study of Thrombotic Venous Disease Vis-è-Vis Occlusive Arterial Disease. Vascular 15:149–153. https://doi.org/10.2310/6670.2007.00031
Bhat AR, Afzalwani M, Kirmani AR (2011) Subarachnoid hemorrhage in Kashmir: Causes, risk factors, and outcome. Asian J Neurosurg 6:57–71. https://doi.org/10.4103/1793-5482.92159
Biswas A, Ranjan R, Meena A et al (2009) Homocystine Levels, Polymorphisms and the Risk of Ischemic Stroke in Young Asian Indians. J Stroke Cerebrovasc Dis 18:103–110. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jstrokecerebrovasdis.2008.09.014
Cacciapuoti F (2013) Lowering homocysteine levels with folic acid and B-vitamins do not reduce early atherosclerosis, but could interfere with cognitive decline and Alzheimer’s disease. J Thromb Thrombolysis 36:258–262. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11239-012-0856-x
Cronin S, Furie KL, Kelly PJ (2005) Dose-Related Association of MTHFR 677T Allele With Risk of Ischemic Stroke: Evidence From a Cumulative Meta-Analysis. Stroke 36:1581–1587. https://doi.org/10.1161/01.STR.0000169946.31639.af
Dayakar S, Goud KI, Reddy TPK et al (2011) Sequence Variation of the Methylene Tetrahydrofolate Reductase Gene (677C>T and 1298A>C) and Traditional Risk Factors in a South Indian Population. Gen Test Mol Biomarkers 15:765–769. https://doi.org/10.1089/gtmb.2011.0024
Dhandapani SS, Manju D, Vivekanandhan S et al (2010) Prospective longitudinal study of biochemical changes in critically ill patients with severe traumatic brain injury: Factors associated and outcome at 6 months. Indian J Neurotrauma 7:23–27. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0973-0508(10)80007-3
Dhandapani S, Aggarwal A, Srinivasan A et al (2015a) Serum lipid profile spectrum and delayed cerebral ischemia following subarachnoid hemorrhage: Is there a relation?. Surgical neurology international. 2015 6(Suppl 21):S543. https://doi.org/10.4103/2152-7806.168067
Dhandapani S, Goudihalli S, Mukherjee KK et al (2015b) Prospective study of the correlation between admission plasma homocysteine levels and neurological outcome following subarachnoid hemorrhage: A case for the reverse epidemiology paradox? Acta Neurochir 157:399–407. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00701-014-2297-0
Dhandapani S, Bajaj A, Gendle C et al (2018) Independent impact of plasma homocysteine levels on neurological outcome following head injury. Neurosurg Rev 41:513–517. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10143-017-0880-6
Duan W, Ladenheim B, Cutler RG et al (2002) Dietary folate deficiency and elevated homocysteine levels endanger dopaminergic neurons in models of Parkinson’s disease. J Neurochem 80:101–110
Ganguly P, Alam SF (2015) Role of homocysteine in the development of cardiovascular disease. Nutr J 14:6. https://doi.org/10.1186/1475-2891-14-6
Hofmann MA, Lalla E, Lu Y et al (2001) Hyperhomocysteinemia enhances vascular inflammation and accelerates atherosclerosis in a murine model. J Clin Invest 107:675–683. https://doi.org/10.1172/JCI10588
Hoque MM, Rahman MZ, Rahman MR (2008) Role of homocysteine in cerebrovascular disease. Mymensingh Medical Journal : MMJ 17:S39–S42
Jiang S, Li J, Zhang Y et al (2017) Methylenetetrahydrofolate reductase C677T polymorphism, hypertension and risk of stroke: a prospective, nested case-control study. Int J Neurosci 127:253–260. https://doi.org/10.1080/00207454.2016.1183126
Kalita J, Srivastava R, Bansal V et al (2006) Methylenetetrahydrofolate reductase gene polymorphism in Indian stroke patients. Neurol India 54:260–263. https://doi.org/10.4103/0028-3886.27148
Kang SS, Wong PW, Zhou JM et al (1988) Thermolabile methylenetetrahydrofolate reductase in patients with coronary artery disease. Metab Clin Exp 37:611–613
Kang S, Zhao X, Liu L et al (2013) Association of the C677T polymorphism in the MTHFR gene with hemorrhagic stroke: a meta-analysis. Gen Test Mol Biomarkers 17:412–417. https://doi.org/10.1089/gtmb.2012.0295
Kumar J, Das SK, Sharma P et al (2005) Homocysteine levels are associated with MTHFR A1298C polymorphism in Indian population. J Hum Genet 50:655–663. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10038-005-0313-1
Kumar M, Modi M, Sandhir R (2017) Hydrogen sulfide attenuates homocysteine-induced cognitive deficits and neurochemical alterations by improving endogenous hydrogen sulfide levels. BioFactors 43:434–450. https://doi.org/10.1002/biof.1354
Li Z, Sun L, Zhang H et al (2003) Elevated Plasma Homocysteine Was Associated With Hemorrhagic and Ischemic Stroke, but Methylenetetrahydrofolate Reductase Gene C677T Polymorphism Was a Risk Factor for Thrombotic Stroke: A Multicenter Case-Control Study in China. Stroke 34:2085–2090. https://doi.org/10.1161/01.STR.0000086753.00555.0D
Liu S, Wu Y, Liu X et al (2017) Lack of association between MTHFR A1298C variant and Alzheimer’s disease: evidence from a systematic review and cumulative meta-analysis. Neurol Res 39:426–434. https://doi.org/10.1080/01616412.2017.1297340
Lv Q-Q, Lu J, Sun H, Zhang J-S (2015) Association of methylenetetrahydrofolate reductase (MTHFR) gene polymorphism with ischemic stroke in the Eastern Chinese Han population. Genet Mol Res 14:4161–4168. https://doi.org/10.4238/2015.April.27.31
Mansoori N, Tripathi M, Luthra K, et al (2012) MTHFR (677 and 1298) and IL-6-174 G/C genes in pathogenesis of Alzheimer’s and vascular dementia and their epistatic interaction. Neurobiol Aging 33:1003.e1–1001003.e8. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neurobiolaging.2011.09.018
Modi M, Prabhakar S, Majumdar S et al (2005) Hyperhomocysteinemia as a risk factor for ischemic stroke: an Indian scenario. Neurol India 53:297-301-2
Moe KT, Woon FP, De Silva DA et al (2008) Association of acute ischemic stroke with the MTHFR C677T polymorphism but not with NOS3 gene polymorphisms in a Singapore population. Eur J Neurol 15:1309–1314. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1468-1331.2008.02308.x
Morita H, Kurihara H, Tsubaki S et al (1998) Methylenetetrahydrofolate reductase gene polymorphism and ischemic stroke in Japanese. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol 18:1465–1469
Najafipour R, Moghbelinejad S, Aleyasin A, Jalilvand A (2017) Effect of B9 and B12 vitamin intake on semen parameters and fertility of men with MTHFR polymorphisms. Andrology 5:704–710. https://doi.org/10.1111/andr.12351
Norambuena PA, Copeland JA, Křenková P et al (2009) Diagnostic method validation: High resolution melting (HRM) of small amplicons genotyping for the most common variants in the MTHFR gene. Clin Biochem 42:1308–1316. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.clinbiochem.2009.04.015
Panigrahi I, Chatterjee T, Biswas A et al (2006) Role of MTHFR C677T polymorphism in ischemic stroke. Neurol India 54:48-50-2
Rai V (2016a) Folate Pathway Gene Methylenetetrahydrofolate Reductase C677T Polymorphism and Alzheimer Disease Risk in Asian Population. Indian J Clin Biochem 31:245–252. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12291-015-0512-2
Rai V (2016b) Association of methylenetetrahydrofolate reductase (MTHFR) gene C677T polymorphism with autism: evidence of genetic susceptibility. Metab Brain Dis 31:727–735. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11011-016-9815-0
Roussotte FF, Hua X, Narr KL et al (2017) Archival Report The C677T Variant in MTHFR Modulates Associations Between Brain Integrity, Mood, and Cognitive Functioning in Old Age. Biol Psychiatry. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bpsc.2016.09.005
Sambrook J, Russell DW (2006) Purification of nucleic acids by extraction with phenol:chloroform. CSH Protocols 2006. https://doi.org/10.1101/pdb.prot4455
Saraswathy KN, Mukhopadhyay R, Sinha E et al (2008) MTHFR C677T polymorphisms among the Ahirs and Jats of Haryana (India). Am J Hum Biol 20:116–117. https://doi.org/10.1002/ajhb.20682
Sawuła W, Banecka-Majkutewicz Z, Kadziński L et al (2008) Improved HPLC method for total plasma homocysteine detection and quantification. Acta Biochim Pol 55:119–125
Serapinas D, Boreikaite E, Bartkeviciute A et al (2017) The importance of folate, vitamins B6 and B12 for the lowering of homocysteine concentrations for patients with recurrent pregnancy loss and MTHFR mutations. Reprod Toxicol 72:159–163. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.reprotox.2017.07.001
Škovierová H, Vidomanová E, Mahmood S, et al (2016) The Molecular and Cellular Effect of Homocysteine Metabolism Imbalance on Human Health. Int J Mol Sci 17. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms17101733
Smith AD, Smith SM, de Jager CA et al (2010) Homocysteine-lowering by b vitamins slows the rate of accelerated brain atrophy in mild cognitive impairment: A randomized controlled trial. PLoS One 5:1–10. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0012244
Tripathi R, Tewari S, Singh PK, Agarwal S (2010) Association of homocysteine and methylene tetrahydrofolate reductase (MTHFR C677T) gene polymorphism with coronary artery disease (CAD) in the population of North India. Genet Mol Biol 33:224–228. https://doi.org/10.1590/S1415-47572010005000026
van Gijn J, Kerr RS, Rinkel GJE et al (2007) Subarachnoid haemorrhage. Lancet (London, England) 369:306–318. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0140-6736(07)60153-6
Wilcken B, Bamforth F, Li Z et al (2003) Geographical and ethnic variation of the 677C>T allele of 5,10 methylenetetrahydrofolate reductase (MTHFR): findings from over 7000 newborns from 16 areas world wide. J Med Genet 40:619–625. https://doi.org/10.1136/jmg.40.8.619
Yadav U, Kumar P, Gupta S, Rai V (2016) Role of MTHFR C677T gene polymorphism in the susceptibility of schizophrenia: An updated meta-analysis. Asian J Psychiatr 20:41–51. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ajp.2016.02.002
Yao E-S, Tang Y, Xie M-J et al (2016) Elevated Homocysteine Level Related to Poor Outcome After Thrombolysis in Acute Ischemic Stroke. Med Sci Monit 22:3268–3273
Zhao M, Wang X, He M et al (2017) Homocysteine and Stroke Risk. Stroke 48:1183–1190. https://doi.org/10.1161/STROKEAHA.116.015324
Zhou F, chen B, Chen C et al (2015) Elevated Homocysteine Levels Contribute to Larger Hematoma Volume in Patients with Intracerebral Hemorrhage. J Stroke Cerebrovasc Dis 24:784–788. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jstrokecerebrovasdis.2014.11.005
Zoccolella S, dell’Aquila C, Specchio LM et al (2010) Elevated homocysteine levels in Parkinson’s Disease: is there anything besides L-dopa treatment? Curr Med Chem 17:213–221
Acknowledgements
The financial assistance provided by Department of Bio-Technology (DBT), Govt. of India, New Delhi [grant number BT/361/NE/TBP/2012] is acknowledged. The fellowship to MK from the University Grants Commission (UGC), New Delhi [F.17-7(J)/2004(SA-1)] is also acknowledged. The authors also acknowledge UGC-Special Assistance Programme (UGC-SAP) Departmental Research Support-II (DRS-II). The financial assistance provided by the Department of Science and Technology (DST), New Delhi under Promotion of University Research and Scientific Excellence (PURSE) grant is also acknowledged. The help of Prof. Suresh K. Sharma from the Department of Statistics, Panjab University in data analysis is gratefully acknowledged.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethical approval
All experiments were accordance with the ethical standards and were approved by the Institutional Ethics Committee of PGIMER (NK/872/M.Ch./542).
Informed consent
Informed consent was obtained from all participants included in the study.
Conflict of interest
The authors state no conflict of interest.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kumar, M., Goudihalli, S., Mukherjee, K. et al. Methylenetetrahydrofolate reductase C677T variant and hyperhomocysteinemia in subarachnoid hemorrhage patients from India. Metab Brain Dis 33, 1617–1624 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11011-018-0268-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11011-018-0268-5