Abstract
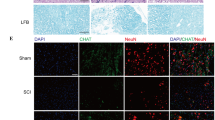
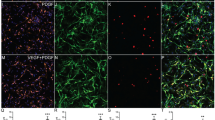
Spinal cord injury (SCI) is a devastating traumatic event which burdens the affected individuals and the health system. Schwann cell (SC) transplantation is a promising repair strategy after SCI. However, a large number of SCs do not survive following transplantation. Previous studies demonstrated that 17β-estradiol (E2) protects different cell types and reduces tissue damage in SCI experimental animal model. In the current study, we evaluated the protective potential of E2 on SCs in vitro and investigated whether the combination of hormonal and SC therapeutic strategy has a better effect on the outcome after SCI. Primary SC cultures were incubated with E2 for 72 h. In a subsequent experiment, thoracic contusion SCI was induced in male rats followed by sustained administration of E2 or vehicle. Eight days after SCI, DiI-labeled SCs were transplanted into the injury epicenter in vehicle and E2-treated animals. The combinatory regimen decreased neurological and behavioral deficits and protected neurons and oligodendrocytes in comparison to vehicle rats. Moreover, E2 and SC significantly decreased the number of Iba-1+ (microglia) and GFAP+ cells (astrocyte) in the SCI group. In addition, we found a significant reduction of mitochondrial fission-markers (Fis1) and an increase of fusion-markers (Mfn1 and Mfn2) in the injured spinal cord after E2 and SC treatment. These data demonstrated that E2 protects SCs against hypoxia-induced SCI and improves the survival of transplanted SCs.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Agudo M, Woodhoo A, Webber D, Mirsky R, Jessen KR, McMahon SB (2008) Schwann cell precursors transplanted into the injured spinal cord multiply, integrate and are permissive for axon growth. Glia 56:1263–1270
Ahuja CS, Nori S, Tetreault L, Wilson J, Kwon B, Harrop J, Choi D, Fehlings MG (2017) Traumatic spinal cord injury-repair and regeneration. Neurosurgery 80:S9–s22
Anderson KD, Guest JD, Dietrich WD, Bartlett Bunge M, Curiel R, Dididze M, Green BA, Khan A, Pearse DD, Saraf-Lavi E, Widerstrom-Noga E, Wood P, Levi AD (2017) Safety of autologous human Schwann cell transplantation in Subacute thoracic spinal cord injury. J Neurotrauma 34:2950–2963
Andrzejewska A, Nowakowski A, Janowski M, Bulte JWM, Gilad AA, Walczak P, Lukomska B (2015) Pre- and postmortem imaging of transplanted cells. Int J Nanomedicine 10:5543–5559
Anna Z, Katarzyna JW, Joanna C, Barczewska M, Joanna W, Wojciech M (2017) Therapeutic potential of olfactory Ensheathing cells and Mesenchymal stem cells in spinal cord injuries. Stem Cells Int 2017:3978595
Arnold S, Beyer C (2009) Neuroprotection by estrogen in the brain: the mitochondrial compartment as presumed therapeutic target. J Neurochem 110:1–11
Arnold S, de Araujo GW, Beyer C (2008) Gender-specific regulation of mitochondrial fusion and fission gene transcription and viability of cortical astrocytes by steroid hormones. J Mol Endocrinol 41:289–300
Assouline JG, Bosch EP, Lim R (1983) Purification of rat Schwann cells from cultures of peripheral nerve: an immunoselective method using surfaces coated with anti-immunoglobulin antibodies. Brain Res 277:389–392
Basso DM (2004) Behavioral testing after spinal cord injury: congruities, complexities, and controversies. J Neurotrauma 21:395–404
Basso DM, Beattie MS, Bresnahan JC (1995) A sensitive and reliable locomotor rating scale for open field testing in rats. J Neurotrauma 12:1–21
Bilsland LG, Nirmalananthan N, Yip J, Greensmith L, Duchen MR (2008) Expression of mutant SOD1 in astrocytes induces functional deficits in motoneuron mitochondria. J Neurochem 107:1271–1283
Bunge MB (2008) Novel combination strategies to repair the injured mammalian spinal cord. J Spinal Cord Med 31:262–269
Bunge MB, Wood PM (2012) Realizing the maximum potential of Schwann cells to promote recovery from spinal cord injury. Handb Clin Neurol 109:523–540
Campbell GR, Mahad DJ (2011) Mitochondria as crucial players in demyelinated axons: lessons from neuropathology and experimental demyelination. Autoimmun Dis 2011:262847
Chakrabarti M, Haque A, Banik NL, Nagarkatti P, Nagarkatti M, Ray SK (2014) Estrogen receptor agonists for attenuation of neuroinflammation and neurodegeneration. Brain Res Bull 109:22–31
Chakrabarti M, Das A, Samantaray S, Smith JA, Banik NL, Haque A, Ray SK (2016) Molecular mechanisms of estrogen for neuroprotection in spinal cord injury and traumatic brain injury. Rev Neurosci 27:271–281
Chan W-M, Mohammed Y, Lee I, Pearse DD (2013) Effect of gender on recovery after spinal cord injury. Transl Stroke Res 4:447–461
Chaovipoch P, Jelks KA, Gerhold LM, West EJ, Chongthammakun S, Floyd CL (2006) 17beta-estradiol is protective in spinal cord injury in post- and pre-menopausal rats. J Neurotrauma 23:830–852
Chen H, Chomyn A, Chan DC (2005) Disruption of fusion results in mitochondrial heterogeneity and dysfunction. J Biol Chem 280:26185–26192
Chen L, Huang H, Xi H, Zhang F, Liu Y, Chen D, Xiao J (2014) A prospective randomized double-blind clinical trial using a combination of olfactory ensheathing cells and Schwann cells for the treatment of chronic complete spinal cord injuries. Cell Transplant 23(Suppl 1):S35–S44
Cuzzocrea S, Genovese T, Mazzon E, Esposito E, Di Paola R, Muia C, Crisafulli C, Peli A, Bramanti P, Chaudry IH (2008) Effect of 17beta-estradiol on signal transduction pathways and secondary damage in experimental spinal cord trauma. Shock (Augusta, Ga) 29:362–371
Dasari VR, Veeravalli KK, Dinh DH (2014) Mesenchymal stem cells in the treatment of spinal cord injuries: a review. World J Stem Cells 6:120–133
Dave KR, Bradley WG, Perez-Pinzon MA (2003) Early mitochondrial dysfunction occurs in motor cortex and spinal cord at the onset of disease in the wobbler mouse. Exp Neurol 182:412–420
Detmer SA, Chan DC (2007) Complementation between mouse Mfn1 and Mfn2 protects mitochondrial fusion defects caused by CMT2A disease mutations. J Cell Biol 176:405–414
Devivo MJ (2012) Epidemiology of traumatic spinal cord injury: trends and future implications. Spinal Cord 50:365–372
Elkabes S, Nicot AB (2014) Sex steroids and neuroprotection in spinal cord injury: a review of preclinical investigations. Exp Neurol 259:28–37
Enomoto M, Bunge MB, Tsoulfas P (2013) A multifunctional neurotrophin with reduced affinity to p75NTR enhances transplanted Schwann cell survival and axon growth after spinal cord injury. Exp Neurol 248:170–182
Fiocchetti M, Ascenzi P, Marino M (2012) Neuroprotective effects of 17β-estradiol rely on estrogen receptor membrane initiated signals. Front Physiol 3:73
Flora G, Joseph G, Patel S, Singh A, Bleicher D, Barakat DJ, Louro J, Fenton S, Garg M, Bunge MB, Pearse DD (2013) Combining neurotrophin-transduced schwann cells and rolipram to promote functional recovery from subacute spinal cord injury. Cell Transplant 22:2203–2217
Furlan JC, Krassioukov AV, Fehlings MG (2005) The effects of gender on clinical and neurological outcomes after acute cervical spinal cord injury. J Neurotrauma 22:368–381
Garcia-Alias G, Lopez-Vales R, Fores J, Navarro X, Verdu E (2004) Acute transplantation of olfactory ensheathing cells or Schwann cells promotes recovery after spinal cord injury in the rat. J Neurosci Res 75:632–641
Golden KL, Pearse DD, Blits B, Garg MS, Oudega M, Wood PM, Bunge MB (2007) Transduced Schwann cells promote axon growth and myelination after spinal cord injury. Exp Neurol 207:203–217
Gonzalez Deniselle MC, Carreras MC, Garay L, Gargiulo-Monachelli G, Meyer M, Poderoso JJ, De Nicola AF (2012) Progesterone prevents mitochondrial dysfunction in the spinal cord of wobbler mice. J Neurochem 122:185–195
Guest J, Santamaria AJ, Benavides FD (2013) Clinical translation of autologous Schwann cell transplantation for the treatment of spinal cord injury. Curr Opin Organ Transplant 18(6):682–689
Haastert K, Mauritz C, Chaturvedi S, Grothe C (2007) Human and rat adult Schwann cell cultures: fast and efficient enrichment and highly effective non-viral transfection protocol. Nat Protoc 2:99–104
Hill CE, Moon LD, Wood PM, Bunge MB (2006) Labeled Schwann cell transplantation: cell loss, host Schwann cell replacement, and strategies to enhance survival. Glia 53:338–343
Hill CE, Guller Y, Raffa SJ, Hurtado A, Bunge MB (2010) A calpain inhibitor enhances the survival of Schwann cells in vitro and after transplantation into the injured spinal cord. J Neurotrauma 27:1685–1695
Holtz A, Nystrom B, Gerdin B (1989) Blocking weight-induced spinal cord injury in rats: effects of TRH or naloxone on motor function recovery and spinal cord blood flow. Acta Neurol Scand 80:215–220
Hunanyan AS, Petrosyan HA, Alessi V, Arvanian VL (2013) Combination of chondroitinase ABC and AAV-NT3 promotes neural plasticity at descending spinal pathways after thoracic contusion in rats. J Neurophysiol 110:1782–1792
Kachadroka S, Hall AM, Niedzielko TL, Chongthammakun S, Floyd CL (2010) Effect of endogenous androgens on 17β-estradiol-mediated protection after spinal cord injury in male rats. J Neurotrauma 27:611–626
Kadam AB, Nyirjesy SC, Millhouse PW, Kong CY, Vaccaro AR, Mounts TI, Laughlin JD, Scuderi GJ, Muñoz WA, Chaudhary SB (2016) 1. Spinal cord injury: stem cells and pharmacologic treatment. Recent advances in spinal. Surgery 1
Kanno H, Pressman Y, Moody A, Berg R, Muir EM, Rogers JH, Ozawa H, Itoi E, Pearse DD, Bunge MB (2014) Combination of engineered Schwann cell grafts to secrete neurotrophin and chondroitinase promotes axonal regeneration and locomotion after spinal cord injury. J Neurosci: Off J Soc Neurosci 34:1838–1855
Kanno H, Pearse DD, Ozawa H, Itoi E, Bunge MB (2015) Schwann cell transplantation for spinal cord injury repair: its significant therapeutic potential and prospectus. Rev Neurosci 26:121–128
Karki P, Smith K, Johnson J, Lee E (2014) Astrocyte-derived growth factors and estrogen neuroprotection: role of transforming growth factor-α in estrogen-induced upregulation of glutamate transporters in astrocytes. Mol Cell Endocrinol 389:58–64
Khalaj AJ, Yoon J, Nakai J, Winchester Z, Moore SM, Yoo T, Martinez-Torres L, Kumar S, Itoh N, Tiwari-Woodruff SK (2013) Estrogen receptor (ER) beta expression in oligodendrocytes is required for attenuation of clinical disease by an ERbeta ligand. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 110:19125–19130
Kloos AD, Fisher LC, Detloff MR, Hassenzahl DL, Basso DM (2005) Stepwise motor and all-or-none sensory recovery is associated with nonlinear sparing after incremental spinal cord injury in rats. Exp Neurol 191:251–265
Kubilus JK, Linsenmayer TF (2010) Developmental corneal innervation: interactions between nerves and specialized apical corneal epithelial cells. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci 51:782–789
Lammerding L, Slowik A, Johann S, Beyer C, Zendedel A (2016) Poststroke Inflammasome expression and regulation in the Peri-infarct area by gonadal steroids after transient focal ischemia in the rat brain. Neuroendocrinology 103:460–475
Lassailly F, Griessinger E, Bonnet D (2010) "Microenvironmental contaminations" induced by fluorescent lipophilic dyes used for noninvasive in vitro and in vivo cell tracking. Blood 115:5347–5354
Lee YJ, Jeong SY, Karbowski M, Smith CL, Youle RJ (2004) Roles of the mammalian mitochondrial fission and fusion mediators Fis1, Drp1, and Opa1 in apoptosis. Mol Biol Cell 15:5001–5011
Lehmann HC (2010) Schwann cells as a therapeutic target for peripheral neuropathies. CNS Neurol Disord Drug Targets 9:801–806
Letaif OB, Cristante AF, Barros Filho TE, Ferreira R, Santos GB, Rocha ID, Marcon RM (2015) Effects of estrogen on functional and neurological recovery after spinal cord injury: an experimental study with rats. Clinics (Sao Paulo, Brazil) 70:700–705
Li J, Lepski G (2013) Cell transplantation for spinal cord injury: a systematic review. Biomed Res Int 2013:786475
Lu HZ, Xu L, Zou J, Wang YX, Ma ZW, Xu XM, Lu PH (2008) Effects of autoimmunity on recovery of function in adult rats following spinal cord injury. Brain Behav Immun 22:1217–1230
Luo Y, Zou Y, Yang L, Liu J, Liu S, Liu J, Zhou X, Zhang W, Wang T (2013) Transplantation of NSCs with OECs alleviates neuropathic pain associated with NGF downregulation in rats following spinal cord injury. Neurosci Lett 549:103–108
Moradi F, Bahktiari M, Joghataei MT, Nobakht M, Soleimani M, Hasanzadeh G, Fallah A, Zarbakhsh S, Hejazian LB, Shirmohammadi M (2012) BD PuraMatrix peptide hydrogel as a culture system for human fetal Schwann cells in spinal cord regeneration. J Neurosci Res 90:2335–2348
Morale MC, Serra PA, L'Episcopo F, Tirolo C, Caniglia S, Testa N, Gennuso F, Giaquinta G, Rocchitta G, Desole MS, Miele E, Marchetti B (2006) Estrogen, neuroinflammation and neuroprotection in Parkinson's disease: glia dictates resistance versus vulnerability to neurodegeneration. Neuroscience 138:869–878
Morrissey TK, Kleitman N, Bunge RP (1991) Isolation and functional characterization of Schwann cells derived from adult peripheral nerve. The Journal of neuroscience : the official journal of the Society for Neuroscience 11:2433–2442
Mosquera L, Colón JM, Santiago JM, Torrado AI, Meléndez M, Segarra AC, Rodríguez-Orengo JF, Miranda JD (2014) Tamoxifen and estradiol improved locomotor function and increased spared tissue in rats after spinal cord injury: their antioxidant effect and role of estrogen receptor alpha. Brain Res 1561:11–22
Nilsen J, Brinton RD (2004) Mitochondria as therapeutic targets of estrogen action in the central nervous system. J Neurosci: Off J Soc Neurosci 3:297–313
Oliveri RS, Bello S, Biering-Sorensen F (2014) Mesenchymal stem cells improve locomotor recovery in traumatic spinal cord injury: systematic review with meta-analyses of rat models. Neurobiol Dis 62:338–353
Oudega M, Xu XM (2006) Schwann cell transplantation for repair of the adult spinal cord. J Neurotrauma 23:453–467
Plemel JR, Keough MB, Duncan GJ, Sparling JS, Yong VW, Stys PK, Tetzlaff W (2014) Remyelination after spinal cord injury: is it a target for repair? Prog Neurobiol 117:54–72
Pourheydar B, Joghataei MT, Bakhtiari M, Mehdizadeh M, Yekta Z, Najafzadeh N (2012) Co- transplantation of bone marrow stromal cells with Schwann cells evokes mechanical Allodynia in the contusion model of spinal cord injury in rats. Cell J 13:213–222
Ray SK, Samntaray S, Banik NL (2016) Future directions for using estrogen receptor agonists in the treatment of acute and chronic spinal cord injury. Neural Regen Res 11:1418–1419
Sabapathy V, Tharion G, Kumar S (2015) Cell therapy augments functional recovery subsequent to spinal cord injury under experimental conditions. Stem Cells Int 2015:132172
Saberi H, Moshayedi P, Aghayan HR, Arjmand B, Hosseini SK, Emami-Razavi SH, Rahimi-Movaghar V, Raza M, Firouzi M (2008) Treatment of chronic thoracic spinal cord injury patients with autologous Schwann cell transplantation: an interim report on safety considerations and possible outcomes. Neurosci Lett 443:46–50
Saberi H, Firouzi M, Habibi Z, Moshayedi P, Aghayan HR, Arjmand B, Hosseini K, Razavi HE, Yekaninejad MS (2011) Safety of intramedullary Schwann cell transplantation for postrehabilitation spinal cord injuries: 2-year follow-up of 33 cases. J Neurosurg Spine 15:515–525
Samantaray S, Sribnick EA, Das A, Thakore NP, Matzelle D, Yu SP, Ray SK, Wei L, Banik NL (2010) Neuroprotective efficacy of estrogen in experimental spinal cord injury in rats. Ann N Y Acad Sci 1199:90–94
Samantaray S, Das A, Matzelle DC, Yu SP, Wei L, Varma A, Ray SK, Banik NL (2016) Administration of low dose-estrogen attenuates gliosis and protects neurons in acute spinal cord injury in rats. J Neurochem 136:1064–1073
Santoro B, Bigini P, Levandis G, Nobile V, Biggiogera M, Botti F, Mennini T, Curti D (2004) Evidence for chronic mitochondrial impairment in the cervical spinal cord of a murine model of motor neuron disease. Neurobiol Dis 17:349–357
Sarveazad A, Babahajian A, Bakhtiari M, Soleimani M, Behnam B, Yari A, Akbari A, Yousefifard M, Janzadeh A, Amini N, Agah S, Fallah A, Joghataei MT (2017) The combined application of human adipose derived stem cells and Chondroitinase ABC in treatment of a spinal cord injury model. Neuropeptides 61:39–47
Shen M, Ji Y, Zhang S, Shi H, Chen G, Gu X, Ding F (2012) A proteome map of primary cultured rat Schwann cells. Proteome Sci 10:20
Siriphorn A, Chompoopong S, Floyd CL (2010) 17β-estradiol protects Schwann cells against H2O2-induced cytotoxicity and increases transplanted Schwann cell survival in a cervical hemicontusion spinal cord injury model. J Neurochem 115:864–872
Sribnick EA, Wingrave JM, Matzelle DD, Wilford GG, Ray SK, Banik NL (2005) Estrogen attenuated markers of inflammation and decreased lesion volume in acute spinal cord injury in rats. J Neurosci Res 82:283–293
Sribnick EA, Matzelle DD, Ray SK, Banik NL (2006) Estrogen treatment of spinal cord injury attenuates calpain activation and apoptosis. J Neurosci Res 84:1064–1075
Sribnick EA, Samantaray S, Das A, Smith J, Matzelle DD, Ray SK, Banik NL (2010) Postinjury estrogen treatment of chronic spinal cord injury improves locomotor function in rats. J Neurosci Res 88:1738–1750
Stojanovski D, Koutsopoulos OS, Okamoto K, Ryan MT (2004) Levels of human Fis1 at the mitochondrial outer membrane regulate mitochondrial morphology. J Cell Sci 117:1201–1210
Wang H, Liu C, Ma X (2012) Alginic acid sodium hydrogel co-transplantation with Schwann cells for rat spinal cord repair. Arch Med Sci 8:563–568
Wiliams RR, Bunge MB (2012a) Schwann cell transplantation: a repair strategy for spinal cord injury? Prog Brain Res 201:295–312
Wiliams RR, Bunge MB (2012b) Chapter 15 - Schwann cell transplantation: A repair strategy for spinal cord injury? In: Progress in Brain Research (Stephen BD, Anders B, eds), pp 295–312: Elsevier
Williams RR, Henao M, Pearse DD, Bunge MB (2015) Permissive Schwann cell graft/spinal cord interfaces for axon regeneration. Cell Transplant 24:115–131
Yang L, Ge Y, Tang J, Yuan J, Ge D, Chen H, Zhang H, Cao X (2015) Schwann cells transplantation improves Locomotor recovery in rat models with spinal cord injury: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Cell Physiol Biochem 37:2171–2182
Zendedel A, Monnink F, Hassanzadeh G, Zaminy A, Ansar MM, Habib P, Slowik A, Kipp M, Beyer C (2018) Estrogen attenuates local Inflammasome expression and activation after spinal cord injury. Mol Neurobiol 55(2):1364–1375
Zhang N, Yin Y, Xu SJ, Wu YP, Chen WS (2012) Inflammation & apoptosis in spinal cord injury. Indian J Med Res 135:287–296
Acknowledgments
The study was supported by a grant from the Iran University of Medical sciences and health services, Tehran, Iran and a START grant from the Medical Faculty of the RWTH Aachen, Germany (AZ).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflicts of interests
None.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Namjoo, Z., Moradi, F., Aryanpour, R. et al. Combined effects of rat Schwann cells and 17β-estradiol in a spinal cord injury model. Metab Brain Dis 33, 1229–1242 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11011-018-0220-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11011-018-0220-8