Abstract
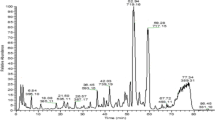
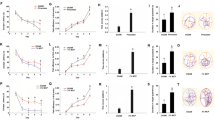
The aim of this study was to explore the neuroprotective effects of active compounds from Schisandra chinensis (Trucz.) Baill. (Magnoliaceae) against the D-galactose (D-gal)-induced neurotoxicity in rat. The Wistar rats were subcutaneously injected with D-gal (150 mg/(kg day)) for six weeks and orally administered with water extract or 95 % ethanol extract (partitioned with petroleum ether (PE), chloroform (CF), ethyl acetate (EA) and n-Butanol (NB), respectively) of the fruits of Schisandra chinensis simultaneously. The alteration of cognitive functions was assessed by using Morris water maze and Step-down type passive avoidance test. The results demonstrated that PE fraction was the most effective fraction to ameliorate cognitive deficits. Further biochemical examination indicated that PE could attenuate the activities decreasing of superoxide dismutase (SOD), catalase (CAT), the total antioxidant (T-AOC) induced by D-gal, and maintain the normal levels of glutathione (GSH), malondialdehyde (MDA) and nitric oxide (NO) in the serum, prefrontal cortex, striatum and hippocampus of the brain of related rat, selectively. Meanwhile, the compounds of PE fraction were also identified as mainly lignans, thus, these results suggest that lignans from the PE fraction of Schisandra chinensis represented a potential source of medicine for the treatment of the aging-associated neurodegenerative diseases.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ahn HS, Jeon TI, Lee JY, Hwang SG, Lim Y, Park DK (2002) Antioxidative activity of persimmon and grape seed extract: in vitro and in vivo. Nutr Res 22:1265–1273
Anbarasi K, Vani G, Balakrishna K, Devi C.S., (2006). Effect of bacoside A on brain antioxidant status in cigarette smoke exposed rats. Life Sci 78, 1378–1384
Calabrese V, Bates TE, Stella AM (2000) NO synthase and NO-dependent signalpathways in brain aging and neurodegenerative disorders: the role of oxidant/antioxidant balance. Neurochem Res 25:1315–1341
Castegna A, Aksenov M, Aksenova M, Thongboonkerd V, Klein JB, Pierce WM (2002) Proteomic identification of oxidatively modified proteins in Alzheimer’s disease brain. Part I: Creatine kinase BB, glutamine synthase, and ubiquitin carboxy-terminal hydrolase L-1. Free Radic Biol Med 33:562–571
Chen, X.Q., Zhang, Y., Zu, Y.G, Fu, Y.J., Wang, W., (2011a). Composition and biological activities of the essential oil from Schisandra chinensis obtained by solvent -free microwave extraction. LWT Food Sci Technol 44, 2047–2052.
Chen WW, He RR, Li YF, Li SB, Tsoi B, Kurihara H (2011b) Pharmacological studies on the anxiolytic effect of standardized Schisandra lignans extract on restraint-stressed mice. Phytomedicine 18:1144–1147
Chinese Pharmacopoeia Commission (2015) The Pharmacopoeia of the People’s Republic of China Version (2015). Press, Beijing, Chin. Med. Sci. Technol
Chiu L, Yang SH (1992) Fructus Schisandrae: possesses anti-cancer and anti- aging activities. Gansu Medical Journal 11:288
Choi YW, Takamatsu SS, Kha SI, Srinivas PV, Ferreira D, Zhao JP, Khan IA (2006) Schisandrene, a Dibenzocyclooctadiene Lignan from Schisandr chinensis: Structure-Antioxidant Activity Relationships of Dibenzocyclooctadiene Lignans. J Nat Prod 69:356–359
Cui X, Zuo P, Zhang Q, Li X, Hu Y, Long J, et al. (2006) Chronic systemic D-galactose exposure induces memory loss, neurodegeneration, and oxidative damage in mice. protective effects of R-alpha-lipoic acid. J Neurosci Res 84:647–654
Freeman BA, Crapo JD (1981) Hyperoxia increases oxygen radical production in rat lungs and lung mitochondrial. J Biol Chem 256:10986–10992
Grune, T., (2000) Oxidative stress, aging and the proteasomal system. Biogerontology1, 31–40
Halliwell B (2007) Biochemistry of oxidative stress. Biochem Soc Trans 35(5):1147–1150
Harman D (1957) Aging: a theory based on free radical and radiation chemistry. J Gerontol Ser 2:298–300
Hsieh MT, Wu CR, Wang WH, Lin LW (2001) The ameliorating effect of the water layer of Fructus Schisandrae on cycloheximide-induced amnesia in rats: interaction with drugs acting at neurotransmitter receptors. Pharmacol Res 43:17–22
Huang YD, Mucke L (2012) Alzheimer Mechanisms and Therapeutic Strategies. Cell 148:1204–1222
Hu D, Li CX, Han N, Miao LJ, Wang D, Liu ZH, Wang H, Yin J (2012) Deoxyschizandrin Isolated from the Fruits of Schisandra chinensis Ameliorates Aβ1-42-induced Memory Impairment in Mice. Planta Med 78:1332–1336
Jeong EJ, Lee HK, Lee KY, Jeon BJ, Kim DH (2013) The effects of lignan-riched extract of Shisandra chinensis on amyloid-β-induced cognitive impairment and neurotoxicity in the cortex and hippocampus of mouse. J Ethnopharmacol 146:347–354
Ko KM, Ip SP, Poon MK, Wu SS, Che CT, Ng KH, Kong YC (1995) Effect of a lignin-enriched fructus schisandrae extract on hepatic glutathione status in rats: protection against carbon tetrachloride toxicity. Planta Med 61(2):134–137
Lee TH, Jung CW, Lee DH (2012) Neuroprotective effects of Schisandrin B against transient focal cerebral ischemia in Sprague–Dawley rats. Food Chem Toxicol 50:4239–4245
Li XM, Ma YL, Liu XJ (2007) Effect of the Lycium barbarum polysaccharides on age-related oxidative stress in aged mice. J Ethnopharmacol 111(3):504–511
Lu H, Liu GT (1991) Effect of dibenzo [a, c] cyclooctene lignans isolated from Fructus schizandrae on lipid peroxidation and antioxidative enzyme activity. Chem Biol Interact 78(1):77–84
Lu, J., Zheng, Y.L., Wu, D.M., Luo, L., Sun, D.X., Shan, Q., (2007) Ursolic acid ameliorates cognition deficits and attenuates oxidative damage in the brain of senescent mice induced by D-galactose. Biochem Pharmacol 74, 1078–1090
Paradies G, Petrosillo G, Paradies V, Ruggiero FM (2011) Mitochondrial dysfunction in brain aging: role of oxidative stress and cardiolipin. Neurochem Int 58:447–457
Pratico D (2008) Oxidative stress hypothesis in Alzheimer’s disease: a reappraisal. Trends Pharmacol Sci 29:609–615
Shan, Q., Lu, J., Zheng, Y.L., Li, J., Zhou, Z., Hu, B., Zhang, Z.F., Fan, S.H., Mao, Z., Wang, Y.J., Ma, D.F., (2009) Purple sweet potato color ameliorates cognition deficits and attenuates oxidative damage and inflammation in aging mouse brain induced by D-galactose. Journal of Biomedicine and Biotechnology, 1–9
Takimoto Y, Qian HY, Yoshigai E, Okumura T, Ikeya Y, Nishizawa M (2013) Gomisin N in the herbal drug gomishi (Schisandra chinensis) suppresses inducible nitric oxide synthase gene via C/EBPβ and NF-κB in rat hepatocytes. Nitric Oxide 28:47–56
Tesseur I, Pimenova AA, Lo d AC, Ciesielska M, S.F L (2013) Chronic 5-HT4 receptor activation decreases Aβproduction and deposition in hAPP/PS1 mice. Neurobiol Aging 34:1779–1789
Tsai SJ, Chiu CP, Yang HT, Yin MC (2011) S-Allyl cysteine, s-ethyl cysteine, and s-propyl cysteine alleviate b-amyloid, glycative, and oxidative injury in brain of mice treated by D-galactose. J Agric Food Chem 59:6319–6326
Wu DM, Lu J, Zheng YL, Zhou Z, Shan Q, Ma DF (2008) Purple sweet potato color repairs D-galactose-induced spatial learning and memory impairment by regulating the expression of synaptic proteins. Neurobiol Learn Mem 90:19–27
Zhang QB, Li N, Zhou GF, Lu XL, Xu ZH, Li Z (2003) In vivo antioxidant activity of poly saccharide fraction from Porphyra haitanesis (Rhodephyta) in aging mice. Pharmacol Res 48:151–155
Zhong SZ, Ge QH, Li Q, Qu R, Ma SP (2009) Peoniflorin attenuates Aß(1-42) mediated neurotoxicity by regulating calcium homeostasis and ameliorating oxidative stress in hippocampus of rats. J Neurol Sci 280:71–78
Zhu JQ, Tuo XP, Chen HS, Lv JY, Jia LY, et al. (2007) Protective effect of Schisandrone on β-amyloid protein-inducedstress injury of hippocampal neurons. Academic Journal of Second Military Medical University 28(9):1015–1016
Acknowledgments
This research was supported by National Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 81573580) and Natural Science Foundation of Liaoning Province of China (No. 2014020076).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of Interest
The authors declare that there are no conflicts of interest.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Yan, T., Shang, L., Wang, M. et al. Lignans from Schisandra chinensis ameliorate cognition deficits and attenuate brain oxidative damage induced by D-galactose in rats. Metab Brain Dis 31, 653–661 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11011-016-9804-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11011-016-9804-3