Abstract
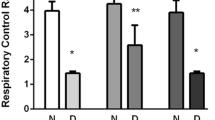
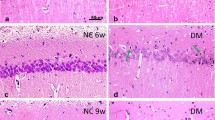
Diabetes mellitus is a disease characterized by increased glucose levels in the blood. Hyperglycemia causes damage to the brain tissue, and induces significant changes in synaptic transmission. In this investigation, we have found a significant alteration in the expression of the molecular motor involved in the synaptic vesicles transport, myosin-Va, and its distribution in rat brains of streptozotocin-induced diabetes model. Brains were removed after 20 days, homogenized and analysed by Western blotting, qRT-PCR and immunohistochemistry. Myosin-Va presented significantly lower levels of both mRNA and protein in diabetic than those observed in non-diabetic animals. Moreover, neuronal and glial cells of the occipital and frontal cortex exhibited decreased myosin-Va immunostaining in diabetic rat brains. In conclusion, diabetic rat brains displayed altered expression and distribution of myosin-Va, and these finding may contribute to the basic understanding about this myosin role in brain function related to diabetes.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Artola A (2008) Diabetes-, stress- and ageing-related changes in synaptic plasticity in hippocampus and neocortex–the same metaplastic process? Eur J Pharmacol 585(1):153–162
Bellush LL, Reid SG, North D (1991) The functional significance of biochemical alterations in streptozotocin-induced diabetes. Physiol Behav 50(5):973–981
Bradford MM (1976) A rapid and sensitive method for the quantitation of microgram quantities of protein utilizing the principle of protein-dye binding. Anal Biochem 72:248–254
Calábria LK, da Cruz GCN, Nascimento R, Carvalho WJ, Gouveia NM, Alves FV, Furtado FB, Ishikawa-Ankerhold HC, de Sousa MV, Goulart LR, Espindola FS (2011) Overexpression of myosin-IIB in the brain of a rat model of streptozotocin-induced diabetes. J Neurol Sci 303(1–2):43–49
de Souza Martins SC, Romao LF, Faria JC, de Holanda Afonso RC, Murray SA, Pellizzon CH, Mercer JA, Cameron LC, Moura-Neto V (2009) Effect of thyroid hormone T3 on myosin-Va expression in the central nervous system. Brain Res 1275:1–9
Drengk AC, Kajiwara JK, Garcia SB, Carmo VS, Larson RE, Zucoloto S, Espreafico EM (2000) Immunolocalisation of myosin-V in the enteric nervous system of the rat. J Auton Nerv Syst 78(2–3):109–112
Espindola FS, Espreafico EM, Coelho MV, Martins AR, Costa FR, Mooseker MS, Larson RE (1992) Biochemical and immunological characterization of p190-calmodulin complex from vertebrate brain: a novel calmodulin-binding myosin. J Cell Biol 118(2):359–368
Espindola FS, Banzi SR, Calabria LK, Custodio RJ, Oliveira RA, Procopio LD, Lima AB, Cunha-Junior JP, Coelho MV, Guedes IM, Pellizzon CH, Larson RE, Espreafico EM (2008) Localization of myosin-Va in subpopulations of cells in rat endocrine organs. Cell Tissue Res 333(2):263–279
Espreafico EM, Cheney RE, Matteoli M, Nascimento AA, De Camilli PV, Larson RE, Mooseker MS (1992) Primary structure and cellular localization of chicken brain myosin-V (p190), an unconventional myosin with calmodulin light chains. J Cell Biol 119(6):1541–1557
Essop MF, Chan WY, Hattingh S (2010) Proteomic analysis of mitochondrial proteins in a mouse model of type 2 diabetes. Cardiovasc J Afr 21:1–4
Fingeroth JM (1996) Dorsal laminectomy. J Am Anim Hosp Assoc 32(3):186–187
Grillo CA, Piroli GG, Wood GE, Reznikov LR, McEwen BS, Reagan LP (2005) Immunocytochemical analysis of synaptic proteins provides new insights into diabetes-mediated plasticity in the rat hippocampus. Neuroscience 136(2):477–486
Hernandez-Fonseca JP, Rincon J, Pedreanez A, Viera N, Arcaya JL, Carrizo E, Mosquera J (2009) Structural and ultrastructural analysis of cerebral cortex, cerebellum, and hypothalamus from diabetic rats. Exp Diabetes Res 2009:329632
Jafari Anarkooli I, Sankian M, Ahmadpour S, Varasteh AR, Haghir H (2008) Evaluation of Bcl-2 family gene expression and Caspase-3 activity in hippocampus STZ-induced diabetic rats. Exp Diabetes Res 2008:638467
Larson RE, Ferro JA, Queiroz EA (1986) Isolation and purification of actomyosin ATPase from mammalian brain. J Neurosci Methods 16(1):47–58
Pastural E, Barrat FJ, Dufourcq-Lagelouse R, Certain S, Sanal O, Jabado N, Seger R, Griscelli C, Fischer A, de Saint BG (1997) Griscelli disease maps to chromosome 15q21 and is associated with mutations in the myosin-Va gene. Nat Genet 16(3):289–292
Persengiev S, Koeleman BP, Downes K, Valdigem G, van der Slik AR, Eerligh P, Monsuur A, Bruining GJ, Wijmenga C, Todd JA, Roep BO, Alizadeh BZ (2010) Association analysis of myosin IXB and type 1 diabetes. Hum Immunol 71(6):598–601
Reck-Peterson SL, Provance DW Jr, Mooseker MS, Mercer JA (2000) Class V myosins. Biochim Biophys Acta 1496(1):36–51
Rodriguez OC, Cheney RE (2002) Human myosin-Vc is a novel class V myosin expressed in epithelial cells. J Cell Sci 115(Pt 5):991–1004
Rudolf R, Bittins CM, Gerdes HH (2010) The role of myosin V in exocytosis and synaptic plasticity. J Neurochem 116(2):177–191
Suter DM, Espindola FS, Lin CH, Forscher P, Mooseker MS (2000) Localization of unconventional myosins V and VI in neuronal growth cones. J Neurobiol 42(3):370–382
Takagishi Y, Murata Y (2006) Myosin Va mutation in rats is an animal model for the human hereditary neurological disease, Griscelli syndrome type 1. Ann N Y Acad Sci 1086:66–80
Takagishi Y, Hashimoto K, Kayahara T, Watanabe M, Otsuka H, Mizoguchi A, Kano M, Murata Y (2007) Diminished climbing fiber innervation of Purkinje cells in the cerebellum of myosin Va mutant mice and rats. Dev Neurobiol 67(7):909–923
Tilelli CQ, Martins AR, Larson RE, Garcia-Cairasco N (2003) Immunohistochemical localization of myosin Va in the adult rat brain. Neuroscience 121(3):573–586
Tomlinson DR, Gardiner NJ (2008) Glucose neurotoxicity. Nat Rev Neurosci 9(1):36–45
Towbin H, Staehelin T, Gordon J (1979) Electrophoretic transfer of proteins from polyacrylamide gels to nitrocellulose sheets: procedure and some applications. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 76(9):4350–4354
Van Gele M, Dynoodt P, Lambert J (2009) Griscelli syndrome: a model system to study vesicular trafficking. Pigment Cell Melanoma Res 22(3):268–282
XiaoMing Z, Xi Z, Fang S, Jilin Z (2004) Specific changes of somatostatin mRNA expression in the frontal cortex and hippocampus of diabetic rats. J Anat 204(Pt 3):221–225
Yin JL, Shackel NA, Zekry A, McGuinness PH, Richards C, Putten KV, McCaughan GW, Eris JM, Bishop GA (2001) Real-time reverse transcriptase-polymerase chain reaction (RT-PCR) for measurement of cytokine and growth factor mRNA expression with fluorogenic probes or SYBR Green I. Immunol Cell Biol 79(3):213–221
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by grants from FAPEMIG to FSE, from CNPq to LRG, by ProBiotec fellowship to AVC, by CAPES fellowship to LKC and RN. We thank Ms. Neire Moura de Gouveia, Fabiana Barcelos Furtado and Fernanda Vieira Alves (INGEB-UFU) for contributions to experimental procedures. We also express our gratitude to the Professor Dr. Marcelo Emílio Beletti at ICBIM-UFU for taking time on many occasions to discuss our immunohistochemistry data with us.
Conflict of interest
The authors are not having any conflict of interest related to this paper.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
da Costa, A.V., Calábria, L.K., Nascimento, R. et al. The streptozotocin-induced rat model of diabetes mellitus evidences significant reduction of myosin-Va expression in the brain. Metab Brain Dis 26, 247–251 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11011-011-9259-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11011-011-9259-5