Abstract
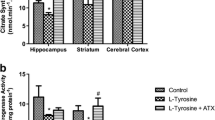
In the present study was evaluated the in vivoeffects of arginine administration on creatine kinase (CK) activity in cerebellum of rats. We also tested the influence of antioxidants, namely α-tocopherol and ascorbic acid and the nitric oxide sinthase inhibitor, Nω-nitro-L-arginine methyl ester (L-NAME), on the effects elicited by Arg in order to investigate the possible participation of nitric oxide (NO) and/or its derivatives peroxynitrite (ONOO−) and other/or free radicals on the effects of arginine on CK activity. Sixty-day-old rats were treated with a single i.p. injection of saline (control, group I), arginine (0.8 g/Kg) (group II), L-NAME (2.0 mg/Kg or 20.0 mg/Kg) (group III) or Arg (0.8 g/Kg) plus L-NAME (2.0 mg/Kg or 20.0 mg/Kg) (group IV) and were killed 1 h later. In another set of experiments, the animals were pretreated for 1 week with daily i.p. administration of saline (control) or α-tocopherol (40 mg/Kg) and ascorbic acid (100 mg/Kg). Twelve hours after the last injection of the antioxidants, the rats received one i.p. injection of arginine (0.8 g/Kg) or saline and were killed 1 h later. Results showed that total and cytosolic CK activities were significantly inhibited by arginine administration in cerebellum of rats, in contrast to mitochondrial CK activity which was not affected by this amino acid. Furthermore, simultaneous injection of L-NAME (20.0 mg/Kg) and treatment with α-tocopherol and ascorbic acid prevented these effects. The data indicate that the reduction of CK activity in cerebellum of rats caused by arginine was probably mediated by NO and/or its derivatives ONOO−and other free radicals. Considering the importance of CK for the maintenance of energy homeostasis in the brain, if this enzyme inhibition also occurs in hyperargininemic patients, it is possible that CK inhibition may be one of the mechanisms by which arginine is neurotoxic in hyperargininemia.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Aksenov MI, Aksenova MV, Payne RM, Smith CD, Markesbery WR, Carney JM (1997) The expression of creatine kinase isoenzymes in neocortex of patients with neurodegenerative disorders: Alzheimer’s and Pick’s disease. Exp Neurol 146:458–465
Aksenov M, Aksenova MV, Butterfield AD, Markesbery WR (2000) Oxidative modification of creatine kinase BB in Alzheimer’s disease brain. J Neurochem 74:2520–2527
Arstall MA, Bailey C, Gross WL, Bak M, Balligand JL, Kelly RA (1998) Reversible S-nitrosation of creatine kinase by nitric oxide in adult rat ventricular myocytes. J Mol Cell Cardiol 30:979–988
Beckman JS, Carson M, Smith CD, Koppenol WH (1993) ALS, SOD and peroxynitrite. Nature 364:584
Blouin JS, Bard C, Paillard J (2004) Contribution of the cerebellum to self-initiated synchronized movements: a PET study. Exp Brain Res 155:63–68
Brusilow SW, Horwich A (2001) Urea Cycle enzymes. In: Scriver CR, Beaudet AL, Sly WS, Valle D (eds) The metabolic and Molecular Bases of Inherited Disease, 8th edn. McGraw-Hill, New York, pp 1909–1963
Brustovetsky N, Brustovetsky T, Dubinsky JM (2001) On the mechanisms of neuroprotection by creatine and phosphocreatine. J Neurochem 76:425–434
Buchmann I, Milakofsky L, Harris N, Hofford JM, Vogel WH (1996) Effect of arginine administration on plasma and brain levels of arginine and various related amino compounds in the rat. Pharmacology 53:133–142
Burmistrov SO, Mashek OP, Kotin AM (1992) The action of acute alcoholic intoxication on antioxidant system and creatine kinase activity in the brain of rat embryos. Eksp Klin Farmakol 55:54–56
Burton GW, Wronska U, Stone L, Foster DO, Ingold KU (1990) Biokinetics of dietary RRR-α-tocopherol in the male guinea-pig at three dietary levels of vitamin C and two levels of vitamin E. Lipids 25:199–210
Cornelio AR, Rodrigues V Jr, Wyse ATS, Dutra-Filho CS, Wajner M, Wannmacher CMD (2004) Tryptophan reduces creatine kinase activity in the brain cortex of rats. Int J Devl Neurosci 22:95–101
Costabeber E, Kessler A, Dutra-Filho CS, Wyse ATS, Wajner M, Wannmacher CMD (2003) Hyperphenylalaninemia reduces creatine kinase activity in the cerebral cortex of rats. Int J Dev Neurosci 21:111–116
David SS, Shoemaker M, Haley BE (1998) Abnormal properties of creatine kinase in Alzheimer’s disease brain: correlation of reduced enzyme activity and active site photolabelling with aberrant cytosol-membrane partitioning. Mol Brain Res 54:276–287
Dawson VL, Dawson TM (1996) Nitric oxide in neuronal degeneration. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med 211:33–40
Dawson VL, Dawson TM (1996) Nitric oxide neurotoxicity. J Chem Neuroanat 10:179–190
Debaere F, Wenderoth N, Sunaert S, Van Hecke P, Swinnen SP (2004) Cerebellar and premotor function in bimanual coordination: parametric neural responses to spatiotemporal complexity and cycling frequency. Neuroimage 21:1416–1427
Delwing D, Delwing D, Wannamacher CMD, Wajner M, Dutra-Filho CS, Wyse ATS (2002) Arginine administration reduces catalase activity in midbrain of rats. NeuroReport 13:1301–1304
Delwing D, Tagliari B, Streck EL, Wannamacher CMD, Wajner M, Wyse ATS (2003) Reduction of energy metabolism in rat hippocampus by aginine administration. Brain Res 983:58–63
Delwing D, Tagliari B, Chiarani F, Wannmacher CMD, Wajner M, Wyse ATS (2006) α-tocopherol and ascorbic acid administration prevents the impairment of brain energy metabolism of hyperargininemic rats. Cell Mol Neurobiol 26:177–189
Dinerman JL, Dawson TM, Schell MJ, Snowman A, Snyder SH (1994) Endothelial nitric oxide synthase localized to hippocampal pyramidal cells: implications for synaptic plasticity. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 91:4214–4218
Fleck RMM, Rodrigues V Jr, Giacomazzi J, Parissoto D, Dutra-Filho CS, Wyse ATS, Wajner M, Wannmacher CMD (2005) Cysteamine prevents and reverses the inhibition of creatine kinase activity caused by cystine in rat brain cortex. Neurochem Int 46:391–397
Flynn NE, Meininger CJ, Haynes TE, Wu G (2002) The metabolic basis of arginine nutrition and pharmacotherapy. Biomed Pharmacother 56:427–438
Gross WL, Bak MI, Ingwall JS, Arstall MA, Smith TW, Balligand JL, Kelly R (1996) Nitric oxide inhibits creatine kinase and regulates heart contractile reserve. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 93:5604–5609
Halliwell B, Gutteridge JMC (1999) Free Radicals in Biology and Medicine, 3rd edn. Oxford University Press, London
Hamman BL, Bittl JA, Jacobus WE, Aleen PD, Spencer RS, Tina R, Ingwall JS (1995) Inhibition of creatine kinase reaction decrease the contractile reserve of isolated rat hearts. Am J Physiol 269:H1030–H1036
Heales SJR, Bolaños JP, Stewart VC, Brookes PS, Land JM, Clark JB (1999) Nitric oxide, mitochondria and neurological disease. Biochem Biophys Acta 1410:215–228
Hensley K, Hall N, Subramaniam R, Cole P, Harris M, Aksenova MV, Aksenov MY, Gabbita SP, Carney JM, Lowell M, Markesbery WR, Butterfield DA (1995) Brain regional correspondence between Alzheimer’s disease histopathology biomarkers of protein oxidation. J Neurochem 65:2146–2156
Hughes BP (1962) A method for estimation of serum creatine kinase and its use in comparing creatine kinase and aldolase activity in normal and pathological sera. Clin Chim Acta 7:597–603
Iyer R, Jenkinson CP, Vockley JG, Kern RM, Grody WW, Cederbaum S (1998) The human arginases and arginase deficiency. J Inherit Metab Dis 21:86–100
Kessler A, Costabeber E, Dutra-Filho CS, Wyse ATS, Wajner M, Wannmacher CMD (2003) Proline reduces creatine kinase activity in the brain cortex of rats. Neurochem Res 28:1175–1180
Konorev E, Hogg N, Kalyanaraman B (1998) Rapid and irreversible inhibition of creatine kinase by peroxynitrite. FEBS Lett 427:171–174
Lincoln J, Hoyle CHV, Burnstock G (1997) Nitric oxide in health and disease. Biochemical Research Topics. Cambridge University Press, Cambridge, pp 3–11
Lipton SA, Choy YB, Pan ZH, Lei SZ, Chen HS, Sucher NJ, Loscalzo J, Singel DJ, Stamler JS (1993) A redox-based mechanism for the neuroprotective effects of nitric oxide and related nitroso-compounds. Nature 364:626–632
Lowry OH, Rosebrough NJ, Farr AL, Randall RJ (1951) Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem 193:265–267
Manos P, Bryan GK, Edmond J (1991) Creatine kinase activity in postnatal rat brain development and in cultured neurons, astrocytes, and oligodendrocytes. J Neurochem 56:2101–2107
Marletta MA (1993) Nitric oxide synthase structure and mechanism. J Biol Chem 268:12231–12234
Mekhfi H, Veksler V, Mateo PH, Maupoil V, Rochette L, Ventura-Clapier R (1996) Creatine kinase in the main target of reactive oxygen species in cardiac myofibrils. Circ Res 17:1016–1027
Nathan C, Xie QW (1994) Nitric oxide synthases: Roles, tools and controls. Cell 78:915–918
Nishikawa T, Kirsch JR, Koehler RC, Bredt SD, Snyder SH, Traystman RJ (1993) Effect of nitric oxide synthase inhibition on cerebral blood flow and injury volume during focal ischemia in cats. Stroke 24:1718–1724
O’Gorman E, Beutner G, Wallimann T, Brdiczka D (1996) Differential effects of creatine depletion on the regulation of enzyme activities and on creatine-stimulated mitochondrial respiration in skeletal muscle. Biochim Biophys Acta 1276:161–170
Pilla C, Cardoso RFO, Dutra-Filho CS, Wyse ATS, Wajner M, Wannmacher CMD (2003) Effect of leucine administration on creatine kinase activity in rat brain. Metab Brain Dis 18:17–25
Reis EA, Oliveira LS, Lamers ML, Netto CA, Wyse ATS (2002) Arginine administration inhibits hippocampal Na+,K+-ATPase activity and impairs retention of an inhibitory avoidance task in rats. Brain Res 951:151–157
Saks VA, Kuznetsov AV, Kuprianov VV, Miceli MV, Jacobus WE (1985) Creatine kinase of rat heart mitochondria. The demonstration of functional coupling to oxidative phosphorylation in an inner membrane-matrix preparation. J Biol Chem 260:7757–7764
Saks VA, Ventura-Clapier R, Aliev MK (1996) Metabolic control and metabolic capacity: two aspects of creatine kinase functioning in the cells. Biochim Biophys Acta 1274:81–88
Schlegel J, Zurbriggen B, Wegmann G, Wyss M, Eppenberger H, Wallimann T (1988) Native mitochondrial creatine kinase forms octameric structures. I. Isolation of two interconvertible mitochondrial creatine kinase forms, dimeric and octameric mitochondrial creatine kinase: Characterization, localization and structurefunction relationships. J Biol Chem 262:16942–16993
Stachowiak O, Dolder M, Wallimann T, Richter C (1998) Mitochondrial creatine kinase is prime target of peroxynitrite-induced modification and inactivation. J Biol Chem 273:16694–16699
Tomimoto H, Yamamoto K, Homburger HA, Yanagihara T (1993) Immunoelectron microscopic investigation of creatine kinase BB-isoenzyme after cerebral ischemia in gerbils. Acta Neuropathol 86:447–455
Turpaev KT (2002) Reactive oxygen species and regulation of gene expression. Biochemistry (Mosc) 67:281–292
Wallimann T, Wyss M, Brdiczka D, Nicolay K (1992) Intracellular compartmentation, structure and function of creatine kinase isoenzymes in tissues with high and fluctuating energy demands: the ‘phosphocreatine circuit’ for cellular energy homeostasis. Biochem J 28:121–140
Wallimann T, Hemmer W (1994) Creatine kinase in non-muscle tissues and cells. Mol Cell Biochem 133/134:193–220
Wallimann T, Dolder M, Schlattner U, Eder M, Hornemann T, Kraft T, Stolz M (1998b) Creatine kinase: an enzyme with a central role in cellular energy metabolism. MAGMA 6:116–119
Wolosker H, Panizzutti R, Englender S (1996) Inhibition of creatine kinase with S-nitrosoglutathione. FEBS Lett 392:274–276
Wyse ATS, Bavaresco CS, Bandinelli C, Streck EL, Franzon R, Dutra-Filho CS, Wajner M (2001) Nitric oxide synthase inhibition by L-NAME prevents the decrease of Na+,K+-ATPase activity in midbrain of rats subjected to arginine administration. Neurochem Res 26:515–520
Wyse ATS, Zugno AI, Streck EL, Matte C, Calcagnotto T, Wannmacher CMD, Wajner M (2002) Inhibition of Na+,K+-ATPase activity in hippocampus of rats subjected to acute administration of homocysteine is prevented by vitamins E and C treatment. Neurochem Res 27:1685–1689
Yuan G, Kaneko M, Masuda H, Hon RG, Kobayashi A, Yamazak N (1992) Decrease in heart mitochondrial creatine kinase activity due to oxygen free radical. Biochim Biophys Acta 1140:78–84
Zarrindast MR, Gholami A, Sahraei H, Haeri-Rohani A (2003) Role of nitric oxide in the acquisition of apomorphine-or morphine-induced locomotor sensitization. Eur J Pharmacol 482:205–213
Acknowledgement
This work was supported in part by grants from Conselho Nacional de Desenvolvimento Científico e Tecnológico (CNPq – Brazil).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Delwing, D., Cornélio, A.R., Wajner, M. et al. Arginine administration reduces creatine kinase activity in rat cerebellum. Metab Brain Dis 22, 13–23 (2007). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11011-006-9028-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11011-006-9028-z