Abstract
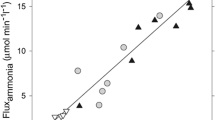
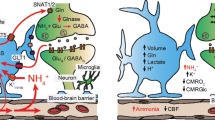
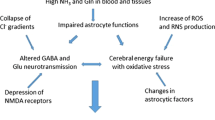
Chronic liver failure leads to hyperammonemia and consequently increased brain ammonia concentrations, resulting in hepatic encephalopathy. When the liver fails to regulate ammonia concentrations, the brain, devoid of a urea cycle, relies solely on the amidation of glutamate to glutamine through glutamine synthetase, to efficiently clear ammonia. Surprisingly, under hyperammonemic conditions, the brain is not capable of increasing its capacity to remove ammonia, which even decreases in some regions of the brain. This non-induction of glutamine synthetase in astrocytes could result from possible limiting substrates or cofactors for the enzyme, or an indirect effect of ammonia on glutamine synthetase expression. In addition, there is evidence that nitration of the enzyme resulting from exposure to nitric oxide could also be implicated. The present review summarizes these possible factors involved in limiting the increase in capacity of glutamine synthetase in brain, in chronic liver failure.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Baltrons, M.A., and Garcia, A. (2001). The nitric oxide/cyclic GMP system in astroglial cells. Prog. Brain Res. 132:325–337.
Butterworth, R.F. (2003). Hepatic encephalopathy. Alcohol Res. Health 27:240–246.
Butterworth, R.F., Girard, G., and Giguere, J.F. (1988). Regional differences in the capacity for ammonia removal by brain following portacaval anastomosis. J. Neurochem. 51:486–490.
Cooper, A.J.L., Mora, S.N., Cruz, N.F., and Gelbard, A.S. (1985). Cerebral ammonia metabolism in hyperammonemic rats. J. Neurochem. 4:1716–1723.
Cremer J.E., Heath, D.F., Teal, H.M., Woods, M.S., and Cavanagh, J.B. (1975). Some dynamic aspects of brain metabolism in rats given a portacaval anastomosis. Neuropathol. Appl. Neurobiol. 3:293–311.
Desjardins, P., Rama Rao, K.V., Michalak, A., Rose, C., and Butterworth, R.F. (1999). Effect of portacaval anastomosis on glutamine synthetase protein and gene expression in brain, liver and skeletal muscle. Metab. Brain Dis. 14:273–280.
Giguere, J.-F., and Butterworth, R.F. (1984). Amino acid changes in regions of the CNS in relation to function in experimental portal-systemic encephalopathy. Neurochem. Res. 9:1309–1321.
Girard, G., Giguere, J.-F., and Butterworth, R.F. (1993). Region-selective reductions in activities of glutamine synthetase in rat brain following portacaval anastomosis. Metab. Brain Dis. 8: 207–215.
Gjedde, A., Lockwood, A.H., Duffy, T.E., and Plum, F. (1978). Cerebral blood flow and metabolism in chronically hyperammonemic rats: Effect of an acute ammonia challenge. Ann. Neurol. 3:325–330.
Hansson, E. (1986). Primary cultures from defined brain areas: III. Effects of seeding time on 3[H]L-glutamate transport and glutamine synthetase activity. Brain Res. 389:203–209.
Hermenegildo, C., Marcaida, G., Montoliu, C., Grisolia, S., Minana, M.D., and Felipo, V. (1996). NMDA receptor antagonists prevent acute ammonia toxicity in mice. Neurochem. Res. 21:1237–1244.
Hermenegildo, C., Monfort, P., and Felipo, V. (2000). Activation of NMDA receptors in rat brain in vivo following acute ammonia intoxication. Characterization by in vivo microdialysis. Hepatology 31:709– 715.
Hindfelt, B., Plum, F., and Duffy, T.E. (1977). Effect of acute ammonia intoxication on cerebral metabolism in rats with portacaval shunts. J. Clin. Invest. 59:386–396.
Marcaida, G., Felipo, V., Hermenegildo, C., Minana, M.D., and Grisolia, S. (1992). Acute ammonia toxicity is mediated by the NMDA type of glutamate receptors. FEBS Lett. 296:67–68.
Montoliu, C., Kosenko, E., Erceg, S., Canales, J.J., and Felipo, V. (2002). Molecular mechanism of acute ammonia toxicity: Role of NMDA receptors. Neurochem. Int. 41:95–102.
Norenberg, M.D. (1987). The role of astrocytes in hepatic encephalopathy. Neurochem. Pathol. 6:13–33.
Peterson, C., Giguere, J.-F., Cotman, C.W., and Butterworth, R.F. (1990). Selective loss of N-methyl-d-aspartate-sensitive L-[3H]glutamate binding sites in rat brain following portacaval anastomosis. J. Neurochem. 55:386–390.
Rao, V.L.R., Audet, R.M., Butterworth, R.F. (1995). Selective alterations of extracellular brain amino acids in relation to function in experimental portal-systemic encephalopathy: Results of an in vivo microdialysis study. J. Neurochem. 65:1221–1228.
Rao, V.L.R., Audet, R.M., and Butterworth, R.F. (1997a). Portacaval shunting and hyperammonemia stimulate the uptake of l-[3H]arginine but not the L-[3H]nitroarginine into rat brain synaptosomes. J. Neurochem. 68:337–343.
Rao, V.L.R., Audet, R.M., and Butterworth, R.F. (1997b). Increased neuronal nitric oxide synthase expression in brain following portacaval anastomosis. Brain Res. 765:169–172.
Rose, C., Butterworth, R.F., Zayed, J., Normandin, L., Todd, K., Michalak, A., Spahr, L., Huet, P.-M., and Pomier-Layrargues, G. (1999). Manganese deposition in basal ganglia structures results from both portal-systemic shunting and liver dysfunction. Gastroenterology 117:640–644.
Schliess, F., Gorg, B., Fisher, R., Desjardins, P., Bidmon, H.J., Herrmann, A., Butterworth, R.F., Zilles, K., and Haussinger, D. (2002). Ammonia induces MK-801-sensitive nitration and phosphorylation of protein tyrosine residues in rat astrocytes. FASEB J. 16:739–741.
Suarez, I., Bodega, G., and Fernandez, B. (2000). Modulation of glutamate transporters (GLAST, GLT-1 and EAAC-1) in the rat cerebellum following portacaval anastomosis. Brain Res. 859:293–302.
Spahr, L., Butterworth, R.F., Fontaine, S., Bui, L., Therrien, G., Milette, P., Lebrun, L.H., Zayed, J., Leblanc, A., and Pomier-Layrargues, G. (1996). Increased blood manganese in cirrhotic patients: Relationship to pallidal magnetic resonance signal hypertensity and neurological symptoms. Hepatology 24:1116– 1120.
Tossman, U., Delin, A., Eriksson, S., and Ungerstedt, U. (1987). Brain cortical amino acids measured by intracerebral dialysis in portacaval shunted rats. Neurochem. Res. 12:265–269.
Tossman, U., Eriksson, S., Delin, A., Hagenfeldt, L., Law, D., Ungerstedt, U. (1983). Brain amino acids measured by intracerebral dialysis in portacaval shunted rats. J. Neurochem. 41:1046–1051.
Ukida, M., Morishita, H., Morimoto, Y., Usui, H., and Nagashima, H. (1988). Limited glutamine synthesis in brains of dogs with a portacaval anastomosis after 15N-ammonium chloride loading. In (P.B. Soeters, J.H.P. Wilson, A.J. Meijer, E. Holm, eds.), Advances in Ammonia Metabolism and Hepatic Encephalopathy, Excerpta Medica, Amsterdam, pp. 433–438.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Rose, C., Felipo, V. Limited Capacity for Ammonia Removal by Brain in Chronic Liver Failure: Potential Role of Nitric Oxide. Metab Brain Dis 20, 275–283 (2005). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11011-005-7906-4
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11011-005-7906-4