Abstract
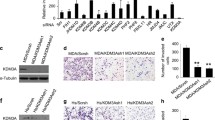
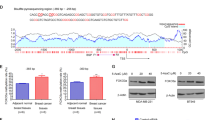
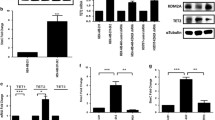
Despite recent advances have been made in clinical treatments of breast cancer, the general prognosis of patients remains poor. Therefore, it is imperative to develop a more effective therapeutic strategy. Lysine demethylase 4B (KDM4B) has been reported to participate in breast cancer development recently, but its exact biological role in breast cancer remains unclear. Here, we observed that KDM4B was down-regulated in human primary BRCA tissues and the low levels of KDM4B expression were correlated with poor survival. Gain- and loss-of-function experiments showed that KDM4B inhibited the proliferation and metastasis of breast cancer cells. Besides, knockdown of KDM4B promoted the epithelial–mesenchymal transition (EMT) and cell stemness in breast cancer cells. Mechanistically, KDM4B down-regulates PHGDH by decreasing the enrichment of H3K36me3 on the promoter region of PHGDH. Knockdown of PHGDH could significantly reversed proliferation, migration, EMT, and cell stemness induced by KDM4B silencing in breast cancer cells. Collectively, we propose a model for a KDM4B/PHGDH axis that provides novel insight into breast cancer development, which may serve as a potential factor for predicting prognosis and a therapeutic target for breast cancer.









Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
Enquiries about data availability should be directed to the authors.
References
Fahad Ullah M (2019) Breast cancer: current perspectives on the disease status. Adv Exp Med Biol 1152:51–64. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-20301-6_4
Sung H, Ferlay J, Siegel RL, Laversanne M, Soerjomataram I, Jemal A, Bray F (2021) Global Cancer Statistics 2020: GLOBOCAN estimates of incidence and mortality worldwide for 36 cancers in 185 countries. CA Cancer J Clin 71:209–249. https://doi.org/10.3322/caac.21660
Wu HJ, Chu PY (2021) Epigenetic regulation of breast cancer stem cells contributing to carcinogenesis and therapeutic implications. Int J Mol Sci 22:8113. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms22158113
Wang Z, Cai H, Zhao E, Cui H (2022) The diverse roles of histone demethylase KDM4B in normal and cancer development and progression. Front Cell Dev Biol 9:790129. https://doi.org/10.3389/fcell.2021.790129
Wei J, Antony J, Meng F, MacLean P, Rhind R, Laible G, Oback B (2017) KDM4B-mediated reduction of H3K9me3 and H3K36me3 levels improves somatic cell reprogramming into pluripotency. Sci Rep 7:7514. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-017-06569-2
Lam UTF, Tan BKY, Poh JJX, Chen ES (2022) Structural and functional specificity of H3K36 methylation. Epigenetics Chromatin 15:17. https://doi.org/10.1186/s13072-022-00446-7
Lee DH, Kim GW, Jeon YH, Yoo J, Lee SW, Kwon SH (2020) Advances in histone demethylase KDM4 as cancer therapeutic targets. FASEB J 34:3461–3484. https://doi.org/10.1096/fj.201902584R
Sun L, Zhang H, Gao P (2022) Metabolic reprogramming and epigenetic modifications on the path to cancer. Protein Cell 13:877–919. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13238-021-00846-7
Spillier Q, Frédérick R (2021) Phosphoglycerate dehydrogenase (PHGDH) inhibitors: a comprehensive review 2015–2020. Expert Opin Ther Pat 31:597–608. https://doi.org/10.1080/13543776.2021.1890028
Li AM, Ye J (2020) The PHGDH enigma: do cancer cells only need serine or also a redox modulator? Cancer Lett 476:97–105. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.canlet.2020.01.036
Li M, Wu C, Yang Y, Zheng M, Yu S, Wang J, Chen L, Li H (2021) 3-Phosphoglycerate dehydrogenase: a potential target for cancer treatment. Cell Oncol 44:541–556. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13402-021-00599-9
El-Sahli S, Wang L (2020) Cancer stem cell-associated pathways in the metabolic reprogramming of breast cancer. Int J Mol Sci 21:9125. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms21239125
Tanabe S, Quader S, Cabral H, Ono R (2020) Interplay of EMT and CSC in cancer and the potential therapeutic strategies. Front Pharmacol 11:904. https://doi.org/10.3389/fphar.2020.00904
Shibue T, Weinberg RA (2017) EMT, CSCs, and drug resistance: the mechanistic link and clinical implications. Nat Rev Clin Oncol 14:611–629. https://doi.org/10.1038/nrclinonc.2017.44
Liu MY, Li HM, Wang XY, Xia R, Li X, Ma YJ, Wang M, Zhang HS (2022) TIGAR drives colorectal cancer ferroptosis resistance through ROS/AMPK/SCD1 pathway. Free Radic Biol Med 182:219–231. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.freeradbiomed.2022.03.002
Zhang HS, Zhang ZG, Du GY, Sun HL, Liu HY, Zhou Z, Gou XM, Wu XH, Yu XY, Huang YH (2019) Nrf2 promotes breast cancer cell migration via up-regulation of G6PD/HIF-1α/Notch1 axis. J Cell Mol Med 23:3451–3463. https://doi.org/10.1111/jcmm.14241
Liu HY, Zhang HS, Liu MY, Li HM, Wang XY, Wang M (2019) GLS1 depletion inhibited colorectal cancer proliferation and migration via redox/Nrf2/autophagy-dependent pathway. Arch Biochem Biophys 708:108964. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.abb.2021.108964
Zhou Z, Zhang HS, Liu Y, Zhang ZG, Du GY, Li H, Yu XY, Huang YH (2018) Loss of TET1 facilitates DLD1 colon cancer cell migration via H3K27me3-mediated down-regulation of E-cadherin. J Cell Physiol 233:1359–1369. https://doi.org/10.1002/jcp.26012
Sun HL, Men JR, Liu HY, Liu MY, Zhang HS (2020) FOXM1 facilitates breast cancer cell stemness and migration in YAP1-dependent manner. Arch Biochem Biophys 685:108349. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.abb.2020.108349
Chandrashekar DS, Karthikeyan SK, Korla PK, Patel H, Shovon AR, Athar M, Netto GJ, Qin ZS, Kumar S, Manne U, Creighton CJ, Varambally S (2022) UALCAN: an update to the integrated cancer data analysis platform. Neoplasia 25:18–27. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neo.2022.01.001
Gyorffy B, Lanczky A, Eklund AC, Denkert C, Budczies J, Li Q, Szallasi Z (2010) An online survival analysis tool to rapidly assess the effect of 22,277 genes on breast cancer prognosis using microarray data of 1809 patients. Breast Cancer Res Treat 123:725–731. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10549-009-0674-9
Vasaikar SV, Straub P, Wang J, Zhang B (2018) LinkedOmics: analyzing multi-omics data within and across 32 cancer types. Nucleic Acids Res 46(D1):D956–D963. https://doi.org/10.1093/nar/gkx1090
Liu CJ, Hu FF, Xia M, Han L, Zhang Q, Guo AY (2018) GSCALite: a web server for gene set cancer analysis. Bioinformatics 34:3771–3772. https://doi.org/10.1093/bioinformatics/bty411
Vagia E, Mahalingam D, Cristofanilli M (2020) The landscape of targeted therapies in TNBC. Cancers 12:916. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers12040916
Bai X, Ni J, Beretov J, Graham P, Li Y (2021) Triple-negative breast cancer therapeutic resistance: where is the Achilles’ heel? Cancer Lett 497:100–111. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.canlet.2020.10.016
Dawson MA, Kouzarides T (2012) Cancer epigenetics: from mechanism to therapy. Cell 150:12–27. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cell.2012.06.013
Yang J, Harris AL, Davidoff AM (2018) Hypoxia and hormone-mediated pathways converge at the histone demethylase KDM4B in cancer. Int J Mol Sci 19:240. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms19010240
Wilson C, Krieg AJ (2019) KDM4B: a nail for every hammer? Genes 10:134. https://doi.org/10.3390/genes10020134
Romano S, Tufano M, D’Arrigo P, Vigorito V, Russo S, Romano MF (2020) Cell stemness, epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition, and immunoevasion: Intertwined aspects in cancer metastasis. Semin Cancer Biol 60:181–190. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.semcancer.2019.08.015
Celia-Terrassa T, Jolly MK (2020) Cancer stem cells and epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition in cancer metastasis. Cold Spring Harb Perspect Med 10:a036905. https://doi.org/10.1101/cshperspect.a036905
Hua Z, White J, Zhou J (2022) Cancer stem cells in TNBC. Semin Cancer Biol 82:26–34. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.semcancer.2021.06.015
Li Q, Qiu J, Yang H, Sun G, Hu Y, Zhu D, Deng Z, Wang X, Tang J, Jiang R (2020) Kinesin family member 15 promotes cancer stem cell phenotype and malignancy via reactive oxygen species imbalance in hepatocellular carcinoma. Cancer Lett 482:112–125. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.canlet.2019.11.008
Xiang Y, Yan K, Zheng Q, Ke H, Cheng J, Xiong W, Shi X, Wei L, Zhao M, Yang F, Wang P, Lu X, Fu L, Lu X, Li F (2019) Histone demethylase KDM4B promotes DNA damage by activating long interspersed nuclear element-1. Cancer Res 79:86–98. https://doi.org/10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-18-1310
Mak KH, Lam YM, Ng RK (2021) Histone demethylase JMJD2B/KDM4B regulates transcriptional program via distinctive epigenetic targets and protein interactors for the maintenance of trophoblast stem cells. Sci Rep 11:884. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-020-79601-7
Acknowledgements
This study was supported by Beijing Natural Science Foundation (Grant No. 7192014); the Open Project of Key Laboratory of Genomics and Precision Medicine, Chinese Academy of Sciences; the National Laboratory of Biomacromolecules (Grant No. 2017kf02); National Natural Sciences Foundation of China (Grant No. 30800580).
Funding
Funding was provided by Beijing Municipal Natural Science Foundation (Grant No. 7192014).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
The research was supervised by ZHS. The research conducted by WXY and LHM. Interpretation of the data were done by XR, LX, ZX and JTZ. Funding was exquisite by ZHS. Writing and reviewing of manuscript were performed by WXY and ZHS and edited by ZHS.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors have no relevant financial or non-financial interests to disclose.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Wang, XY., Li, HM., Xia, R. et al. KDM4B down-regulation facilitated breast cancer cell stemness via PHGDH upregulation in H3K36me3-dependent manner. Mol Cell Biochem 479, 915–928 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11010-023-04777-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11010-023-04777-1