Abstract
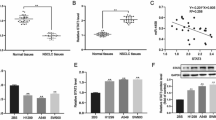
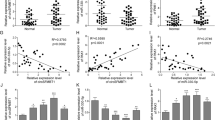
Pancreatic cancer (PC) is one of the most aggressive malignant tumors in human beings. Tumor capacity of evading immune-mediated lysis is a critical step in PC malignant progression. We aimed to evaluate the underlying regulatory mechanism of miR-4299 in the proliferation, metastasis, apoptosis, and immune escape in PC. miR-4299 and ADAM17 expressions in PC tissues and cell lines were detected using qRT-PCR. MTT assay and flow cytometry were used to detect cell viability and apoptosis, respectively. A luciferase reporter gene assay was conducted to confirm the targeted relationship between miR-4299 and ADAM17. Xenograft tumors in nude mice were used to detect tumorigenesis in vivo. PC cells were co-cultured with NK cells for determining the immune escape ability. NKG2D-positive rate of NK cells was detected using flow cytometry; NK cell-killing ability was detected using MTT assay. miR-4299 was downregulated in PC tissues and cell lines. miR-4299 inhibited PC cell proliferation and invasion, promoted cell apoptosis, and reduced PC tumor growth in vivo. ADAM17 3′UTR directly bound to miR-4299. ADAM17 overexpression could reverse miR-4299 effects on PC cell viability, invasion, apoptosis, and immune escape. miR-4299 exerted suppressive effects on PC cell proliferation, invasion, and immune escape via targeting ADAM17 expression. This study revealed a novel miR-4299/ADAM17 axis-modulating PC progression and proposed to concern the immune regulatory mechanism of miRNAs in PC development.







Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
Please contact the authors for data requests.
References
McGuigan A, Kelly P, Turkington RC, Jones C, Coleman HG, McCain RS (2018) Pancreatic cancer: a review of clinical diagnosis, epidemiology, treatment and outcomes. World J Gastroenterol 24:4846–4861. https://doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v24.i43.4846
Tempero MA (2019) NCCN guidelines updates: pancreatic cancer. J Natl Compr Canc Netw 17:603–605. https://doi.org/10.6004/jnccn.2019.5007
Yadav D, Lowenfels AB (2013) The epidemiology of pancreatitis and pancreatic cancer. Gastroenterology 144:1252–1261. https://doi.org/10.1053/j.gastro.2013.01.068
Neoptolemos JP, Kleeff J, Michl P, Costello E, Greenhalf W, Palmer DH (2018) Therapeutic developments in pancreatic cancer: current and future perspectives. Nat Rev Gastroenterol Hepatol 15:333–348. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41575-018-0005-x
Gupta R, Amanam I, Chung V (2017) Current and future therapies for advanced pancreatic cancer. J Surg Oncol 116:25–34. https://doi.org/10.1002/jso.24623
Zhu H, Li T, Du Y, Li M (2018) Pancreatic cancer: challenges and opportunities. BMC Med 16:214. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12916-018-1215-3
Bhaskaran M, Mohan M (2014) MicroRNAs: history, biogenesis, and their evolving role in animal development and disease. Vet Pathol 51:759–774. https://doi.org/10.1177/0300985813502820
Saliminejad K, Khorram Khorshid HR, Soleymani Fard S, Ghaffari SH (2019) An overview of microRNAs: biology, functions, therapeutics, and analysis methods. J Cell Physiol 234:5451–5465. https://doi.org/10.1002/jcp.27486
Lu TX, Rothenberg ME (2018) MicroRNA. J Allergy Clin Immunol 141:1202–1207. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jaci.2017.08.034
Xie M, Steitz JA (2014) Versatile microRNA biogenesis in animals and their viruses. RNA Biol 11:673–681. https://doi.org/10.4161/rna.28985
Wang J, Zhu Z, Qiu H, Liu C, Chang X, Qi Y, Lv Q (2020) LncRNA NKILA inhibits the proliferation and promotes the apoptosis of CSCC cells by downregulating miRNA-21. J Cell Physiol 235:7863–7869. https://doi.org/10.1002/jcp.29439
Du YL, Liang Y, Shi GQ, Cao Y, Qiu J, Yuan L, Yong Z, Liu L, Li J (2020) LINC00689 participates in proliferation, chemoresistance and metastasis via miR-31-5p/YAP/beta-catenin axis in colorectal cancer. Exp Cell Res 395:112176. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.yexcr.2020.112176
Sur S, Steele R, Shi X, Ray RB (2019) miRNA-29b Inhibits prostate tumor growth and induces apoptosis by increasing Bim expression. Cells. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells8111455
Wang JK, Wang Z, Li G (2019) MicroRNA-125 in immunity and cancer. Cancer Lett 454:134–145. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.canlet.2019.04.015
Zhou X, Lu Z, Wang T, Huang Z, Zhu W, Miao Y (2018) Plasma miRNAs in diagnosis and prognosis of pancreatic cancer: a miRNA expression analysis. Gene 673:181–193. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.gene.2018.06.037
Fang C, Dai CY, Mei Z, Jiang MJ, Gu DN, Huang Q, Tian L (2018) microRNA-193a stimulates pancreatic cancer cell repopulation and metastasis through modulating TGF-beta2/TGF-betaRIII signalings. J Exp Clin Cancer Res 37:25. https://doi.org/10.1186/s13046-018-0697-3
Yang G, Cui M, Jiang W, Sheng J, Yang Y, Zhang X (2021) Molecular switch in human diseases-disintegrin and metalloproteinases, ADAM17. Aging 13:16859–16872. https://doi.org/10.18632/aging.203200
Jones JC, Rustagi S, Dempsey PJ (2016) ADAM proteases and gastrointestinal function. Annu Rev Physiol 78:243–276. https://doi.org/10.1146/annurev-physiol-021014-071720
Soto-Gamez A, Chen D, Nabuurs AGE, Quax WJ, Demaria M, Boersma YL (2020) A bispecific inhibitor of the EGFR/ADAM17 axis decreases cell proliferation and migration of EGFR-dependent cancer cells. Cancers. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers12020411
Wu J, Mishra HK, Walcheck B (2019) Role of ADAM17 as a regulatory checkpoint of CD16A in NK cells and as a potential target for cancer immunotherapy. J Leukoc Biol 105:1297–1303. https://doi.org/10.1002/JLB.2MR1218-501R
Ma Z, Gao Y, Liu W, Zheng L, Jin B, Duan B, Xie H, Guo P, Zeng J, Wang K, Xu S, Wang X, He D, Li L (2020) CD82 suppresses ADAM17-dependent E-cadherin cleavage and cell migration in prostate cancer. Dis Markers 2020:8899924. https://doi.org/10.1155/2020/8899924
Hong Y, Chen X, Liang Z, Xu Z, Li Y, Pan Y (2020) MiR-338-3p inhibits cell migration and invasion in human hypopharyngeal cancer via downregulation of ADAM17. Anticancer Drugs 31:925–931. https://doi.org/10.1097/CAD.0000000000000919
Zhang Q, Wang C, Han X, Yang G, Ge Z, Zhang G (2018) Knockdown of ADAM17 inhibits cell proliferation and increases oxaliplatin sensitivity in HCT-8 colorectal cancer through EGFR-PI3K-AKT activation. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 503:2333–2339. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bbrc.2018.06.158
Ren J, Nie Y, Lv M, Shen S, Tang R, Xu Y, Hou Y, Zhao S, Wang T (2015) Estrogen upregulates MICA/B expression in human non-small cell lung cancer through the regulation of ADAM17. Cell Mol Immunol 12:768–776. https://doi.org/10.1038/cmi.2014.101
Arai J, Goto K, Tanoue Y, Ito S, Muroyama R, Matsubara Y, Nakagawa R, Kaise Y, Lim LA, Yoshida H, Kato N (2018) Enzymatic inhibition of MICA sheddase ADAM17 by lomofungin in hepatocellular carcinoma cells. Int J Cancer 143:2575–2583. https://doi.org/10.1002/ijc.31615
Lanier LL (2015) NKG2D Receptor and its ligands in host defense. Cancer Immunol Res 3:575–582. https://doi.org/10.1158/2326-6066.CIR-15-0098
Ferrari de Andrade L, Tay RE, Pan D, Luoma AM, Ito Y, Badrinath S, Tsoucas D, Franz B, May KF Jr, Harvey CJ, Kobold S, Pyrdol JW, Yoon C, Yuan GC, Hodi FS, Dranoff G, Wucherpfennig KW (2018) Antibody-mediated inhibition of MICA and MICB shedding promotes NK cell-driven tumor immunity. Science 359:1537–1542. https://doi.org/10.1126/science.aao0505
Chen Y, Peng C, Chen J, Chen D, Yang B, He B, Hu W, Zhang Y, Liu H, Dai L, Xie H, Zhou L, Wu J, Zheng S (2019) WTAP facilitates progression of hepatocellular carcinoma via m6A-HuR-dependent epigenetic silencing of ETS1. Mol Cancer 18:127. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12943-019-1053-8
Zhang H, Zhang X, Li X, Meng WB, Bai ZT, Rui SZ, Wang ZF, Zhou WC, Jin XD (2018) Effect of CCNB1 silencing on cell cycle, senescence, and apoptosis through the p53 signaling pathway in pancreatic cancer. J Cell Physiol 234:619–631. https://doi.org/10.1002/jcp.26816
Yang WB, Zhang WP, Shi JL, Wang JW (2018) MiR-4299 suppresses non-small cell lung cancer cell proliferation, migration and invasion through modulating PTEN/AKT/PI3K pathway. Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci 22:3408–3414. https://doi.org/10.26355/eurrev_201806_15163
Waldhauer I, Goehlsdorf D, Gieseke F, Weinschenk T, Wittenbrink M, Ludwig A, Stevanovic S, Rammensee HG, Steinle A (2008) Tumor-associated MICA is shed by ADAM proteases. Cancer Res 68:6368–6376. https://doi.org/10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-07-6768
Shah R, Ostapoff KT, Kuvshinoff B, Hochwald SN (2018) Ablative therapies for locally advanced pancreatic cancer. Pancreas 47:6–11. https://doi.org/10.1097/MPA.0000000000000948
Miao X, Jia L, Zhou H, Song X, Zhou M, Xu J, Zhao L, Feng X, Zhao Y (2016) miR-4299 mediates the invasive properties and tumorigenicity of human follicular thyroid carcinoma by targeting ST6GALNAC4. IUBMB Life 68:136–144. https://doi.org/10.1002/iub.1467
Hu J, Xu Y, Cai S (2015) Specific microRNAs as novel biomarkers for combination chemotherapy resistance detection of colon adenocarcinoma. Eur J Med Res 20:95. https://doi.org/10.1186/s40001-015-0183-8
Islam MA, Reesor EK, Xu Y, Zope HR, Zetter BR, Shi J (2015) Biomaterials for mRNA delivery. Biomater Sci 3:1519–1533. https://doi.org/10.1039/c5bm00198f
Palau V, Pascual J, Soler MJ, Riera M (2019) Role of ADAM17 in kidney disease. Am J Physiol Renal Physiol 317:F333–F342. https://doi.org/10.1152/ajprenal.00625.2018
Dusterhoft S, Lokau J, Garbers C (2019) The metalloprotease ADAM17 in inflammation and cancer. Pathol Res Pract 215:152410. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.prp.2019.04.002
Pelullo M, Nardozza F, Zema S, Quaranta R, Nicoletti C, Besharat ZM, Felli MP, Cerbelli B, d’Amati G, Palermo R, Capalbo C, Talora C, Di Marcotullio L, Giannini G, Checquolo S, Screpanti I, Bellavia D (2019) Kras/ADAM17-dependent Jag1-ICD reverse signaling sustains colorectal cancer progression and chemoresistance. Cancer Res 79:5575–5586. https://doi.org/10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-19-0145
Zhang Y, Li D, Jiang Q, Cao S, Sun H, Chai Y, Li X, Ren T, Yang R, Feng F, B-a Li, Zhao Q (2018) Novel ADAM-17 inhibitor ZLDI-8 enhances the in vitro and in vivo chemotherapeutic effects of Sorafenib on hepatocellular carcinoma cells. Cell Death Dis 9:743. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41419-018-0804-6
Bear AS, Vonderheide RH, O’Hara MH (2020) Challenges and opportunities for pancreatic cancer immunotherapy. Cancer Cell 38:788–802. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ccell.2020.08.004
Wu SY, Fu T, Jiang YZ, Shao ZM (2020) Natural killer cells in cancer biology and therapy. Mol Cancer 19:120. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12943-020-01238-x
Xie G, Dong H, Liang Y, Ham JD, Rizwan R, Chen J (2020) CAR-NK cells: a promising cellular immunotherapy for cancer. EBioMedicine 59:102975. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ebiom.2020.102975
Courau T, Bonnereau J, Chicoteau J, Bottois H, Remark R, Assante Miranda L, Toubert A, Blery M, Aparicio T, Allez M, Le Bourhis L (2019) Cocultures of human colorectal tumor spheroids with immune cells reveal the therapeutic potential of MICA/B and NKG2A targeting for cancer treatment. J Immunother Cancer 7:74. https://doi.org/10.1186/s40425-019-0553-9
Romee R, Foley B, Lenvik T, Wang Y, Zhang B, Ankarlo D, Luo X, Cooley S, Verneris M, Walcheck B, Miller J (2013) NK cell CD16 surface expression and function is regulated by a disintegrin and metalloprotease-17 (ADAM17). Blood 121:3599–3608. https://doi.org/10.1182/blood-2012-04-425397
Pham DH, Kim JS, Kim SK, Shin DJ, Uong NT, Hyun H, Yoon MS, Kang SJ, Ryu YJ, Cho JS, Yoon JH, Lee JS, Cho D, Lee SH, Park MH (2017) Effects of ADAM10 and ADAM17 inhibitors on natural killer cell expansion and antibody-dependent cellular cytotoxicity against breast cancer cells in vitro. Anticancer Res 37:5507–5513. https://doi.org/10.21873/anticanres.11981
Kong Y, Li Y, Luo Y, Zhu J, Zheng H, Gao B, Guo X, Li Z, Chen R, Chen C (2020) circNFIB1 inhibits lymphangiogenesis and lymphatic metastasis via the miR-486-5p/PIK3R1/VEGF-C axis in pancreatic cancer. Mol Cancer 19:82. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12943-020-01205-6
Hou Y, Zhang Q, Pang W, Hou L, Liang Y, Han X, Luo X, Wang P, Zhang X, Li L, Meng X (2021) YTHDC1-mediated augmentation of miR-30d in repressing pancreatic tumorigenesis via attenuation of RUNX1-induced transcriptional activation of Warburg effect. Cell Death Differ 28:3105–3124. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41418-021-00804-0
Qi Y, Wang D, Huang W, Wang B, Huang D, Xiong F, Chen X, Chen Y (2019) CyclinD1 inhibits dicer and crucial miRNA expression by chromatin modification to promote the progression of intrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma. J Exp Clin Cancer Res 38:413. https://doi.org/10.1186/s13046-019-1415-5
Acknowledgements
None.
Funding
This work was supported by Guangxi Provincial Natural Science Foundation (2018GXNSFDA281003), Guangxi Natural Science Foundation (2017GXNSFAA198039 and 2022GXNSFAA035509) and Guangxi Key Laboratory of Molecular Medicine in Liver Injury and Repair (No. GXLIRMMKL-K202009).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
JL, LY, KL, and TZ made substantial contributions to the conception and design of the work; LS, QM analyzed and interpreted the data; LY and JL drafted the manuscript; SL, QC and YY revised the work critically for important intellectual content; QC and YY collected grants; JL and TW performed the animal experiments. All authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors confirm that there are no conflicts of interest.
Ethical approval
All procedures performed in studies involving human participants were in accordance with the ethical standards of Affiliated Hospital of Guilin Medical University Hospital and with the 1964 Helsinki declaration. The guidelines for the care and use of animals were approved by the Medicine Animal Welfare Committee of Affiliated Hospital of Guilin Medical University Hospital.
Consent to participate
Informed consent to participate in the study has been obtained from participants.
Consent for publication
Consent for publication was obtained from the participants.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
11010_2022_4617_MOESM1_ESM.tif
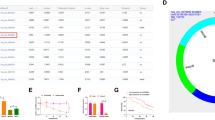
Supplementary file1 (TIF 1666 kb)Figure S1. microarray analyses of differentially expressed miRNAs within PC tissues. (A) Volcano plots of abnormally expressed miRNAs in PC tissue samples based on GSE43797 dataset were displayed; green plots represented downregulated miRNAs, and red plots represented upregulated miRNAs. (B) Hierarchical clustering heatmap showing differentially expressed miRNAs in PC tissue samples and normal pancreatic tissue samples based on the GSE43793 dataset were displayed. (C) Volcano plots for the GSE43797 dataset were displayed. (D) Hierarchical clustering heatmap for the GSE60980 dataset was displayed.
11010_2022_4617_MOESM2_ESM.tif
Supplementary file2 (TIF 2028 kb)Figure S2. Microarray analysis and prognostic analysis for the differentially expressed miRNAs in PC tissues. (A-B) Volcano plots and hierarchical clustering heatmap of abnormally expressed mRNAs in PC tissue samples based on the GSE15471 (A) and GSE16515 (B) datasets were displayed. (C-D) The expression of the selected 9 genes in GSE15471 and GSE16515 datasets.
11010_2022_4617_MOESM3_ESM.tif
Supplementary file3 (TIF 1099 kb)Figure S3. Univariate and multivariate Cox risk regression analyses of selected 5 genes were performed for the overall survival of pancreatic cancer patients based on GSE57495 (A) and TCGA-PAAD (B) datasets.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Liu, J., Ye, L., Lin, K. et al. miR-4299 inhibits tumor progression in pancreatic cancer through targeting ADAM17. Mol Cell Biochem 478, 1727–1742 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11010-022-04617-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11010-022-04617-8