Abstract
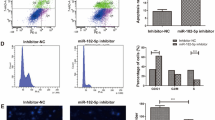
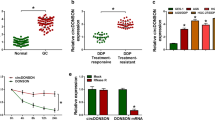
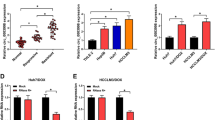
Circular RNAs (circRNAs) are key regulators in tumor metastasis and drug resistance. This study was designed to investigate circ_0082182 function and mechanism in oxaliplatin (OXA) resistance and cancer progression of colorectal cancer (CRC). The circ_0082182, microRNA-326 (miR-326), and nuclear factor I B (NFIB) levels were quantified by reverse transcription-quantitative polymerase chain reaction (RT-qPCR). Cell sensitization was analyzed by Cell Counting Kit-8 assay. The proliferation ability was determined via EdU assay, and apoptosis was measured by flow cytometry. Transwell assay and wound healing assay were performed to assess cell invasion and migration. The protein level was examined through Western blot. The binding interaction was conducted via dual-luciferase reporter assay. Xenograft tumor assay was used to explore the circ_0082182 function in vivo. The circ_0082182 level was upregulated in OXA-resistant CRC samples and cells. Downregulation of circ_0082182 suppressed OXA resistance, proliferation, invasion, and migration but promoted apoptosis of OXA-resistant CRC cells. Circ_0082182 acted as a sponge for miR-326. The regulatory role of circ_0082182 was ascribed to the miR-326 sponging function. MiR-326 directly targeted NFIB to impede OXA resistance and cancer progression in CRC cells. NFIB level was regulated by circ_0082182 via sponging miR-326. Circ_0082182 promoted tumor growth in OXA-resistant xenograft tumor model through mediating the miR-326/NFIB axis. These data suggested that circ_0082182 elevated the NFIB expression to regulate OXA resistance and CRC progression by absorbing miR-326.








Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
Not applicable.
References
Keum N, Giovannucci E (2019) Global burden of colorectal cancer: emerging trends, risk factors and prevention strategies. Nat Rev Gastroenterol Hepatol 16(12):713–732. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41575-019-0189-8
Biller LH, Schrag D (2021) Diagnosis and treatment of metastatic colorectal cancer: a review. JAMA 325(7):669–685. https://doi.org/10.1001/jama.2021.0106
Dzunic M, Petkovic I, Cvetanovic A, Vrbic S, Pejcic I (2019) Current and future targets and therapies in metastatic colorectal cancer. J BUON 24(5):1785–1792
Van der Jeught K, Xu HC, Li YJ, Lu XB, Ji G (2018) Drug resistance and new therapies in colorectal cancer. World J Gastroenterol 24(34):3834–3848. https://doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v24.i34.3834
Bahrami A, Amerizadeh F, Hassanian SM, ShahidSales S, Khazaei M, Maftouh M, Ghayour-Mobarhan M, Ferns GA, Avan A (2018) Genetic variants as potential predictive biomarkers in advanced colorectal cancer patients treated with oxaliplatin-based chemotherapy. J Cell Physiol 233(3):2193–2201. https://doi.org/10.1002/jcp.25966
Piawah S, Venook AP (2019) Targeted therapy for colorectal cancer metastases: a review of current methods of molecularly targeted therapy and the use of tumor biomarkers in the treatment of metastatic colorectal cancer. Cancer 125(23):4139–4147. https://doi.org/10.1002/cncr.32163
Oliveres H, Pesantez D, Maurel J (2021) Lessons to learn for adequate targeted therapy development in metastatic colorectal cancer patients. Int J Mol Sci. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms22095019
Ghafouri-Fard S, Taheri M, Hussen BM, Vafaeimanesh J, Abak A, Vafaee R (2021) Function of circular RNAs in the pathogenesis of colorectal cancer. Biomed Pharmacother. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biopha.2021.111721
Zeng K, Wang S (2020) Circular RNAs: the crucial regulatory molecules in colorectal cancer. Pathol Res Pract 216(4):152861. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.prp.2020.152861
Ye DX, Wang SS, Huang Y, Chi P (2019) A 3-circular RNA signature as a noninvasive biomarker for diagnosis of colorectal cancer. Cancer Cell Int. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12935-019-0995-7
Liu R, Deng P, Zhang Y, Wang Y, Peng C (2021) Circ_0082182 promotes oncogenesis and metastasis of colorectal cancer in vitro and in vivo by sponging miR-411 and miR-1205 to activate the Wnt/beta-catenin pathway. World J Surg Oncol 19(1):51. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12957-021-02164-y
Pan S, Liu Y, Liu Q, Xiao Y, Liu B, Ren X, Qi X, Zhou H, Zeng C, Jia L (2019) HOTAIR/miR-326/FUT6 axis facilitates colorectal cancer progression through regulating fucosylation of CD44 via PI3K/AKT/mTOR pathway. Biochim Biophys Acta Mol Cell Res 1866(5):750–760. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bbamcr.2019.02.004
Liu J, Huang S, Liao X, Chen Z, Li L, Yu L, Zhan W, Li R (2021) LncRNA EWSAT1 promotes colorectal cancer progression through sponging miR-326 to modulate FBXL20 expression. Onco Targets Ther. https://doi.org/10.2147/OTT.S272895
Weldon Furr J, Morales-Scheihing D, Manwani B, Lee J, McCullough LD (2019) Cerebral amyloid angiopathy, Alzheimer’s disease and microRNA: miRNA as diagnostic biomarkers and potential therapeutic targets. Neuromolecular Med 21(4):369–390. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12017-019-08568-0
Wu L, Hui H, Wang LJ, Wang H, Liu QF, Han SX (2015) MicroRNA-326 functions as a tumor suppressor in colorectal cancer by targeting the nin one binding protein. Oncol Rep 33(5):2309–2318. https://doi.org/10.3892/or.2015.3840
Bao Z, Gao S, Tang Q, Zhang B, Shi W, Tian Q (2021) A novel role of miR-326 in colorectal carcinoma by regulating E2F1 expression. J BUON 26(2):528–535
Sun L, Fang Y, Wang X, Han Y, Du F, Li C, Hu H, Liu H, Liu Q, Wang J, Liang J, Chen P, Yang H, Nie Y, Wu K, Fan D, Coffey RJ, Lu Y, Zhao X, Wang X (2019) miR-302a inhibits metastasis and cetuximab resistance in colorectal cancer by targeting NFIB and CD44. Theranostics 9(26):8409–8425. https://doi.org/10.7150/thno.36605
Xu W, Chen B, Ke D, Chen X (2020) MicroRNA-138–5p targets the NFIB-Snail1 axis to inhibit colorectal cancer cell migration and chemoresistance. Cancer Cell Int. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12935-020-01573-5
Panda AC (2018) Circular RNAs Act as miRNA Sponges. Adv Exp Med Biol. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-981-13-1426-1_6
Eisenhauer EA, Therasse P, Bogaerts J, Schwartz LH, Sargent D, Ford R, Dancey J, Arbuck S, Gwyther S, Mooney M, Rubinstein L, Shankar L, Dodd L, Kaplan R, Lacombe D, Verweij J (2009) New response evaluation criteria in solid tumours: revised RECIST guideline (version 1.1). Eur J Cancer 45(2):228–247
Song W, Qian Y, Zhang MH, Wang H, Wen X, Yang XZ, Dai WJ (2020) The long non-coding RNA DDX11-AS1 facilitates cell progression and oxaliplatin resistance via regulating miR-326/IRS1 axis in gastric cancer. Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci 24(6):3049–3061
Livak KJ, Schmittgen TD (2001) Analysis of relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and the 2(-Delta Delta C(T)) Method. Methods 25(4):402–408. https://doi.org/10.1006/meth.2001.1262
Zhou D, Lin X, Wang P, Yang Y, Zheng J, Zhou D (2021) Circular RNA circ_0001162 promotes cell proliferation and invasion of glioma via the miR-936/ERBB4 axis. Bioengineered 12(1):2106–2118. https://doi.org/10.1080/21655979.2021.1932221
Li P, Song R, Yin F, Liu M, Liu H, Ma S, Jia X, Lu X, Zhong Y, Yu L, Li X, Li X (2021) circMRPS35 promotes malignant progression and cisplatin resistance in hepatocellular carcinoma. Mol Ther. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ymthe.2021.08.027
Huang W, Lu Y, Wang F, Huang X, Yu Z (2020) Circular RNA circRNA_103809 accelerates bladder cancer progression and enhances chemo-resistance by activation of miR-516a-5p/FBXL18 axis. Cancer Manag Res. https://doi.org/10.2147/CMAR.S263083
Liu YY, Zhang LY, Du WZ (2019) Circular RNA circ-PVT1 contributes to paclitaxel resistance of gastric cancer cells through the regulation of ZEB1 expression by sponging miR-124-3p. Biosci Rep. https://doi.org/10.1042/BSR20193045
Shen Z, Zhou L, Zhang C, Xu J (2020) Reduction of circular RNA Foxo3 promotes prostate cancer progression and chemoresistance to docetaxel. Cancer Lett. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.canlet.2019.10.006
Li A, Wang WC, McAlister V, Zhou Q, Zheng X (2021) Circular RNA in colorectal cancer. J Cell Mol Med 25(8):3667–3679. https://doi.org/10.1111/jcmm.16380
Xu Y, Qiu A, Peng F, Tan X, Wang J, Gong X (2021) Exosomal transfer of circular RNA FBXW7 ameliorates the chemoresistance to oxaliplatin in colorectal cancer by sponging miR-18b-5p. Neoplasma 68(1):108–118. https://doi.org/10.4149/neo_2020_200417N414
Li S, Zheng S (2020) Down-regulation of Circ_0032833 sensitizes colorectal cancer to 5-fluorouracil and oxaliplatin partly depending on the regulation of miR-125–5p and MSI1. Cancer Manag Res. https://doi.org/10.2147/CMAR.S270123
Lai M, Liu G, Li R, Bai H, Zhao J, Xiao P, Mei J (2020) Hsa_circ_0079662 induces the resistance mechanism of the chemotherapy drug oxaliplatin through the TNF-alpha pathway in human colon cancer. J Cell Mol Med 24(9):5021–5027. https://doi.org/10.1111/jcmm.15122
Zhao K, Cheng X, Ye Z, Li Y, Peng W, Wu Y, Xing C (2021) Exosome-mediated transfer of circ_0000338 enhances 5-fluorouracil resistance in colorectal cancer through regulating MicroRNA 217 (miR-217) and miR-485–3p. Mol Cell Biol. https://doi.org/10.1128/MCB.00517-20
He X, Ma J, Zhang M, Cui J, Yang H (2020) Circ_0007031 enhances tumor progression and promotes 5-fluorouracil resistance in colorectal cancer through regulating miR-133b/ABCC5 axis. Cancer Biomark 29(4):531–542. https://doi.org/10.3233/CBM-200023
Jian X, He H, Zhu J, Zhang Q, Zheng Z, Liang X, Chen L, Yang M, Peng K, Zhang Z, Liu T, Ye Y, Jiao H, Wang S, Zhou W, Ding Y, Li T (2020) Hsa_circ_001680 affects the proliferation and migration of CRC and mediates its chemoresistance by regulating BMI1 through miR-340. Mol Cancer 19(1):20. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12943-020-1134-8
Acknowledgements
None
Funding
This study does not receive any financial support as well as any role of funding bodies.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
All the authors have been involved in the management of the patient and in the conception of the manuscript. The specific authors’ contribution is as follows: WZF and LJM were involved in writing the drafting of the manuscript; YT collected data; WQQ performed analysis and interpretation; LR provided software; and TJL contributed to reviewing and editing.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflicts of interest.
Ethical approval
This study was permitted by the Ethics Committee of Shanxi Provincial People’s Hospital, and the approval number is 2019JS124.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Wang, Z., Liu, J., Yang, T. et al. Circ_0082182 upregulates the NFIB level via sponging miR-326 to promote oxaliplatin resistance and malignant progression of colorectal cancer cells. Mol Cell Biochem 478, 1045–1057 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11010-022-04551-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11010-022-04551-9