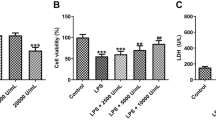
Abstract
Acute kidney injury (AKI) is one of frequent complications of sepsis with high mortality. Mitochondria is the center of energy metabolism participating in the pathogenesis of sepsis-associated AKI, and SIRT1/PGC1-α signaling pathway plays a crucial role in the modulation of energy metabolism. Erythropoietin (EPO) exerts protective functions on chronic kidney disease. We aimed to assess the effects of EPO on cell damage and energy metabolism in a cell model of septic AKI. Renal tubular epithelial cells HK-2 were treated with LPS and human recombinant erythropoietin (rhEPO). Cell viability was detected by CCK-8 and mitochondrial membrane potential was determined using JC-1 fluorescent probe. Then the content of ATP, ADP and NADPH, as well as lactic acid, were measured for the assessment of energy metabolism. Oxidative stress was evaluated by detecting the levels of ROS, MDA, SOD and GSH. Pro-inflammatory cytokines, including TNF-α, IL-6, and IL-1β, were measured with ELISA. Moreover, qRT-PCR and western blot were performed to detect mRNA and protein expressions. shSIRT1 was used to knockdown SIRT1, while EX527 and SR-18292 were applied to inhibit SIRT1 and PGC1-α, respectively, to investigate the regulatory mechanism of rhEPO on inflammatory injury and energy metabolism. In LPS-exposed HK-2 cells, rhEPO attenuated cell damage, inflammation and abnormal energy metabolism, as indicated by the elevated cell viability, the inhibited oxidative stress, cell apoptosis and inflammation, as well as the increased mitochondrial membrane potential and energy metabolism. However, these protective effects induced by rhEPO were reversed after SIRT1 or PGC1-α inhibition. EPO activated SIRT1/PGC1-α pathway to alleviate LPS-induced abnormal energy metabolism and cell damage in HK-2 cells. Our study suggested that rhEPO played a renoprotective role through SIRT1/PGC1-α pathway, which supported its therapeutic potential in septic AKI.






Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
The datasets used or analyzed during the current study are available from the corresponding author on reasonable request.
Code availability
Not applicable.
References
Kellum JA, Romagnani P, Ashuntantang G, Ronco C, Zarbock A, Anders HJ (2021) Acute kidney injury. Nat Rev Dis Primers 7:52. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41572-021-00284-z
Agapito Fonseca J, Gameiro J, Marques F, Lopes JA (2020) Timing of initiation of renal replacement therapy in sepsis-associated acute kidney injury. J Clin Med. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm9051413
Klingele M, Baerens L (2021) Impact of renal replacement therapy on mortality in critically Ill patients-the nephrologist’s view within an interdisciplinary intensive care team. J Clin Med. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm10153379
Gomez H, Ince C, De Backer D, Pickkers P, Payen D, Hotchkiss J, Kellum JA (2014) A unified theory of sepsis-induced acute kidney injury: inflammation, microcirculatory dysfunction, bioenergetics, and the tubular cell adaptation to injury. Shock 41:3–11. https://doi.org/10.1097/SHK.0000000000000052
Huang Y, Wang S, Zhou J, Liu Y, Du C, Yang K, Bi X, Liu M, Han W, Wang K, Xiong J, Wang S, Wang Y, Nie L, Liu C, Zhang D, Gu J, Zeng C, Zhao J (2020) IRF1-mediated downregulation of PGC1alpha contributes to cardiorenal syndrome type 4. Nat Commun 11:4664. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41467-020-18519-0
Havasi A, Borkan SC (2011) Apoptosis and acute kidney injury. Kidney Int 80:29–40. https://doi.org/10.1038/ki.2011.120
Quinn GZ, Dhillon P, Susztak K (2020) It takes two to tango: the role of dysregulated metabolism and inflammation in kidney disease development. Semin Nephrol 40:199–205. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.semnephrol.2020.01.010
Yoshimoto K, Komaru Y, Iwagami M, Doi K (2020) Acute kidney injury in sepsis: evidence from Asia. Semin Nephrol 40:489–497. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.semnephrol.2020.08.005
Landau D, London L, Bandach I, Segev Y (2018) The hypoxia inducible factor/erythropoietin (EPO)/EPO receptor pathway is disturbed in a rat model of chronic kidney disease related anemia. PLoS ONE 13:e0196684. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0196684
Zhang Y, Zhu X, Huang X, Wei X, Zhao D, Jiang L, Zhao X, Du Y (2020) Advances in understanding the effects of erythropoietin on renal fibrosis. Front Med (Lausanne) 7:47. https://doi.org/10.3389/fmed.2020.00047
Hardee ME, Arcasoy MO, Blackwell KL, Kirkpatrick JP, Dewhirst MW (2006) Erythropoietin biology in cancer. Clin Cancer Res 12:332–339. https://doi.org/10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-05-1771
Teng R, Gavrilova O, Suzuki N, Chanturiya T, Schimel D, Hugendubler L, Mammen S, Yver DR, Cushman SW, Mueller E, Yamamoto M, Hsu LL, Noguchi CT (2011) Disrupted erythropoietin signalling promotes obesity and alters hypothalamus proopiomelanocortin production. Nat Commun 2:520. https://doi.org/10.1038/ncomms1526
Heitrich M, Garcia DM, Stoyanoff TR, Rodriguez JP, Todaro JS, Aguirre MV (2016) Erythropoietin attenuates renal and pulmonary injury in polymicrobial induced-sepsis through EPO-R, VEGF and VEGF-R2 modulation. Biomed Pharmacother 82:606–613. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biopha.2016.05.045
Coldewey SM, Khan AI, Kapoor A, Collino M, Rogazzo M, Brines M, Cerami A, Hall P, Sheaff M, Kieswich JE, Yaqoob MM, Patel NS, Thiemermann C (2013) Erythropoietin attenuates acute kidney dysfunction in murine experimental sepsis by activation of the beta-common receptor. Kidney Int 84:482–490. https://doi.org/10.1038/ki.2013.118
Liu F, Yang N (2020) Multiscale landscape of molecular mechanism of SIRT1 activation by STACs. Phys Chem Chem Phys 22:826–837. https://doi.org/10.1039/c9cp04931b
Yamaji T, Yamashita A, Wakui H, Azushima K, Uneda K, Fujikawa Y, Haku S, Kobayashi R, Ohki K, Haruhara K, Kinguchi S, Ishii T, Yamada T, Urate S, Suzuki T, Abe E, Tanaka S, Kamimura D, Ishigami T, Toya Y, Takahashi H, Tamura K (2019) Angiotensin II type 1 receptor-associated protein deficiency attenuates sirtuin1 expression in an immortalised human renal proximal tubule cell line. Sci Rep 9:16550. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-019-52566-y
Wei S, Gao Y, Dai X, Fu W, Cai S, Fang H, Zeng Z, Chen Z (2019) SIRT1-mediated HMGB1 deacetylation suppresses sepsis-associated acute kidney injury. Am J Physiol Renal Physiol 316:F20–F31. https://doi.org/10.1152/ajprenal.00119.2018
Khajevand-Khazaei MR, Mohseni-Moghaddam P, Hosseini M, Gholami L, Baluchnejadmojarad T, Roghani M (2018) Rutin, a quercetin glycoside, alleviates acute endotoxemic kidney injury in C57BL/6 mice via suppression of inflammation and up-regulation of antioxidants and SIRT1. Eur J Pharmacol 833:307–313. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ejphar.2018.06.019
Fanibunda SE, Deb S, Maniyadath B, Tiwari P, Ghai U, Gupta S, Figueiredo D, Weisstaub N, Gingrich JA, Vaidya ADB, Kolthur-Seetharam U, Vaidya VA (2019) Serotonin regulates mitochondrial biogenesis and function in rodent cortical neurons via the 5-HT2A receptor and SIRT1-PGC-1alpha axis. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 116:11028–11037. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.1821332116
Fontecha-Barriuso M, Martin-Sanchez D, Martinez-Moreno JM, Carrasco S, Ruiz-Andres O, Monsalve M, Sanchez-Ramos C, Gomez MJ, Ruiz-Ortega M, Sanchez-Nino MD, Cannata-Ortiz P, Cabello R, Gonzalez-Enguita C, Ortiz A, Sanz AB (2019) PGC-1alpha deficiency causes spontaneous kidney inflammation and increases the severity of nephrotoxic AKI. J Pathol 249:65–78. https://doi.org/10.1002/path.5282
Ruiz-Andres O, Suarez-Alvarez B, Sanchez-Ramos C, Monsalve M, Sanchez-Nino MD, Ruiz-Ortega M, Egido J, Ortiz A, Sanz AB (2016) The inflammatory cytokine TWEAK decreases PGC-1alpha expression and mitochondrial function in acute kidney injury. Kidney Int 89:399–410. https://doi.org/10.1038/ki.2015.332
Yuan L, Yuan Y, Liu F, Li L, Liu J, Chen Y, Cheng J, Lu Y (2021) PGC-1alpha alleviates mitochondrial dysfunction via TFEB-mediated autophagy in cisplatin-induced acute kidney injury. Aging (Albany NY) 13:8421–8439. https://doi.org/10.18632/aging.202653
Peasley K, Chiba T, Goetzman E, Sims-Lucas S (2021) Sirtuins play critical and diverse roles in acute kidney injury. Pediatr Nephrol. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00467-020-04866-z
Tran MT, Zsengeller ZK, Berg AH, Khankin EV, Bhasin MK, Kim W, Clish CB, Stillman IE, Karumanchi SA, Rhee EP, Parikh SM (2016) PGC1alpha drives NAD biosynthesis linking oxidative metabolism to renal protection. Nature 531:528–532. https://doi.org/10.1038/nature17184
Li K, Liu TX, Li JF, Ma YR, Liu ML, Wang YQ, Wu R, Li B, Shi LZ, Chen C (2019) rhEPO inhibited cell apoptosis to alleviate acute kidney injury in sepsis by AMPK/SIRT1 activated autophagy. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 517:557–565. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bbrc.2019.07.027
Poston JT, Koyner JL (2019) Sepsis associated acute kidney injury. BMJ 364:k4891. https://doi.org/10.1136/bmj.k4891
Scholz H, Boivin FJ, Schmidt-Ott KM, Bachmann S, Eckardt KU, Scholl UI, Persson PB (2021) Kidney physiology and susceptibility to acute kidney injury: implications for renoprotection. Nat Rev Nephrol 17:335–349. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41581-021-00394-7
Sun J, Zhang J, Tian J, Virzi GM, Digvijay K, Cueto L, Yin Y, Rosner MH, Ronco C (2019) Mitochondria in sepsis-induced AKI. J Am Soc Nephrol 30:1151–1161. https://doi.org/10.1681/ASN.2018111126
Peerapornratana S, Manrique-Caballero CL, Gomez H, Kellum JA (2019) Acute kidney injury from sepsis: current concepts, epidemiology, pathophysiology, prevention and treatment. Kidney Int 96:1083–1099. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.kint.2019.05.026
Zhao M, Liu S, Wang C, Wang Y, Wan M, Liu F, Gong M, Yuan Y, Chen Y, Cheng J, Lu Y, Liu J (2021) Mesenchymal stem cell-derived extracellular vesicles attenuate mitochondrial damage and inflammation by stabilizing mitochondrial DNA. ACS Nano 15:1519–1538. https://doi.org/10.1021/acsnano.0c08947
Lee K, Gusella GL, He JC (2021) Epithelial proliferation and cell cycle dysregulation in kidney injury and disease. Kidney Int 100:67–78. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.kint.2021.03.024
Stoyanoff TR, Todaro JS, Aguirre MV, Zimmermann MC, Brandan NC (2014) Amelioration of lipopolysaccharide-induced acute kidney injury by erythropoietin: involvement of mitochondria-regulated apoptosis. Toxicology 318:13–21. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tox.2014.01.011
Stoyanoff TR, Rodriguez JP, Todaro JS, Colavita JPM, Torres AM, Aguirre MV (2018) Erythropoietin attenuates LPS-induced microvascular damage in a murine model of septic acute kidney injury. Biomed Pharmacother 107:1046–1055. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biopha.2018.08.087
Souza AC, Volpini RA, Shimizu MH, Sanches TR, Camara NO, Semedo P, Rodrigues CE, Seguro AC, Andrade L (2012) Erythropoietin prevents sepsis-related acute kidney injury in rats by inhibiting NF-kappaB and upregulating endothelial nitric oxide synthase. Am J Physiol Renal Physiol 302:F1045–F1054. https://doi.org/10.1152/ajprenal.00148.2011
Cui L, Guo J, Zhang Q, Yin J, Li J, Zhou W, Zhang T, Yuan H, Zhao J, Zhang L, Carmichael PL, Peng S (2017) Erythropoietin activates SIRT1 to protect human cardiomyocytes against doxorubicin-induced mitochondrial dysfunction and toxicity. Toxicol Lett 275:28–38. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.toxlet.2017.04.018
Jacobs RA, Aboouf MA, Koester-Hegmann C, Muttathukunnel P, Laouafa S, Arias-Reyes C, Thiersch M, Soliz J, Gassmann M, Schneider Gasser EM (2021) Erythropoietin promotes hippocampal mitochondrial function and enhances cognition in mice. Commun Biol 4:938. https://doi.org/10.1038/s42003-021-02465-8
Hao CM, Haase VH (2010) Sirtuins and their relevance to the kidney. J Am Soc Nephrol 21:1620–1627. https://doi.org/10.1681/ASN.2010010046
Zhou S, Qiao YM, Liu YG, Liu D, Hu JM, Liao J, Li M, Guo Y, Fan LP, Li LY, Zhao M (2020) Bone marrow derived mesenchymal stem cells pretreated with erythropoietin accelerate the repair of acute kidney injury. Cell Biosci 10:130. https://doi.org/10.1186/s13578-020-00492-2
Wang L, Teng R, Di L, Rogers H, Wu H, Kopp JB, Noguchi CT (2013) PPARalpha and Sirt1 mediate erythropoietin action in increasing metabolic activity and browning of white adipocytes to protect against obesity and metabolic disorders. Diabetes 62:4122–4131. https://doi.org/10.2337/db13-0518
Morigi M, Perico L, Benigni A (2018) Sirtuins in renal health and disease. J Am Soc Nephrol 29:1799–1809. https://doi.org/10.1681/ASN.2017111218
Gao R, Chen J, Hu Y, Li Z, Wang S, Shetty S, Fu J (2014) Sirt1 deletion leads to enhanced inflammation and aggravates endotoxin-induced acute kidney injury. PLoS ONE 9:e98909. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0098909
Piao L, Zhao G, Zhu E, Inoue A, Shibata R, Lei Y, Hu L, Yu C, Yang G, Wu H, Xu W, Okumura K, Ouchi N, Murohara T, Kuzuya M, Cheng XW (2017) Chronic psychological stress accelerates vascular senescence and impairs ischemia-induced neovascularization: the role of dipeptidyl peptidase-4/glucagon-like peptide-1-adiponectin axis. J Am Heart Assoc. https://doi.org/10.1161/JAHA.117.006421
Li M, Meng N, Guo X, Niu X, Zhao Z, Wang W, Xie X, Lv P (2020) Dl-3-n-butylphthalide promotes remyelination and suppresses inflammation by regulating AMPK/SIRT1 and STAT3/NF-kappaB signaling in chronic cerebral hypoperfusion. Front Aging Neurosci 12:137. https://doi.org/10.3389/fnagi.2020.00137
Wang H, Guan Y, Karamercan MA, Ye L, Bhatti T, Becker LB, Baur JA, Sims CA (2015) Resveratrol rescues kidney mitochondrial function following hemorrhagic shock. Shock 44:173–180. https://doi.org/10.1097/SHK.0000000000000390
Li SY, Susztak K (2018) The role of peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor gamma coactivator 1alpha (PGC-1alpha) in kidney disease. Semin Nephrol 38:121–126. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.semnephrol.2018.01.003
Miranda D, Jara C, Mejias S, Ahumada V, Cortez-San Martin M, Ibanez J, Hirsch S, Montoya M (2018) Deficient mitochondrial biogenesis in IL-2 activated NK cells correlates with impaired PGC1-alpha upregulation in elderly humans. Exp Gerontol 110:73–78. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.exger.2018.05.014
Zhou Z, Ma D, Li P, Wang P, Liu P, Wei D, Wang J, Qin Z, Fang Q, Wang J (2020) Sirt1 gene confers adriamycin resistance in DLBCL via activating the PCG-1alpha mitochondrial metabolic pathway. Aging (Albany NY) 12:11364–11385. https://doi.org/10.18632/aging.103174
Singh V, Prakhar P, Rajmani RS, Mahadik K, Borbora SM, Balaji KN (2017) Histone methyltransferase SET8 epigenetically reprograms host immune responses to assist mycobacterial survival. J Infect Dis 216:477–488. https://doi.org/10.1093/infdis/jix322
Wang Z, Ma K, Liu C, Hu X, Que W, Ito H, Takahashi K, Nakajima M, Tanaka T, Ren K, Guo WZ, Yi SQ, Li XK (2021) 5-Aminolevulinic acid combined with sodium ferrous citrate (5-ALA/SFC) ameliorated liver injury in a murine acute graft-versus-host disease model by reducing inflammation responses through PGC1-alpha activation. Drug Discov Ther 14:304–312. https://doi.org/10.5582/ddt.2020.03112
Pang D, Yang C, Luo Q, Li C, Liu W, Li L, Zou Y, Feng B, Chen Z, Huang C (2020) Soy isoflavones improve the oxidative stress induced hypothalamic inflammation and apoptosis in high fat diet-induced obese male mice through PGC1-alpha pathway. Aging (Albany NY) 12:8710–8727. https://doi.org/10.18632/aging.103197
Acknowledgements
Thanks to the members of our laboratory for their contributions.
Funding
This work was supported by National Natural Science Foundation of Gansu Province (Grant No. 20JR5RA350), Innovation and Entrepreneurship Action Plan Project for students of the First Clinical Medical School of Lanzhou University, and Excellence Program Project for students of the First Clinical Medical School of Lanzhou University.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
KL: concepts, design, experimental studies, writing—original draft preparation, supervision. LG: data analysis. SZ: experimental studies. Y-RM: data analysis. XX: experimental studies. QJ: data acquisition. Z-HK: data acquisition. M-LL: writing—reviewing and editing. T-XL: writing—reviewing and editing, funding acquisition, supervision. All the authors approved for the final version.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Ethical approval
Not Applicable. This article does not contain any studies with human participants or animals performed by any of the authors.
Consent for publication
Not applicable.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Li, K., Gao, L., Zhou, S. et al. Erythropoietin promotes energy metabolism to improve LPS-induced injury in HK-2 cells via SIRT1/PGC1-α pathway. Mol Cell Biochem 478, 651–663 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11010-022-04540-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11010-022-04540-y