Abstract
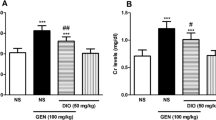
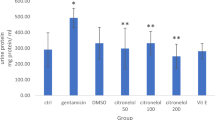
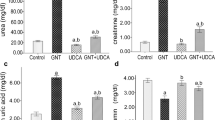
Gentamicin (GM) is an aminoglycoside antibiotic that induces nephrotoxicity. GM also causes necrosis of cells in the renal proximal tubules, resulting in acute tubular necrosis, followed by acute renal failure. Morphological alteration of blood cells, leukocytes and platelets count, as well as biochemical effects of l-cysteine (Cys) and antibiotic gentamicin, in clinically healthy male Wistar rats, were studied. Rats were divided into four groups: control (injected with 0.9% saline i.p.), GM (80 mg/kg b.w.; gentamicin injected i.p.), Cys-GM (100 mg/kg b.w.; l-cysteine and 80 mg/kg b.w. gentamicin injected i.p.), and Cys-GM-Cys (administered double dosage of 100 mg/kg b.w. l-cysteine and 80 mg/kg b.w. gentamicin i.p.). Biochemical and hematological analyses were performed on blood samples taken six days after treatments. Total proteins, albumin concentration and A/G ratio were significantly lower in experimental groups. Cholesterol, triglycerides, urea, and creatinine concentrations were significantly higher in relation to control. GM-induced lymphocytopenia, thrombocytopenia and neutrophilia. Echinocytosis and platelet disaggregation were found in all GM-treated animals. GM caused renal injury which indirectly led to erythrocyte abnormalities, changes in platelet aggregation, decreased protein fractions, and increased lipid and nitrogen components. The results suggest that GM-induced renal injury leads to significant biochemical changes in blood plasma, erythrocyte membrane impairment which can consequently cause anemia. Therefore, Cys might represent a novel therapeutic tool in the prevention and treatment of gentamicin-induced renal injury and blood cell disorders.





Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
Not applicable.
Code availability
Not applicable.
References
Krause KM, Serio AW, Kane TR, Connolly LE (2016) Aminoglycosides: an overview. Cold Spring Harb Perspect Med 6(6):a027029. https://doi.org/10.1101/cshperspect.a027029
Kotra LP, Haddad J, Mobashery S (2000) Aminoglycosides: perspectives on mechanisms of action and resistance and strategies to counter resistance. Antimicrob Agents Chemother 44(12):3249–3256. https://doi.org/10.1128/AAC.44.12.3249-3256.2000
Chang J, Jung HH, Yang JY, Choi J, Im GJ, Chae SW (2011) Protective role of antidiabetic drug metformin against gentamicin induced apoptosis in auditory cell line. Hear Res 282:92–96. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.heares.2011.09.005
Wilson DN (2014) Ribosome-targeting antibiotics and mechanisms of bacterial resistance. Nat Rev Microbiol 12(1):35–48. https://doi.org/10.1038/nrmicro3155
Erdem A, Gündoğan NU, Usubütün A, Kilinç K, Erdem SR, Kara A, Bozkurt A (2000) The protective effect of taurine against gentamicin-induced acute tubular necrosis in rats. Nephrol Dial Transplant 15(8):1175–1182. https://doi.org/10.1093/ndt/15.8.1175
Babu SV, Urolagin DK, Veeresh B, Attanshetty N (2011) Anogeissus latifolia prevents gentamicin induced nephrotoxicity in rats. Int J Pharm Sci 3(1):1091–1095
Stevens LA, Lafayette RA, Perrone RD, Levey AS, Schrier RW (2007) Laboratory evaluation of kidney function. In: Schrier RW (ed) Diseases of the kidney and urinary tract, 8th edn. Lippincott, Williams and Wilkins, Philadelphia, pp 299–336
Kore KJ, Shete RV, Kale BN, Borade AS (2011) Protective role of hydroalcoholic extract of Ficus carica in gentamicin induced nephrotoxicity in rats. Int J Pharm Life Sci 2:978–982
Chaware VJ, Chaudhary BP, Vaishnav MK, Biyani KR (2011) Protective effect of the aqueous extract of Momordica charantia leaves on gentamicin-induced nephrotoxicity in rats. Int J Pharm Tech Res 3(1):553–555
Amici M, Eusebi F, Miledi R (2005) Effects of the antibiotic gentamicin on nicotinic acetylcholine receptors. Neuropharmacology 49(5):79–88. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neuropharm.2005.04.015
Parlakpinar H, Tasdemir S, Polat A, Bay-Karabulut A, Vardi N, Ucar M, Acet A (2005) Protective role of caffeic acid phenethyl ester (cape) on gentamicin-induced acute renal toxicity in rats. Toxicol 207:169–177. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tox.2004.08.024
Abe A, Shayman JA (2009) The role of negatively charged lipids in lysosomal phospholipase A2 function. J Lipid Res 50:2027–2035. https://doi.org/10.1194/jlr.M900008-JLR200
Stojiljkovic N, Mihajlović D, Veljković S, Stoiljković M, Jovanović I (2008) Glomerular basement membrane alterations induced by gentamicin administration in rats. Exp Toxicol Pathol 60(1):69–75. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.etp.2008.02.007
Khan SA, Priyamvada S, Farooq N, Khan S, Khan MW, Yusufi AN (2009) Protective effect of green tea extract on gentamicin-induced nephrotoxicity and oxidative damage in rat kidney. Pharmacol Res 59:254–262. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.phrs.2008.12.009
Alarifi S, Al-Doaiss A, Alkahtani S, Al-Farraj SA, Saad Al-Eissa M, Al-Dahmash B, Al-Yahya H, Mubarak M (2012) Blood chemical changes and renal histological alterations induced by gentamicin in rats. Saudi J Biol Sci 19:103–110. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.sjbs.2011.11.002
Mehta RL, Kellum JA, Shah SV, Molitoris BA, Ronco C, Warnock DG, Levin A (2007) Acute kidney injury network: report of an initiative to improve outcomes in acute kidney injury. Crit Care 11(2):R31. https://doi.org/10.1186/cc5713
Chen CY, Wooster A, Bowser PR (2004) Comparative blood chemistry and histopathology of tilapia infected with Vibrio vulnificus or Streptococcus iniae or exposed to carbon tetrachloride, gentamicin, or copper sulfate. Aquaculture 239:421–443. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.aquaculture.2004.05.033
Marino SM, Gladyshev VN (2012) Analysis and functional prediction of reactive cysteine residues. J Biol Chem 287:4419–4425. https://doi.org/10.1074/jbc.R111.275578
Pace NJ, Weerapana E (2014) A competitive chemical-proteomic platform to identify zinc-binding cysteines. ACS Chem Biol 9:258–265. https://doi.org/10.1021/cb400622q
Reddie KG, Carroll KS (2008) Expanding the functional diversity of proteins through cysteine oxidation. Curr Opin Chem Biol 12:746–754. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cbpa.2008.07.028
Cremers CM, Jakob U (2013) Oxidant sensing by reversible disulfide bond formation. J Biol Chem 288:26489–26496. https://doi.org/10.1074/jbc.R113.462929
Erel O, Neselioglu S (2014) A novel and automated assay for thiol/disulphide homeostasis. Clin Biochem 47(18):326–332. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.clinbiochem.2014.09.026
Giustarini D, Milzani A, Dalle-Donne I, Tsikas D, Rossi R (2012) N-Acetylcysteine ethyl ester (NACET): a novel lipophilic cell-permeable cysteine derivative with an unusual pharmacokinetic feature and remarkable antioxidant potential. Biochem Pharmacol 84(1):1522–1533. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bcp.2012.09.010
Naidu MU, Shifow AA, Kumar KV, Ratnakar KS (2000) Ginkgo biloba extract ameliorates gentamicin-induced nephrotoxicity in rats. Phytomedicine 7(3):191–197. https://doi.org/10.1016/s0944-7113(00)80003-3
Silan C, Uzun O, Comunoğlu NU, Gokçen S, Bedirhan S, Cengiz M (2007) Gentamicin-induced nephrotoxicity in rats ameliorated and healing effects of resveratrol. Biol Pharm Bull 30(1):79–83. https://doi.org/10.1248/bpb.30.79
Abdel-Gayoum AA, Ali BH, Ghawarsha K, Bashir AA (1993) Plasma lipid profile in rats with gentamicin-induced nephrotoxicity. Hum Exp Toxicol 12(5):371–375. https://doi.org/10.1177/096032719301200505
Hamza R, El-Shenawy N (2017) The beneficial effects of L-cysteine on brain antioxidants of rats affected by sodium valproate. Hum Exp Toxicol 36(11):1212–1221. https://doi.org/10.1177/0960327117695634
Al-Salmi FA, Al-Eisa R, Hamza RZ, Khaled HE, El-Shenaw NS (2019) Protective effect of L-cysteine against sodium valproate-induced oxidant injury in testis of rats. Int J Pharm 15:248–256. https://doi.org/10.3923/ijp.2019.248.256
Suljević D, Mahmutović L, Mehinović L (2015) Biohemijska analitika I. Univerzitet u Sarajevu
Edwards JR, Diamantakos EA, Peuler JD, Lamar PC, Prozialeck WC (2007) A novel method for the evaluation of proximal tubule epithelial cellular necrosis in the intact rat kidney using ethidium homodimer. BMC Physiol 7:1. https://doi.org/10.1186/1472-6793-7-1
Li J, Li QX, Xie XF, Ao Y, Tie CR, Song RJ (2009) Differential roles of dihydropyridine calcium antagonist nifedipine, nitrendipine and amlodipine on gentamicin-induced renal tubular toxicity in rats. Eur J Pharmacol 620(1–3):97–104. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ejphar.2009.08.021
Dhanarasu S, Selvam MS, Alkhalaf AA, Aloraifi AKK, Al-Shammari NKA (2018) Ameliorative and erythrocytes membrane stabilizing effects of Mentha piperita on experimentally induced nephrotoxicity by gentamicin. EAJBS 3(10):23–37. https://doi.org/10.21608/eajbsc.2018.13653
Miri S, Safari T, Komeili GR, Nematbakhsh M, Niazi AA, Jahantigh M, Bagheri H, Maghool F (2018) Sex difference in gentamicin-induced nephrotoxicity: influence of L-arginine in rat model. Int J Prev Med 24:9–108. https://doi.org/10.4103/ijpvm.IJPVM_54_17
Gowda S, Desai PB, Kulkarni SS, Hull VV, Math AA, Vernekar SN (2010) Markers of renal function tests. N Am J Med Sci 2(4):170–173
Firdus A, Avdagić N, Fočak M, Mitrašinović-Brulić M, Suljević D (2022) Protective role of antithrombin III in suppressing acute responses in a rat model of renal ischemia-reperfusion injury. Mol Cell Biochem 477(2):627–634. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11010-021-04322-y
Wiedermann CJ, Wiedermann W, Joannidis M (2017) Causal relationship between hypoalbuminemia and acute kidney injury. World J Nephrol 6(4):176–187. https://doi.org/10.5527/wjn.v6.i4.176
Lee KW, Kyo Won L, Tae Min K, Kyeong Sik K, Seunghwan L, Junhun C, Jae Berm P, Ghee Young K, Sung Joo K (2018) Renal ischemia reperfusion injury in a diabetic monkey model and therapeutic testing of human bone marrow-derived mesenchymal stem cells. J Diabetes Res. https://doi.org/10.1155/2018/5182606
Cernaro V, Sfacteria A, Rifici C, Macri F, Maricchiolo G, Lacquaniti A, Alberto Ricciardi C, Buemi A, Costantino G, Santoro D, Buemi M (2017) Renoprotective effect of erythropoietin in zebrafish after administration of gentamicin: an immunohistochemical study for β-catenin and c-kit expression. J Nephrol 30(3):385–391. https://doi.org/10.1007/s40620-016-0353-y
Trevisan R, Dodesini AR, Lepore G (2006) Lipids and renal disease. J Am Soc Nephrol 4(2):145–147. https://doi.org/10.1681/ASN.2005121320
Abrass CK (2004) Cellular lipid metabolism and the role of lipids in progressive renal disease. Am J Nephrol 24(1):46–53. https://doi.org/10.1159/000075925
Vaziri ND, Sato T, Liang K (2003) Molecular mechanisms of altered cholesterol metabolism in rats with spontaneous focal glomerulosclerosis. Kidney Int 63(5):1756–1763. https://doi.org/10.1046/j.1523-1755.2003.00911.x
Eritsland J (2000) Safety considerations of polyunsaturated fatty acids. Am J Clin Nutr 71(1):197–201. https://doi.org/10.1093/ajcn/71.1.197S
Kondera E, Bojarski B, Lugowska K, Kot B, Witeska M (2020) Effects of oxytetracycline and gentamicin therapeutic doses on hematological, biochemical and hematopoietic parameters in Cyprinus carpio juveniles. Animals 2278:1–12. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani10122278
Lijana RC, Williams MC (1986) The effects of antibiotics on hemolytic behavior of red blood cell. Cell Biophys 8(4):223–242. https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02788514
Sakurai S, Shiojima I, Tanigawa T, Nakahara K (1997) Aminoglycosides prevent and dissociate the aggregation of platelets in patients with EDTA-dependent pseudothrombocytopenia. Br J Haematol 99(4):817–823. https://doi.org/10.1046/j.1365-2141.1997.4773280.x
Chen G, Fei X, Ling J (2012) The effects of aminoglycoside antibiotics on platelet aggregation and blood coagulation. CATH 18(5):538–541. https://doi.org/10.1177/1076029611430955
Otasevic V, Korac B (2016) Amino acids: metabolism. In: Caballero B, Paul M, Finglas M, Toldrá F (eds) Encyclopedia of food and health. Academic Press, Cambridge, pp 149–155
Poole LB (2015) The basics of thiols and cysteines in redox biology and chemistry. Free Radic Biol Med 80:148–157. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.freeradbiomed.2014.11.013
Sen CK, Packer L (2000) Thiol homeostasis and supplements in physical exercise. Am J Clin Nutr 72(2):653–669. https://doi.org/10.1093/ajcn/72.2.653S
Nitescu N, Ricksten SE, Marcussen N, Haraldsson B, Nilsson U, Basu S, Guron G (2006) N-Acetylcysteine attenuates kidney injury in rats subjected to renal ischaemia-reperfusion. Nephrol Dial Transplant 21(5):1240–1247. https://doi.org/10.1093/ndt/gfk032
Polat C, Tokyol C, Kahraman A, Sabuncuoğlu B, Yìlmaz S (2006) The effects of desferrioxamine and quercetin on hepatic ischemia–reperfusion induced renal disturbance. Prostaglandins Leukot Essent Fatty Acids 74(6):379–383. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.plefa.2006.03.007
Funding
Not applicable.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
DS: Conceptualization, Methodology, Validation, Formal analysis, Data curation, Writing—original draft, Writing—review and editing. MMB: Methodology, Validation, Formal analysis. MF: Formal analysis, Methodology, Data curation, Writing—original draft, Writing—review and editing.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Ethical approval
All applicable international, national, and institutional guidelines for the care and use of animals were followed by the authors.
Consent to participate
Not applicable.
Consent for publication
Not applicable.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Suljević, D., Mitrašinović-Brulić, M. & Fočak, M. l-cysteine protective effects against platelet disaggregation and echinocyte occurrence in gentamicin-induced kidney injury. Mol Cell Biochem 478, 13–22 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11010-022-04498-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11010-022-04498-x