Abstract
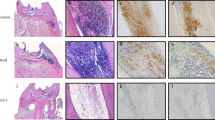
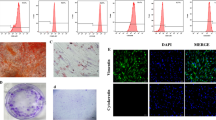
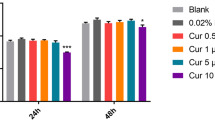
The aim of this study is to investigate the role of calcium-sensing receptor (CaSR) in the expression of inflammatory mediators of lipopolysaccharide (LPS)-treated human dental pulp cells (hDPCs). The expression profile of CaSR in LPS-simulated hDPCs was detected using immunofluorescence, real time quantitative PCR (RT-qPCR), and Western blot analyses. Then, its regulatory effects on the expression of specific inflammatory mediators such as interleukin (IL)-1β, IL-6, cyclooxygenase 2 (COX2)-derived prostaglandin E2 (PGE2), tumor necrosis factor (TNF)-α, and IL-10 were determined by RT-qPCR and enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA). LPS significantly downregulated the gene expression of CaSR, but upregulated its protein expression level in hDPCs. Treatments by CaSR agonist R568 or its antagonist Calhex231, and their combinations with protein kinase B (AKT) inhibitor LY294002 showed obvious effects on the expression of selected inflammatory mediators in a time-dependent manner. Meanwhile, an opposite direction was found between the action of R568 and Calhex231, as well as the expression of the pro- (IL-1β, IL-6, COX2-derived PGE2, and TNF-α) and anti-inflammatory (IL-10) mediators. The results provide the first evidence that CaSR-phosphatidylinositol-3 kinase (PI3K)-AKT-signaling pathway is involved in the release of inflammatory mediators in LPS-treated hDPCs, suggesting that the activation or blockade of CaSR may provide a novel therapeutic strategy for the treatment of pulp inflammatory diseases.




Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
The datasets used and/or analyzed during the current study available from the corresponding author on reasonable request.
References
Hahn CL, Liewehr FR (2007) Innate immune responses of the dental pulp to caries. J Endod 33(6):643–651. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.joen.2007.01.001
Goldberg M, Njeh A, Uzunoglu E (2015) Is pulp inflammation a prerequisite for pulp healing and regeneration? Mediat Inflamm 2015:347649. https://doi.org/10.1155/2015/347649
Fawzy El-Sayed KM, Elsalawy R, Ibrahim N, Gadalla M, Albargasy H, Zahra N, Mokhtar S, El Nahhas N, El Kaliouby Y, Dorfer CE (2019) The dental pulp stem/progenitor cells-mediated inflammatory-regenerative axis. Tissue Eng B 25(5):445–460. https://doi.org/10.1089/ten.TEB.2019.0106
He W, Wang Z, Luo Z, Yu Q, Jiang Y, Zhang Y, Zhou Z, Smith AJ, Cooper PR (2015) LPS promote the odontoblastic differentiation of human dental pulp stem cells via MAPK signaling pathway. J Cell Physiol 230(3):554–561. https://doi.org/10.1002/jcp.24732
Chmilewsky F, Jeanneau C, Laurent P, About I (2015) LPS induces pulp progenitor cell recruitment via complement activation. J Dent Res 94(1):166–174. https://doi.org/10.1177/0022034514555524
Wang HY, Liu XY, Han G, Wang ZY, Li XX, Jiang ZM, Jiang CM (2013) LPS induces cardiomyocyte injury through calcium-sensing receptor. Mol Cell Biochem 379(1–2):153–159. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11010-013-1637-3
Orecchioni M, Ghosheh Y, Pramod AB, Ley K (2019) Macrophage polarization: different gene signatures in M1(LPS+) vs. classically and M2(LPS−) vs. alternatively activated macrophages. Front Immunol 10:1084. https://doi.org/10.3389/fimmu.2019.01084
Owen JL, Cheng SX, Ge Y, Sahay B, Mohamadzadeh M (2016) The role of the calcium-sensing receptor in gastrointestinal inflammation. Semin Cell Dev Biol 49:44–51. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.semcdb.2015.10.040
Chavez-Abiega S, Mos I, Centeno PP, Elajnaf T, Schlattl W, Ward DT, Goedhart J, Kallay E (2020) Sensing extracellular calcium—an insight into the structure and function of the calcium-sensing receptor (CaSR). Adv Exp Med Biol 1131:1031–1063. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-12457-1_41
Leach K, Hannan FM, Josephs TM, Keller AN, Moller TC, Ward DT, Kallay E, Mason RS, Thakker RV, Riccardi D, Conigrave AD, Brauner-Osborne H (2020) International union of basic and clinical pharmacology. CVIII. Calcium-sensing receptor nomenclature, pharmacology, and function. Pharmacol Rev 72(3):558–604. https://doi.org/10.1124/pr.119.018531
Mizumachi H, Yoshida S, Tomokiyo A, Hasegawa D, Hamano S, Yuda A, Sugii H, Serita S, Mitarai H, Koori K, Wada N, Maeda H (2017) Calcium-sensing receptor-ERK signaling promotes odontoblastic differentiation of human dental pulp cells. Bone 101:191–201. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bone.2017.05.012
Chen Y, Gao Y, Tao Y, Lin D, An S (2019) Identification of a calcium-sensing receptor in human dental pulp cells that regulates mineral trioxide aggregate-induced mineralization. J Endod 45(7):907–916. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.joen.2019.03.019
Hendy GN, Canaff L (2016) Calcium-sensing receptor, proinflammatory cytokines and calcium homeostasis. Semin Cell Dev Biol 49:37–43. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.semcdb.2015.11.006
Sun K, Luo J, Guo J, Yao X, Jing X, Guo F (2020) The PI3K/AKT/mTOR signaling pathway in osteoarthritis: a narrative review. Osteoarthr Cartil 28(4):400–409. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.joca.2020.02.027
Miyauchi M, Takata T, Ito H, Ogawa I, Kobayashi J, Nikai H, Ijuhin N (1996) Immunohistochemical demonstration of prostaglandins E2, F2 alpha, and 6-keto-prostaglandin F1 alpha in rat dental pulp with experimentally induced inflammation. J Endod 22(11):600–602. https://doi.org/10.1016/s0099-2399(96)80029-x
Hirsch V, Wolgin M, Mitronin AV, Kielbassa AM (2017) Inflammatory cytokines in normal and irreversibly inflamed pulps: a systematic review. Arch Oral Biol 82:38–46. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.archoralbio.2017.05.008
Khorasani MMY, Hassanshahi G, Brodzikowska A, Khorramdelazad H (2020) Role(s) of cytokines in pulpitis: latest evidence and therapeutic approaches. Cytokine 126:154896. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cyto.2019.154896
Duncan HF, Cooper PR (2020) Pulp innate immune defense: translational opportunities. J Endod 46(9S):S10–S18. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.joen.2020.06.019
Lee JW, Park HA, Kwon OK, Park JW, Lee G, Lee HJ, Lee SJ, Oh SR, Ahn KS (2017) NPS 2143, a selective calcium-sensing receptor antagonist inhibits lipopolysaccharide-induced pulmonary inflammation. Mol Immunol 90:150–157. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.molimm.2017.07.012
Lee GS, Subramanian N, Kim AI, Aksentijevich I, Goldbach-Mansky R, Sacks DB, Germain RN, Kastner DL, Chae JJ (2012) The calcium-sensing receptor regulates the NLRP3 inflammasome through Ca2+ and cAMP. Nature 492(7427):123–127. https://doi.org/10.1038/nature11588
Klein GL, Castro SM, Garofalo RP (2016) The calcium-sensing receptor as a mediator of inflammation. Semin Cell Dev Biol 49:52–56. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.semcdb.2015.08.006
Wang ZJ, Zhang FM, Wang LS, Yao YW, Zhao Q, Gao X (2009) Lipopolysaccharides can protect mesenchymal stem cells (MSCs) from oxidative stress-induced apoptosis and enhance proliferation of MSCs via toll-like receptor(TLR)-4 and PI3K/Akt. Cell Biol Int 33(6):665–674. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cellbi.2009.03.006
Liu J, Du J, Chen X, Yang L, Zhao W, Song M, Wang Z, Wang Y (2019) The effects of mitogen-activated protein kinase signaling pathways on lipopolysaccharide-mediated osteo/odontogenic differentiation of stem cells from the apical papilla. J Endod 45(2):161–167. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.joen.2018.10.009
Zhang J, Zhang Y, Lv H, Yu Q, Zhou Z, Zhu Q, Wang Z, Cooper PR, Smith AJ, Niu Z, He W (2013) Human stem cells from the apical papilla response to bacterial lipopolysaccharide exposure and anti-inflammatory effects of nuclear factor I C. J Endod 39(11):1416–1422. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.joen.2013.07.018
Liu H, Tan B, Huang B, Li J, Wang J, Liao P, Guan G, Ji P, Yin Y (2018) Involvement of calcium-sensing receptor activation in the alleviation of intestinal inflammation in a piglet model by dietary aromatic amino acid supplementation. Br J Nutr 120(12):1321–1331. https://doi.org/10.1017/S0007114518002891
Guo Y, Xiao P, Lei S, Deng F, Xiao GG, Liu Y, Chen X, Li L, Wu S, Chen Y, Jiang H, Tan L, Xie J, Zhu X, Liang S, Deng H (2008) How is mRNA expression predictive for protein expression? A correlation study on human circulating monocytes. Acta Biochim Biophys Sin (Shanghai) 40(5):426–436. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1745-7270.2008.00418.x
Shui C, Spelsberg TC, Riggs BL, Khosla S (2003) Changes in Runx2/Cbfa1 expression and activity during osteoblastic differentiation of human bone marrow stromal cells. J Bone Miner Res 18(2):213–221. https://doi.org/10.1359/jbmr.2003.18.2.213
Sudhakar S, Li Y, Katz MS, Elango N (2001) Translational regulation is a control point in RUNX2/Cbfa1 gene expression. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 289(2):616–622. https://doi.org/10.1006/bbrc.2001.6033
Widbiller M, Eidt A, Wolflick M, Lindner SR, Schweikl H, Hiller KA, Buchalla W, Galler KM (2018) Interactive effects of LPS and dentine matrix proteins on human dental pulp stem cells. Int Endod J 51(8):877–888. https://doi.org/10.1111/iej.12897
Tomic S, Djokic J, Vasilijic S, Vucevic D, Todorovic V, Supic G, Colic M (2011) Immunomodulatory properties of mesenchymal stem cells derived from dental pulp and dental follicle are susceptible to activation by toll-like receptor agonists. Stem Cells Dev 20(4):695–708. https://doi.org/10.1089/scd.2010.0145
Nemeth EF, Goodman WG (2016) Calcimimetic and calcilytic drugs: feats, flops, and futures. Calcif Tissue Int 98(4):341–358. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00223-015-0052-z
Wu CL, Wu QY, Du JJ, Zeng JY, Li TT, Xu CQ, Sun YH (2015) Calcium-sensing receptor in the T lymphocyte enhanced the apoptosis and cytokine secretion in sepsis. Mol Immunol 63(2):337–342. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.molimm.2014.08.007
Hu B, Tong F, Xu L, Shen Z, Yan L, Xu G, Shen R (2018) Role of calcium sensing receptor in streptozotocin-induced diabetic rats exposed to renal ischemia reperfusion injury. Kidney Blood Press Res 43(1):276–286. https://doi.org/10.1159/000487685
Zhang H, Kovacs-Nolan J, Kodera T, Eto Y, Mine Y (2015) gamma-Glutamyl cysteine and gamma-glutamyl valine inhibit TNF-alpha signaling in intestinal epithelial cells and reduce inflammation in a mouse model of colitis via allosteric activation of the calcium-sensing receptor. Biochem Biophys Acta 1852(5):792–804. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bbadis.2014.12.023
Zhai TY, Cui BH, Zou L, Zeng JY, Gao S, Zhao Q, Wang Y, Xie WL, Sun YH (2017) Expression and role of the calcium-sensing receptor in rat peripheral blood polymorphonuclear neutrophils. Oxid Med Cell Longev 2017:3869561. https://doi.org/10.1155/2017/3869561
Greenberg HZE, Jahan KS, Shi J, Vanessa Ho WS, Albert AP (2016) The calcilytics Calhex-231 and NPS 2143 and the calcimimetic Calindol reduce vascular reactivity via inhibition of voltage-gated Ca(2+) channels. Eur J Pharmacol 791:659–668. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ejphar.2016.10.008
Yamamura A, Nayeem MJ, Sato M (2019) Calcilytics inhibit the proliferation and migration of human prostate cancer PC-3 cells. J Pharmacol Sci 139(3):254–257. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jphs.2019.01.008
Liu W, Sun J, Guo Y, Liu N, Ding X, Zhang X, Chi J, Kang N, Liu Y, Yin X (2020) Calhex231 ameliorates myocardial fibrosis post myocardial infarction in rats through the autophagy-NLRP3 inflammasome pathway in macrophages. J Cell Mol Med. https://doi.org/10.1111/jcmm.15969
Ren Z, Yang K, Zhao M, Liu W, Zhang X, Chi J, Shi Z, Zhang X, Fu Y, Liu Y, Yin X (2020) Calcium-sensing receptor on neutrophil promotes myocardial apoptosis and fibrosis after acute myocardial infarction via NLRP3 inflammasome activation. Can J Cardiol 36(6):893–905. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cjca.2019.09.026
Deng L, Qiu S, Wang C, Bian H, Wang L, Li Y, Wu B, Liu M (2019) Effects of the blood urea nitrogen to creatinine ratio on haemorrhagic transformation in AIS patients with diabetes mellitus. BMC Neurol 19(1):63. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12883-019-1290-x
Funding
This study was supported by the Guangdong Basic and Applied Basic Research Foundation (Grant No. 2019A1515010072), and National Science Foundation of China (Grant No. 81700957).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
YC, YL and TY performed the experiments and analyzed the data. SA and YH designed and supervised this project jointly. SA analyzed the data, drafted the first manuscript and revised the manuscript finally.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors deny any conflict of interest related to this study.
Ethical approval
All experimental protocols were approved by the Ethics Committee of Guanghua School of Stomatology, Sun Yat-sen University, Guangzhou, Guangdong, China (No. KQEC-2022-18-01).
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
An, S., Chen, Y., Yang, T. et al. A role for the calcium-sensing receptor in the expression of inflammatory mediators in LPS-treated human dental pulp cells. Mol Cell Biochem 477, 2871–2881 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11010-022-04486-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11010-022-04486-1