Abstract
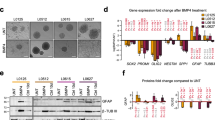
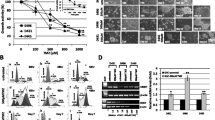
Glioblastomas (GBMs) are aggressive brain tumors that are resistant to chemotherapy and radiation. Bone morphogenetic protein (BMP) ligand BMP4 is being examined as a potential therapeutic for GBMs because it induces differentiation of cancer stem cells (CSCs) to an astrocyte phenotype. ID1 is reported to promote self-renewal and inhibit CSC differentiation. In most cancers, ID1 is transcriptionally upregulated by BMP4 promoting invasion and stemness. This conflicting data bring into question whether BMP signaling is growth suppressive or growth promoting in GBMs. We utilized BMP inhibitors DMH1, JL5, and Ym155 to examine the role of BMP signaling on the growth of GBMs. DMH1 targets BMP type 1 receptors whereas JL5 inhibits both the type 1 and type 2 BMP receptors. Ym155 does not bind the BMP receptors but rather inhibits BMP signaling by inducing the degradation of BMPR2. We show that JL5, DMH1, and Ym155 decreased the expression of ID1 in SD2 and U87 cells. JL5 and Ym155 also decreased the expression of BMPR2 and its downstream target inhibitor of apoptosis protein XIAP. JL5 treatment resulted in significant cell death and suppressed self-renewal to a greater extent than that induced by BMP4 ligand. The lysosome inhibitor chloroquine increases the localization of BMPR2 to the plasma membrane enhancing JL5-induced downregulation of ID1 and cell death in SD2 cells. We show that BMP signaling is growth promoting in GBMs. These studies suggest the need for development of BMP inhibitors and evaluation as potential therapeutic for GBMs.







Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
Data will be made available on reasonable request.
Abbreviations
- GBMs:
-
Glioblastomas
- CSCs:
-
Cancer stem cells
- BMPs:
-
Bone morphogenetic proteins
- BMPR:
-
Bone morphogenetic protein receptor
- ID1:
-
Inhibitor of differentiation protein 1
- CO2:
-
Carbon dioxide
- PBS:
-
Phosphate-buffered saline
- NIH:
-
National Institute of Health
- XIAP:
-
X-linked inhibitor of apoptosis protein
- TAK1:
-
Transforming growth factor-β-activated kinase 1
References
Blázquez-Medela AM, Jumabay M, Boström KI (2019) Beyond the bone: bone morphogenetic protein signaling in adipose tissue. Obes Rev 20:648–658. https://doi.org/10.1111/obr.12822
Stupp R, Mason WP, van den Bent MJ, Weller M, Fisher B, Taphoorn MJ, Belanger K, Brandes AA, Marosi C, Bogdahn U, Curschmann J, Janzer RC, Ludwin SK, Gorlia T, Allgeier A, Lacombe D, Cairncross JG, Eisenhauer E, Mirimanoff RO (2005) Radiotherapy plus concomitant and adjuvant temozolomide for glioblastoma. N Engl J Med 352:987–996. https://doi.org/10.1056/NEJMoa043330
Chen J, Li Y, Yu TS, McKay RM, Burns DK, Kernie SG, Parada LF (2012) A restricted cell population propagates glioblastoma growth after chemotherapy. Nature 488:522–526. https://doi.org/10.1038/nature11287
Bao S, Wu Q, McLendon RE, Hao Y, Shi Q, Hjelmeland AB, Dewhirst MW, Bigner DD, Rich JN (2006) Glioma stem cells promote radioresistance by preferential activation of the DNA damage response. Nature 444:756–760. https://doi.org/10.1038/nature05236
Gross RE, Mehler MF, Mabie PC, Zang Z, Santschi L, Kessler JA (1996) Bone morphogenetic proteins promote astroglial lineage commitment by mammalian subventricular zone progenitor cells. Neuron 17:595–606
Piccirillo SG, Reynolds BA, Zanetti N, Lamorte G, Binda E, Broggi G, Brem H, Olivi A, Dimeco F, Vescovi AL (2006) Bone morphogenetic proteins inhibit the tumorigenic potential of human brain tumour-initiating cells. Nature 444:761–765. https://doi.org/10.1038/nature05349
Gonzalez-Gomez P, Crecente-Campo J, Zahonero C, de la Fuente M, Hernandez-Lain A, Mira H, Sanchez-Gomez P, Garcia-Fuentes M (2015) Controlled release microspheres loaded with BMP7 suppress primary tumors from human glioblastoma. Oncotarget 6:10950–10963. https://doi.org/10.18632/oncotarget.3459
Xi G, Best B, Mania-Farnell B, James CD, Tomita T (2017) Therapeutic potential for bone morphogenetic protein 4 in human malignant glioma. Neoplasia 19:261–270. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neo.2017.01.006
Lee J, Son MJ, Woolard K, Donin NM, Li A, Cheng CH, Kotliarova S, Kotliarov Y, Walling J, Ahn S, Kim M, Totonchy M, Cusack T, Ene C, Ma H, Su Q, Zenklusen JC, Zhang W, Maric D, Fine HA (2008) Epigenetic-mediated dysfunction of the bone morphogenetic protein pathway inhibits differentiation of glioblastoma-initiating cells. Cancer Cell 13:69–80
Nickel J, Sebald W, Groppe JC, Mueller TD (2009) Intricacies of BMP receptor assembly. Cytokine Growth Factor Rev 20:367–377
Hollnagel A, Oehlmann V, Heymer J, Ruther U, Nordheim A (1999) Id genes are direct targets of bone morphogenetic protein induction in embryonic stem cells. J Biol Chem 274:19838–19845
Katagiri T, Imada M, Yanai T, Suda T, Takahashi N, Kamijo R (2002) Identification of a BMP-responsive element in Id1, the gene for inhibition of myogenesis. Genes Cells 7:949–960
Korchynskyi O, ten Dijke P (2002) Identification and functional characterization of distinct critically important bone morphogenetic protein-specific response elements in the Id1 promoter. J Biol Chem 277:4883–4891
Langenfeld E, Deen M, Zachariah E, Langenfeld J (2013) Small molecule antagonist of the bone morphogenetic protein type I receptors suppresses growth and expression of Id1 and Id3 in lung cancer cells expressing Oct4 or nestin. Mol Cancer 12:129
Clement JH, Marr N, Meissner A, Schwalbe M, Sebald W, Kliche KO, Hoffken K, Wolfl S (2000) Bone morphogenetic protein 2 (BMP-2) induces sequential changes of Id gene expression in the breast cancer cell line MCF-7. J Cancer Res Clin Oncol 126:271–279
Sachdeva R, Wu M, Johnson K, Kim H, Celebre A, Shahzad U, Graham MS, Kessler JA, Chuang JH, Karamchandani J, Bredel M, Verhaak R, Das S (2019) BMP signaling mediates glioma stem cell quiescence and confers treatment resistance in glioblastoma. Sci Rep 9:14569. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-019-51270-1
Langenfeld EM, Langenfeld J (2004) Bone morphogenetic protein-2 stimulates angiogenesis in developing tumors. Mol Cancer Res 2:141–149
Langenfeld EM, Calvano SE, Abou-Nukta F, Lowry SF, Amenta P, Langenfeld J (2003) The mature bone morphogenetic protein-2 is aberrantly expressed in non-small cell lung carcinomas and stimulates tumor growth of A549 cells. Carcinogenesis 24:1445–1454
Augeri DJ, Langenfeld E, Castle M, Gilleran JA, Langenfeld J (2016) Inhibition of BMP and of TGFbeta receptors downregulates expression of XIAP and TAK1 leading to lung cancer cell death. Mol Cancer 15:27. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12943-016-0511-9
Newman JH, Augeri DJ, NeMoyer R, Malhotra J, Langenfeld E, Chesson CB, Dobias NS, Lee MJ, Tarabichi S, Jhawar SR, Bommareddy PK, Marshall S, Sadimin ET, Kerrigan JE, Goedken M, Minerowicz C, Jabbour SK, Li S, Carayannopolous MO, Zloza A, Langenfeld J (2018) Novel bone morphogenetic protein receptor inhibitor JL5 suppresses tumor cell survival signaling and induces regression of human lung cancer. Oncogene. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41388-018-0156-9
Owens P, Pickup MW, Novitskiy SV, Giltnane JM, Gorska AE, Hopkins CR, Hong CC, Moses HL (2015) Inhibition of BMP signaling suppresses metastasis in mammary cancer. Oncogene 34:2437–2449. https://doi.org/10.1038/onc.2014.189
Le Page C, Puiffe ML, Meunier L, Zietarska M, de Ladurantaye M, Tonin PN, Provencher D, Mes-Masson AM (2009) BMP-2 signaling in ovarian cancer and its association with poor prognosis. J Ovarian Res 2:4
Balboni AL, Hutchinson JA, DeCastro AJ, Cherukuri P, Liby K, Sporn MB, Schwartz GN, Wells WA, Sempere LF, Yu PB, DiRenzo J (2013) DeltaNp63alpha-mediated activation of bone morphogenetic protein signaling governs stem cell activity and plasticity in normal and malignant mammary epithelial cells. Cancer Res 73:1020–1030. https://doi.org/10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-12-2862
Jin X, Jin X, Kim LJY, Dixit D, Jeon HY, Kim EJ, Kim JK, Lee SY, Yin J, Rich JN, Kim H (2018) Inhibition of ID1-BMPR2 intrinsic signaling sensitizes glioma stem cells to differentiation therapy. Clin Cancer Res 24:383–394. https://doi.org/10.1158/1078-0432.ccr-17-1529
Langenfeld E, Hong CC, Lanke G, Langenfeld J (2013) Bone morphogenetic protein type I receptor antagonists decrease growth and induce cell death of lung cancer cell lines. PLoS ONE 8:e61256. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0061256
Langenfeld EM, Kong Y, Langenfeld J (2006) Bone morphogenetic protein 2 stimulation of tumor growth involves the activation of Smad-1/5. Oncogene 25:685–692
Fontebasso AM, Papillon-Cavanagh S, Schwartzentruber J, Nikbakht H, Gerges N, Fiset PO, Bechet D, Faury D, De Jay N, Ramkissoon LA, Corcoran A, Jones DT, Sturm D, Johann P, Tomita T, Goldman S, Nagib M, Bendel A, Goumnerova L, Bowers DC, Leonard JR, Rubin JB, Alden T, Browd S, Geyer JR, Leary S, Jallo G, Cohen K, Gupta N, Prados MD, Carret AS, Ellezam B, Crevier L, Klekner A, Bognar L, Hauser P, Garami M, Myseros J, Dong Z, Siegel PM, Malkin H, Ligon AH, Albrecht S, Pfister SM, Ligon KL, Majewski J, Jabado N, Kieran MW (2014) Recurrent somatic mutations in ACVR1 in pediatric midline high-grade astrocytoma. Nat Genet 46:462–466. https://doi.org/10.1038/ng.2950
Shore EM, Xu M, Feldman GJ, Fenstermacher DA, Cho TJ, Choi IH, Connor JM, Delai P, Glaser DL, LeMerrer M, Morhart R, Rogers JG, Smith R, Triffitt JT, Urtizberea JA, Zasloff M, Brown MA, Kaplan FS (2006) A recurrent mutation in the BMP type I receptor ACVR1 causes inherited and sporadic fibrodysplasia ossificans progressiva. Nat Genet 38:525–527. https://doi.org/10.1038/ng1783
van Dinther M, Visser N, de Gorter DJ, Doorn J, Goumans MJ, de Boer J, ten Dijke P (2010) ALK2 R206H mutation linked to fibrodysplasia ossificans progressiva confers constitutive activity to the BMP type I receptor and sensitizes mesenchymal cells to BMP-induced osteoblast differentiation and bone formation. J Bone Miner Res 25:1208–1215. https://doi.org/10.1359/jbmr.091110
Sanchez-Duffhues G, Williams E, Goumans MJ, Heldin CH, Ten Dijke P (2020) Bone morphogenetic protein receptors: structure, function and targeting by selective small molecule kinase inhibitors. Bone 138:115472. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bone.2020.115472
Hoeman CM, Cordero FJ, Hu G, Misuraca K, Romero MM, Cardona HJ, Nazarian J, Hashizume R, McLendon R, Yu P, Procissi D, Gadd S, Becher OJ (2019) ACVR1 R206H cooperates with H3.1K27M in promoting diffuse intrinsic pontine glioma pathogenesis. Nat Commun 10:1023. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41467-019-08823-9
Tejero R, Huang Y, Katsyv I, Kluge M, Lin JY, Tome-Garcia J, Daviaud N, Wang Y, Zhang B, Tsankova NM, Friedel CC, Zou H, Friedel RH (2019) Gene signatures of quiescent glioblastoma cells reveal mesenchymal shift and interactions with niche microenvironment. EBioMedicine 42:252–269. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ebiom.2019.03.064
Shannon S, Jia D, Entersz I, Beelen P, Yu M, Carcione C, Carcione J, Mahtabfar A, Vaca C, Weaver M, Shreiber D, Zahn JD, Liu L, Lin H, Foty RA (2017) Inhibition of glioblastoma dispersal by the MEK inhibitor PD0325901. BMC Cancer 17:121. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12885-017-3107-x
Mehta M, Khan A, Danish S, Haffty BG, Sabaawy HE (2015) Radiosensitization of primary human glioblastoma stem-like cells with low-dose AKT inhibition. Mol Cancer Ther 14:1171–1180. https://doi.org/10.1158/1535-7163.mct-14-0708
Newman JH, Augeri DJ, NeMoyer R, Malhotra J, Langenfeld E, Chesson CB, Dobias NS, Lee MJ, Tarabichi S, Jhawar SR, Bommareddy PK, Marshall S, Sadimin ET, Kerrigan JE, Goedken M, Minerowicz C, Jabbour SK, Li S, Carayannopolous MO, Zloza A, Langenfeld J (2018) Novel bone morphogenetic protein receptor inhibitor JL5 suppresses tumor cell survival signaling and induces regression of human lung cancer. Oncogene 37:3672–3685. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41388-018-0156-9
NeMoyer R, Mondal A, Vora M, Langenfeld E, Glover D, Scott M, Lairson L, Rongo C, Augeri DJ, Peng Y, Jabbour SK, Langenfeld J (2019) Targeting bone morphogenetic protein receptor 2 sensitizes lung cancer cells to TRAIL by increasing cytosolic Smac/DIABLO and the downregulation of X-linked inhibitor of apoptosis protein. Cell Commun Signal 17:150. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12964-019-0469-5
Engers DW, Frist AY, Lindsley CW, Hong CC, Hopkins CR (2013) Synthesis and structure-activity relationships of a novel and selective bone morphogenetic protein receptor (BMP) inhibitor derived from the pyrazolo[1.5-a]pyrimidine scaffold of dorsomorphin: the discovery of ML347 as an ALK2 versus ALK3 selective MLPCN probe. Bioorg Med Chem Lett 23:3248–3252. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bmcl.2013.03.113
Nakahara T, Kita A, Yamanaka K, Mori M, Amino N, Takeuchi M, Tominaga F, Hatakeyama S, Kinoyama I, Matsuhisa A, Kudoh M, Sasamata M (2007) YM155, a novel small-molecule survivin suppressant, induces regression of established human hormone-refractory prostate tumor xenografts. Cancer Res 67:8014–8021. https://doi.org/10.1158/0008-5472.Can-07-1343
Mondal A, NeMoyer R, Vora M, Napoli L, Syed Z, Langenfeld E, Jia D, Peng Y, Gilleran J, Roberge J, Rongo C, Jabbour SK, Langenfeld J (2021) Bone morphogenetic protein receptor 2 inhibition destabilizes microtubules promoting the activation of lysosomes and cell death of lung cancer cells. Cell Commun Signal 19:97. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12964-021-00743-w
Diaz-Moreno M, Armenteros T, Gradari S, Hortiguela R, Garcia-Corzo L, Fontan-Lozano A, Trejo JL, Mira H (2018) Noggin rescues age-related stem cell loss in the brain of senescent mice with neurodegenerative pathology. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 115:11625–11630. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.1813205115
Dunmore BJ, Drake KM, Upton PD, Toshner MR, Aldred MA, Morrell NW (2013) The lysosomal inhibitor, chloroquine, increases cell surface BMPR-II levels and restores BMP9 signalling in endothelial cells harbouring BMPR-II mutations. Hum Mol Genet 22:3667–3679. https://doi.org/10.1093/hmg/ddt216
Caren H, Beck S, Pollard SM (2016) Differentiation therapy for glioblastoma—too many obstacles? Mol Cell Oncol 3:e1124174. https://doi.org/10.1080/23723556.2015.1124174
Dalmo E, Johansson P, Niklasson M, Gustavsson I, Nelander S, Westermark B (2020) Growth inhibitory activity of bone morphogenetic protein 4 in human glioblastoma cell lines is heterogeneous and dependent on reduced SOX2 expression. Mol Cancer Res. https://doi.org/10.1158/1541-7786.mcr-19-0638
Caren H, Stricker SH, Bulstrode H, Gagrica S, Johnstone E, Bartlett TE, Feber A, Wilson G, Teschendorff AE, Bertone P, Beck S, Pollard SM (2015) Glioblastoma stem cells respond to differentiation cues but fail to undergo commitment and terminal cell-cycle arrest. Stem Cell Rep 5:829–842. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.stemcr.2015.09.014
Sachdeva R, Wu M, Smiljanic S, Kaskun O, Ghannad-Zadeh K, Celebre A, Isaev K, Morrissy AS, Guan J, Tong J, Chan J, Wilson TM, Al-Omaishi S, Munoz DG, Dirks PB, Moran MF, Taylor MD, Reimand J, Das S (2019) ID1 Is critical for tumorigenesis and regulates chemoresistance in glioblastoma. Cancer Res 79:4057–4071. https://doi.org/10.1158/0008-5472.can-18-1357
Guo P, Lan J, Ge J, Mao Q, Qiu Y (2013) ID1 regulates U87 human cell proliferation and invasion. Oncol Lett 6:921–926. https://doi.org/10.3892/ol.2013.1507
Soroceanu L, Murase R, Limbad C, Singer E, Allison J, Adrados I, Kawamura R, Pakdel A, Fukuyo Y, Nguyen D, Khan S, Arauz R, Yount GL, Moore DH, Desprez PY, McAllister SD (2013) Id-1 is a key transcriptional regulator of glioblastoma aggressiveness and a novel therapeutic target. Cancer Res 73:1559–1569. https://doi.org/10.1158/0008-5472.Can-12-1943
Garnier D, Renoult O, Alves-Guerra MC, Paris F, Pecqueur C (2019) Glioblastoma stem-like cells, metabolic strategy to kill a challenging target. Front Oncol 9:118. https://doi.org/10.3389/fonc.2019.00118
Jankovic V, Ciarrocchi A, Boccuni P, DeBlasio T, Benezra R, Nimer SD (2007) Id1 restrains myeloid commitment, maintaining the self-renewal capacity of hematopoietic stem cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 104:1260–1265. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.0607894104
O’Brien CA, Kreso A, Ryan P, Hermans KG, Gibson L, Wang Y, Tsatsanis A, Gallinger S, Dick JE (2012) ID1 and ID3 regulate the self-renewal capacity of human colon cancer-initiating cells through p21. Cancer Cell 21:777–792. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ccr.2012.04.036
Yamaguchi K, Nagai S, Ninomiya-Tsuji J, Nishita M, Tamai K, Irie K, Ueno N, Nishida E, Shibuya H, Matsumoto K (1999) XIAP, a cellular member of the inhibitor of apoptosis protein family, links the receptors to TAB1-TAK1 in the BMP signaling pathway. Embo J 18:179–187. https://doi.org/10.1093/emboj/18.1.179
Jiao G, Guo W, Ren T, Lu Q, Sun Y, Liang W, Ren C, Yang K, Sun K (2014) BMPR2 inhibition induced apoptosis and autophagy via destabilization of XIAP in human chondrosarcoma cells. Cell Death Dis 5:e1571. https://doi.org/10.1038/cddis.2014.540
Hover LD, Owens P, Munden AL, Wang J, Chambless LB, Hopkins CR, Hong CC, Moses HL, Abel TW (2016) Bone morphogenetic protein signaling promotes tumorigenesis in a murine model of high-grade glioma. Neuro Oncol 18:928–938. https://doi.org/10.1093/neuonc/nov310
Gleason RJ, Akintobi AM, Grant BD, Padgett RW (2014) BMP signaling requires retromer-dependent recycling of the type I receptor. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 111:2578–2583. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.1319947111
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by grants from National Institute of Health (NIH) R01 CA225830 and 3R01CA225830-01S1, and Rutgers University and NIH HealthAdvance grant, #U01HL150852.
Funding
This work was funded by grants from National Institute of Health (NIH) R01 CA225830, 3R01CA225830-01S1, and HealthAdvance/REACH program, Rutgers University and NIH, #U01HL150852.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
JK contributed to data acquisition and figure preparation and co-wrote the method section. AM contributed to acquisition of data, co-wrote the methods section, and edited drafted manuscript. RF critically reviewed and edited the manuscript. DJ contributed to data acquisition. JL contributed to study design, preparation of figures, and wrote the manuscript. All authors approved the manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Ethical approval
The use of BMP inhibitors and cell lines has been approved by Rutgers University Institutional Biosafety Committee #13-424.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kaye, J., Mondal, A., Foty, R. et al. Bone morphogenetic protein receptor inhibitors suppress the growth of glioblastoma cells. Mol Cell Biochem 477, 1583–1595 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11010-022-04383-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11010-022-04383-7