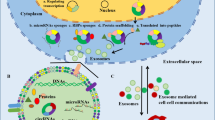
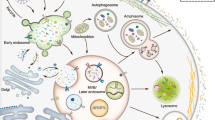
Abstract
In recent years, processing bodies (P-bodies) formed by liquid–liquid phase separation, have attracted growing scientific attention due to their involvement in numerous cellular activities, including the regulation of mRNAs decay or storage. These cytoplasmic dynamic membraneless granules contain mRNA storage and decay components such as deadenylase and decapping factors. In addition, different mRNA metabolic regulators, including m6A readers and gene-mediated miRNA-silencing, are also associated with such P-bodies. Cancerous cells may profit from these mRNA decay shredders by up-regulating the expression level of oncogenes and down-regulating tumor suppressor genes. The main challenges of cancer treatment are drug resistance, metastasis, and cancer relapse likely associated with cancer stem cells, heterogeneity, and plasticity features of different tumors. The mRNA metabolic regulators based on P-bodies play a great role in cancer development and progression. The dysregulation of P-bodies mediators affects mRNA metabolism. However, less is known about the relationship between P-bodies mediators and cancerous behavior. The current review summarizes the recent studies on P-bodies mediators, their contribution to tumor development, and their potential in the clinical setting, particularly highlighting the P-bodies as potential drug-carriers such as exosomes to anticancer in the future.



Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
Not applicable.
Abbreviations
- AGO:
-
Argonaute
- BRF1:
-
TFIIB-related factor 1
- CPEB:
-
Cytoplasmic polyadenylation element binging protein
- CSC:
-
Cancer stem cell
- DCP:
-
Decapping enzyme
- Edc3:
-
Enhancer of mRNA-decapping protein 3
- elF3:
-
Eukaryotic initiation factor 3
- EMT:
-
Epithelial-mesenchyme transition
- FTO:
-
Fat mass and obesity-associated protein
- HCC:
-
Hepatocellular carcinoma
- Lsm1:
-
U6 snRNA-associated Sm-like protein LSm1
- LLPS:
-
Liquid–liquid phase separation
- m6A:
-
RNA N6-methyladenosine
- m7G:
-
7-Methylguanosine cap
- miRNA:
-
MicroRNA
- MSC:
-
Mesenchymal stem cell
- NMD:
-
Nonsense-mediated mRNA decay
- PABP:
-
Poly(A)-binding protein
- P-bodies:
-
Processing bodies
- RNP:
-
Ribonucleoprotein
- Sbp1:
-
Single-stranded nucleic acid- binding protein
- TTP:
-
Tristetraprolin protein
- Upf:
-
Up-frameshift
- UTR:
-
Untranslated region
- WTAP:
-
Wilms tumor 1-associated protein
References
Bray F, Ferlay J, Soerjomataram I, Siegel RL, Torre LA, Jemal A (2018) Global cancer statistics 2018: GLOBOCAN estimates of incidence and mortality worldwide for 36 cancers in 185 countries. CA Cancer J Clin 68(6):394–424. https://doi.org/10.3322/caac.21492
Han J, Puri RK (2018) Analysis of the cancer genome atlas (TCGA) database identifies an inverse relationship between interleukin-13 receptor α1 and α2 gene expression and poor prognosis and drug resistance in subjects with glioblastoma multiforme. J Neurooncol 136(3):463–474. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11060-017-2680-9
Zugazagoitia J, Guedes C, Ponce S, Ferrer I, Molina-Pinelo S, Paz-Ares L (2016) Current challenges in cancer treatment. Clin Ther 38(7):1551–1566. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.clinthera.2016.03.026
Tanabe S, Quader S, Cabral H, Ono R (2020) Interplay of EMT and CSC in cancer and the potential therapeutic strategies. Front Pharmacol 11:904. https://doi.org/10.3389/fphar.2020.00904
Alam R, Abdolmaleky HM, Zhou JR (2017) Microbiome, inflammation, epigenetic alterations, and mental diseases. Am J Med Genet B Neuropsychiatr Genet 174(6):651–660. https://doi.org/10.1002/ajmg.b.32567
Bouchard JJ, Otero JH, Scott DC, Szulc E, Martin EW, Sabri N, Granata D, Marzahn MR, Lindorff-Larsen K, Salvatella X, Schulman BA, Mittag T (2018) Cancer mutations of the tumor suppressor SPOP disrupt the formation of active, phase-separated compartments. Mol Cell 72(1):19-36.e8. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.molcel.2018.08.027
Nozawa RS, Yamamoto T, Takahashi M, Tachiwana H, Maruyama R, Hirota T, Saitoh N (2020) Nuclear microenvironment in cancer: control through liquid-liquid phase separation. Cancer Sci 111(9):3155–3163. https://doi.org/10.1111/cas.14551
Gosline SJ, Gurtan AM, JnBaptiste CK, Bosson A, Milani P, Dalin S, Matthews BJ, Yap YS, Sharp PA, Fraenkel E (2016) Elucidating MicroRNA regulatory networks using transcriptional, post-transcriptional, and histone modification measurements. Cell Rep 14(2):310–319. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.celrep.2015.12.031
Mishra R, Haldar S, Suchanti S, Bhowmick NA (2019) Epigenetic changes in fibroblasts drive cancer metabolism and differentiation. Endocr Relat Cancer 26(12):R673–R688. https://doi.org/10.1530/ERC-19-0347
Patranabis S, Bhattacharyya SN (2018) P-body-induced inactivation of let-7a miRNP prevents the death of growth factor-deprived neuronal cells. FASEB J 32(3):1493–1509. https://doi.org/10.1096/fj.201700633R
Sahu S, Wang Z, Jiao X, Gu C, Jork N, Wittwer C, Li X, Hostachy S, Fiedler D, Wang H, Jessen HJ, Kiledjian M, Shears SB (2020) InsP7 is a small-molecule regulator of NUDT3-mediated mRNA decapping and processing-body dynamics. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 117(32):19245–19253. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.1922284117
Mort M, Ivanov D, Cooper DN, Chuzhanova NA (2008) A meta-analysis of nonsense mutations causing human genetic disease. Hum Mutat 29(8):1037–1047. https://doi.org/10.1002/humu.20763
Costa-Pinheiro P, Montezuma D, Henrique R, Jerónimo C (2015) Diagnostic and prognostic epigenetic biomarkers in cancer. Epigenomics 7(6):1003–1015. https://doi.org/10.2217/epi.15.56
Mitrea DM, Kriwacki RW (2016) Phase separation in biology; functional organization of a higher order. Cell Commun Signal 14:1. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12964-015-0125-7
Gomes E, Shorter J (2019) The molecular language of membraneless organelles. J Biol Chem 294(18):7115–7127. https://doi.org/10.1074/jbc.TM118.001192
Bhattacharyya SN, Habermacher R, Martine U, Closs EI, Filipowicz W (2006) Stress-induced reversal of microRNA repression and mRNA P-body localization in human cells. Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant Biol 71:513–521. https://doi.org/10.1101/sqb.2006.71.038
Bashkirov VI, Scherthan H, Solinger JA, Buerstedde JM, Heyer WD (1997) A mouse cytoplasmic exoribonuclease (mXRN1p) with preference for G4 tetraplex substrates. J Cell Biol 136(4):761–773. https://doi.org/10.1083/jcb.136.4.761
Sheth U, Parker R (2003) Decapping and decay of messenger RNA occur in cytoplasmic processing bodies. Science 300(5620):805–808. https://doi.org/10.1126/science.1082320
Huch S, Nissan T (2017) An mRNA decapping mutant deficient in P body assembly limits mRNA stabilization in response to osmotic stress. Sci Rep 7:44395. https://doi.org/10.1038/srep44395
Suzuki A, Igarashi K, Aisaki K, Kanno J, Saga Y (2010) NANOS2 interacts with the CCR4-NOT deadenylation complex and leads to suppression of specific RNAs. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 107(8):3594–3599. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.0908664107
Chicois C, Scheer H, Garcia S, Zuber H, Mutterer J, Chicher J, Hammann P, Gagliardi D, Garcia D (2018) The UPF1 interactome reveals interaction networks between RNA degradation and translation repression factors in Arabidopsis. Plant J 96(1):119–132. https://doi.org/10.1111/tpj.14022
Jagannath A, Wood MJ (2009) Localization of double-stranded small interfering RNA to cytoplasmic processing bodies is Ago2 dependent and results in up-regulation of GW182 and Argonaute-2. Mol Biol Cell 20(1):521–529. https://doi.org/10.1091/mbc.e08-08-0796
Frydryskova K, Masek T, Borcin K, Mrvova S, Venturi V, Pospisek M (2016) Distinct recruitment of human eIF4E isoforms to processing bodies and stress granules. BMC Mol Biol 17(1):21. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12867-016-0072-x
Jain S, Parker R (2013) The discovery and analysis of P Bodies. Adv Exp Med Biol 768:23–43. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-1-4614-5107-5_3
Frischmeyer PA, van Hoof A, O’Donnell K, Guerrerio AL, Parker R, Dietz HC (2002) An mRNA surveillance mechanism that eliminates transcripts lacking termination codons. Science 295(5563):2258–2261. https://doi.org/10.1126/science.1067338
Gao M, Fritz DT, Ford LP, Wilusz J (2000) Interaction between a poly(A)-specific ribonuclease and the 5’ cap influences mRNA deadenylation rates in vitro. Mol Cell 5(3):479–488. https://doi.org/10.1016/s1097-2765(00)80442-6
Stewart M (2019) Polyadenylation and nuclear export of mRNAs. J Biol Chem 294(9):2977–2987. https://doi.org/10.1074/jbc.REV118.005594
Rauch S, He C, Dickinson BC (2018) Targeted m6A reader proteins to study epitranscriptomic regulation of single RNAs. J Am Chem Soc 140(38):11974–11981. https://doi.org/10.1021/jacs.8b05012
Horikawa W, Endo K, Wada M, Ito K (2016) Mutations in the G-domain of Ski7 cause specific dysfunction in non-stop decay. Sci Rep 6:29295. https://doi.org/10.1038/srep29295
Szádeczky-Kardoss I, Gál L, Auber A, Taller J, Silhavy D (2018) The No-go decay system degrades plant mRNAs that contain a long A-stretch in the coding region. Plant Sci 275:19–27. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.plantsci.2018.07.008
Zeng L, Chen Y, Wang Y, Yu LR, Knox B, Chen J, Shi T, Chen S, Ren Z, Guo L, Wu Y, Liu D, Huang K, Tong W, Yu D, Ning B (2017) MicroRNA hsa-miR-370-3p suppresses the expression and induction of CYP2D6 by facilitating mRNA degradation. Biochem Pharmacol 140:139–149. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bcp.2017.05.018
Chen Q, Han Y, Liu H, Wang X, Sun J, Zhao B, Li W, Tian J, Liang Y, Yan J, Yang X, Tian F (2018) Genome-wide association analyses reveal the importance of alternative splicing in diversifying gene function and regulating phenotypic variation in maize. Plant Cell 30(7):1404–1423. https://doi.org/10.1105/tpc.18.00109
Yi H, Park J, Ha M, Lim J, Chang H, Kim VN (2018) PABP cooperates with the CCR4-NOT complex to promote mRNA deadenylation and block precocious decay. Mol Cell 70(6):1081-1088.e5. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.molcel.2018.05.009
Maryati M, Kaur I, Jadhav GP, Olotu-Umoren L, Oveh B, Hashmi L, Fischer PM, Winkler GS (2014) A fluorescence-based assay suitable for quantitative analysis of deadenylase enzyme activity. Nucleic Acids Res 42(5):e30. https://doi.org/10.1093/nar/gkt972
Maryati M, Airhihen B, Winkler GS (2015) The enzyme activities of Caf1 and Ccr4 are both required for deadenylation by the human Ccr4-not nuclease module. Biochem J 469(1):169–176. https://doi.org/10.1042/BJ20150304
Taverniti V, Séraphin B (2015) Elimination of cap structures generated by mRNA decay involves the new scavenger mRNA decapping enzyme Aph1/FHIT together with DcpS. Nucleic Acids Res 43(1):482–492. https://doi.org/10.1093/nar/gku1251
Chu JM, Ye TT, Ma CJ, Lan MD, Liu T, Yuan BF, Feng YQ (2018) Existence of internal N7-methylguanosine modification in mRNA determined by differential enzyme treatment coupled with mass spectrometry analysis. ACS Chem Biol 13(12):3243–3250. https://doi.org/10.1021/acschembio.7b00906
He F, Celik A, Wu C, Jacobson A (2018) General decapping activators target different subsets of inefficiently translated mRNAs. Elife 7:e34409. https://doi.org/10.7554/eLife.34409
Jung MY, Lorenz L, Richter JD (2006) Translational control by neuroguidin, a eukaryotic initiation factor 4E and CPEB binding protein. Mol Cell Biol 26(11):4277–4287. https://doi.org/10.1128/MCB.02470-05
Costello JL, Kershaw CJ, Castelli LM, Talavera D, Rowe W, Sims PFG, Ashe MP, Grant CM, Hubbard SJ, Pavitt GD (2017) Dynamic changes in eIF4F-mRNA interactions revealed by global analyses of environmental stress responses. Genome Biol 18(1):201. https://doi.org/10.1186/s13059-017-1338-4
Joshi B, Cameron A, Jagus R (2004) Characterization of mammalian eIF4E-family members. Eur J Biochem 271(11):2189–2203. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1432-1033.2004.04149.x
Iwatani-Yoshihara M, Ito M, Ishibashi Y, Oki H, Tanaka T, Morishita D, Ito T, Kimura H, Imaeda Y, Aparicio S, Nakanishi A, Kawamoto T (2017) Discovery and characterization of a eukaryotic initiation factor 4A–3-selective inhibitor that suppresses nonsense-mediated mRNA decay. ACS Chem Biol 12(7):1760–1768. https://doi.org/10.1021/acschembio.7b00041
Haimov O, Sehrawat U, Tamarkin-Ben Harush A, Bahat A, Uzonyi A, Will A, Hiraishi H, Asano K, Dikstein R (2018) Dynamic interaction of eukaryotic initiation factor 4G1 (eIF4G1) with eIF4E and eIF1 underlies scanning-dependent and -independent translation. Mol Cell Biol 38(18):e00139-e218. https://doi.org/10.1128/MCB.00139-18
Grüner S, Peter D, Weber R, Wohlbold L, Chung MY, Weichenrieder O, Valkov E, Igreja C, Izaurralde E (2016) The structures of eIF4E-eIF4G complexes reveal an extended interface to regulate translation initiation. Mol Cell 64(3):467–479. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.molcel.2016.09.020
Page MF, Carr B, Anders KR, Grimson A, Anderson P (1999) SMG-2 is a phosphorylated protein required for mRNA surveillance in Caenorhabditiselegans and related to Upf1p of yeast. Mol Cell Biol 19(9):5943–5951. https://doi.org/10.1128/mcb.19.9.5943
Lykke-Andersen J (2002) Identification of a human decapping complex associated with hUpf proteins in nonsense-mediated decay. Mol Cell Biol 22(23):8114–8121. https://doi.org/10.1128/mcb.22.23.8114-8121.2002
Loh B, Jonas S, Izaurralde E (2013) The SMG5-SMG7 heterodimer directly recruits the CCR4-NOT deadenylase complex to mRNAs containing nonsense codons via interaction with POP2. Genes Dev 27(19):2125–2138. https://doi.org/10.1101/gad.226951.113
Bono F, Cook AG, Grünwald M, Ebert J, Conti E (2010) Nuclear import mechanism of the EJC component Mago-Y14 revealed by structural studies of importin 13. Mol Cell 37(2):211–222. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.molcel.2010.01.007
Stebbins-Boaz B, Cao Q, de Moor CH, Mendez R, Richter JD (1999) Maskin is a CPEB-associated factor that transiently interacts with elF-4E. Mol Cell 4(6):1017–1027. https://doi.org/10.1016/s1097-2765(00)80230-0
Morgado A, Almeida F, Teixeira A, Silva AL, Romão L (2012) Unspliced precursors of NMD-sensitive β-globin transcripts exhibit decreased steady-state levels in erythroid cells. PLoS ONE 7(6):e38505. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0038505
Behm-Ansmant I, Gatfield D, Rehwinkel J, Hilgers V, Izaurralde E (2007) A conserved role for cytoplasmic poly(A)-binding protein 1 (PABPC1) in nonsense-mediated mRNA decay. EMBO J 26(6):1591–1601. https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.emboj.7601588
Mérai Z, Benkovics AH, Nyikó T, Debreczeny M, Hiripi L, Kerényi Z, Kondorosi É, Silhavy D (2013) The late steps of plant nonsense-mediated mRNA decay. Plant J 73(1):50–62. https://doi.org/10.1111/tpj.12015
Chuang TW, Chang WL, Lee KM, Tarn WY (2013) The RNA-binding protein Y14 inhibits mRNA decapping and modulates processing body formation. Mol Biol Cell 24(1):1–13. https://doi.org/10.1091/mbc.E12-03-0217
Chen L, Wang P, Bahal R, Manautou JE, Zhong XB (2019) Ontogenic mRNA expression of RNA modification writers, erasers, and readers in mouse liver. PLoS ONE 14(12):e0227102. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0227102
Du Y, Hou G, Zhang H, Dou J, He J, Guo Y, Li L, Chen R, Wang Y, Deng R, Huang J, Jiang B, Xu M, Cheng J, Chen GQ, Zhao X, Yu J (2018) SUMOylation of the m6A-RNA methyltransferase METTL3 modulates its function. Nucleic Acids Res 46(10):5195–5208. https://doi.org/10.1093/nar/gky156
Kobayashi M, Ohsugi M, Sasako T, Awazawa M, Umehara T, Iwane A, Kobayashi N, Okazaki Y, Kubota N, Suzuki R, Waki H, Horiuchi K, Hamakubo T, Kodama T, Aoe S, Tobe K, Kadowaki T, Ueki K (2018) The RNA methyltransferase complex of WTAP, METTL3, and METTL14 regulates mitotic clonal expansion in adipogenesis. Mol Cell Biol 38(16):e00116-e118. https://doi.org/10.1128/MCB.00116-18
Hallman DM, Friedel VC, Eissa MA, Boerwinkle E, Huber JC Jr, Harrist RB, Srinivasan SR, Chen W, Dai S, Labarthe DR, Berenson GS (2012) The association of variants in the FTO gene with longitudinal body mass index profiles in non-Hispanic white children and adolescents. Int J Obes (Lond) 36(1):61–68. https://doi.org/10.1038/ijo.2011.190
Tang C, Klukovich R, Peng H, Wang Z, Yu T, Zhang Y, Zheng H, Klungland A, Yan W (2018) ALKBH5-dependent m6A demethylation controls splicing and stability of long 3’-UTR mRNAs in male germ cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 115(2):E325–E333. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.1717794115
Liao S, Sun H, Xu C (2018) YTH domain: A family of N6-methyladenosine (m6A) readers. Genomics Proteomics Bioinform 16(2):99–107. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.gpb.2018.04.002
Wang X, Zhao BS, Roundtree IA, Lu Z, Han D, Ma H, Weng X, Chen K, Shi H, He C (2015) N(6)-methyladenosine modulates messenger RNA translation efficiency. Cell 161(6):1388–1399. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cell.2015.05.014
Du H, Zhao Y, He J, Zhang Y, Xi H, Liu M, Ma J, Wu L (2016) YTHDF2 destabilizes m(6)A-containing RNA through direct recruitment of the CCR4-NOT deadenylase complex. Nat Commun 7:12626. https://doi.org/10.1038/ncomms12626
Liu J, Gao M, Xu S, Chen Y, Wu K, Liu H, Wang J, Yang X, Wang J, Liu W, Bao X, Chen J (2020) YTHDF2/3 are required for somatic reprogramming through different RNA deadenylation pathways. Cell Rep 32(10):108120. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.celrep.2020.108120
Bodi Z, Bottley A, Archer N, May ST, Fray RG (2015) Yeast m6A methylated mRNAs are enriched on translating ribosomes during meiosis, and under rapamycin treatment. PLoS ONE 10(7):e0132090. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0132090
Ries RJ, Zaccara S, Klein P, Olarerin-George A, Namkoong S, Pickering BF, Patil DP, Kwak H, Lee JH, Jaffrey SR (2019) m6A enhances the phase separation potential of mRNA. Nature 571(7765):424–428. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41586-019-1374-1
Park OH, Ha H, Lee Y, Boo SH, Kwon DH, Song HK, Kim YK (2019) Endoribonucleolytic cleavage of m6A-containing RNAs by RNase P/MRP complex. Mol Cell 74(3):494-507.e8. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.molcel.2019.02.034
Fu Y, Zhuang X (2020) m6A-binding YTHDF proteins promote stress granule formation. Nat Chem Biol 16(9):955–963. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41589-020-0524-y
Wu X, Xu FL, Xia X, Wang BJ, Yao J (2020) MicroRNA-15a, microRNA-15b and microRNA-16 inhibit the human dopamine D1 receptor expression in four cell lines by targeting 3’UTR -12 bp to + 154 bp. Artif Cells Nanomed Biotechnol 48(1):276–287. https://doi.org/10.1080/21691401.2019.1703729
Kourtidis A, Necela B, Lin WH, Lu R, Feathers RW, Asmann YW, Thompson EA, Anastasiadis PZ (2017) Cadherin complexes recruit mRNAs and RISC to regulate epithelial cell signaling. J Cell Biol 216(10):3073–3085. https://doi.org/10.1083/jcb.201612125
Matsuyama H, Suzuki HI (2019) Systems and synthetic microRNA biology: from biogenesis to disease pathogenesis. Int J Mol Sci 21(1):132. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms21010132
Fukaya T, Iwakawa HO, Tomari Y (2014) MicroRNAs block assembly of eIF4F translation initiation complex in Drosophila. Mol Cell 56(1):67–78. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.molcel.2014.09.004
Zekri L, Huntzinger E, Heimstädt S, Izaurralde E (2009) The silencing domain of GW182 interacts with PABPC1 to promote translational repression and degradation of microRNA targets and is required for target release. Mol Cell Biol 29(23):6220–6231. https://doi.org/10.1128/MCB.01081-09
Flamand MN, Wu E, Vashisht A, Jannot G, Keiper BD, Simard MJ, Wohlschlegel J, Duchaine TF (2016) Poly(A)-binding proteins are required for microRNA-mediated silencing and to promote target deadenylation in C. elegans. Nucleic Acids Res 44(12):5924–5935. https://doi.org/10.1093/nar/gkw276
Park J, Seo JW, Ahn N, Park S, Hwang J, Nam JW (2019) UPF1/SMG7-dependent microRNA-mediated gene regulation. Nat Commun 10(1):4181. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41467-019-12123-7
Arvola RM, Chang CT, Buytendorp JP, Levdansky Y, Valkov E, Freddolino PL, Goldstrohm AC (2020) Unique repression domains of Pumilio utilize deadenylation and decapping factors to accelerate destruction of target mRNAs. Nucleic Acids Res 48(4):1843–1871. https://doi.org/10.1093/nar/gkz1187
Karam R, Carvalho J, Bruno I, Graziadio C, Senz J, Huntsman D, Carneiro F, Seruca R, Wilkinson MF, Oliveira C (2008) The NMD mRNA surveillance pathway downregulates aberrant E-cadherin transcripts in gastric cancer cells and in CDH1 mutation carriers. Oncogene 27(30):4255–4260. https://doi.org/10.1038/onc.2008.62
Pinyol M, Bea S, Plà L, Ribrag V, Bosq J, Rosenwald A, Campo E, Jares P (2007) Inactivation of RB1 in mantle-cell lymphoma detected by nonsense-mediated mRNA decay pathway inhibition and microarray analysis. Blood 109(12):5422–5429. https://doi.org/10.1182/blood-2006-11-057208
Bernasconi NL, Wormhoudt TA, Laird-Offringa IA (2000) Post-transcriptional deregulation of myc genes in lung cancer cell lines. Am J Respir Cell Mol Biol 23(4):560–565. https://doi.org/10.1165/ajrcmb.23.4.4233
Lindeboom RG, Supek F, Lehner B (2016) The rules and impact of nonsense-mediated mRNA decay in human cancers. Nat Genet 48(10):1112–1118. https://doi.org/10.1038/ng.3664
Luo G, Costanzo M, Boone C, Dickson RC (2011) Nutrients and the Pkh1/2 and Pkc1 protein kinases control mRNA decay and P-body assembly in yeast. J Biol Chem 286(11):8759–8770. https://doi.org/10.1074/jbc.M110.196030
Shinde A, Hardy SD, Kim D, Akhand SS, Jolly MK, Wang WH, Anderson JC, Khodadadi RB, Brown WS, George JT, Liu S, Wan J, Levine H, Willey CD, Krusemark CJ, Geahlen RL, Wendt MK (2019) Spleen tyrosine kinase-mediated autophagy is required for epithelial-mesenchymal plasticity and metastasis in breast cancer. Cancer Res 79(8):1831–1843. https://doi.org/10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-18-2636
Hardy SD, Shinde A, Wang WH, Wendt MK, Geahlen RL (2017) Regulation of epithelial-mesenchymal transition and metastasis by TGF-β, P-bodies, and autophagy. Oncotarget 8(61):103302–103314. https://doi.org/10.18632/oncotarget.21871
Little EC, Camp ER, Wang C, Watson PM, Watson DK, Cole DJ (2016) The CaSm (LSm1) oncogene promotes transformation, chemoresistance and metastasis of pancreatic cancer cells. Oncogenesis 5(1):e182. https://doi.org/10.1038/oncsis.2015.45
Takahashi S, Suzuki S, Inaguma S, Cho YM, Ikeda Y, Hayashi N, Inoue T, Sugimura Y, Nishiyama N, Fujita T, Ushijima T, Shirai T (2002) Down-regulation of Lsm1 is involved in human prostate cancer progression. Br J Cancer 86(6):940–946. https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.bjc.6600163
Delorme-Axford E, Abernathy E, Lennemann NJ, Bernard A, Ariosa A, Coyne CB, Kirkegaard K, Klionsky DJ (2018) The exoribonuclease Xrn1 is a post-transcriptional negative regulator of autophagy. Autophagy 14(5):898–912. https://doi.org/10.1080/15548627.2018.1441648
Zhou X, Wang X, Feng Y, Xie M (2016) Expressions of SMG-1, ATM and P53 in laryngeal squamous cell carcinoma and their clinical significance. Nan Fang Yi KeDaXueXueBao 36(1):50–55
Shao L, He Q, Liu Y, Liu X, Zheng J, Ma J, Liu L, Li H, Li Z, Xue Y (2019) UPF1 regulates the malignant biological behaviors of glioblastoma cells via enhancing the stability of Linc-00313. Cell Death Dis 10(9):629. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41419-019-1845-1
Vicente C, Stirparo R, Demeyer S, de Bock CE, Gielen O, Atkins M, Yan J, Halder G, Hassan BA, Cools J (2018) The CCR4-NOT complex is a tumor suppressor in Drosophila melanogaster eye cancer models. J Hematol Oncol 11(1):108. https://doi.org/10.1186/s13045-018-0650-0
Almasmoum HA, Airhihen B, Seedhouse C, Winkler GS (2020) Frequent loss of BTG1 activity and impaired interactions with the Caf1 subunit of the Ccr4-Not deadenylase in non-Hodgkin lymphoma. Leuk Lymphoma 6:1–10. https://doi.org/10.1080/10428194.2020.1827243
Xi C, Wang L, Yu J, Ye H, Cao L, Gong Z (2018) Inhibition of eukaryotic translation initiation factor 4E is effective against chemo-resistance in colon and cervical cancer. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 503(4):2286–2292. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bbrc.2018.06.150
Kyou Kwon J, Kim SJ, Hoon Kim J, Mee Lee K, Ho CI (2014) Dual inhibition by S6K1 and Elf4E is essential for controlling cellular growth and invasion in bladder cancer. Urol Oncol 32(1):51.e27–35. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.urolonc.2013.08.005
Crew JP, Fuggle S, Bicknell R, Cranston DW, de Benedetti A, Harris AL (2000) Eukaryotic initiation factor-4E in superficial and muscle invasive bladder cancer and its correlation with vascular endothelial growth factor expression and tumour progression. Br J Cancer 82(1):161–166. https://doi.org/10.1054/bjoc.1999.0894
Xu M, Fang S, Song J, Chen M, Zhang Q, Weng Q, Fan X, Chen W, Wu X, Wu F, Tu J, Zhao Z, Ji J (2018) CPEB1 mediates hepatocellular carcinoma cancer stemness and chemoresistance. Cell Death Dis 9(10):957. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41419-018-0974-2
Xiong H, Chen R, Liu S, Lin Q, Chen H, Jiang Q (2018) MicroRNA-183 induces epithelial-mesenchymal transition and promotes endometrial cancer cell migration and invasion in by targeting CPEB1. J Cell Biochem 119(10):8123–8137. https://doi.org/10.1002/jcb.26763
Wang Y, Yang J, Chen P, Song Y, An W, Zhang H, Butegeleqi B, Yan J (2020) MicroRNA-320a inhibits invasion and metastasis in osteosarcoma by targeting cytoplasmic polyadenylation element-binding protein 1. Cancer Med 9(8):2833–2845. https://doi.org/10.1002/cam4.2919
Shen H, Li W, Tian Y, Xu P, Wang H, Zhang J, Li Y (2015) Upregulation of miR-362-3p modulates proliferation and anchorage-independent growth by directly targeting Tob2 in hepatocellular carcinoma. J Cell Biochem 116(8):1563–1573. https://doi.org/10.1002/jcb.25110
Yu BL, Peng XH, Zhao FP, Liu X, Lu J, Wang L, Li G, Chen HH, Li XP (2014) MicroRNA-378 functions as an onco-miR in nasopharyngeal carcinoma by repressing TOB2 expression. Int J Oncol 44(4):1215–1222. https://doi.org/10.3892/ijo.2014.2283
Feng M, Li Z, Aau M, Wong CH, Yang X, Yu Q (2011) Myc/miR-378/TOB2/cyclin D1 functional module regulates oncogenic transformation. Oncogene 30(19):2242–2251. https://doi.org/10.1038/onc.2010.602
Liu HL, Huo JF, Liu ZJ, Chen XB (2015) Interference on cytoplasmic polyadenylation element-binding proteins affects the invasion ability of glioma stem cells. Genet Mol Res 14(4):13504–13510. https://doi.org/10.4238/2015.October.28.11
Zhijun L, Dapeng W, Hong J, Guicong W, Bingjian Y, Honglin L (2017) Overexpression of CPEB4 in glioma indicates a poor prognosis by promoting cell migration and invasion. Tumour Biol 39(4):1010428317694538. https://doi.org/10.1177/1010428317694538
Shi Y, Wang H, Wang J, Liu X, Lin F, Lu J (2019) N6-methyladenosine RNA methylation is involved in virulence of the rice blast fungus Pyriculariaoryzae (syn. Magnaportheoryzae). FEMS Microbiol Lett 366(1):50. https://doi.org/10.1093/femsle/fny286
Nathans R, Chu CY, Serquina AK, Lu CC, Cao H, Rana TM (2009) Cellular microRNA and P bodies modulate host-HIV-1 interactions. Mol Cell 34(6):696–709. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.molcel.2009.06.003
Yang Z, Li J, Feng G, Gao S, Wang Y, Zhang S, Liu Y, Ye L, Li Y, Zhang X (2017) MicroRNA-145 modulates N6-methyladenosine levels by targeting the 3’-untranslated mRNA region of the N6-methyladenosine binding YTH domain family 2 protein. J Biol Chem 292(9):3614–3623. https://doi.org/10.1074/jbc.M116.749689
Han J, Wang JZ, Yang X, Yu H, Zhou R, Lu HC, Yuan WB, Lu JC, Zhou ZJ, Lu Q, Wei JF, Yang H (2019) METTL3 promote tumor proliferation of bladder cancer by accelerating pri-miR221/222 maturation in m6A-dependent manner. Mol Cancer 18(1):110. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12943-019-1036-9
Huang H, Weng H, Sun W, Qin X, Shi H, Wu H, Zhao BS, Mesquita A, Liu C, Yuan CL, Hu YC, Hüttelmaier S, Skibbe JR, Su R, Deng X, Dong L, Sun M, Li C, Nachtergaele S, Wang Y, Hu C, Ferchen K, Greis KD, Jiang X, Wei M, Qu L, Guan JL, He C, Yang J, Chen J (2018) Recognition of RNA N6-methyladenosine by IGF2BP proteins enhances mRNA stability and translation. Nat Cell Biol 20(3):285–295. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41556-018-0045-z
Müller S, Glaß M, Singh AK, Haase J, Bley N, Fuchs T, Lederer M, Dahl A, Huang H, Chen J, Posern G, Hüttelmaier S (2019) IGF2BP1 promotes SRF-dependent transcription in cancer in a m6A- and miRNA-dependent manner. Nucleic Acids Res 47(1):375–390. https://doi.org/10.1093/nar/gky1012
Ke S, Alemu EA, Mertens C, Gantman EC, Fak JJ, Mele A, Haripal B, Zucker-Scharff I, Moore MJ, Park CY, Vågbø CB, Kusśnierczyk A, Klungland A, Darnell JE Jr, Darnell RB (2015) A majority of m6A residues are in the last exons, allowing the potential for 3’ UTR regulation. Genes Dev 29(19):2037–2053. https://doi.org/10.1101/gad.269415.115
Naeli P, Mirzadeh Azad F, Malakootian M, Seidah NG, Mowla SJ (2017) Post-transcriptional regulation of PCSK9 by miR-191, miR-222, and miR-224. Front Genet 8:189. https://doi.org/10.3389/fgene.2017.00189
Zhang SY, Zhang SW, Fan XN, Zhang T, Meng J, Huang Y (2019) FunDMDeep-m6A: identification and prioritization of functional differential m6A methylation genes. Bioinformatics 35(14):i90–i98. https://doi.org/10.1093/bioinformatics/btz316
Wang X, Lu Z, Gomez A, Hon GC, Yue Y, Han D, Fu Y, Parisien M, Dai Q, Jia G, Ren B, Pan T, He C (2014) N6-methyladenosine-dependent regulation of messenger RNA stability. Nature 505(7481):117–120. https://doi.org/10.1038/nature12730
Li F, Yi Y, Miao Y, Long W, Long T, Chen S, Cheng W, Zou C, Zheng Y, Wu X, Ding J, Zhu K, Chen D, Xu Q, Wang J, Liu Q, Zhi F, Ren J, Cao Q, Zhao W (2019) N6-Methyladenosine modulates nonsense-mediated mRNA decay in human glioblastoma. Cancer Res 79(22):5785–5798. https://doi.org/10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-18-2868
Visvanathan A, Patil V, Arora A, Hegde AS, Arivazhagan A, Santosh V, Somasundaram K (2018) Essential role of METTL3-mediated m6A modification in glioma stem-like cells maintenance and radioresistance. Oncogene 37(4):522–533. https://doi.org/10.1038/onc.2017.351
Vu LP, Pickering BF, Cheng Y, Zaccara S, Nguyen D, Minuesa G, Chou T, Chow A, Saletore Y, MacKay M, Schulman J, Famulare C, Patel M, Klimek VM, Garrett-Bakelman FE, Melnick A, Carroll M, Mason CE, Jaffrey SR, Kharas MG (2017) The N6-methyladenosine (m6A)-forming enzyme METTL3 controls myeloid differentiation of normal hematopoietic and leukemia cells. Nat Med 23(11):1369–1376. https://doi.org/10.1038/nm.4416
Cui Q, Shi H, Ye P, Li L, Qu Q, Sun G, Sun G, Lu Z, Huang Y, Yang CG, Riggs AD, He C, Shi Y (2017) m6A RNA methylation regulates the self-renewal and tumorigenesis of glioblastoma stem cells. Cell Rep 18(11):2622–2634. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.celrep.2017.02.059
Weng H, Huang H, Wu H, Qin X, Zhao BS, Dong L, Shi H, Skibbe J, Shen C, Hu C, Sheng Y, Wang Y, Wunderlich M, Zhang B, Dore LC, Su R, Deng X, Ferchen K, Li C, Sun M, Lu Z, Jiang X, Marcucci G, Mulloy JC, Yang J, Qian Z, Wei M, He C, Chen J (2018) METTL14 inhibits hematopoietic stem/progenitor differentiation and promotes leukemogenesis via mRNA m6A modification. Cell Stem Cell 22(2):191-205.e9. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.stem.2017.11.016
Gu C, Wang Z, Zhou N, Li G, Kou Y, Luo Y, Wang Y, Yang J, Tian F (2019) Mettl14 inhibits bladder TIC self-renewal and bladder tumorigenesis through N6-methyladenosine of Notch1. Mol Cancer 18(1):168. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12943-019-1084-1
Chen L, Wang X (2018) Relationship between the genetic expression of WTAP and bladder cancer and patient prognosis. Oncol Lett 16(6):6966–6970. https://doi.org/10.3892/ol.2018.9554
Ma H, Shen L, Yang H, Gong H, Du X, Li J (2020) m6A methyltransferase Wilms’ tumor 1-associated protein facilitates cell proliferation and cisplatin resistance in NK/T cell lymphoma by regulating dual-specificity phosphatases 6 expression via m6A RNA methylation. IUBMB Life. https://doi.org/10.1002/iub.2410
Yu HL, Ma XD, Tong JF, Li JQ, Guan XJ, Yang JH (2019) WTAP is a prognostic marker of high-grade serous ovarian cancer and regulates the progression of ovarian cancer cells. Onco Targets Ther 12:6191–6201. https://doi.org/10.2147/OTT.S205730
Xie W, Liu N, Wang X, Wei L, Xie W, Sheng X (2021) Wilms’ Tumor 1-associated protein contributes to chemo-resistance to cisplatin through the Wnt/β-catenin pathway in endometrial cancer. Front Oncol 11:598344. https://doi.org/10.3389/fonc.2021.598344
Paris J, Morgan M, Campos J, Spencer GJ, Shmakova A, Ivanova I, Mapperley C, Lawson H, Wotherspoon DA, Sepulveda C, Vukovic M, Allen L, Sarapuu A, Tavosanis A, Guitart AV, Villacreces A, Much C, Choe J, Azar A, van de Lagemaat LN, Vernimmen D, Nehme A, Mazurier F, Somervaille TCP, Gregory RI, O’Carroll D, Kranc KR (2019) Targeting the RNA m6A reader YTHDF2 selectively compromises cancer stem cells in acute myeloid leukemia. Cell Stem Cell 25(1):137-148.e6. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.stem.2019.03.021
Zhang C, Huang S, Zhuang H, Ruan S, Zhou Z, Huang K, Ji F, Ma Z, Hou B, He X (2020) YTHDF2 promotes the liver cancer stem cell phenotype and cancer metastasis by regulating OCT4 expression via m6A RNA methylation. Oncogene 39(23):4507–4518. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41388-020-1303-7
Chen J, Sun Y, Xu X, Wang D, He J, Zhou H, Lu Y, Zeng J, Du F, Gong A, Xu M (2017) YTH domain family 2 orchestrates epithelial-mesenchymal transition/proliferation dichotomy in pancreatic cancer cells. Cell Cycle 16(23):2259–2271. https://doi.org/10.1080/15384101.2017.1380125
Hao L, Wang JM, Liu BQ, Yan J, Li C, Jiang JY, Zhao FY, Qiao HY, Wang HQ (2021) m6A-YTHDF1-mediated TRIM29 upregulation facilitates the stem cell-like phenotype of cisplatin-resistant ovarian cancer cells. Biochim BiophysActa Mol Cell Res 1868(1):118878. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bbamcr.2020.118878
Patel PH, Barbee SA, Blankenship JT (2016) GW-bodies and P-bodies constitute two separate pools of sequestered non-translating RNAs. PLoS ONE 11(3):e0150291. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0150291
Lu H, Qi Z, Lin L, Ma L, Li L, Zhang H, Feng L, Su Y (2016) The E6-TAp63β-Dicer feedback loop involves in miR-375 downregulation and epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition in HR-HPV+ cervical cancer cells. Tumour Biol. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13277-016-5378-2
Lai HH, Li JN, Wang MY, Huang HY, Croce CM, Sun HL, Lyu YJ, Kang JW, Chiu CF, Hung MC, Suzuki HI, Chen PS (2018) HIF-1α promotes autophagic proteolysis of Dicer and enhances tumor metastasis. J Clin Invest 128(2):625–643. https://doi.org/10.1172/JCI89212
Zhang X, Shen B, Cui Y (2019) Ago HITS-CLIP expands microRNA-mRNA interactions in nucleus and cytoplasm of gastric cancer cells. BMC Cancer 19(1):29. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12885-018-5246-0
Rabien A, Ratert N, Högner A, Erbersdobler A, Jung K, Ecke TH, Kilic E (2018) Diagnostic and prognostic potential of MicroRNA maturation regulators drosha, AGO1 and AGO2 in urothelial carcinomas of the bladder. Int J Mol Sci 19(6):1622. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms19061622
Morgado AL, Rodrigues CM, Solá S (2016) MicroRNA-145 regulates neural stem cell differentiation through the Sox2-Lin28/let-7 signaling pathway. Stem Cells 34(5):1386–1395. https://doi.org/10.1002/stem.2309
Lin Z, He H, Wang M, Liang J (2019) MicroRNA-130a controls bone marrow mesenchymal stem cell differentiation towards the osteoblastic and adipogenic fate. Cell Prolif 52(6):e12688. https://doi.org/10.1111/cpr.12688
Lynam-Lennon N, Heavey S, Sommerville G, Bibby BA, Ffrench B, Quinn J, Gasch C, O’Leary JJ, Gallagher MF, Reynolds JV, Maher SG (2017) MicroRNA-17 is downregulated in esophageal adenocarcinoma cancer stem-like cells and promotes a radioresistant phenotype. Oncotarget 8(7):11400–11413. https://doi.org/10.18632/oncotarget.13940
Song XL, Huang B, Zhou BW, Wang C, Liao ZW, Yu Y, Zhao SC (2018) miR-1301-3p promotes prostate cancer stem cell expansion by targeting SFRP1 and GSK3β. Biomed Pharmacother 99:369–374. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biopha.2018.01.086
Liu C, Kelnar K, Liu B, Chen X, Calhoun-Davis T, Li H, Patrawala L, Yan H, Jeter C, Honorio S, Wiggins JF, Bader AG, Fagin R, Brown D, Tang DG (2011) The microRNA miR-34a inhibits prostate cancer stem cells and metastasis by directly repressing CD44. Nat Med 17(2):211–215. https://doi.org/10.1038/nm.2284
Mamoori A, Wahab R, Vider J, Gopalan V, Lam AK (2019) The tumour suppressor effects and regulation of cancer stem cells by macrophage migration inhibitory factor targeted miR-451 in colon cancer. Gene 697:165–174. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.gene.2019.02.046
Zhao M, Li L, Zhou J, Cui X, Tian Q, Jin Y, Zhu Y (2018) MiR-2861 behaves as a biomarker of lung cancer stem cells and regulates the HDAC5-ERK system genes. Cell Reprogram 20(2):99–106. https://doi.org/10.1089/cell.2017.0045
Qiu J, Zhang Y, Chen H, Guo Z (2018) MicroRNA-488 inhibits proliferation, invasion and EMT in osteosarcoma cell lines by targeting aquaporin 3. Int J Oncol 53(4):1493–1504. https://doi.org/10.3892/ijo.2018.4483
Ghoncheh M, Pournamdar Z, Salehiniya H (2016) Incidence and mortality and epidemiology of breast cancer in the world. Asian Pac J Cancer Prev 17(S3):43–46. https://doi.org/10.7314/apjcp.2016.17.s3.43
Linger BR, Morin GB, Price CM (2011) The Pot1a-associated proteins Tpt1 and Pat1 coordinate telomere protection and length regulation in Tetrahymena. Mol Biol Cell 22(21):4161–4170. https://doi.org/10.1091/mbc.E11-06-0551
Grudzien-Nogalska E, Jiao X, Song MG, Hart RP, Kiledjian M (2016) Nudt3 is an mRNA decapping enzyme that modulates cell migration. RNA 22(5):773–781. https://doi.org/10.1261/rna.055699.115
Fang Z, Yi Y, Shi G, Li S, Chen S, Lin Y, Li Z, He Z, Li W, Zhong S (2017) Role of Brf1 interaction with ERα, and significance of its overexpression, in human breast cancer. Mol Oncol 11(12):1752–1767. https://doi.org/10.1002/1878-0261.12141
Perrin-Vidoz L, Sinilnikova OM, Stoppa-Lyonnet D, Lenoir GM, Mazoyer S (2002) The nonsense-mediated mRNA decay pathway triggers degradation of most BRCA1 mRNAs bearing premature termination codons. Hum Mol Genet 11(23):2805–2814. https://doi.org/10.1093/hmg/11.23.2805
Nagaoka K, Fujii K, Zhang H, Usuda K, Watanabe G, Ivshina M, Richter JD (2016) CPEB1 mediates epithelial-to-mesenchyme transition and breast cancer metastasis. Oncogene 35(22):2893–2901. https://doi.org/10.1038/onc.2015.350
Peng F, Xu J, Cui B, Liang Q, Zeng S, He B, Zou H, Li M, Zhao H, Meng Y, Chen J, Liu B, Lv S, Chu P, An F, Wang Z, Huang J, Zhan Y, Liao Y, Lu J, Xu L, Zhang J, Sun Z, Li Z, Wang F, Lam EW, Liu Q (2021) Oncogenic AURKA-enhanced N6-methyladenosine modification increases DROSHA mRNA stability to transactivate STC1 in breast cancer stem-like cells. Cell Res 31(3):345–361. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41422-020-00397-2
Cheng L, Zhang X, Huang YZ, Zhu YL, Xu LY, Li Z, Dai XY, Shi L, Zhou XJ, Wei JF, Ding Q (2021) Metformin exhibits antiproliferation activity in breast cancer via miR-483-3p/METTL3/m6A/p21 pathway. Oncogenesis 10(1):7. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41389-020-00290-y
Perconti G, Rubino P, Contino F, Bivona S, Bertolazzi G, Tumminello M, Feo S, Giallongo A, Coronnello C (2019) RIP-Chip analysis supports different roles for AGO2 and GW182 proteins in recruiting and processing microRNA targets. BMC Bioinform 20(Suppl 4):120. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12859-019-2683-y
Fawzy MS, Toraih EA, Alelwani W, Kattan SW, Alnajeebi AM, Hassan R (2020) The prognostic value of microRNA-biogenesis genes Argonaute 1 and 2 variants in breast cancer patients. Am J Transl Res 12(5):1994–2006
Yu J, Lei R, Zhuang X, Li X, Li G, Lev S, Segura MF, Zhang X, Hu G (2016) MicroRNA-182 targets SMAD7 to potentiate TGFβ-induced epithelial-mesenchymal transition and metastasis of cancer cells. Nat Commun 7:13884. https://doi.org/10.1038/ncomms13884
Chu J, Li Y, Fan X, Ma J, Li J, Lu G, Zhang Y, Huang Y, Li W, Huang X, Fu Z, Yin Y, Yuan H (2018) MiR-4319 suppress the malignancy of triple-negative breast cancer by regulating self-renewal and tumorigenesis of stem cells. Cell Physiol Biochem 48(2):593–604. https://doi.org/10.1159/000491888
Kang L, Mao J, Tao Y, Song B, Ma W, Lu Y, Zhao L, Li J, Yang B, Li L (2015) MicroRNA-34a suppresses the breast cancer stem cell-like characteristics by downregulating Notch1 pathway. Cancer Sci 106(6):700–708. https://doi.org/10.1111/cas.12656
Zou Y, Chen Y, Yao S, Deng G, Liu D, Yuan X, Liu S, Rao J, Xiong H, Yuan X, Yu S, Zhu F, Wang Y, Xiong H (2018) MiR-422a weakened breast cancer stem cells properties by targeting PLP2. Cancer Biol Ther 19(5):436–444. https://doi.org/10.1080/15384047.2018.1433497
Zhao C, Ling X, Li X, Hou X, Zhao D (2019) MicroRNA-138-5p inhibits cell migration, invasion and EMT in breast cancer by directly targeting RHBDD1. Breast Cancer 26(6):817–825. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12282-019-00989-w
Yang D, Liu Y, Bai C, Wang X, Powell CA (2020) Epidemiology of lung cancer and lung cancer screening programs in China and the United States. Cancer Lett 468:82–87. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.canlet.2019.10.009
Jing L, Zhai ME, Cui J, Fan XY, Cheng YY, Jiang JL, Chen ZN (2019) CNOT3 contributes to cisplatin resistance in lung cancer through inhibiting RIPK3 expression. Apoptosis 24(7–8):673–685. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10495-019-01550-y
Kim EO, Kang SE, Choi M, Rhee KJ, Yun M (2020) CCR4-NOT transcription complex subunit 2 regulates TRAIL sensitivity in non-small-cell lung cancer cells via the STAT3 pathway. Int J Mol Med 45(2):324–332. https://doi.org/10.3892/ijmm.2019.4425
Zhang H, Wang Y, Dou J, Guo Y, He J, Li L, Liu X, Chen R, Deng R, Huang J, Xie R, Zhao X, Yu J (2019) Acetylation of AGO2 promotes cancer progression by increasing oncogenic miR-19b biogenesis. Oncogene 38(9):1410–1431. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41388-018-0530-
Wang L, Qu J, Zhou L, Liao F, Wang J (2018) MicroRNA-373 inhibits cell proliferation and invasion via targeting BRF2 in human non-small cell lung cancer A549 cell line. Cancer Res Treat 50(3):936–949. https://doi.org/10.4143/crt.2017.302
Wu H, Li F, Zhu R (2021) miR-338-5p inhibits cell growth and migration via inhibition of the METTL3/m6A/c-Myc pathway in lung cancer. Acta Biochim Biophys Sin (Shanghai) 53(3):304–316. https://doi.org/10.1093/abbs/gmaa170
Robinson JR, Newcomb PA, Hardikar S, Cohen SA, Phipps AI (2017) Stage IV colorectal cancer primary site and patterns of distant metastasis. Cancer Epidemiol 48:92–95. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.canep.2017.04.003
Wu C, Zhu X, Tao K, Liu W, Ruan T, Wan W, Zhang C, Zhang W (2018) MALAT1 promotes the colorectal cancer malignancy by increasing DCP1A expression and miR203 downregulation. Mol Carcinog 57(10):1421–1431. https://doi.org/10.1002/mc.22868
Wu C, Liu W, Ruan T, Zhu X, Tao K, Zhang W (2018) Overexpression of mRNA-decapping enzyme 1a affects survival rate in colorectal carcinoma. Oncol Lett 16(1):1095–1100. https://doi.org/10.3892/ol.2018.8730
Lin F, Wang R, Shen JJ, Wang X, Gao P, Dong K, Zhang HZ (2008) Knockdown of RCK/p54 expression by RNAi inhibits proliferation of human colorectal cancer cells in vitro and in vivo. Cancer Biol Ther 7(10):1669–1676. https://doi.org/10.4161/cbt.7.10.6660
Jo YS, Song SY, Kim MS, Yoo NJ, Lee SH (2017) Frameshift mutations of SMG7 essential for nonsense-mediated mRNA decay in gastric and colorectal cancers. Pathol Oncol Res 23(1):221–222. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12253-016-0141-y
Bordonaro M, Lazarova D (2019) Amlexanox and UPF1 Modulate Wnt signaling and apoptosis in HCT-116 colorectal cancer cells. J Cancer 10(2):287–292. https://doi.org/10.7150/jca.28331
Wang X, Lai Q, He J, Li Q, Ding J, Lan Z, Gu C, Yan Q, Fang Y, Zhao X, Liu S (2019) LncRNA SNHG6 promotes proliferation, invasion and migration in colorectal cancer cells by activating TGF-β/Smad signaling pathway via targeting UPF1 and inducing EMT via regulation of ZEB1. Int J Med Sci 16(1):51–59. https://doi.org/10.7150/ijms.27359
He X, Lin X, Cai M, Fan D, Chen X, Wang L, Wu X, Lan P, Wang J (2017) High expression of cytoplasmic polyadenylation element-binding protein 4 correlates with poor prognosis of patients with colorectal cancer. Virchows Arch 470(1):37–45. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00428-016-2037-3
Liu X, Liu L, Dong Z, Li J, Yu Y, Chen X, Ren F, Cui G, Sun R (2019) Expression patterns and prognostic value of m6A-related genes in colorectal cancer. Am J Transl Res 11(7):3972–3991
Bai Y, Yang C, Wu R, Huang L, Song S, Li W, Yan P, Lin C, Li D, Zhang Y (2019) YTHDF1 regulates tumorigenicity and cancer stem cell-like activity in human colorectal carcinoma. Front Oncol 9:332. https://doi.org/10.3389/fonc.2019.00332
Yue C, Chen J, Li Z, Li L, Chen J, Guo Y (2020) microRNA-96 promotes occurrence and progression of colorectal cancer via regulation of the AMPKα2-FTO-m6A/MYC axis. J Exp Clin Cancer Res 39(1):240. https://doi.org/10.1186/s13046-020-01731-7
Karimi P, Islami F, Anandasabapathy S, Freedman ND, Kamangar F (2014) Gastric cancer: descriptive epidemiology, risk factors, screening, and prevention. Cancer Epidemiol Biomark Prev 23(5):700–713. https://doi.org/10.1158/1055-9965
Ruan T, Zhang Y, Liu W, Li Y, Wang D, Du Z, Tao K, Wu C (2020) Expression of DCP1a in gastric cancer and its biological function and mechanism in chemotherapy resistance in gastric cancer cells. Dig Liver Dis 52(11):1351–1358. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.dld.2020.06.031
Chen Y, Yang F, Fang E, Xiao W, Mei H, Li H, Li D, Song H, Wang J, Hong M, Wang X, Huang K, Zheng L, Tong Q (2019) Circular RNA circAGO2 drives cancer progression through facilitating HuR-repressed functions of AGO2-miRNA complexes. Cell Death Differ 26(7):1346–1364. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41418-018-0220-6
Crane R, Craig R, Murray R, Dunand-Sauthier I, Humphrey T, Norbury C (2000) A fission yeast homolog of Int-6, the mammalian oncoprotein and eIF3 subunit, induces drug resistance when overexpressed. Mol Biol Cell 11(11):3993–4003. https://doi.org/10.1091/mbc.11.11.3993
Huang Y, Fang C, Shi JW, Wen Y, Liu D (2017) Identification of hMex-3A and its effect on human bladder cancer cell proliferation. Oncotarget 8(37):61215–61225. https://doi.org/10.18632/oncotarget.18050
Jiang H, Zhang X, Luo J, Dong C, Xue J, Wei W, Chen J, Zhou J, Gao Y, Yang C (2012) Knockdown of hMex-3A by small RNA interference suppresses cell proliferation and migration in human gastric cancer cells. Mol Med Rep 6(3):575–580. https://doi.org/10.3892/mmr.2012.943
Liu YF, Sun XY, Zhang JK, Wang ZH, Ren ZG, Li J, Guo WZ, Zhang SJ (2020) Original Article/Liver hMex-3A is associated with poor prognosis and contributes to the progression of hepatocellular carcinoma. Hepatobiliary Pancreat Dis Int 2020:143. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.hbpd.2020.03.005
Guan K, Liu X, Li J, Ding Y, Li J, Cui G, Cui X, Sun R (2020) Expression status and prognostic value of M6A-associated genes in gastric cancer. J Cancer 11(10):3027–3040. https://doi.org/10.7150/jca.40866
Li H, Su Q, Li B, Lan L, Wang C, Li W, Wang G, Chen W, He Y, Zhang C (2020) High expression of WTAP leads to poor prognosis of gastric cancer by influencing tumour-associated T lymphocyte infiltration. J Cell Mol Med 24(8):4452–4465. https://doi.org/10.1111/jcmm.15104
Yue B, Song C, Yang L, Cui R, Cheng X, Zhang Z, Zhao G (2019) METTL3-mediated N6-methyladenosine modification is critical for epithelial-mesenchymal transition and metastasis of gastric cancer. Mol Cancer 18(1):142. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12943-019-1065-4
He H, Wu W, Sun Z, Chai L (2019) MiR-4429 prevented gastric cancer progression through targeting METTL3 to inhibit m6A-caused stabilization of SEC62. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 517(4):581–587. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bbrc.2019.07.058
Ma Y, Yan F, Wei W, Deng J, Li L, Liu L, Sun J (2019) MicroRNA-598 inhibits the growth and maintenance of gastric cancer stem-like cells by down-regulating RRS1. Cell Cycle 18(20):2757–2769. https://doi.org/10.1080/15384101.2019.1657338
Du M, Zhuang Y, Tan P, Yu Z, Zhang X, Wang A (2020) microRNA-95 knockdown inhibits epithelial-mesenchymal transition and cancer stem cell phenotype in gastric cancer cells through MAPK pathway by upregulating DUSP5. J Cell Physiol 235(2):944–956. https://doi.org/10.1002/jcp.29010
Peng C, Huang K, Liu G, Li Y, Yu C (2019) MiR-876-3p regulates cisplatin resistance and stem cell-like properties of gastric cancer cells by targeting TMED3. J Gastroenterol Hepatol 34(10):1711–1719. https://doi.org/10.1111/jgh.14649
Feng Y, Sun T, Yu Y, Gao Y, Wang X, Chen Z (2018) MicroRNA-370 inhibits the proliferation, invasion and EMT of gastric cancer cells by directly targeting PAQR4. J Pharmacol Sci 138(2):96–106. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jphs.2018.08.004
Deng NN, Huck WTS (2017) Microfluidic formation of monodisperse coacervate organelles in liposomes. Angew Chem Int Ed Engl 56(33):9736–9740. https://doi.org/10.1002/anie.201703145
Gress RE, Miller JS, Battiwalla M, Bishop MR, Giralt SA, Hardy NM, Kröger N, Wayne AS, Landau DA, Wu CJ (2013) Proceedings from the National Cancer Institute’s Second International Workshop on the biology, prevention, and treatment of relapse after hematopoietic stem cell transplantation: part I Biology of relapse after transplantation. Biol Blood Marrow Transpl 19(11):1537–1545. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bbmt.2013.08.010
Lohcharoenkal W, Wang L, Chen YC, Rojanasakul Y (2014) Protein nanoparticles as drug delivery carriers for cancer therapy. Biomed Res Int 2014:180549. https://doi.org/10.1155/2014/180549
Rugo HS, Barry WT, Moreno-Aspitia A, Lyss AP, Cirrincione C, Leung E, Mayer EL, Naughton M, Toppmeyer D, Carey LA, Perez EA, Hudis C, Winer EP (2015) Randomized phase III trial of paclitaxel once per week compared with nanoparticle albumin-bound nab-paclitaxel once per week or ixabepilone with bevacizumab as first-line chemotherapy for locally recurrent or metastatic breast cancer: CALGB 40502/NCCTG N063H (Alliance). J ClinOncol 33(21):2361–2369. https://doi.org/10.1200/JCO.2014.59.5298
Gao J, Liu J, Xie F, Lu Y, Yin C, Shen X (2019) Co-delivery of docetaxel and salinomycin to target both breast cancer cells and stem cells by PLGA/TPGS nanoparticles. Int J Nanomedicine 14:9199–9216. https://doi.org/10.2147/IJN.S230376
Das S, Mukherjee P, Chatterjee R, Jamal Z, Chatterji U (2019) Enhancing chemosensitivity of breast cancer stem cells by downregulating SOX2 and ABCG2 using wedelolactone-encapsulated nanoparticles. Mol Cancer Ther 18(3):680–692. https://doi.org/10.1158/1535-7163.MCT-18-0409
Chen D, Pan X, Xie F, Lu Y, Zou H, Yin C, Zhang Y, Gao J (2018) Codelivery of doxorubicin and elacridar to target both liver cancer cells and stem cells by polylactide-co-glycolide/d-alpha-tocopherol polyethylene glycol 1000 succinate nanoparticles. Int J Nanomedicine 13:6855–6870. https://doi.org/10.2147/IJN.S181928
Zhao Y, Zhao W, Lim YC, Liu T (2019) Salinomycin-loaded gold nanoparticles for treating cancer stem cells by ferroptosis-induced cell death. Mol Pharm 16(6):2532–2539. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.molpharmaceut.9b00132
Abu-Serie MM, El-Rashidy FH (2017) In vitro collapsing colon cancer cells by selectivity of disulfiram-loaded charge switchable nanoparticles against cancer stem cells. Recent Pat Anticancer Drug Discov 12(3):260–271. https://doi.org/10.2174/1574892812666170424144925
Ibrahim KE, Al-Mutary MG, Bakhiet AO, Khan HA (2018) Histopathology of the liver, kidney, and spleen of mice exposed to gold nanoparticles. Molecules 23(8):1848. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules23081848
RahimiKalateh SMG, Seyedi SMR, Karimi E, Homayouni-Tabrizi M (2019) The cytotoxic properties of zinc oxide nanoparticles on the rat liver and spleen, and its anticancer impacts on human liver cancer cell lines. J Biochem Mol Toxicol 33(7):e22324. https://doi.org/10.1002/jbt.22324
He C, Zheng S, Luo Y, Wang B (2018) Exosome theranostics: biology and translational medicine. Theranostics 8(1):237–255. https://doi.org/10.7150/thno.21945
Baglio SR, Rooijers K, Koppers-Lalic D, Verweij FJ, Pérez Lanzón M, Zini N, Naaijkens B, Perut F, Niessen HW, Baldini N, Pegtel DM (2015) Human bone marrow- and adipose-mesenchymal stem cells secrete exosomes enriched in distinctive miRNA and tRNA species. Stem Cell Res Ther 6(1):127. https://doi.org/10.1186/s13287-015-0116-z
Hannafon BN, Trigoso YD, Calloway CL, Zhao YD, Lum DH, Welm AL, Zhao ZJ, Blick KE, Dooley WC, Ding WQ (2016) Plasma exosome microRNAs are indicative of breast cancer. Breast Cancer Res 18(1):90. https://doi.org/10.1186/s13058-016-0753-x
Yang Z, Zhao N, Cui J, Wu H, Xiong J, Peng T (2020) Exosomes derived from cancer stem cells of gemcitabine-resistant pancreatic cancer cells enhance drug resistance by delivering miR-210. Cell Oncol (Dordr) 43(1):123–136. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13402-019-00476-6
Narita M, Kanda T, Abe T, Uchiyama T, Iwafuchi M, Zheng Z, Liu A, Kaifu T, Kosugi S, Minagawa M, Itoh K, Takahashi M (2015) Immune responses in patients with esophageal cancer treated with SART1 peptide-pulsed dendritic cell vaccine. Int J Oncol 46(4):1699–1709. https://doi.org/10.3892/ijo.2015.2846
Sohn EJ, Jung DB, Lee H, Han I, Lee J, Lee H, Kim SH (2018) CNOT2 promotes proliferation and angiogenesis via VEGF signaling in MDA-MB-231 breast cancer cells. Cancer Lett 412:88–98. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.canlet.2017.09.052
Zhong Q, Xi S, Liang J, Shi G, Huang Y, Zhang Y, Levy D, Zhong S (2016) The significance of Brf1 overexpression in human hepatocellular carcinoma. Oncotarget 7(5):6243–6254. https://doi.org/10.18632/oncotarget.6668
Glück AA, Orlando E, Leiser D, Poliaková M, Nisa L, Quintin A, Gavini J, Stroka DM, Berezowska S, Bubendorf L, Blaukat A, Aebersold DM, Medová M, Zimmer Y (2018) Identification of a MET-eIF4G1 translational regulation axis that controls HIF-1α levels under hypoxia. Oncogene 37(30):4181–4196. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41388-018-0256-6
Luo H, Cowen L, Yu G, Jiang W, Tang Y (2016) SMG7 is a critical regulator of p53 stability and function in DNA damage stress response. Cell Discov 2:15042. https://doi.org/10.1038/celldisc.2015.42
Brito M, Malta-Vacas J, Carmona B, Aires C, Costa P, Martins AP, Ramos S, Conde AR, Monteiro C (2005) Polyglycine expansions in eRF3/GSPT1 are associated with gastric cancer susceptibility. Carcinogenesis 26(12):2046–2049. https://doi.org/10.1093/carcin/bgi168
Wu GJ, Sinclair CS, Paape J, Ingle JN, Roche PC, James CD, Couch FJ (2000) 17q23 amplifications in breast cancer involve the PAT1, RAD51C, PS6K, and SIGma1B genes. Cancer Res 60(19):5371–5375
Lu L, Katsaros D, Shaverdashvili K, Qian B, Wu Y, de la Longrais IA, Preti M, Menato G, Yu H (2009) Pluripotent factor lin-28 and its homologue lin-28b in epithelial ovarian cancer and their associations with disease outcomes and expression of let-7a and IGF-II. Eur J Cancer 45(12):2212–2218. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ejca.2009.05.003
Li Z, Qian P, Shao W, Shi H, He XC, Gogol M, Yu Z, Wang Y, Qi M, Zhu Y, Perry JM, Zhang K, Tao F, Zhou K, Hu D, Han Y, Zhao C, Alexander R, Xu H, Chen S, Peak A, Hall K, Peterson M, Perera A, Haug JS, Parmely T, Li H, Shen B, Zeitlinger J, He C, Li L (2018) Suppression of m6A reader Ythdf2 promotes hematopoietic stem cell expansion. Cell Res 28(9):904–917. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41422-018-0072-0
Su R, Dong L, Li Y, Gao M, Han L, Wunderlich M, Deng X, Li H, Huang Y, Gao L, Li C, Zhao Z, Robinson S, Tan B, Qing Y, Qin X, Prince E, Xie J, Qin H, Li W, Shen C, Sun J, Kulkarni P, Weng H, Huang H, Chen Z, Zhang B, Wu X, Olsen MJ, Müschen M, Marcucci G, Salgia R, Li L, Fathi AT, Li Z, Mulloy JC, Wei M, Horne D, Chen J (2020) Targeting FTO suppresses cancer stem cell maintenance and immune evasion. Cancer Cell; 8(1):79–96e11. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ccell.2020.04.017.
Huang H, Wang Y, Kandpal M, Zhao G, Cardenas H, Ji Y, Chaparala A, Tanner EJ, Chen J, Davuluri RV, Matei D (2020) FTO-dependent N6-methyladenosine modifications inhibit ovarian cancer stem cell self-renewal by blocking cAMP signaling. Cancer Res 80(16):3200–3214. https://doi.org/10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-19-4044
Li CY, Miao KL, Chen Y, Liu LY, Zhao GB, Lin MH, Jiang C (2018) Jagged2 promotes cancer stem cell properties of triple negative breast cancer cells and paclitaxel resistance via regulating microRNA-200. Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci 22(18):6008–6014. https://doi.org/10.26355/eurrev_201809_15936
Hongdan L, Feng L (2018) miR-3120-5p promotes colon cancer stem cell stemness and invasiveness through targeting Axin2. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 496(2):302–308. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bbrc.2018.01.021
Yata K, Beder LB, Tamagawa S, Hotomi M, Hirohashi Y, Grenman R, Yamanaka N (2015) MicroRNA expression profiles of cancer stem cells in head and neck squamous cell carcinoma. Int J Oncol 47(4):1249–1256. https://doi.org/10.3892/ijo.2015.3145
Acknowledgements
Not applicable.
Funding
This work was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (No.31371386 SP.J).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
BN collected the data, and prepared the manuscript. WW conceived and supervised the review. BN, FAK, EEN, YJ, YJ, and XZ organized the manuscript. SJ revised this review. All authors read and approve the final manuscript.
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
All authors declare that they have no conflict of interests.
Ethical approval
Not applicable.
Consent for publication
All authors consent to publication.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Nsengimana, B., Khan, F.A., Ngowi, E.E. et al. Processing body (P-body) and its mediators in cancer. Mol Cell Biochem 477, 1217–1238 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11010-022-04359-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11010-022-04359-7