Abstract
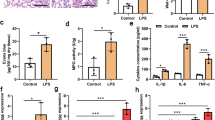
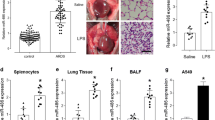
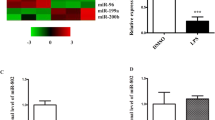
The present study aimed to evaluate the potential roles of MIR3142HG, a novel long non-coding RNA (lncRNA) in lipopolysaccharide (LPS)-induced acute lung injury (ALI). ALI was simulated by the treatment of LPS in human pulmonary microvascular endothelial cells (HPMECs). The expression of MIR3142HG, miR-450b-5p and high-mobility group box 1 (HMGB1) was determined by real-time PCR and western blotting. Functional analysis was performed through the assessment of cell viability, apoptosis and the production of proinflammatory cytokines. The interactions among MIR3142HG, miR-450b-5p and HMGB1 were analyzed by bioinformatics methods, dual-luciferase reporter and RNA pull-down assays. Using gain- and loss-of-function approaches, the in vitro functions of MIR3142HG and miR-450b-5p were subsequently assessed. MIR3142HG expression was upregulated, while miR-450b-5p was decreased in LPS-treated HPMECs. MIR3142HG knockdown protected against ALI induced by LPS through alleviating the apoptosis and inflammation of HPMECs. MIR3142HG impaired miR-450b-5p-mediated inhibition of HMGB1. Besides, the effects of MIR3142HG silencing could be alleviated by miR-4262 inhibition or HMGB1 overexpression. MIR3142HG mediated LPS-induced injury of HPMECs by targeting miR-450b-5p/HMGB1, suggesting that MIR3142HG might serve as a therapeutic potential for the treatment of ALI.






Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
All data generated or analyzed during this study are included in this published article.
References
Mowery NT, Terzian WTH, Nelson AC (2020) Acute lung injury. Curr Probl Surg 57:100777. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cpsurg.2020.100777
Wu Z, Hu Z, Cai X, Ren W, Dai F, Liu H, Chang J, Li B (2017) Interleukin 22 attenuated angiotensin II induced acute lung injury through inhibiting the apoptosis of pulmonary microvascular endothelial cells. Sci Rep 7:2210. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-017-02056-w
Yin J, Lv L, Zhai P, Long T, Zhou Q, Pan H, Botwe G, Wang L, Wang Q, Tan L, Kuebler WM (2019) Connexin 40 regulates lung endothelial permeability in acute lung injury via the ROCK1-MYPT1- MLC20 pathway. Am J Physiol Lung Cell Mol Physiol 316:L35–L44. https://doi.org/10.1152/ajplung.00012.2018
Gross CM, Kellner M, Wang T, Lu Q, Sun X, Zemskov EA, Noonepalle S, Kangath A, Kumar S, Gonzalez-Garay M, Desai AA, Aggarwal S, Gorshkov B, Klinger C, Verin AD, Catravas JD, Jacobson JR, Yuan JX, Rafikov R, Garcia JGN, Black SM (2018) LPS-induced acute lung injury involves NF-kappaB-mediated downregulation of SOX18. Am J Respir Cell Mol Biol 58:614–624. https://doi.org/10.1165/rcmb.2016-0390OC
Li L, Wei J, Mallampalli RK, Zhao Y, Zhao J (2019) TRIM21 mitigates human lung microvascular endothelial cells’ inflammatory responses to LPS. Am J Respir Cell Mol Biol 61:776–785. https://doi.org/10.1165/rcmb.2018-0366OC
Zhang J, Zhu Y, Wang R (2018) Long noncoding RNAs in respiratory diseases. Histol Histopathol 33:747–756. https://doi.org/10.14670/HH-11-966
Liao K, Xu J, Yang W, You X, Zhong Q, Wang X (2018) The research progress of LncRNA involved in the regulation of inflammatory diseases. Mol Immunol 101:182–188. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.molimm.2018.05.030
Li H, Shi H, Ma N, Zi P, Liu Q, Sun R (2018) BML-111 alleviates acute lung injury through regulating the expression of lncRNA MALAT1. Arch Biochem Biophys 649:15–21. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.abb.2018.04.016
Ji Q, Pan C, Wang J, Yang Z, Li C, Yang C, Zhang W, Wang M, Dong M, Sun Z, Nie S (2020) Long non-coding RNA Hsp4 alleviates lipopolysaccharide-induced apoptosis of lung epithelial cells via miRNA-466m-3p/DNAjb6 axis. Exp Mol Pathol 117:104547. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.yexmp.2020.104547
Hadjicharalambous MR, Roux BT, Feghali-Bostwick CA, Murray LA, Clarke DL, Lindsay MA (2018) Long non-coding RNAs are central regulators of the IL-1beta-induced inflammatory response in normal and idiopathic pulmonary lung fibroblasts. Front Immunol 9:2906. https://doi.org/10.3389/fimmu.2018.02906
Wang D, Gu C, Liu M, Liu G, Liu H, Wang Y (2019) Analysis of long noncoding RNA expression profile in human pulmonary microvascular endothelial cells exposed to lipopolysaccharide. Cell Physiol Biochem 52:653–667. https://doi.org/10.33594/000000046
Wang J, Li R, Peng Z, Hu B, Rao X, Li J (2020) HMGB1 participates in LPSinduced acute lung injury by activating the AIM2 inflammasome in macrophages and inducing polarization of M1 macrophages via TLR2, TLR4, and RAGE/NFkappaB signaling pathways. Int J Mol Med 45:61–80. https://doi.org/10.3892/ijmm.2019.4402
Fei YX, Zhao B, Yin QY, Qiu YY, Ren GH, Wang BW, Wang YF, Fang WR, Li YM (2019) Ma Xing Shi Gan Decoction Attenuates PM2.5 Induced Lung Injury via Inhibiting HMGB1/TLR4/NFkappaB Signal Pathway in Rat. Front Pharmacol. https://doi.org/10.3389/fphar.2019.01361
Mu S, Liu Y, Jiang J, Ding R, Li X, Li X, Ma X (2018) Unfractionated heparin ameliorates pulmonary microvascular endothelial barrier dysfunction via microtubule stabilization in acute lung injury. Respir Res 19:220. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12931-018-0925-6
Liu H, Yu X, Yu S, Kou J (2015) Molecular mechanisms in lipopolysaccharide-induced pulmonary endothelial barrier dysfunction. Int Immunopharmacol 29:937–946. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.intimp.2015.10.010
Zhou Y, Hao C, Li C, Huang X, Li X, Tang Y, Huang Y, Tang S, Liu W, Feng D, Xu J, Yue S, Xie H, Luo Z (2018) Omentin-1 protects against bleomycin-induced acute lung injury. Mol Immunol 103:96–105. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.molimm.2018.09.007
Siddiqui MR, Akhtar S, Shahid M, Tauseef M, McDonough K, Shanley TP (2019) miR-144-mediated Inhibition of ROCK1 Protects against LPS-induced Lung Endothelial Hyperpermeability. Am J Respir Cell Mol Biol 61:257–265. https://doi.org/10.1165/rcmb.2018-0235OC
Li X, Zhang Q, Yang Z (2019) Silence of MEG3 intensifies lipopolysaccharide-stimulated damage of human lung cells through modulating miR-4262. Artif Cells Nanomed Biotechnol 47:2369–2378. https://doi.org/10.1080/21691401.2019.1623233
Zhu J, Bai J, Wang S, Dong H (2019) Down-regulation of long non-coding RNA SNHG14 protects against acute lung injury induced by lipopolysaccharide through microRNA-34c-3p-dependent inhibition of WISP1. Respir Res 20:233. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12931-019-1207-7
Yao MY, Zhang WH, Ma WT, Liu QH, Xing LH, Zhao GF (2020) Long non-coding RNA MALAT1 exacerbates acute respiratory distress syndrome by upregulating ICAM-1 expression via microRNA-150-5p downregulation. Aging (Albany NY) 12:6570–6585. https://doi.org/10.18632/aging.102953
Tay Y, Rinn J, Pandolfi PP (2014) The multilayered complexity of ceRNA crosstalk and competition. Nature 505:344–352. https://doi.org/10.1038/nature12986
Li Y, Zou L, Yang X, Chu L, Ni J, Chu X, Guo T, Zhu Z (2019) Identification of lncRNA, MicroRNA, and mRNA-associated CeRNA network of radiation-induced lung injury in a mice model. Dose Response 17:1559325819891012. https://doi.org/10.1177/1559325819891012
Zhang ZW, Chen JJ, Xia SH, Zhao H, Yang JB, Zhang H, He B, Jiao J, Zhan BT, Sun CC (2018) Long intergenic non-protein coding RNA 319 aggravates lung adenocarcinoma carcinogenesis by modulating miR-450b-5p/EZH2. Gene 650:60–67. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.gene.2018.01.096
Ye P, Lv X, Aizemaiti R, Cheng J, Xia P, Di M (2020) H3K27ac-activated LINC00519 promotes lung squamous cell carcinoma progression by targeting miR-450b-5p/miR-515-5p/YAP1 axis. Cell Prolif 53:e12797. https://doi.org/10.1111/cpr.12797
Lin S, Zhang R, Xu L, Ma R, Xu L, Zhu L, Hu J, An X (2020) LncRNA Hoxaas3 promotes lung fibroblast activation and fibrosis by targeting miR-450b-5p to regulate Runx1. Cell Death Dis 11:706. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41419-020-02889-w
Jin Y, Jiang Z, Guan X, Chen Y, Tang Q, Wang G, Wang X (2016) miR-450b-5p suppresses stemness and the development of chemoresistance by targeting SOX2 in colorectal cancer. DNA Cell Biol 35:249–256. https://doi.org/10.1089/dna.2015.3120
Han H, Shao Q, Liu X (2020) LINC00441 promotes cervical cancer progression by modulating miR-450b-5p/RAB10 axis. Cancer Cell Int 20:368. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12935-020-01400-x
Huang Z, Mou T, Luo Y, Pu X, Pu J, Wan L, Gong J, Yang H, Liu Y, Li Z, Shen A, Wu Z (2020) Inhibition of miR-450b-5p ameliorates hepatic ischemia/reperfusion injury via targeting CRYAB. Cell Death Dis 11:455. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41419-020-2648-0
Deng M, Tang Y, Li W, Wang X, Zhang R, Zhang X, Zhao X, Liu J, Tang C, Liu Z, Huang Y, Peng H, Xiao L, Tang D, Scott MJ, Wang Q, Liu J, Xiao X, Watkins S, Li J, Yang H, Wang H, Chen F, Tracey KJ, Billiar TR, Lu B (2018) The endotoxin delivery protein HMGB1 mediates caspase-11-dependent lethality in sepsis. Immunity 49(740–753):e7. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.immuni.2018.08.016
Wu T, Zhang W, Yang G, Li H, Chen Q, Song R, Zhao L (2016) HMGB1 overexpression as a prognostic factor for survival in cancer: a meta-analysis and systematic review. Oncotarget 7:50417–50427. https://doi.org/10.18632/oncotarget.10413
Meng L, Li L, Lu S, Li K, Su Z, Wang Y, Fan X, Li X, Zhao G (2018) The protective effect of dexmedetomidine on LPS-induced acute lung injury through the HMGB1-mediated TLR4/NF-kappaB and PI3K/Akt/mTOR pathways. Mol Immunol 94:7–17. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.molimm.2017.12.008
Qu L, Chen C, Chen Y, Li Y, Tang F, Huang H, He W, Zhang R, Shen L (2019) High-mobility group box 1 (HMGB1) and autophagy in acute lung injury (ALI): a review. Med Sci Monit 25:1828–1837. https://doi.org/10.12659/MSM.912867
Wang S, Zhang Y (2020) HMGB1 in inflammation and cancer. J Hematol Oncol 13:116. https://doi.org/10.1186/s13045-020-00950-x
Musumeci D, Roviello GN, Montesarchio D (2014) An overview on HMGB1 inhibitors as potential therapeutic agents in HMGB1-related pathologies. Pharmacol Ther 141:347–357. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.pharmthera.2013.11.001
Funding
This work was supported by the Biomedical and Engineering (Science) Interdisciplinary Study Fund of Shanghai Jiaotong University (YG2019QNA04 to Xiaolei Gong), the National Nature Science Foundation of China (81970439 to Jinlong Liu), Shanghai International Science and Technology Cooperation Projects (18410721400 to Jinlong Liu), and Fund of Shanghai Science and Technology Committee (17441903300 to Jinlong Liu; 17DZ2253100 to Jinfen Liu).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
XLG, LMZ and JLL conceived and designed the experiments, CXL and ZMX analyzed and interpreted the results of the experiments, JFL and HBZ performed the experiments; all authors have read and approved the manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors state that there are no conflicts of interest to disclose.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
11010_2021_4209_MOESM1_ESM.tif
MiR-450b-5p/HMGB1 acts on LPS-treated HPMECs through TLR4 and RAGEsignaling pathways. HPMECs were transfected with miR-450b-5p mimic or in combination with HMGB1before treatment with LPS (100ng/mL, 24h). (A) The protein levels of TLR4 andRAGE were detected by western blotting; (B) the mRNA expression of TLR4 andRAGE were detected by qRT‑ PCR. Data were shown as mean ± SD, n = 3. **P <0.01 (tif 1477 KB)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Gong, X., Zhu, L., Liu, J. et al. MIR3142HG promotes lipopolysaccharide-induced acute lung injury by regulating miR-450b-5p/HMGB1 axis. Mol Cell Biochem 476, 4205–4215 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11010-021-04209-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11010-021-04209-y