Abstract
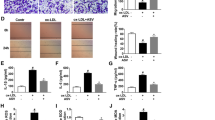
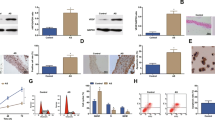
A large number of long non-coding RNAs have been confirmed to play vital roles in regulating various biological processes. Abnormal expression of growth arrest-specific transcript 5 (GAS5) is reported to be involved in the development of atherosclerosis (AS). This work is to explore the detailed mechanism underling how GAS5 regulates AS progression. We found that the abundance of GAS5 was markedly increased, and miR-135a was decreased in AS patient serums and ox-LDL-induced human THP-1 cells dose and time dependently. Interference of GAS5 suppressed inflammation and oxidative stress induced by ox-LDL in THP-1 cells. Mechanistically, GAS5 acted as a molecular sponge of microRNA-135a (miR-135a). Rescue assays indicated that knockdown of miR-135a partially rescued small interference RNA for GAS5-inhibited inflammatory cytokines release and oxidative stress in ox-LDL-triggered THP-1 cells. In conclusion, the absence of GAS5-inhibited inflammatory response and oxidative stress induced by ox-LDL in THP-1 cells via sponging miR-135a, providing a deep insight into the molecular target for AS treatment.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Libby P (2012) Inflammation in atherosclerosis. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol 32:2045–2051. https://doi.org/10.1161/ATVBAHA.108.179705
Cahill PA, Redmond EM (2016) Vascular endothelium-gatekeeper of vessel health. Atherosclerosis 248:97–109. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.atherosclerosis.2016.03.007
Lusis AJ (2000) Atherosclerosis Nature 407:233–241. https://doi.org/10.1038/35025203
Sobenin IA, Zhelankin AV, Sinyov VV, Bobryshev YV, Orekhov AN (2015) Mitochondrial aging: focus on mitochondrial DNA damage in atherosclerosis-a mini-review. Gerontology 61:343–349. https://doi.org/10.1159/000368923
Chistiakov DA, Orekhov AN, Bobryshev YV (2016) LOX-1-mediated effects on vascular cells in atherosclerosis. Cell Physiol Biochem 38:1851–1859. https://doi.org/10.1159/000443123
Bunch H (2017) Gene regulation of mammalian long non-coding RNA. Mol Genet Genomics 293(1):1–15. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00438-017-1370-9
Liu Y, Zheng L, Wang Q, Hu YW (2017) Emerging roles and mechanisms of long noncoding RNAs in atherosclerosis. Int J Cardiol 228:570–582. https://doi.org/10.1155/2019/7159592
Zhou T, Ding JW, Wang XA, Zheng XX (2016) Long noncoding RNAs and atherosclerosis. Atherosclerosis 248:51–61. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.atherosclerosis.2016.02.025
Chen C, Cheng G, Yang X, Li C, Shi R, Zhao N (2016) Tanshinol suppresses endothelial cells apoptosis in mice with atherosclerosis via lncRNA TUG1 up-regulating the expression of miR-26a. Am J Transl Res 8:2981–2891
Wu G, Cai J, Han Y, Chen J, Huang ZP, Chen C, Cai Y, Huang H, Yang Y, Liu Y, Xu Z, He D, Zhang X, Hu X, Pinello L, Zhong D, He F, Yuan GC, Wang DZ, Zeng C (2014) LincRNA-p21 regulates neointima formation, vascular smooth muscle cell proliferation, apoptosis, and atherosclerosis by enhancing p53 activity. Circulation 130:1452–1465. https://doi.org/10.1161/CIRCULATIONAHA.114.011675
Schneider C, King RM, Philipson L (1988) Genes specifically expressed at growth arrest of mammalian cells. Cell 54:787–793. https://doi.org/10.1016/s0092-8674(88)91065-3
Liu Z, Wang W, Jiang J, Bao E, Xu D, Zeng Y, Tao L, Qiu J (2013) Downregulation of GAS5 promotes bladder cancer cell proliferation, partly by regulating CDK6. PLoS ONE 8:e73991. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0073991
Pickard MR, Williams GT (2014) Regulation of apoptosis by long non-coding RNA GAS5 in breast cancer cells: implications for chemotherapy. Breast Cancer Res Treat 145:359–370. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10549-014-2974-y
Cao S, Liu W, Li F, Zhao W, Qin C (2014) Decreased expression of lncRNA GAS5 predicts a poor prognosis in cervical cancer. Int J Clin Exp Pathol 7:6776–6783
Sun M, Jin FY, Xia R, Kong R, Li JH, Xu TP, Liu YW, Zhang EB, Liu XH, De W (2014) Decreased expression of long noncoding RNA GAS5 indicates a poor prognosis and promotes cell proliferation in gastric cancer. BMC Cancer 14:319. https://doi.org/10.1186/1471-2407-14-319
Yin D, He X, Zhang E, Kong R, De W, Zhang Z (2014) Long noncoding RNA GAS5 affects cell proliferation and predicts a poor prognosis in patients with colorectal cancer. Med Oncol 31:253. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12032-014-0253-8
Mayama T, Marr AK, Kino T (2016) Differential expression of glucocorticoid receptor noncoding RNA repressor gas5 in autoimmune and inflammatory diseases. Horm Metab Res 48:550–557. https://doi.org/10.1055/s-0042-106898
Chen L, Yang W, Guo Y, Chen W, Zheng P, Zeng J, Tong W (2017) Exosomal lncRNA GAS5 regulates the apoptosis of macrophages and vascular endothelial cells in atherosclerosis. PLoS ONE 12:e0185406. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0185406
Herrington W, Lacey B, Sherliker P, Armitage J, Lewington S (2016) Epidemiology of atherosclerosis and the potential to reduce the global burden of atherothrombotic disease. Circ Res 118:535–546. https://doi.org/10.1161/CIRCRESAHA.115.307611
Lee YW, Kim PH, Lee WH, Hirani AA (2010) Interleukin-4, oxidative stress, vascular inflammation and atherosclerosis. Biomol Ther (Seoul) 18:135–144. https://doi.org/10.4062/biomolther.2010.18.2.135
Pirillo A, Norata GD, Catapano AL (2013) LOX-1, oxLDL, and atherosclerosis. Mediators Inflamm 2013:152786. https://doi.org/10.1155/2013/152786
Shen Z, She Q (2018) Association between the deletion allele of ins/del polymorphism (rs145204276) in the promoter region of gas5 with the risk of atherosclerosis. Cell Physiol Biochem 49:1431–1443. https://doi.org/10.1159/000493447
Liang W, Fan T, Liu L, Zhang L (2019) Knockdown of growth-arrest specific transcript 5 restores oxidized low-density lipoprotein-induced impaired autophagy flux via upregulating miR-26a in human endothelial cells. Eur J Pharmacol 843:154–161. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ejphar.2018.11.005
Shen S, Zhen X, Zhu Z, Zhao S, Zhou Q, Song Z, Wang G, Wang Z (2019) Silencing of GAS5 represses the malignant progression of atherosclerosis through upregulation of miR-135a. Biomed Pharmacother 118:109302. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biopha.2019.109302
Ye J, Wang C, Wang D, Yuan H (2018) LncRBA GSA5, up-regulated by ox-LDL, aggravates inflammatory response and MMP expression in THP-1 macrophages by acting like a sponge for miR-221. Exp Cell Res 369:348–355. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.yexcr.2018.05.039
Jian L, Jian D, Chen Q, Zhang L (2016) Long noncoding RNAs in atherosclerosis. J Atheroscler Thromb 23:376–384. https://doi.org/10.5551/jat.33167
Wu H, Huang M, Cao P, Wang T, Shu Y, Liu P (2012) MiR-135a targets JAK2 and inhibits gastric cancer cell proliferation. Cancer Biol Ther 13:281–288. https://doi.org/10.4161/cbt.18943
Tang W, Jiang Y, Mu X, Xu L, Cheng W, Wang X (2014) MiR-135a functions as a tumor suppressor in epithelial ovarian cancer and regulates HOXA10 expression. Cell Signal 26:1420–1426. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cellsig.2014.03.002
Leung CO, Deng W, Ye TM, Ngan HY, Tsao SW, Cheung AN, Pang RT, Yeung WS (2014) miR-135a leads to cervical cancer cell transformation through regulation of β-catenin via a SIAH1-dependent ubiquitin proteosomal pathway. Carcinogenesis 35:1931–1940. https://doi.org/10.1093/carcin/bgu032
Lu X, Yin D, Zhou B, Li T (2018) MiR-135a promotes inflammatory responses of vascular smooth muscle cells from db/db mice via downregulation of FOXO1. Int Heart J 59:170–179. https://doi.org/10.1536/ihj.17-040
Desgagné V, Guay SP, Guérin R, Corbin F, Couture P, Lamarche B, Bouchard L (2016) Variations in HDL-carried miR-223 and miR-135a concentrations after consumption of dietary trans fat are associated with changes in blood lipid and inflammatory markers in healthy men - an exploratory study. Epigenetics 11:438–448. https://doi.org/10.1080/15592294.2016.1176816
Lou C, Li Y (2018) Functional role of microRNA-135a in colitis. J Inflamm (Lond) 15:7. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12950-018-0181-z
Yan X, Li W, Yang L, Dong W, Chen W, Mao Y, Xu P, Li D, Yuan H, Li YH (2018) MiR-135a protects vascular endothelial cells against ventilator-induced lung injury by inhibiting PHLPP2 to activate PI3K/Akt pathway. Cell Physiol Biochem 48:1245–1258. https://doi.org/10.1159/000492010
Salmena L, Poliseno L, Tay Y, Kats L, Pandolfi PP (2011) A ceRNA hypothesis: the Rosetta Stone of a hidden RNA language? Cell 146:353–358. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cell.2011.07.014
Zhang Z, Zhu Z, Watabe K, Zhang X, Bai C, Xu M, Wu F, Mo YY (2013) Negative regulation of lncRNA GAS5 by miR-21. Cell Death Differ 20:1558–1568. https://doi.org/10.1038/cdd.2013.110
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors have no potential conflicts of interest to disclose.
Ethical approval
The present study was performed with the approval of the Research Ethics Committee of Taizhou Hospital of Zhejiang Province Affiliated to Wenzhou Medical University, and all participants signed the written informed consent prior to this study.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
11010_2020_3962_MOESM1_ESM.tif
Supplementary file1 The correlation analysis between GAS5 and inflammatory factors in AS patients. (A-C) Inflammatory cytokines IL-1β, IL-6, and TNF-α in serums samples from AS patients (n=26) and healthy donors (n=18) was detected. (D-F) Pearson correlation analysis was applied to evaluate the expression association between GAS5 and Inflammatory cytokines IL-1β, IL-6, and TNF-α in AS patients. GAS5= growth-arrest specific transcript 5, I = interleukin, TNF = tumor necrosis factor. *P < 0.05 (TIF 929 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhang, Y., Lu, X., Yang, M. et al. GAS5 knockdown suppresses inflammation and oxidative stress induced by oxidized low-density lipoprotein in macrophages by sponging miR-135a. Mol Cell Biochem 476, 949–957 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11010-020-03962-w
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11010-020-03962-w