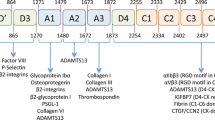
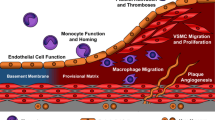
Abstract
Integrins are a group of transmembrane glycoprotein receptors that are responsible for platelet activation through bidirectional signalling. These receptors have left their footprints in various cellular events and have intrigued many groups of scientists that have led to some significant discoveries. A lot of the recent understanding of haemostasis has been possible due to the integrins filling the gaps in between several cellular mechanism. Apart from this, other important functions carried out by integrins are growth and maturation of cardiomyocytes, mechano-transduction, and interaction with actin cytoskeleton. The signalling cascade for integrin activation involves certain intracellular interacting proteins, which initiates the step-by-step activation procedure through ‘inside-out’ signalling. The signalling cascade gets activated through ‘outside-in’ signalling with the involvement of agonists such as ADP, Fibronectin, Vitronectin, and so on. This is a crucial step for the downstream processes of platelet spreading, followed by aggregation, clot progression and finally thrombus formation. Researchers throughout the world have shown direct relation of integrins with CVD and cardiac remodelling. The present review aims to summarize the information available so far on the involvement of integrins in thrombosis and its relationship to DVT. This information could be a bedrock of hidden answers to several questions on pathogenesis of deep vein thrombosis.






Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- ADP:
-
Adenosine diphosphate
- ATP:
-
Adenosine triphosphate
- bFGF:
-
basic fibroblast growth factor
- CRP:
-
Collagen-related peptide
- CVD:
-
Cardiovascular disease
- EC:
-
Endothelial cell
- ECM:
-
Extracellular matrix
- EGF:
-
Epidermal growth factor
- ESPRIT:
-
Enhanced suppression of the Platelet IIb/IIIa Receptor with Integrilin Therapy
- FDA:
-
Food and Drug Administration
- FERM:
-
protein 4.1, ezrin, radixin, moesin
- FERMT:
-
Fermitin family member
- FN:
-
Fibronectin
- GI:
-
Gastrointestinal
- GPCR:
-
G-Protein coupled receptor
- GPVI:
-
Glycoprotein VI
- IgG:
-
Immunoglobulin
- ILK:
-
Integrin linked kinase
- LV:
-
Left ventricle
- MIG2:
-
Multicopy inhibitor of GAL gene 2
- NPXY:
-
Asn-Pro-x-Tyr
- OPN:
-
Osteopontin
- oxLDL:
-
Oxidized low-density lipoprotein
- PHSRN:
-
Pro-His-Ser-Arg-Asn
- PLCβ:
-
Phospholipase C beta
- PTB:
-
Phosphotyrosine binding domain
- RGD:
-
Arginine-glycine-Aspartic acid
- ST:
-
Sinus Tachycardia
- THD:
-
Terminal head domain
- tPA:
-
tissue Plasminogen Activator
- TxA2:
-
Thromboxane A2
- URP:
-
Urotensin-II-related peptide
- VASP:
-
Vasodilator-stimulator phosphoprotein
- VCAM-1:
-
Vascular cell adhesion molecule-1
- VN:
-
Vitronectin
- WT:
-
Wild type
References
Ruoslahti E (1991) Integrins. J Clin Invest 87(1):1–5
Piotrowicz RS, Orchekowski RP, Nugent DJ, Yamada KY, Kunicki TJ (1988) Glycoprotein Ic-IIa functions as an activation-independent fibronectin receptor on human platelets. J Cell Biol 106(4):1359–1364
Tamkun JW, DeSimone DW, Fonda D, Patel RS, Buck C, Horwitz AF, Hynes RO (1986) Structure of integrin, a glycoprotein involved in the transmembrane linkage between fibronectin and actin. Cell 46(2):271–282
Holbro T, Hynes NE (2004) ErbB receptors: directing key signaling networks throughout life. Annu Rev Pharmacol Toxicol 44:195–217
Larson RS, Springer TA (1990) Structure and function of leukocyte integrins. Immunol Rev 114:181–217
Lu C, Oxvig C, Springer TA (1998) The structure of the β-propeller domain and C-terminal region of the integrin αM subunit dependence on β subunit association and prediction of domains. J Biol Chem 273(24):15138–15147
Campbell ID, Humphries MJ (2011) Integrin structure, activation, and interactions. Cold Spring Harb Perspect Biol 3(3):a004994
Gullberg D, Gehlsen KR, Turner DC, Ahlen K, Zijenah LS, Barnes MJ, Rubin K (1992) Analysis of alpha 1 beta 1, alpha 2 beta 1 and alpha 3 beta 1 integrins in cell – collagen interactions: identification of conformation dependent alpha 1 beta 1 binding sites in collagen type I. EMBO J 11(11):3865–3873
Gullberg D, Turner DC, Borg TK, Terracio L, Rubin K (1990) Different β1-integrin collagen receptors on rat hepatocytes and cardiac fibroblasts. Exp Cell Res 190(2):254–264
Schiro JA, Chan BM, Roswit WT, Kassner PD, Pentland AP, Hemler ME et al (1991) Integrin α2β1 (VLA-2) mediates reorganization and contraction of collagen matrices by human cells. Cell 67(2):403–410
Tiger CF, Fougerousse F, Grundström G, Velling T, Gullberg D (2001) α11β1 integrin is a receptor for interstitial collagens involved in cell migration and collagen reorganization on mesenchymal nonmuscle cells. Dev Biol 237(1):116–129
Ginsberg MH, Partridge A, Shattil SJ (2005) Integrin regulation. Curr Opin Cell Biol 5:509–516
Hynes RO (2002) Integrins: bidirectional, allosteric signaling machines. Cell 110(6):673–687
Calderwood DA, Yan B, de Pereda JM, Alvarez BG, Fujioka Y, Liddington RC, Ginsberg MH (2002) The phosphotyrosine binding-like domain of talin activates integrins. J BiolChem 277(24):21749–21758
Bouaouina M, Lad Y, Calderwood DA (2008) The N-terminal domains of talin cooperate with the phosphotyrosine binding-like domain to activate β1 and β3 integrins. J Biol Chem 283(10):6118–6125
Nieswandt B, Varga-Szabo D, Elvers M (2009) Integrins in platelet activation. J Thromb Haemost Suppl 1:206–209
Calderwood DA (2004) Integrin activation. J Cell Sci 117:657–666
Nieswandt B, Moser M, Pleines I, Varga-Szabo D, Monkley S, Critchley D, Fässler R (2007) Loss of talin1 in platelets abrogates integrin activation, platelet aggregation, and thrombus formation in vitro and in vivo. J Exp Med 204(13):3113–3118
Petrich BG, Fogelstrand P, Partridge AW, Yousefi N, Ablooglu AJ, Shattil SJ, Ginsberg MH (2007) The antithrombotic potential of selective blockade of talin-dependent integrin α IIb β 3 (platelet GPIIb–IIIa) activation. J Clin Invest 117(8):2250–2259
Hodivala-Dilke KM, McHugh KP, Tsakiris DA, Rayburn H, Crowley D, Ullman-Culleré M et al (1999) β3-integrin–deficient mice are a model for Glanzmann thrombasthenia showing placental defects and reduced survival. J Clin Invest 103(2):229–238
Larjava H, Plow EF, Wu C (2008) Kindlins: essential regulators of integrin signalling and cell–matrix adhesion. EMBO Rep 9(12):1203–1208
Shattil SJ, Kim C, Ginsberg MH (2010) The final steps of integrin activation: the end game. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol 11(4):288–300
Legate KR, Wickström SA, Fässler R (2009) Genetic and cell biological analysis of integrin outside-in signaling. Genes Dev 23:397–418
Mackinnon AC, Qadota H, Norman KR, Moerman DG, Williams BD (2002) C. elegans PAT-4/ILK functions as an adaptor protein within integrin adhesion complexes. Curr Biol 12(10):787–797
Tao L, Zhang Y, Xi X, Kieffer N (2010) Recent advances in the understanding of the molecular mechanisms regulating platelet integrin αIIbβ3 activation. Protein Cell 1(7):627–637
Montanez E, Ussar S, Schifferer M, Bösl M, Zent R, Moser M, Fässler R (2008) Kindlin-2 controls bidirectional signaling of integrins. Genes Dev 22:1325–1330
Kloeker S, Major MB, Calderwood DA, Ginsberg MH, Jones DA, Beckerle MC (2004) The Kindler syndrome protein is regulated by transforming growth factor-β and involved in integrin-mediated adhesion. J Biol Chem 279(8):6824–6833
Tu Y, Wu S, Shi X, Chen K, Wu C (2003) Migfilin and Mig-2 link focal adhesions to filamin and the actin cytoskeleton and function in cell shape modulation. Cell 113(1):37–47
Moser M, Nieswandt B, Ussar S, Pozgajova M, Fässler R (2008) Kindlin-3 is essential for integrin activation and platelet aggregation. Nat Med 3:325–330
Moser M, Legate KR, Zent R, Fässler R (2009) The tail of integrins, talin, and kindlins. Science 324(5929):895–899
Li Z, Zhang G, Feil R, Han J, Du X (2006) Sequential activation of p38 and ERK pathways by cGMP-dependent protein kinase leading to activation of the platelet integrin αIIbβ3. Blood 107(3):965–972
Robbins SM, Suttorp VV, Weeks G, Spiegelman GB (1990) A ras-related gene from the lower eukaryote Dictyostelium that is highly conserved relative to the human rap genes. Nucleic Acids Res 18(17):5265–5269
Hariharan IK, Carthew RW, Rubin GM (1991) The Drosophila roughened mutation: activation of a rap homolog disrupts eye development and interferes with cell determination. Cell 67(4):717–722
Robbins SM, Khosla M, Thiery R, Weeks G, Spiegelman GB (1991) Ras-related genes in Dictyosteliumdiscoideum. Dev Genet 12(1-2):147–153
Díez J, Querejeta R, López B, González A, Larman M, Martínez Ubago JL (2002) Losartan-dependent regression of myocardial fibrosis is associated with reduction of left ventricular chamber stiffness in hypertensive patients. Circulation 105(21):2512–2517
Brilla CG, Maisch B, Weber KT (1992) Myocardial collagen matrix remodelling in arterial hypertension. Eur Heart J 13(suppl_D):24–32
Camelliti P, Borg TK, Kohl P (2005) Structural and functional characterisation of cardiac fibroblasts. Cardiovasc Res 65(1):40–51
Chrzanowska-Wodnicka M, Smyth SS, Schoenwaelder SM, Fischer TH, White GC (2005) Rap1b is required for normal platelet function and hemostasis in mice. J Clin Invest 115(3):680–687
Ieda M, Tsuchihashi T, Ivey KN, Ross RS, Hong TT, Shaw RM, Srivastava D (2009) Cardiac fibroblasts regulate myocardial proliferation through β1 integrin signaling. Dev Cell 16(2):233–244
Lopez-Sanchez C, Climent V, Schoenwolf GC, Alvarez IS, Garcia-Martinez V (2002) Induction of cardiogenesis by Hensen’s node and fibroblast growth factors. Cell Tissue Res 309:237–249
Kamkin A, Kiseleva I, Lozinsky I, Scholz H (2005) Electrical interaction of mechanosensitive fibroblasts and myocytes in the heart. Basic Res Cardiol 100:337–345
Aneja A, Tang WW, Bansilal S, Garcia MJ, Farkouh ME (2008) Diabetic cardiomyopathy: insights into pathogenesis, diagnostic challenges, and therapeutic options. Am J Med 121(9):748–757
Hinz B (2015) The extracellular matrix and transforming growth factor-β1: tale of a strained relationship. Matrix Biol 47:54–65
Nicoletti A, Michel JB (1999) Cardiac fibrosis and inflammation: interaction with hemodynamic and hormonal factors. Cardiovasc Res 41(3):532–543
Barczyk MM, Lu N, Popova SN, Bolstad AI, Gullberg D (2013) α11β1 integrin-mediated MMP-13-dependent collagen lattice contraction by fibroblasts: evidence for integrin-coordinated collagen proteolysis. J Cell Physiol 228(5):1108–1119
Carracedo S, Lu N, Popova SN, Jonsson R, Eckes B, Gullberg D (2010) The fibroblast integrin α11β1 is induced in a mechanosensitive manner involving activin A and regulates myofibroblast differentiation. J Biol Chem 285(14):10434–10445
Civitarese RA, Talior-Volodarsky I, Desjardins JF, Kabir G, Switzer J, Mitchell M et al (2016) The α11 integrin mediates fibroblast–extracellular matrix–cardiomyocyte interactions in health and disease. Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol 311(1):H96–H106
Kai H, Muraishi A, Sugiu Y, Nishi H, Seki Y, Kuwahara F et al (1998) Expression of proto-oncogenes and gene mutation of sarcomeric proteins in patients with hypertrophic cardiomyopathy. Circ Res 83(6):594–601
Samarel AM (2005) Costameres, focal adhesions, and cardiomyocyte mechanotransduction. Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol 289(6):H2291–H2301
Maitra N, Flink IL, Bahl JJ, Morkin E (2000) Expression of α and β integrins during terminal differentiation of cardiomyocytes. Cardiovasc Res 47(4):715–725
Bouzeghrane F, Mercure C, Reudelhuber TL, Thibault G (2004) α8β1 integrin is upregulated in myofibroblasts of fibrotic and scarring myocardium. J Mol Cell Cardiol 3:343–353
Arora PD, Narani N, McCulloch CA (1999) The compliance of collagen gels regulates transforming growth factor-β induction of α-smooth muscle actin in fibroblasts. Am J Pathol 154(3):871–882
Topol E, Califf R, Weisman H, Ellis S, Tcheng J, Worley S et al (1994) Randomised trial of coronary intervention with antibody against platelet IIb/IIIa integrin for reduction of clinical restenosis: results at six months. Lancet 343(8902):881–886
Coller BS (1997) Platelet GPIIb/IIIa antagonists: the first anti-integrin receptor therapeutics. J Clin Invest 99(7):1467–1471
Thannickal VJ, Lee DY, White ES, Cui Z, Larios JM, Chacon R et al (2003) Myofibroblast differentiation by transforming growth factor-β1 is dependent on cell adhesion and integrin signaling via focal adhesion kinase. J Biol Chem 278(14):12384–12389
Kleiman NS, Raizner AE, Jordan R, Wang AL, Norton D, Mace KF et al (1995) Differential inhibition of platelet aggregation induced by adenosine diphosphate or a thrombin receptor-activating peptide in patients treated with bolus chimeric 7E3 Fab: implications for inhibition of the internal pool of GPIIb/IIIa receptors. J Am Coll Cardiol 26(7):1665–1671
Kereiakes DJ (2003) Inflammation as a therapeutic target: a unique role for abciximab. Am Heart J 146(4):S1–S4
Blindt R, Bosserhoff AK, Krott N, Vogt F, Hanrath P, Demircan L, vom Dahl J (2002) Decrease of vascular smooth muscle cell locomotion by abciximab, but not tirofiban: a possible role of different affinity to alpha v beta 3 integrins. Coron Artery Dis 13(7):357–364
O’Shea JC, Hafley GE, Greenberg S, Hasselblad V, Lorenz TJ, Kitt MM et al (2001) Platelet glycoprotein IIb/IIIa integrin blockade with eptifibatide in coronary stent intervention: the ESPRIT trial: a randomized controlled trial. JAMA 285(19):2468–2473
Leclerc JR (2002) Platelet glycoprotein IIb/IIIa antagonists: lessons learned from clinical trials and future directions. Crit Care Med 30(5 Suppl):S332–S340
Jennings LK (2005) Current strategies with eptifibatide and other antiplatelet agents in percutaneous coronary intervention and acute coronary syndromes. Expert Opin Drug Metab Toxicol 1(4):727–737
Brener SJ, Barr LA, Burchenal JEB, Katz S, George BS, Jones AA et al (1998) Randomized, placebo-controlled trial of platelet glycoprotein IIb/IIIa blockade with primary angioplasty for acute myocardial infarction. Circulation 98(8):734–741
Grines CL, Cox DA, Stone GW, Garcia E, Mattos LA, Giambartolomei A et al (1999) Coronary angioplasty with or without stent implantation for acute myocardial infarction. N Engl J Med 341:1949–1956
Smith SC Jr (2006) American College of Cardiology/American Heart Association Task Force on Practice Guidelines; American College of Cardiology/American Heart Association/Society for Cardiovascular Angiography and Interventions Writing Committee to update the 2001 guidelines for percutaneous coronary intervention. ACC/AHA/SCAI 2005 guideline update for percutaneous coronary intervention-summary article: a report of the American College of Cardiology/American Heart Association Task Force on Practice Guidelines (ACC/AHA/SCAI). Circulation 113(1):156–175
Yoganathan TN, Costello P, Chen X, Jabali M, Yan J, Leung D et al (2000) Integrin-linked kinase (ILK): a “hot” therapeutic target. Biochem Pharmacol 60(8):1115–1119
Zhang X, Hu K, Li CY (2001) Protection against oxidized low-density lipoprotein–induced vascular endothelial cell death by integrin-linked kinase. Circulation 104(23):2762–2766
Fang CC, Chou TH, Huang JW, Lee CC, Chen SC (2018) The small molecule inhibitor QLT-0267 decreases the production of fibrin-induced inflammatory cytokines and prevents post-surgical peritoneal adhesions. Sci Rep 8:9481
Zhang ZC, Li SJ, Yang YZ, Chen RZ, Ge JB, Chen HZ (2004) Microarray analysis of extracellular matrix genes expression in myocardium of mouse with Coxsackie virus B3 myocarditis. Chin Med J 117(8):1228–1231
Uehata M, Ishizaki T, Satoh H, Ono T, Kawahara T, Morishita T, Tamakawa H, Yamagami K, Inui J, Maekawa M, Narumiya S (1997) Calcium sensitization of smooth muscle mediated by a Rho-associated protein kinase in hypertension. Nature 389(6654):990–994
Hattori T, Shimokawa H, Higashi M, Hiroki J, Mukai Y, Tsutsui H et al (2004) Long-term inhibition of Rho-kinase suppresses left ventricular remodeling after myocardial infarction in mice. Circulation 109(18):2234–2239
Qvigstad E, Sjaastad I, Brattelid T, Nunn C, Swift F, Birkeland JAK et al (2005) Dual serotonergic regulation of ventricular contractile force through 5-HT2A and 5-HT4 receptors induced in the acute failing heart. Circ Res 97:268–276
Ishizaki T, Uehata M, Tamechika I, Keel J, Nonomura K, Maekawa M, Narumiya S (2000) Pharmacological properties of Y-27632, a specific inhibitor of rho-associated kinases. Mol Pharmacol 57(5):976–983
Inokuchi K, Ito A, Fukumoto Y, Matoba T, Shiose A, Nishida T et al (2004) Usefulness of fasudil, a Rho-kinase inhibitor, to treat intractable severe coronary spasm after coronary artery bypass surgery. J Cardiovasc Pharmacol 44(3):275–277
Guijarro C, Blanco-Colio LM, Ortego M, Alonso C, Ortiz A, Plaza JJ et al (1998) 3-Hydroxy-3-methylglutaryl coenzyme a reductase and isoprenylation inhibitors induce apoptosis of vascular smooth muscle cells in culture. Circ Res 83(5):490–500
Kern A, Eble J, Golbik R, Kühn K (1993) Interaction of type IV collagen with the isolated integrins α1β1 and α2β1.Eur. J Biochem 215(1):151–159
Kamata T, Takada Y (1994) Direct binding of collagen to the I domain of integrin alpha 2 beta 1 (VLA-2, CD49b/CD29) in a divalent cation-independent manner. J Biol Chem 269(42):26006–26010
Nykvist P, Tu H, Ivaska J, Käpylä J, Pihlajaniemi T, Heino J (2000) Distinct recognition of collagen subtypes by α1β1 and α2β1 integrins α1β1 mediates cell adhesion to type Xiii collagen. J Biol Chem 275(11):8255–8261
Pfaff M, Göhring W, Brown JC, Timpl R (1994) Binding of purified collagen receptors (α1β1, α2β1) and RGD-dependent integrins to laminins and laminin fragments. Eur J Biochem 225(3):975–984
Decline F, Rousselle P (2001) Keratinocyte migration requires alpha2beta1 integrin-mediated interaction with the laminin 5 gamma2 chain. J Cell Sci 114(Pt 4):811–823
Zotz RB, Winkelmann BR, Müller C, Boehm BO, März W, Scharf RE (2005) Association of polymorphisms of platelet membrane integrins αIIbβ3 (HPA-1b/PlA2) and α2β1 (α2807TT) with premature myocardial infarction. J Thromb Haemost 3(7):1522–1529
Funahashi Y, Sugi NH, Semba T, Yamamoto Y, Hamaoka S, Tsukahara-Tamai N et al (2002) Sulfonamide derivative, E7820, is a unique angiogenesis inhibitor suppressing an expression of integrin α2 subunit on endothelium. Cancer Res 62(21):6116–6123
Semba T, Funahashi Y, Ono N, Yamamoto Y, Sugi NH, Asada M et al (2004) An angiogenesis inhibitor E7820 shows broad-spectrum tumor growth inhibition in a xenograft model: possible value of integrin α2 on platelets as a biological marker. Clin Cancer Res 10(4):1430–1438
Springer TA (1994) Traffic signals for lymphocyte recirculation and leukocyte emigration: the multistep paradigm. Cell 76(2):301–314
Noseworthy JH, Kirkpatrick P (2005) Natalizumab. Nat Rev Drug Discov 4(2):101–102
Léger OJ, Yednock TA, Tanner L, Horner HC, Hines DK, Keen S et al (1997) Humanization of a mouse antibody against human alpha-4 integrin: a potential therapeutic for the treatment of multiple sclerosis. Hum Antibodies 8(1):3–16
Stoeltzing O, Liu W, Reinmuth N, Fan F, Parry GC, Parikh AA et al (2003) Inhibition of integrin α5β1 function with a small peptide (ATN-161) plus continuous 5-FU infusion reduces colorectal liver metastases and improves survival in mice. Int J Cancer 104(4):496–503
Cheresh DA (1987) Human endothelial cells synthesize and express an Arg-Gly-Asp-directed adhesion receptor involved in attachment to fibrinogen and von Willebrand factor. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 84(18):6471–6475
Stromblad S, Becker JC, Yebra M, Brooks PC, Cheresh DA (1996) Suppression of p53 activity and p21WAF1'C'P1 expression by vascular cell integrin a& during angiogenesis. J Clin Invest 98(2):426–433
Brooks PC, Montgomery AM, Rosenfeld M, Reisfeld RA, Hu T, Klier G, Cheresh DA (1994) Integrin αvβ3 antagonists promote tumor regression by inducing apoptosis of angiogenic blood vessels. Cell 79(7):1157–1164
Pc B, Clark RA, Cheresh DA (1994) Requirement of vascular integrin alpha v beta 3 for angiogenesis. Science. 264(5158):569–571
Brooks PC, Strömblad S, Klemke R, Visscher D, Sarkar FH, Cheresh DA (1995) Antiintegrin alpha v beta 3 blocks human breast cancer growth and angiogenesis in human skin. J Clin Invest 96(4):1815–1822
Marcinkiewicz C, Rosenthal LA, Mosser DM, Kunicki TJ, Niewiarowski S (1996) Immunological characterization of eristostatin and echistatin binding sites on αIIb β3 and αVβ3 integrins. Biochem J 317(Pt 3):817–825
Guidance on the use of glycoprotein IIb/IIIa inhibitors in the treatment of acute coronary syndromes. National Institute for Clinical Excellence, 2000. https://www.nice.org.uk/guidance/ta47/resources/guidance-on-the-use-of-glycoprotein-iibiiia-inhibitors-in-the-treatment-of-acute-coronary-syndromes-pdf-2294582158789
Marso SP, Lincoff AM, Ellis SG, Bhatt DL, Tanguay JF, Kleiman NS et al (1999) Optimizing the percutaneous interventional outcomes for patients with diabetes mellitus: results of the EPISTENT (Evaluation of platelet IIb/IIIa inhibitor for stenting trial) diabetic substudy. Circulation. 100:2477–2484
Kastrati A, Mehilli J, Dirschinger J, Schricke U, Neverve J, Pache J et al (2002) Myocardial salvage after coronary stenting plus abciximab versus fibrinolysis plus abciximab in patients with acute myocardial infarction: a randomised trial. Lancet. 359(9310):920–925
Admiral Investigators (2005) Three-year duration of benefit from abciximab in patients receiving stents for acute myocardial infarction in the randomized double-blind ADMIRAL study. Eur Heart J 26(23):2520–2523
Lynch DK, Ellis CA, Edwards PA, Hiles ID (1999) Integrin-linked kinase regulates phosphorylation of serine 473 of protein kinase B by an indirect mechanism. Oncogene. 18(56):8024–8032
Nemerow GR, Stewart PL (1999) Role of αv integrins in adenovirus cell entry and gene delivery. Microbiol Mol Biol Rev 63(3):725–734
Vootukuri S et al (2019) Preclinical studies of RUC-4, a novel platelet αIIbβ3 antagonist, in non-human primates and with human platelets. J Clin Transl Sci 3(2-3):65–74
Bentur OS, Coller BS (2019) In vitro effects of the novel platelet αIIbβ3 receptor antagonist RUC-4 on the verifynow assays: potential for point-of-care monitoring of RUC-4 therapy. Blood 134(Supplement_1):166
Simons P et al (2018) Small-volume flow cytometry-based multiplex analysis of the activity of small GTPases. Rho GTPases. Methods Mol Biol 1821:177–195
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Ms NG involved in literature survey and writing. Dr IG participated in conceptualization, wiring, and editing. Dr SS involved inpreparation of figures and proof reading. Dr BK did editing and proof reading.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors have declared that no competing interests exist.
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ghosh, N., Garg, I., Srivastava, S. et al. Influence of integrins on thrombus formation: a road leading to the unravelling of DVT. Mol Cell Biochem 476, 1489–1504 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11010-020-03961-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11010-020-03961-x