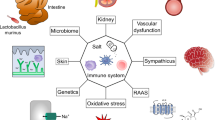
Abstract
Worldwide, more than 1 billion people have elevated blood pressure, with up to 45% of adults affected by the disease. In 2016 the global health study report on patients from 67 countries was released in Lancet, which identified hypertension as the world’s leading cause for death and disability-adjusted years since 1990. This paper aims to analyze the pathophysiological connection between hemodynamic inflammatory reactions through sodium balance, salt sensitivity, and potential pathophysiological reactions. Besides, we explore how sodium consumption enhances the expression of transient receptor potential channel 3 (TrpC3) mRNA and facilitates the release of calcium inside immune cell groups, together with elevated blood pressure in essential hypertensive patients.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
(2012) Salt restrictions. Med Lett Drugs Ther 54:13
Ando K (2000) Salt sensitivity in essential hypertension. Nihon Rinsho 58(Suppl 1):698–702
Arakawa K, Sakaki M, Sakata S, Oniki H, Tominaga M, Tsuchihashi T (2015) Variability of urinary salt excretion estimated by spot urine in treated hypertensive patients. ClinExpHypertens 37:445–448. https://doi.org/10.3109/10641963.2015.1057831
Beard TC (1990) A salt-hypertension hypothesis. J CardiovascPharmacol 16(Suppl 7):S35–S38
Beevers DG (2002) The epidemiology of salt and hypertension. ClinAuton Res 12:353–357. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10286-002-0061-7
Blaustein MP, Zhang J, Chen L, Hamilton BP (2006) How does salt retention raise blood pressure? Am J PhysiolRegulIntegr Comp Physiol 290:R514–R523. https://doi.org/10.1152/ajpregu.00819.2005
Borah PK, Sharma M, Kalita HC, Pasha MAQ, Paine SK, Hazarika D, Bhattacharjee CK, Mahanta J (2018) Salt-sensitive phenotypes: a community-based exploratory study from northeastern India. Natl Med J India 31:140–145. https://doi.org/10.4103/0970-258x.255754
Bos WJ, Navis GJ (2016) Is a salt-restricted diet now up for discussion? Ned TijdschrGeneeskd 160:D786
Brooks VL, Haywood JR, Johnson AK (2005) Translation of salt retention to central activation of the sympathetic nervous system in hypertension. ClinExpPharmacolPhysiol 32:426–432. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1440-1681.2005.04206.x
Caudarella R, Vescini F, Rizzoli E, Francucci CM (2009) Salt intake, hypertension, and osteoporosis. J EndocrinolInvestig 32:15–20
Dua K, Sheshala R, Al-Waeli HA, Gupta G, Chellappan DK (2015) Antimicrobial efficacy of extemporaneously prepared herbal mouth-washes. Rec Pat Drug DelivFormul 9:257–261
Gupta G, Dahiya R, Singh M, Tiwari J, Sah S, Ashwathanarayana M, Krishna G, Dua K (2018) Role of liraglutide in a major complication of diabetes: a critical review of clinical studies. Bull Pharm Res 8:155–164
Chrysant GS, Bakir S, Oparil S (1999) Dietary salt reduction in hypertension—what is the evidence and why is it still controversial? ProgCardiovasc Dis 42:23–38. https://doi.org/10.1016/s0033-0620(99)70007-1
de la Sierra A, Giner V, Bragulat E, Coca A (2002) Lack of correlation between two methods for the assessment of salt sensitivity in essential hypertension. J Hum Hypertens 16:255–260. https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.jhh.1001375
Dustan HP, Kirk KA (1989) Corcoran lecture: the case for or against salt in hypertension. Arthur Curtis Corcoran, MD (1909–1965). Tribute and prelude to Corcoran Lecture of 1988. Hypertension 13:696–705. https://doi.org/10.1161/01.hyp.13.6.696
Gupta G, Kazmi I, Afzal M, Rahman M, Saleem S, Ashraf MS, Khusroo MJ, Nazeer K, Ahmed S, Mujeeb M (2012) Sedative, antiepileptic and antipsychotic effects of Viscum album L. (Loranthaceae) in mice and rats. J Ethnopharmacol 141:810–816
Hatware KV, Sharma S, Patil K, Rajput H, Gupta G (2020) Therapeutic role of natural agents in the management of coronary artery disease: a review. J Environ Pathol Toxicol Oncol 39:159–177
Elijovich F, Laffer CL, Amador E, Gavras H, Bresnahan MR, Schiffrin EL (2001) Regulation of plasma endothelin by salt in salt-sensitive hypertension. Circulation 103:263–268. https://doi.org/10.1161/01.cir.103.2.263
Gupta G, Pathak S, Dahiya R, Awasthi R, Mishra A, Sharma RK, Agrawal M, Dua K (2019) Aqueous extract of wood ear mushroom, Auricularia polytricha (Agaricomycetes), demonstrated antiepileptic activity against seizure induced by maximal electroshock and isoniazid in experimental animals. Int J Med Mushrooms 21:29–35
Kazmi I, Gupta G, Afzal M, Anwar F (2012) Anticonvulsant and depressant-like activity of ursolic acid stearoylglucoside isolated from Lantana camara L. (verbanaceae). Asian Pac J Trop Dis 2:S453–S456
Ellison DH (2017) Treatment of disorders of sodium balance in chronic kidney disease. Adv Chronic Kidney Dis 24:332–341. https://doi.org/10.1053/j.ackd.2017.07.003
Ergul A (2000) Hypertension in black patients: an emerging role of the endothelin system in salt-sensitive hypertension. Hypertension 36:62–67. https://doi.org/10.1161/01.hyp.36.1.62
Espinel CH (1992) The Salt Step Test: its usage in the diagnosis of salt-sensitive hypertension and in the detection of the salt hypertension threshold. J Am CollNutr 11:526–531. https://doi.org/10.1080/07315724.1992.10718257
Freis ED (1979) Salt in hypertension and the effects of diuretics. Annu Rev PharmacolToxicol 19:13–23. https://doi.org/10.1146/annurev.pa.19.040179.000305
Freis ED (1992) The role of salt in hypertension. Blood Press 1:196–200. https://doi.org/10.3109/08037059209077662
Fujita M, Fujita T (2013) The role of CNS in salt-sensitive hypertension. CurrHypertens Rep 15:390–394. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11906-013-0358-z
Hinge N, Pandey MM, Singhvi G, Gupta G, Mehta M, Satija S, Gulati M, Dureja H, Dua K (2020) Nanomedicine advances in cancer therapy. Advanced 3D-printed systems and nanosystems for drug delivery and tissue engineering. Elsevier, Amsterdam, pp 219–253
Liu X, Sharma RK, Mishra A, Chinnaboina GK, Gupta G, Singh M (2019) Role of aqueous extract of the wood ear mushroom, Auricularia polytricha (agaricomycetes), in avoidance of haloperidol-induced catalepsy via oxidative stress in rats. Int J Med Mushrooms 21:323–330
Graudal N (2016) Con: Reducing salt intake at the population level: is it really a public health priority? Nephrol Dial Transplant 31:1398–1403. https://doi.org/10.1093/ndt/gfw280
Gupta N, Jani KK, Gupta N (2011) Hypertension: salt restriction, sodium homeostasis, and other ions. Indian J Med Sci 65:121–132. https://doi.org/10.4103/0019-5359.104787
Haddy FJ (2006) Role of dietary salt in hypertension. Life Sci 79:1585–1592. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.lfs.2006.05.017
Haddy FJ, Pamnani MB (1995) Role of dietary salt in hypertension. J Am CollNutr 14:428–438. https://doi.org/10.1080/07315724.1995.10718533
Hall CE, Holland OB, Hall O (1967) Benign and malignant hypertension after adrenal enucleation in the rat. Relationship to salt intake, response to hydrochlorothiazide, and similarity to essential hypertension. J Exp Med 126:35–52. https://doi.org/10.1084/jem.126.1.35
Henson ZK, Fülöp T (2016) Dietary salt restriction: how much education is enough? J ClinHypertens (Greenwich) 18:383–384. https://doi.org/10.1111/jch.12767
Herrera Acosta J (2001) Salt-dependent arterial hypertension. Arch CardiolMex 71(Suppl 1):S76–S80
Hu JW, Wang Y, Chu C, Mu JJ (2018) Effect of salt intervention on serum levels of fibroblast growth factor 23 (FGF23) in Chinese adults: an intervention study. Med SciMonit 24:1948–1954. https://doi.org/10.12659/msm.906489
Gupta G, Pathak S, Rawat S, Mishra A, Singh Y, Mehta M, Satija S, Khurana N, Pinto TdJA, Shukla S (2020) Oxidative stress in neurology and in neurodegenerative processes. Role of oxidative stress in pathophysiology of diseases. Springer, Singapore, pp 49–65
Madhu A, Gupta G, Arali B, Chellappan DK, Dua K (2017) Anti-psychotic activity of aqueous root extract of Hemidesmusindicus: a time bound study in rats. Recent Pat DelivFormul 11:36–41
Imaizumi Y, Eguchi K, Murakami T, Arakawa K, Tsuchihashi T, Kario K (2016) High salt intake is independently associated with hypertensive target organ damage. J ClinHypertens (Greenwich) 18:315–321. https://doi.org/10.1111/jch.12668
Johnson C, Santos JA, McKenzie B, Thout SR, Trieu K, McLean R, Petersen KS, Campbell NRC, Webster J (2017) The Science of Salt: a regularly updated systematic review of the implementation of salt reduction interventions (September 2016–February 2017). J ClinHypertens (Greenwich) 19:928–938. https://doi.org/10.1111/jch.13099
Gupta G, Verma R, David SR, Chellappan DK, Anwar F, Dua K (2014) Hepatoprotective activity of moralbosteroid, a steroidal glycoside isolated from Morus alba. Orient Pharm Exp Med 14:285–289
Kantaria N, Pantsulaia I, Andronikashvili I, Simonia G (2016) Possible mechanism of development of salt sensitive essential hypertension. Georgian Med News 258:28–32
Kawano Y, Ando K, Matsuura H, Tsuchihashi T, Fujita T, Ueshima H (2007) Report of the Working Group for Dietary Salt Reduction of the Japanese Society of Hypertension: (1) rationale for salt restriction and salt-restriction target level for the management of hypertension. Hypertens Res 30:879–886. https://doi.org/10.1291/hypres.30.879
Krekels MM, de Leeuw PW (1997) Salt sensitive blood pressure and the renin–angiotensin system in hypertension. Ned TijdschrGeneeskd 141:2285–2289
Gupta G, Singh Y, Kumar Chellappan D, Dua K (2020) New emerging dermatological symptoms in coronavirus pandemic. J Cosmet Dermatol 19:2447–2448. https://doi.org/10.1111/jocd.13466
Maurya H, Dhiman S, Dua K, Gupta G (2016) Pharmacological effect of berberine chloride in propyl thiouracil induced thyroidal dysfunction—a time bound study in female rats. Recent Pat Drug DelivFormul 10:165–173
Krzesinski JM, Cohen EP (2007) Salt, the kidneys, and arterial hypertension. ActaClinBelg 62:348–357. https://doi.org/10.1179/acb.2007.053
Kurtz TW, DiCarlo SE, Pravenec M, Morris RC Jr (2018) The pivotal role of renal vasodysfunction in salt sensitivity and the initiation of salt-induced hypertension. CurrOpinNephrolHypertens 27:83–92. https://doi.org/10.1097/mnh.0000000000000394
Laffer CL, Bolterman RJ, Romero JC, Elijovich F (2006) Effect of salt on isoprostanes in salt-sensitive essential hypertension. Hypertension 47:434–440. https://doi.org/10.1161/01.hyp.0000202480.06735.82
Luft FC (1998) Salt and hypertension at the close of the millenium. Wien KlinWochenschr 110:459–466
Manhiani MM, Quigley JE, Socha MJ, Motamed K, Imig JD (2007) IL6 suppression provides renal protection independent of blood pressure in a murine model of salt-sensitive hypertension. Kidney Blood Press Res 30:195–202. https://doi.org/10.1159/000104094
Michell AR (1978) Salt appetite, salt intake, and hypertension: a deviation of perspective. PerspectBiol Med 21:335–347. https://doi.org/10.1353/pbm.1978.0006
Miyamoto K, Iwakuma M, Nakayama T (2017) Effect of genetic information regarding salt-sensitive hypertension on the intent to maintain a reduced salt diet: implications for health communication in Japan. J ClinHypertens (Greenwich) 19:270–279. https://doi.org/10.1111/jch.12897
Hu Y, Xia W, Li Y, Wang Q, Lin S, Wang B, Zhou C, Cui Y, Jiang Y, Pu X, Wei X, Wu H, Zhang H, Zhu Z, Liu D, Li Z (2020) High-salt intake increases TRPC3 expression and enhances TRPC3-mediated calcium influx and systolic blood pressure in hypertensive patients. Hypertens Res 43(7):679–687. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41440-020-0409-1
Nicolaysen G, Iversen PO (2004) Salt and hypertension—100 years of unresolved issues. TidsskrNorLaegeforen 124:3191–3193
Singh Y, Gupta G, Satija S, Negi P, Chellappan DK, Dua K (2020) RAAS blockers in hypertension posing a higher risk towards the COVID‐19. Dermatol Ther. https://doi.org/10.1111/dth.13501
Singhvi G, Manchanda P, Hans N, Dubey SK, Gupta G (2019) Microsponge: an emerging drug delivery strategy. Drug Dev Res 80:200–208
Ohta Y, Ohta K, Ishizuka A, Hayashi S, Kishida M, Iwashima Y, Yoshihara F, Nakamura S, Kawano Y (2015) Awareness of salt restriction and actual salt intake in hypertensive patients at a hypertension clinic and general clinic. ClinExpHypertens 37:172–175. https://doi.org/10.3109/10641963.2014.933965
Pao AC, Chang TI (2017) An experimentumcrucis in salt sensitivity. Am J PhysiolRenPhysiol 312:F190–F191. https://doi.org/10.1152/ajprenal.00510.2016
PinjuhMarkota N, Rumboldt M, Rumboldt Z (2015) Emphasized warning reduces salt intake: a randomized controlled trial. J Am SocHypertens 9:214–220. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jash.2014.12.022
Polonia J, Monteiro J, Almeida J, Silva JA, Bertoquini S (2016) High salt intake is associated with a higher risk of cardiovascular events: a 7.2-year evaluation of a cohort of hypertensive patients. Blood Press Monit 21:301–306. https://doi.org/10.1097/mbp.0000000000000205
Radhika G, Sathya RM, Sudha V, Ganesan A, Mohan V (2007) Dietary salt intake and hypertension in an urban south Indian population—[CURES-53]. J Assoc Physicians India 55:405–411
Raij L (1999) Nitric oxide, salt sensitivity, and cardiorenal injury in hypertension. SeminNephrol 19:296–303
Resnick LM (1994) Calciotropic hormones in salt-sensitive essential hypertension: 1,25-dihydroxyvitamin D and parathyroid hypertensive factor. J HypertensSuppl 12:S3–S9
Richardson SI, Freedman BI, Ellison DH, Rodriguez CJ (2013) Salt sensitivity: a review with a focus on non-Hispanic blacks and Hispanics. J Am SocHypertens 7:170–179. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jash.2013.01.003
Rios-Leyvraz M, Bloetzer C, Chatelan A, Bochud M, Burnier M, Santschi V, Paradis G, Tabin R, Bovet P, Chiolero A (2019) Sodium intake and blood pressure in children with clinical conditions: a systematic review with meta-analysis. J ClinHypertens (Greenwich) 21:118–126. https://doi.org/10.1111/jch.13436
Rorije NMG, Rademaker E, Schrooten EM, Wouda RD, Homan Van Der Heide JJ, Van Den Born BH, Vogt L (2019) High-salt intake affects sublingual microcirculation and is linked to body weight change in healthy volunteers: a randomized cross-over trial. J Hypertens 37:1254–1261. https://doi.org/10.1097/hjh.0000000000002015
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
All authors declare that they do not have any conflicts of interest.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kazmi, I., Al-Maliki, W.H., Ali, H. et al. Biochemical interaction of salt sensitivity: a key player for the development of essential hypertension. Mol Cell Biochem 476, 767–773 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11010-020-03942-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11010-020-03942-0