Abstract
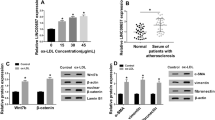
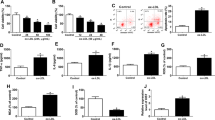
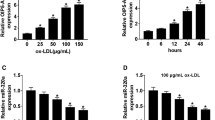
Cerebrovascular diseases have a high mortality and disability rate in developed countries. Endothelial cell injury is the main cause of atherosclerosis and cerebrovascular disease. Long non-coding RNA (lncRNA) has been proved to participate in the progression of endothelial cell. Our study aimed to develop the function of lncRNA opa-interacting protein 5 antisense RNA 1 (OIP5-AS1) in oxidative low-density lipoprotein (ox-LDL)-induced endothelial cell injury. The expression of OIP5-AS1, miR-98-5p and High-mobility group protein box-1 (HMGB1) was detected by quantitative real-time polymerase chain reaction (qRT-PCR). 3-(4,5-dimethyl-2-thiazolyl)-2,5-diphenyl-2-H-tetrazolium bromide (MTT) assay and flow cytometry were used to detect the cell proliferation and apoptosis. The levels of cyclinD1, Bcl-2 Associated X Protein (Bax), Cleaved-caspase-3, Toll like receptors 4 (TLR4), phosphorylation of p65 (p-P65), phosphorylation of nuclear factor-kappa B inhibitor α (p-IκB-α) and HMGB1 were measured by Western blot. The concentrations of Interleukin-6 (IL-6), Interleukin-1β (IL-1β) and Tumor necrosis factor-α (TNF-α) were detected by Enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA). The production of Reactive oxygen species (ROS), Superoxide Dismutase (SOD) and malondialdehyde (MDA) was detected by the corresponding kit. The targets of OIP5-AS and miR-98-5p were predicted by starBase 3.0 and TargetScan and confirmed by dual-luciferase reporter assay and RNA immunoprecipitation (RIP) assay. The expression of OIP5-AS1 was upregulated, while miR-98-5p was downregulated in ox-LDL-induced human umbilical vein endothelial cells (HUVECs). Functionally, knockdown of OIP5-AS1 induced proliferation and inhibited apoptosis, inflammatory injury and oxidative stress injury in ox-LDL-induced HUVEC cells. Interestingly, miR-98-5p was a target of OIP5-AS1 and miR-98-5p inhibition abolished the effects of OIP5-AS1 downregulation on ox-LDL-induced HUVECs injury. More importantly, miR-98-5p directly targeted HMGB1, and OIP5-AS1 regulated the expression of HMGB1 by sponging miR-98-5p. Finally, OIP5-AS1 regulated the TLR4/nuclear factor-kappa B (NF-κB) signaling pathway through miR-98-5p/HMGB1 axis. LncRNA OIP5-AS1 accelerates ox-LDL-induced endothelial cell injury through regulating HMGB1 mediated by miR-98-5p via the TLR4/NF-κB signaling pathway.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Santulli G (2013) Epidemiology of cardiovascular disease in the 21st century: updated numbers and updated facts. J Cardiovasc Dis Res 1:1–2
Koton S, Schneider AL, Rosamond WD, Shahar E, Sang Y, Gottesman RF, Coresh J (2014) Stroke incidence and mortality trends in US communities, 1987 to 2011. JAMA 312:259–268. https://doi.org/10.1001/jama.2014.7692
Della-Morte D, Pacifici F, Rundek T (2016) Genetic susceptibility to cerebrovascular disease. Curr Opin Lipidol 27:187–195. https://doi.org/10.1097/MOL.0000000000000275
Inaba Y, Chen JA, Bergmann SR (2012) Carotid plaque, compared with carotid intima-media thickness, more accurately predicts coronary artery disease events: a meta-analysis. Atherosclerosis 220:128–133. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.atherosclerosis.2011.06.044
Fujihara K, Suzuki H, Sato A, Ishizu T, Kodama S, Heianza Y, Saito K, Iwasaki H, Kobayashi K, Yatoh S, Takahashi A, Yahagi N, Sone H, Shimano H (2014) Comparison of the framingham risk score, UK Prospective Diabetes Study (UKPDS) risk engine, Japanese atherosclerosis longitudinal study-existing cohorts combine (JALS-ECC) and maximum carotid intima-media thickness for predicting coronary artery stenosis in patients with asymptomatic type 2 diabetes. J Atheroscler Thromb 21:799–815. https://doi.org/10.5551/jat.20487
Forstermann U, Xia N, Li H (2017) Roles of vascular oxidative stress and nitric oxide in the pathogenesis of atherosclerosis. Circ Res 120:713–735. https://doi.org/10.1161/CIRCRESAHA.116.309326
Di X, Tang X, Di X (2017) Montelukast inhibits oxidized low-density lipoproteins (ox-LDL) induced vascular endothelial attachment: an implication for the treatment of atherosclerosis. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 486:58–62. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bbrc.2017.02.125
Chen G, Wang Z, Wang D, Qiu C, Liu M, Chen X, Zhang Q, Yan G, Cui Q (2013) LncRNADisease: a database for long-non-coding RNA-associated diseases. Nucleic Acids Res 41:D983–986. https://doi.org/10.1093/nar/gks1099
Li Y, Han X, Feng H, Han J (2019) Long noncoding RNA OIP5-AS1 in cancer. Clin Chim Acta 499:75–80. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cca.2019.08.031
Wang M, Liu Y, Li C, Zhang Y, Zhou X, Lu C (2019) Long noncoding RNA OIP5-AS1 accelerates the ox-LDL mediated vascular endothelial cells apoptosis through targeting GSK-3beta via recruiting EZH2. Am J Transl Res 11:1827–1834
Hua Y, Duan S, Murmann AE, Larsen N, Kjems J, Lund AH, Peter ME (2011) miRConnect: identifying effector genes of miRNAs and miRNA families in cancer cells. PLoS ONE 6:e26521. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0026521
Ballantyne MD, McDonald RA, Baker AH (2016) lncRNA/MicroRNA interactions in the vasculature. Clin Pharmacol Ther 99:494–501. https://doi.org/10.1002/cpt.355
Guo Z, He C, Yang F, Qin L, Lu X, Wu J (2019) Long non-coding RNA-NEAT1, a sponge for miR-98-5p, promotes expression of oncogene HMGA2 in prostate cancer. Biosci Rep. https://doi.org/10.1042/BSR20190635
Chen Z, Wang M, He Q, Li Z, Zhao Y, Wang W, Ma J, Li Y, Chang G (2017) MicroRNA-98 rescues proliferation and alleviates ox-LDL-induced apoptosis in HUVECs by targeting LOX-1. Exp Ther Med 13:1702–1710. https://doi.org/10.3892/etm.2017.4171
Yan S, Fang C, Cao L, Wang L, Du J, Sun Y, Tong X, Lu Y, Wu X (2019) Protective effect of glycyrrhizic acid on cerebral ischemia/reperfusion (I/R) injury via inhibiting HMGB1 mediated TLR4/NF-kappaB pathway. Biotechnol Appl Biochem. https://doi.org/10.1002/bab.1825
Zhu X, Zhang H, Shang F, Zang K, Zhang X (2019) Effect of intensive insulin therapy on high mobility group box-1/nuclear factor-KappaB pathway in severe traumatic brain injury patient with stress hyperglycemia. Zhonghua Wei Zhong Bing Ji Jiu Yi Xue 31:949–952. https://doi.org/10.3760/cma.j.issn.2095-4352.2019.08.007
Wu CY, Zhou ZF, Wang B, Ke ZP, Ge ZC, Zhang XJ (2018) MicroRNA-328 ameliorates oxidized low-density lipoprotein-induced endothelial cells injury through targeting HMGB1 in atherosclerosis. J Cell Biochem. https://doi.org/10.1002/jcb.27469
Zhang J, Zhao T, Tian L, Li Y (2019) LncRNA OIP5-AS1 promotes the proliferation of hemangioma vascular endothelial cells via regulating miR-195-5p/NOB1 axis. Front Pharmacol 10:449. https://doi.org/10.3389/fphar.2019.00449
Li R, Teng X, Zhu H, Han T, Liu Q (2019) MiR-4500 regulates PLXNC1 and inhibits papillary thyroid cancer progression. Horm Cancer. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12672-019-00366-1
Huan CC, Wang HX, Sheng XX, Wang R, Wang X, Liao Y, Liu QF, Tong GZ, Ding C, Fan HJ, Wu JQ, Mao X (2016) Porcine epidemic diarrhea virus nucleoprotein contributes to HMGB1 transcription and release by interacting with C/EBP-beta. Oncotarget 7:75064–75080. https://doi.org/10.18632/oncotarget.11991
Wan CX, Xu M, Huang SH, Wu QQ, Yuan Y, Deng W, Tang QZ (2018) Baicalein protects against endothelial cell injury by inhibiting the TLR4/NF-κB signaling pathway. Mol Med Rep 17:3085–3091. https://doi.org/10.3892/mmr.2017.8266
Meng L, Li L, Lu S, Li K, Su Z, Wang Y, Fan X, Li X, Zhao G (2018) The protective effect of dexmedetomidine on LPS-induced acute lung injury through the HMGB1-mediated TLR4/NF-κB and PI3K/Akt/mTOR pathways. Mol Immunol 94:7–17. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.molimm.2017.12.008
Yang G, Wang Y, Zeng Y, Gao GF, Liang X, Zhou M, Wan X, Yu S, Jiang Y, Naghavi M, Vos T, Wang H, Lopez AD, Murray CJ (2013) Rapid health transition in China, 1990–2010: findings from the Global Burden of Disease Study 2010. Lancet 381:1987–2015. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0140-6736(13)61097-1
Forstermann U (2008) Oxidative stress in vascular disease: causes, defense mechanisms and potential therapies. Nat Clin Pract Cardiovasc Med 5:338–349. https://doi.org/10.1038/ncpcardio1211
Zhang M, Wang X, Yao J, Qiu Z (2019) Long non-coding RNA NEAT1 inhibits oxidative stress-induced vascular endothelial cell injury by activating the miR-181d-5p/CDKN3 axis. Artif Cells Nanomed Biotechnol 47:3129–3137. https://doi.org/10.1080/21691401.2019.1646264
Cao L, Zhang Z, Li Y, Zhao P, Chen Y (2019) LncRNA H19/miR-let-7 axis participates in the regulation of ox-LDL-induced endothelial cell injury via targeting periostin. Int Immunopharmacol 72:496–503. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.intimp.2019.04.042
Chen L, Zhou Y, Li H (2018) LncRNA, miRNA and lncRNA-miRNA interaction in viral infection. Virus Res 257:25–32. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.virusres.2018.08.018
Zheng D, Wang B, Zhu X, Hu J, Sun J, Xuan J, Ge Z (2019) LncRNA OIP5-AS1 inhibits osteoblast differentiation of valve interstitial cells via miR-137/TWIST11 axis. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 511:826–832. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bbrc.2019.02.109
Zhou Z, Chen Y, Zhang D, Wu S, Liu T, Cai G, Qin S (2019) MicroRNA-30-3p suppresses inflammatory factor-induced endothelial cell injury by targeting TCF21. Mediators Inflamm 2019:1342190. https://doi.org/10.1155/2019/1342190
Qu Y, Zhan Y, Yang S, Ren S, Qiu X, Rehamn ZU, Tan L, Sun Y, Meng C, Song C, Yu S, Ding C (2018) Newcastle disease virus infection triggers HMGB1 release to promote the inflammatory response. Virology 525:19–31. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.virol.2018.09.001
Huebener P, Gwak GY, Schwabe RF (2015) Comment on: HMGB1-dependent and -independent autophagy. Autophagy 11:1187–1188. https://doi.org/10.1080/15548627.2015.1054593
Yang YL, Liu M, Cheng X, Li WH, Zhang SS, Wang YH, Du GH (2019) Myricitrin blocks activation of NF-kappaB and MAPK signaling pathways to protect nigrostriatum neuron in LPS-stimulated mice. J Neuroimmunol 337:577049. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jneuroim.2019.577049
Jiang H, Duan J, Xu K, Zhang W (2019) Resveratrol protects against asthma-induced airway inflammation and remodeling by inhibiting the HMGB1/TLR4/NF-kappaB pathway. Exp Ther Med 18:459–466. https://doi.org/10.3892/etm.2019.7594
Michel HE, Menze ET (2019) Tetramethylpyrazine guards against cisplatin-induced nephrotoxicity in rats through inhibiting HMGB1/TLR4/NF-kappaB and activating Nrf2 and PPAR-gamma signaling pathways. Eur J Pharmacol 857:172422. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ejphar.2019.172422
Funding
None.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors have no interests to disclose.
Ethical approval
All authors have read the Journal’s position on issues involved in ethical publication, and all authors have approved the final version of the manuscript.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zheng, Z., Zhang, G., Liang, X. et al. LncRNA OIP5-AS1 facilitates ox-LDL-induced endothelial cell injury through the miR-98-5p/HMGB1 axis. Mol Cell Biochem 476, 443–455 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11010-020-03921-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11010-020-03921-5