Abstract
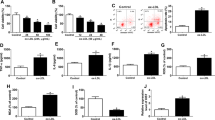
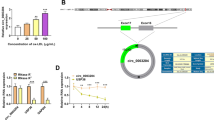
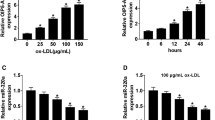
Long noncoding RNAs (lncRNAs) play pivotal roles in the pathogenesis, development, and treatment of atherosclerosis (AS). The endothelial cell injury is a feature of AS. However, the role and mechanism of lncRNA LINC00657 in oxidized low-density lipoprotein (ox-LDL)-induced endothelial cell injury remain unclear. The serum samples were collected from 32 AS patients and normal volunteers. Ox-LDL-treated human umbilical vein endothelial cells (HUVEC) were used for the experiments in vitro. The levels of LINC00657, microRNA (miR)-30c-5p and Wnt family member 7B (Wnt7b) were measured by quantitative real-time polymerase chain reaction or western blot. The expression levels of proteins in Wnt7b/β-catenin pathway or endothelial-mesenchymal transition (EndMT) were detected by western blot. The secretion of inflammatory cytokine was examined by enzyme linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA). Cell viability and apoptosis were determined by 3-(4,5-dimethylthiazol-2-yl)-2,5-diphenyl-tetrazolium bromide, flow cytometry, and western blot. The target association of miR-30c-5p and LINC00657/Wnt7b was analyzed via dual-luciferase reporter assay and RNA pull-down assay. LINC00657 expression was increased in AS serum and ox-LDL-treated HUVEC cells. LINC00657 knockdown suppressed ox-LDL-induced Wnt7b/β-catenin activation, EndMT, inflammatory response, and apoptosis in HUVEC cells. MiR-30c-5p was bound to LINC00657 and it knockdown reversed the role of LINC00657 inhibition in ox-LDL-induced HUVEC cell injury. MiR-30c-5p targeted Wnt7b to inhibit ox-LDL-induced Wnt7b/β-catenin activation, EndMT, inflammatory response, and apoptosis in HUVEC cells. Silence of LINC00657 repressed ox-LDL-induced injury via inhibiting EndMT, inflammatory response, and apoptosis in HUVEC cells by regulating miR-30c-5p/Wnt7b/β-catenin, indicating a potential target for treatment of AS.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Libby P, Buring JE, Badimon L, Hansson GK, Deanfield J, Bittencourt MS, Tokgozoglu L, Lewis EF (2019) Atherosclerosis. Nat Rev Dis Primers 5:56. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41572-019-0106-z
Weber C, Noels H (2011) Atherosclerosis: current pathogenesis and therapeutic options. Nat Med 17:1410–1422. https://doi.org/10.1038/nm.2538
Cibor D, Domagala-Rodacka R, Rodacki T, Jurczyszyn A, Mach T, Owczarek D (2016) Endothelial dysfunction in inflammatory bowel diseases: Pathogenesis, assessment and implications. World J Gastroenterol 22:1067–1077. https://doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v22.i3.1067
Tousoulis D, Oikonomou E, Economou EK, Crea F, Kaski JC (2016) Inflammatory cytokines in atherosclerosis: current therapeutic approaches. Eur Heart J 37:1723–1732. https://doi.org/10.1093/eurheartj/ehv759
Cho JG, Lee A, Chang W, Lee MS, Kim J (2018) Endothelial to mesenchymal transition represents a key link in the interaction between inflammation and endothelial dysfunction. Front Immunol 9:294. https://doi.org/10.3389/fimmu.2018.00294
Hao YM, Yuan HQ, Ren Z, Qu SL, Liu LS, Dang H, Yin K, Fu M, Jiang ZS (2019) Endothelial to mesenchymal transition in atherosclerotic vascular remodeling. Clin Chim Acta 490:34–38. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cca.2018.12.018
Kattoor AJ, Kanuri SH, Mehta JL (2019) Role of Ox-LDL and LOX-1 in atherogenesis. Curr Med Chem 26:1693–1700. https://doi.org/10.2174/0929867325666180508100950
Yin G, Yang X, Li B, Yang M, Ren M (2014) Connexin43 siRNA promotes HUVEC proliferation and inhibits apoptosis induced by ox-LDL: an involvement of ERK signaling pathway. Mol Cell Biochem 394:101–107. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11010-014-2085-4
Hu WN, Duan ZY, Wang Q, Zhou DH (2019) The suppression of ox-LDL-induced inflammatory response and apoptosis of HUVEC by lncRNA XIAT knockdown via regulating miR-30c-5p/PTEN axis. Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci 23:7628–7638. https://doi.org/10.26355/eurrev_201909_18886
Su Q, Sun Y, Ye Z, Yang H, Li L (2018) Oxidized low density lipoprotein induces endothelial-to-mesenchymal transition by stabilizing Snail in human aortic endothelial cells. Biomed Pharmacother 106:1720–1726. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biopha.2018.07.122
Uchida S, Dimmeler S (2015) Long noncoding RNAs in cardiovascular diseases. Circ Res 116:737–750. https://doi.org/10.1161/CIRCRESAHA.116.302521
Singh KK, Matkar PN, Pan Y, Quan A, Gupta V, Teoh H, Al-Omran M, Verma S (2017) Endothelial long non-coding RNAs regulated by oxidized LDL. Mol Cell Biochem 431:139–149. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11010-017-2984-2
Hu B, Cai H, Zheng R, Yang S, Zhou Z, Tu J (2017) Long non-coding RNA 657 suppresses hepatocellular carcinoma cell growth by acting as a molecular sponge of miR-106a-5p to regulate PTEN expression. Int J Biochem Cell Biol 92:34–42. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biocel.2017.09.008
Shen F, Zheng H, Zhou L, Li W, Zhang Y, Xu X (2019) LINC00657 expedites neuropathic pain development by modulating miR-136/ZEB1 axis in a rat model. J Cell Biochem 120:1000–1010. https://doi.org/10.1002/jcb.27466
Sun Y, Wang J, Pan S, Yang T, Sun X, Wang Y, Shi X, Zhao X, Guo J, Zhang X (2018) LINC00657 played oncogenic roles in esophageal squamous cell carcinoma by targeting miR-615-3p and JunB. Biomed Pharmacother 108:316–324. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biopha.2018.09.003
Chu L, Yu L, Liu J, Song S, Yang H, Han F, Liu F, Hu Y (2019) Long intergenic non-coding LINC00657 regulates tumorigenesis of glioblastoma by acting as a molecular sponge of miR-190a-3p. Aging (Albany NY) 11:1456–1470. https://doi.org/10.18632/aging.101845
Bao MH, Li GY, Huang XS, Tang L, Dong LP, Li JM (2018) Long noncoding RNA LINC00657 acting as a miR-590-3p sponge to facilitate low concentration oxidized low-density lipoprotein-induced angiogenesis. Mol Pharmacol 93:368–375. https://doi.org/10.1124/mol.117.110650
Schober A, Weber C (2016) Mechanisms of microRNAs in atherosclerosis. Annu Rev Pathol 11:583–616. https://doi.org/10.1146/annurev-pathol-012615-044135
Li P, Zhong X, Li J, Liu H, Ma X, He R, Zhao Y (2018) MicroRNA-30c-5p inhibits NLRP3 inflammasome-mediated endothelial cell pyroptosis through FOXO3 down-regulation in atherosclerosis. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 503:2833–2840. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bbrc.2018.08.049
Zou YF, Liao WT, Fu ZJ, Zhao Q, Chen YX, Zhang W (2017) MicroRNA-30c-5p ameliorates hypoxia-reoxygenation-induced tubular epithelial cell injury via HIF1alpha stabilization by targeting SOCS3. Oncotarget 8:92801–92814. https://doi.org/10.18632/oncotarget.21582
Vilahur G (2017) Relevance of low miR-30c-5p levels in atherogenesis: a promising predictive biomarker and potential therapeutic target. Cardiovasc Res 113:1536–1537. https://doi.org/10.1093/cvr/cvx194
Vallee A, Vallee JN, Lecarpentier Y (2019) Metabolic reprogramming in atherosclerosis: opposed interplay between the canonical WNT/beta-catenin pathway and PPARgamma. J Mol Cell Cardiol 133:36–46. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.yjmcc.2019.05.024
Livak KJ, Schmittgen TD (2001) Analysis of relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and the 2(-Delta Delta C(T)) method. Methods 25:402–408. https://doi.org/10.1006/meth.2001.1262
Viola J, Soehnlein O (2015) Atherosclerosis—a matter of unresolved inflammation. Semin Immunol 27:184–193. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.smim.2015.03.013
Gimbrone MA Jr, Garcia-Cardena G (2016) Endothelial cell dysfunction and the pathobiology of atherosclerosis. Circ Res 118:620–636. https://doi.org/10.1161/CIRCRESAHA.115.306301
Scheller J, Garbers C, Rose-John S (2014) Interleukin-6: from basic biology to selective blockade of pro-inflammatory activities. Semin Immunol 26:2–12. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.smim.2013.11.002
Khan R, Rheaume E, Tardif JC (2018) Examining the role of and treatment directed at IL-1beta in atherosclerosis. Curr Atheroscler Rep 20:53. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11883-018-0754-6
Kleinbongard P, Heusch G, Schulz R (2010) TNFalpha in atherosclerosis, myocardial ischemia/reperfusion and heart failure. Pharmacol Ther 127:295–314. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.pharmthera.2010.05.002
Chen PY, Qin L, Baeyens N, Li G, Afolabi T, Budatha M, Tellides G, Schwartz MA, Simons M (2015) Endothelial-to-mesenchymal transition drives atherosclerosis progression. J Clin Invest 125:4514–4528. https://doi.org/10.1172/JCI82719
Li H, Zhao Q, Chang L, Wei C, Bei H, Yin Y, Chen M, Wang H, Liang J, Wu Y (2019) LncRNA MALAT1 modulates ox-LDL induced EndMT through the Wnt/beta-catenin signaling pathway. Lipids Health Dis 18:62. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12944-019-1006-7
Li M, Duan L, Li Y, Liu B (2019) Long noncoding RNA/circular noncoding RNA-miRNA-mRNA axes in cardiovascular diseases. Life Sci 233:116440. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.lfs.2019.04.066
Yu Z, Jiang Y, Sun C (2019) Glucocorticoids inhibits the repair of airway epithelial cells via the activation of wnt pathway. Respir Physiol Neurobiol 271:103283. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.resp.2019.103283
Funding
None.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of Interests
The authors have no interests to disclose.
Ethical approval
All authors have read the Journal’s position on issues involved in ethical publication, and all authors have approved the final version of the manuscript.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wu, H., Liu, T. & Hou, H. Knockdown of LINC00657 inhibits ox-LDL-induced endothelial cell injury by regulating miR-30c-5p/Wnt7b/β-catenin. Mol Cell Biochem 472, 145–155 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11010-020-03793-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11010-020-03793-9