Abstract
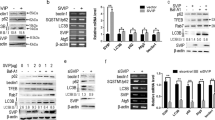
Circadian rhythms help organisms adapt to changes of external environment by regulating energy metabolism and remaining the balance of homeostasis. Numerous researches have proved that the physiological function of liver was precisely controlled by circadian rhythms. Clock, one of core circadian genes, has been demonstrated to regulate the oxidative phosphorylation process of mitochondrial, which provides energy for living cells and acts as one of the hub for apoptosis. However, whether Clock gene regulates mitochondrial apoptosis pathways in liver cells remains less explored. In the present study, we used lentiviral vector to establish a stable AML12 cell lines which were capable of expressing specific shRNA to interfere the expression of Clock gene and investigated the effect of Clock on mitochondrial apoptosis pathways. Herein, we found that the interference of Clock gene could significantly suppress mitochondrial apoptosis pathways by stabilizing mitochondrial membrane potential and inhibiting mitochondria out membrane permeablization, which might be a result of lower expression of BAD and BIM proteins. Moreover, the interference of Clock gene could downregulate the expression of mitochondrial apoptosis factors, i.e. AIF, CYCS, APAF-1 and SMAC, which will suppress the formation of apoptosome and the process of DNA degradation to further inhibit apoptosis process. This work provides an insight on the important role of Clock gene participating in mitochondrial apoptosis pathways of hepatocytes and unveils a probable pathogenesis of how circadian rhythm regulates liver diseases.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Loudon AS (2012) Circadian biology: a 2.5 billion year old clock. Curr Biol 22(14):570–571. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cub.2012.06.023
Takahashi JS, Hong HK, Ko CH, McDearmon EL (2008) The genetics of mammalian circadian order and disorder: implications for physiology and disease. Nat Rev Genet 9(10):764–775. https://doi.org/10.1038/nrg2430
Preussner M, Heyd F (2016) Post-transcriptional control of the mammalian circadian clock: implications for health and disease. Pflug Arch 468(6):983–991. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00424-016-1820-y
Wang J, Symul L, Yeung J, Gobet C, Sobel J, Luck S, Westermark PO, Molina N, Naef F (2018) Circadian clock-dependent and -independent posttranscriptional regulation underlies temporal mRNA accumulation in mouse liver. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 115(8):E1916–E1925. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.1715225115
Jacobi D, Liu S, Burkewitz K, Kory N, Knudsen NH, Alexander RK, Unluturk U, Li X, Kong X, Hyde AL, Gangl MR, Mair WB, Lee CH (2015) Hepatic Bmal1 regulates rhythmic mitochondrial dynamics and promotes metabolic fitness. Cell Metab 22(4):709–720. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cmet.2015.08.006
Peek CB, Affinati AH, Ramsey KM, Kuo HY, Yu W, Sena LA, Ilkayeva O, Marcheva B, Kobayashi Y, Omura C, Levine DC, Bacsik DJ, Gius D, Newgard CB, Goetzman E, Chandel NS, Denu JM, Mrksich M, Bass J (2013) Circadian clock NAD+ cycle drives mitochondrial oxidative metabolism in mice. Science 342(6158):1243417. https://doi.org/10.1126/science.1243417
Ferrell JM, Chiang JY (2015) Circadian rhythms in liver metabolism and disease. Acta Pharm Sin B 5(2):113–122. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apsb.2015.01.003
Li XM, Jing L, Lin F, Huang H, Chen ZZ, Chen Y, Wang LN, Lin X, Guo TL, Yang J, Ruan JM, Lin KY, Li CJ, You ZB, He LL, Chen JK, Li ZZ, Zhu PL, Chen G (2018) Diurnal rhythm of follicle-stimulating hormone is associated with nonalcoholic fatty liver disease in a Chinese elderly population. Eur J Obstet Gyn R B 222:166–170. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ejogrb.2018.01.034
Mindikoglu AL, Opekun AR, Gagan SK, Devaraj S (2017) Impact of time-restricted feeding and dawn-to-sunset fasting on circadian rhythm, obesity, metabolic syndrome, and nonalcoholic fatty liver disease. Gastroenterol Res Pract 2017:3932491. https://doi.org/10.1155/2017/3932491
Tahara Y, Shibata S (2016) Circadian rhythms of liver physiology and disease: experimental and clinical evidence. Nat Rev Gastroenterol Hepatol 13(4):217–226. https://doi.org/10.1038/nrgastro.2016.8
Lee JH, Sancar A (2011) Regulation of apoptosis by the circadian clock through NF-kappa B signaling. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 108(29):12036–12041. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.1108125108
Yuan P, Li J, Zhou F, Huang Q, Zhang J, Guo X, Lyu Z, Zhang H, Xing J (2017) NPAS2 promotes cell survival of hepatocellular carcinoma by transactivating CDC25A. Cell Death Dis 8(3):e2704. https://doi.org/10.1038/cddis.2017.131
Matsunaga N, Kohno Y, Kakimoto K, Hayashi A, Koyanagi S, Ohdo S (2011) Influence of CLOCK on cytotoxicity induced by diethylnitrosamine in mouse primary hepatocytes. Toxicology 280(3):144–151. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tox.2010.12.005
Yoshitane H, Ozaki H, Terajima H, Du NH, Suzuki Y, Fujimori T, Kosaka N, Shimba S, Sugano S, Takagi T, Iwasaki W, Fukada Y (2014) CLOCK-controlled polyphonic regulation of circadian rhythms through canonical and noncanonical E-boxes. Mol Cell Biol 34(10):1776–1787. https://doi.org/10.1128/MCB.01465-13
Balsalobre A, Damiola F, Schibler U (1998) A serum shock induces circadian gene expression in mammalian tissue culture cells. Cell 93(6):929–937. https://doi.org/10.1016/s0092-8674(00)81199-x
Andersen AZ, Poulsen AK, Brasen JC, Olsen LF (2007) On-line measurements of oscillating mitochondrial membrane potential in glucose-fermenting Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Yeast 24(9):731–739. https://doi.org/10.1002/yea.1508
Jiang X, Jiang H, Shen Z, Wang X (2014) Activation of mitochondrial protease OMA1 by Bax and Bak promotes cytochrome c release during apoptosis. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 111(41):14782–14787. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.1417253111
Head B, Griparic L, Amiri M, Gandre-Babbe S, van der Bliek AM (2009) Inducible proteolytic inactivation of OPA1 mediated by the OMA1 protease in mammalian cells. J Cell Biol 187(7):959–966. https://doi.org/10.1083/jcb.200906083
Martinou JC, Youle RJ (2011) Mitochondria in apoptosis: Bcl-2 family members and mitochondrial dynamics. Dev Cell 21(1):92–101. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.devcel.2011.06.017
Chipuk JE, Moldoveanu T, Llambi F, Parsons MJ, Green DR (2010) The BCL-2 family reunion. Mol Cell 37(3):299–310. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.molcel.2010.01.025
Moldoveanu T, Follis AV, Kriwacki RW, Green DR (2014) Many players in BCL-2 family affairs. Trends Biochem Sci 39(3):101–111. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tibs.2013.12.006
Scrima R, Cela O, Merla G, Augello B, Rubino R, Quarato G, Fugetto S, Menga M, Fuhr L, Relogio A, Piccoli C, Mazzoccoli G, Capitanio N (2016) Clock-genes and mitochondrial respiratory activity: Evidence of a reciprocal interplay. Biochem Biophys Acta 8:1344–1351. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bbabio.2016.03.035
Cela O, Scrima R, Pazienza V, Merla G, Benegiamo G, Augello B, Fugetto S, Menga M, Rubino R, Fuhr L, Relogio A, Piccoli C, Mazzoccoli G, Capitanio N (2016) Clock genes-dependent acetylation of complex I sets rhythmic activity of mitochondrial OxPhos. Biochem Biophys Acta 4:596–606. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bbamcr.2015.12.018
Llambi F, Moldoveanu T, Tait SW, Bouchier-Hayes L, Temirov J, McCormick LL, Dillon CP, Green DR (2011) A unified model of mammalian BCL-2 protein family interactions at the mitochondria. Mol Cell 44(4):517–531. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.molcel.2011.10.001
Kalkavan H, Green DR (2018) MOMP, cell suicide as a BCL-2 family business. Cell Death Differ 25(1):46–55. https://doi.org/10.1038/cdd.2017.179
Szczesny RJ, Obriot H, Paczkowska A, Jedrzejczak R, Dmochowska A, Bartnik E, Formstecher P, Polakowska R, Stepien PP (2007) Down-regulation of human RNA/DNA helicase SUV3 induces apoptosis by a caspase- and AIF-dependent pathway. Biol Cell 99(6):323–332. https://doi.org/10.1042/BC20060108
Zhang X, Chen J, Graham SH, Du L, Kochanek PM, Draviam R, Guo F, Nathaniel PD, Szabo C, Watkins SC, Clark RS (2002) Intranuclear localization of apoptosis-inducing factor (AIF) and large scale DNA fragmentation after traumatic brain injury in rats and in neuronal cultures exposed to peroxynitrite. J Neurochem 82(1):181–191
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by Open fund of Key Laboratory of Herbal-Tebitan Drug Screening and Deep Processing of Gansu Province and National Basic Research Program of China (No. 2011CB711000).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Conception and design: Shuhong Yang, Yanyou Liu, Shuting Cheng; Data collection: Shuhong Yang, Yimei Guo, Fang Qi, Xiaoxue Li,; Data analysis and interpretation: Shuhong Yang, Rong Liu, Hang Yu; Drafting the article: Shuhong Yang; Critical revision of the article: Shuting Cheng, Zhengrong Wang.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Yang, S., Liu, Y., Guo, Y. et al. Circadian gene Clock participates in mitochondrial apoptosis pathways by regulating mitochondrial membrane potential, mitochondria out membrane permeablization and apoptosis factors in AML12 hepatocytes. Mol Cell Biochem 467, 65–75 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11010-020-03701-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11010-020-03701-1