Abstract
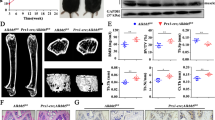
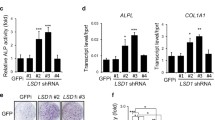
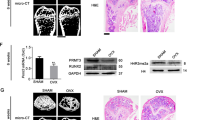
As a m6A methylation modifier, METTL3 is functionally involved in various biological processes. Nevertheless, the role of METTL3 in osteogenesis is not determined up to date. In the current study, METTL3 is identified as a crucial regulator in the progression of osteogenic differentiation. Loss of METTL3 significantly augments calcium deposition and enhances alkaline phosphatase activity of mesenchymal stem cells, uncovering an inhibitory role of METTL3 in osteogenesis. More importantly, the underlying molecular basis by which METTL3 regulates osteogenesis is illustrated. We find that METTL3 positively regulates expression of MYD88, a critical upstream regulator of NF-κB signaling, by facilitating m6A methylation modification to MYD88-RNA, subsequently inducing the activation of NF-κB which is widely regarded as a repressor of osteogenesis and therefore suppressing osteogenic progression. Moreover, the METTL3-mediated m6A methylation is found to be dynamically reversed by the demethylase ALKBH5. In summary, this study highlights the functional importance of METTL3 in osteogenic differentiation and METTL3 may serve as a promising molecular target in regenerative medicine, as well as in the field of bone tissue engineering.





Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
All data generated or analyzed during this study are shown in this article.
Abbreviations
- MSCs:
-
Mesenchymal stem cells
- m6A:
-
N6-methyladenosine
- MenSCs:
-
Menstrual blood-derived mesenchymal stem cells
- ALP:
-
Alkaline phosphatase
References
Barba M, Di Taranto G, Lattanzi W (2017) Adipose-derived stem cell therapies for bone regeneration. Expert Opin Biol Ther 17:677–689. https://doi.org/10.1080/14712598.2017.1315403
Chen M, Xu Y, Zhang T, Ma Y, Liu J, Yuan B, Chen X, Zhou P, Zhao X, Pang F, Liang W (2019) Mesenchymal stem cell sheets: a new cell-based strategy for bone repair and regeneration. Biotechnol Lett 41:305–318. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10529-019-02649-7
Fujii Y, Kawase-Koga Y, Hojo H, Yano F, Sato M, Chung UI, Ohba S, Chikazu D (2018) Bone regeneration by human dental pulp stem cells using a helioxanthin derivative and cell-sheet technology. Stem Cell Res Ther 9:24. https://doi.org/10.1186/s13287-018-0783-7
Shah AR, Cornejo A, Guda T, Sahar DE, Stephenson SM, Chang S, Krishnegowda NK, Sharma R, Wang HT (2014) Differentiated adipose-derived stem cell cocultures for bone regeneration in polymer scaffolds in vivo. J Craniofac Surg 25:1504–1509. https://doi.org/10.1097/SCS.0000000000000755
Zigdon H, Levin L (2012) Stem cell therapy for bone regeneration: present and future strategies. Alpha Omegan 105:35–38
Lin TH, Gibon E, Loi F, Pajarinen J, Cordova LA, Nabeshima A, Lu L, Yao Z, Goodman SB (2017) Decreased osteogenesis in mesenchymal stem cells derived from the aged mouse is associated with enhanced NF-kappaB activity. J Orthop Res 35:281–288. https://doi.org/10.1002/jor.23270
Liu C, Zhang H, Tang X, Feng R, Yao G, Chen W, Li W, Liang J, Feng X, Sun L (2018) Mesenchymal stem cells promote the osteogenesis in collagen-induced arthritic mice through the inhibition of TNF-alpha. Stem Cells Int 2018:4069032. https://doi.org/10.1155/2018/4069032
Wang N, Zhou Z, Wu T, Liu W, Yin P, Pan C, Yu X (2016) TNF-alpha-induced NF-kappaB activation upregulates microRNA-150-3p and inhibits osteogenesis of mesenchymal stem cells by targeting beta-catenin. Open Biol. https://doi.org/10.1098/rsob.150258
Batista PJ, Molinie B, Wang J, Qu K, Zhang J, Li L, Bouley DM, Lujan E, Haddad B, Daneshvar K, Carter AC, Flynn RA, Zhou C, Lim KS, Dedon P, Wernig M, Mullen AC, Xing Y, Giallourakis CC, Chang HY (2014) m(6)A RNA modification controls cell fate transition in mammalian embryonic stem cells. Cell Stem Cell 15:707–719. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.stem.2014.09.019
Geula S, Moshitch-Moshkovitz S, Dominissini D, Mansour AA, Kol N, Salmon-Divon M, Hershkovitz V, Peer E, Mor N, Manor YS, Ben-Haim MS, Eyal E, Yunger S, Pinto Y, Jaitin DA, Viukov S, Rais Y, Krupalnik V, Chomsky E, Zerbib M, Maza I, Rechavi Y, Massarwa R, Hanna S, Amit I, Levanon EY, Amariglio N, Stern-Ginossar N, Novershtern N, Rechavi G, Hanna JH (2015) Stem cells. m6A mRNA methylation facilitates resolution of naive pluripotency toward differentiation. Science 347:1002–1006. https://doi.org/10.1126/science.1261417
Lin S, Choe J, Du P, Triboulet R, Gregory RI (2016) The m(6)A methyltransferase METTL3 promotes translation in human cancer cells. Mol Cell 62:335–345. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.molcel.2016.03.021
Zhang C, Chen Y, Sun B, Wang L, Yang Y, Ma D, Lv J, Heng J, Ding Y, Xue Y, Lu X, Xiao W, Yang YG, Liu F (2017) m(6)A modulates haematopoietic stem and progenitor cell specification. Nature 549:273–276. https://doi.org/10.1038/nature23883
Cheng M, Sheng L, Gao Q, Xiong Q, Zhang H, Wu M, Liang Y, Zhu F, Zhang Y, Zhang X, Yuan Q, Li Y (2019) The m(6)A methyltransferase METTL3 promotes bladder cancer progression via AFF4/NF-kappaB/MYC signaling network. Oncogene. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41388-019-0683-z
Maity A, Das B (2016) N6-methyladenosine modification in mRNA: machinery, function and implications for health and diseases. FEBS J 283:1607–1630. https://doi.org/10.1111/febs.13614
Vu LP, Pickering BF, Cheng Y, Zaccara S, Nguyen D, Minuesa G, Chou T, Chow A, Saletore Y, MacKay M, Schulman J, Famulare C, Patel M, Klimek VM, Garrett-Bakelman FE, Melnick A, Carroll M, Mason CE, Jaffrey SR, Kharas MG (2017) The N(6)-methyladenosine (m(6)A)-forming enzyme METTL3 controls myeloid differentiation of normal hematopoietic and leukemia cells. Nat Med 23:1369–1376. https://doi.org/10.1038/nm.4416
Yue Y, Liu J, He C (2015) RNA N6-methyladenosine methylation in post-transcriptional gene expression regulation. Genes Dev 29:1343–1355. https://doi.org/10.1101/gad.262766.115
Lin Z, Hsu PJ, Xing X, Fang J, Lu Z, Zou Q, Zhang KJ, Zhang X, Zhou Y, Zhang T, Zhang Y, Song W, Jia G, Yang X, He C, Tong MH (2017) Mettl3-/Mettl14-mediated mRNA N(6)-methyladenosine modulates murine spermatogenesis. Cell Res 27:1216–1230. https://doi.org/10.1038/cr.2017.117
Liu J, Yue Y, Han D, Wang X, Fu Y, Zhang L, Jia G, Yu M, Lu Z, Deng X, Dai Q, Chen W, He C (2014) A METTL3-METTL14 complex mediates mammalian nuclear RNA N6-adenosine methylation. Nat Chem Biol 10:93–95. https://doi.org/10.1038/nchembio.1432
Yao QJ, Sang L, Lin M, Yin X, Dong W, Gong Y, Zhou BO (2018) Mettl3-Mettl14 methyltransferase complex regulates the quiescence of adult hematopoietic stem cells. Cell Res 28:952–954. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41422-018-0062-2
Kobayashi M, Ohsugi M, Sasako T, Awazawa M, Umehara T, Iwane A, Kobayashi N, Okazaki Y, Kubota N, Suzuki R, Waki H, Horiuchi K, Hamakubo T, Kodama T, Aoe S, Tobe K, Kadowaki T, Ueki K (2018) The RNA methyltransferase complex of WTAP, METTL3, and METTL14 regulates mitotic clonal expansion in adipogenesis. Mol Cell Biol. https://doi.org/10.1128/MCB.00116-18
Selberg S, Blokhina D, Aatonen M, Koivisto P, Siltanen A, Mervaala E, Kankuri E, Karelson M (2019) Discovery of small molecules that activate RNA methylation through cooperative binding to the METTL3-14-WTAP complex active site. Cell Rep 26(3762–3771):e5. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.celrep.2019.02.100
Piette ER, Moore JH (2018) Identification of epistatic interactions between the human RNA demethylases FTO and ALKBH5 with gene set enrichment analysis informed by differential methylation. BMC Proc 12:59. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12919-018-0122-0
Shen F, Huang W, Huang JT, Xiong J, Yang Y, Wu K, Jia GF, Chen J, Feng YQ, Yuan BF, Liu SM (2015) Decreased N(6)-methyladenosine in peripheral blood RNA from diabetic patients is associated with FTO expression rather than ALKBH5. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 100:E148–E154. https://doi.org/10.1210/jc.2014-1893
Song H, Feng X, Zhang H, Luo Y, Huang J, Lin M, Jin J, Ding X, Wu S, Huang H, Yu T, Zhang M, Hong H, Yao S, Zhao Y, Zhang Z (2019) METTL3 and ALKBH5 oppositely regulate m(6)A modification of TFEB mRNA, which dictates the fate of hypoxia/reoxygenation-treated cardiomyocytes. Autophagy. https://doi.org/10.1080/15548627.2019.1586246
Zhu X, Yu J, Du J, Zhong G, Qiao L, Lin J (2019) LncRNA HOXA-AS2 positively regulates osteogenesis of mesenchymal stem cells through inactivating NF-kappaB signalling. J Cell Mol Med 23:1325–1332. https://doi.org/10.1111/jcmm.14034
Zou Z, Huang B, Wu X, Zhang H, Qi J, Bradner J, Nair S, Chen LF (2014) Brd4 maintains constitutively active NF-kappaB in cancer cells by binding to acetylated RelA. Oncogene 33:2395–2404. https://doi.org/10.1038/onc.2013.179
Wang H, Hu X, Huang M, Liu J, Gu Y, Ma L, Zhou Q, Cao X (2019) Mettl3-mediated mRNA m(6)A methylation promotes dendritic cell activation. Nat Commun 10:1898. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41467-019-09903-6
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by grants from the National Natural Science Foundation of China (31502045) and Xinxiang Medical University Foundation (300-505307).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
JL, MC, and XZ are responsible for designing the project. JY and LS performed most of the experiments. YL contributed to data analysis. XZ wrote the draft of this manuscript. All authors take part in discussions.
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that there is no conflict of interest.
Ethical approval
The MenSCs used in this study were obtained with the informed consent of the donors. All experiments in this manuscript meet the “Declaration of Helsinki” and were approved by the Ethics Committee of Xinxiang Medical University.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Yu, J., Shen, L., Liu, Y. et al. The m6A methyltransferase METTL3 cooperates with demethylase ALKBH5 to regulate osteogenic differentiation through NF-κB signaling. Mol Cell Biochem 463, 203–210 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11010-019-03641-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11010-019-03641-5