Abstract
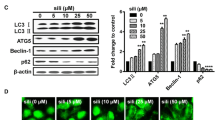
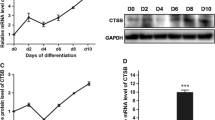
Migration of fibroblast-like preadipocytes is important for the development of adipose tissue, whereas excessive migration is often responsible for impaired adipose tissue related with obesity and fibrotic diseases. Type I collagen (collagen I) is the most abundant component of extracellular matrix and has been shown to regulate fibroblast migration in vitro, but its role in adipose tissue is not known. Silibinin is a bioactive natural flavonoid with antioxidant and antimetastasis activities. In this study, we found that type I collagen coating promoted the proliferation and migration of murine 3T3-L1 preadipocytes in a dose-dependent manner, implying that collagen I could be an extracellular signal. Regarding the mechanisms of collagen I-stimulated 3T3-L1 migration, we found that NF-κB p65 is activated, including the increased nuclear translocation of NF-κB p65 as well as the upregulation of NF-κB p65 phosphorylation and acetylation, accompanied by the increased expressions of proinflammatory factors and the generation of reactive oxygen species (ROS). Reduction of collagen I-enhanced migration of cells by treatment with silibinin was associated with suppression of NF-κB p65 activity and ROS generation, and negatively correlated with the increasing sirt1 expression. Taken together, the enhanced migration of 3T3-L1 cells induced on collagen I-coated dish is mediated by the activation of NF-κB p65 function and ROS generation that can be alleviated with silibinin by upregulation of sirt1, leading to the repression of NF-κB p65 function and ROS generation.



















Similar content being viewed by others
References
Hausman GJ (2012) Meat science and muscle biology symposium: the influence of extracellular matrix on intramuscular and extramuscular adipogenesis. J Anim Sci 90:942–949. doi:10.2527/jas.2011-4616
Sul HS, Smas C, Mei B, Zhou L (2000) Function of pref-1 as an inhibitor of adipocyte differentiation. Int J Obes Relat Metab Disord 24(Suppl 4):S15–S19
Mariman EC, Wang P (2010) Adipocyte extracellular matrix composition, dynamics and role in obesity. Cell Mol Life Sci 67:1277–1292. doi:10.1007/s00018-010-0263-4
Chen SZ, Ning LF, Xu X, Jiang WY, Xing C, Jia WP, Chen XL, Tang QQ, Huang HY (2016) The miR-181d-regulated metalloproteinase Adamts1 enzymatically impairs adipogenesis via ECM remodeling. Cell Death Differ 23:1778–1791. doi:10.1038/cdd.2016.66
Olaso E, Labrador JP, Wang L, Ikeda K, Eng FJ, Klein R, Lovett DH, Lin HC, Friedman SL (2002) Discoidin domain receptor 2 regulates fibroblast proliferation and migration through the extracellular matrix in association with transcriptional activation of matrix metalloproteinase-2. J Biol Chem 277:3606–3613. doi:10.1074/jbc.M107571200
Li W, Fan J, Chen M, Guan S, Sawcer D, Bokoch GM, Woodley DT (2004) Mechanism of human dermal fibroblast migration driven by type I collagen and platelet-derived growth factor-BB. Mol Biol Cell 15:294–309. doi:10.1091/mbc.E03-05-0352
Torii T, Miyamoto Y, Sanbe A, Nishimura K, Yamauchi J, Tanoue A (2010) Cytohesin-2/ARNO, through its interaction with focal adhesion adaptor protein paxillin, regulates preadipocyte migration via the downstream activation of Arf6. J Biol Chem 285:24270–24281. doi:10.1074/jbc.M110.125658
Crandall DL, Busler DE, McHendry-Rinde B, Groeling TM, Kral JG (2000) Autocrine regulation of human preadipocyte migration by plasminogen activator inhibitor-1. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 85:2609–2614. doi:10.1210/jcem.85.7.6678
Kim JH, Park SH, Nam SW, Kwon HJ, Kim BW, Kim WJ, Choi YH (2011) Curcumin stimulates proliferation, stemness acting signals and migration of 3T3-L1 preadipocytes. Int J Mol Med 28:429–435. doi:10.3892/ijmm.2011.680
Pachon-Pena G, Serena C, Ejarque M, Petriz J, Duran X, Oliva-Olivera W, Simo R, Tinahones FJ, Fernandez-Veledo S, Vendrell J (2016) Obesity determines the immunophenotypic profile and functional characteristics of human mesenchymal stem cells from adipose tissue. Stem Cells Transl Med 5:464–475. doi:10.5966/sctm.2015-0161
Keophiphath M, Achard V, Henegar C, Rouault C, Clement K, Lacasa D (2009) Macrophage-secreted factors promote a profibrotic phenotype in human preadipocytes. Mol Endocrinol 23:11–24. doi:10.1210/me.2008-0183
Muir LA, Neeley CK, Meyer KA, Baker NA, Brosius AM, Washabaugh AR, Varban OA, Finks JF, Zamarron BF, Flesher CG, Chang JS, DelProposto JB, Geletka L, Martinez-Santibanez G, Kaciroti N, Lumeng CN, O’Rourke RW (2016) Adipose tissue fibrosis, hypertrophy, and hyperplasia: correlations with diabetes in human obesity. Obesity (Silver Spring) 24:597–605. doi:10.1002/oby.21377
Buechler C, Krautbauer S, Eisinger K (2015) Adipose tissue fibrosis. World J. Diabetes 6:548–553. doi:10.4239/wjd.v6.i4.548
Chiang RS, Borovikova AA, King K, Banyard DA, Lalezari S, Toranto JD, Paydar KZ, Wirth GA, Evans GR, Widgerow AD (2016) Current concepts related to hypertrophic scarring in burn injuries. Wound Repair Regen. doi:10.1111/wrr.12432
Davies JC, Tamaddon-Jahromi S, Jannoo R, Kanamarlapudi V (2014) Cytohesin 2/ARF6 regulates preadipocyte migration through the activation of ERK1/2. Biochem Pharmacol 92:651–660. doi:10.1016/j.bcp.2014.09.023
Wang Q, Zou L, Liu W, Hao W, Tashiro S, Onodera S, Ikejima T (2011) Inhibiting NF-kappaB activation and ROS production are involved in the mechanism of silibinin’s protection against d-galactose-induced senescence. Pharmacol Biochem Behav 98:140–149. doi:10.1016/j.pbb.2010.12.006
Liu W, Li Y, Zheng X, Zhang K, Du Z (2015) Potent inhibitory effect of silibinin from milk thistle on skin inflammation stimuli by 12-O-tetradecanoylphorbol-13-acetate. Food Funct 6:3712–3719. doi:10.1039/c5fo00899a
Tewari-Singh N, Jain AK, Inturi S, Agarwal C, White CW, Agarwal R (2012) Silibinin attenuates sulfur mustard analog-induced skin injury by targeting multiple pathways connecting oxidative stress and inflammation. PLoS ONE 7:e46149. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0046149
Suh HJ, Cho SY, Kim EY, Choi HS (2015) Blockade of lipid accumulation by silibinin in adipocytes and zebrafish. Chem Biol Interact 227:53–62. doi:10.1016/j.cbi.2014.12.027
Barbagallo I, Vanella L, Cambria MT, Tibullo D, Godos J, Guarnaccia L, Zappala A, Galvano F, Li Volti G (2015) Silibinin regulates lipid metabolism and differentiation in functional human adipocytes. Front Pharmacol 6:309. doi:10.3389/fphar.2015.00309
Ka SO, Kim KA, Kwon KB, Park JW, Park BH (2009) Silibinin attenuates adipogenesis in 3T3-L1 preadipocytes through a potential upregulation of the insig pathway. Int J Mol Med 23:633–637
Yoshizaki T, Milne JC, Imamura T, Schenk S, Sonoda N, Babendure JL, Lu JC, Smith JJ, Jirousek MR, Olefsky JM (2009) SIRT1 exerts anti-inflammatory effects and improves insulin sensitivity in adipocytes. Mol Cell Biol 29:1363–1374. doi:10.1128/MCB.00705-08
Lin QQ, Yan CF, Lin R, Zhang JY, Wang WR, Yang LN, Zhang KF (2012) SIRT1 regulates TNF-alpha-induced expression of CD40 in 3T3-L1 adipocytes via NF-kappaB pathway. Cytokine 60:447–455. doi:10.1016/j.cyto.2012.05.025
Kong X, Guan J, Li J, Wei J, Wang R (2016) P66Shc-SIRT1 regulation of oxidative stress protects against cardio-cerebral vascular disease. Mol Neurobiol. doi:10.1007/s12035-016-0073-2
Karin M, Ben-Neriah Y (2000) Phosphorylation meets ubiquitination: the control of NF-[kappa]B activity. Annu Rev Immunol 18:621–663. doi:10.1146/annurev.immunol.18.1.621
Chiu S, Bharat A (2016) Role of monocytes and macrophages in regulating immune response following lung transplantation. Curr Opin Organ Transplant. doi:10.1097/MOT.0000000000000313
Fujisaki H, Hattori S (2002) Keratinocyte apoptosis on type I collagen gel caused by lack of laminin 5/10/11 deposition and Akt signaling. Exp Cell Res 280:255–269
Reing JE, Zhang L, Myers-Irvin J, Cordero KE, Freytes DO, Heber-Katz E, Bedelbaeva K, McIntosh D, Dewilde A, Braunhut SJ, Badylak SF (2009) Degradation products of extracellular matrix affect cell migration and proliferation. Tissue Eng Part A 15:605–614. doi:10.1089/ten.tea.2007.0425
Chang M (2016) Restructuring of the extracellular matrix in diabetic wounds and healing: a perspective. Pharmacol Res 107:243–248. doi:10.1016/j.phrs.2016.03.008
Chao J, Dai X, Pena T, Doyle DA, Guenther TM, Carlson MA (2015) MCPIP1 regulates fibroblast migration in 3-D collagen matrices downstream of MAP kinases and NF-kappaB. J Invest Dermatol 135:2944–2954. doi:10.1038/jid.2015.334
Wang W, Lin Q, Lin R, Zhang J, Ren F, Ji M, Li Y (2013) PPARalpha agonist fenofibrate attenuates TNF-alpha-induced CD40 expression in 3T3-L1 adipocytes via the SIRT1-dependent signaling pathway. Exp Cell Res 319:1523–1533. doi:10.1016/j.yexcr.2013.04.007
Koike K, Kondo Y, Sekiya M, Sato Y, Tobino K, Iwakami SI, Goto S, Takahashi K, Maruyama N, Seyama K, Ishigami A (2010) Complete lack of vitamin C intake generates pulmonary emphysema in senescence marker protein-30 knockout mice. Am J Physiol Lung Cell Mol Physiol 298:L784–L792. doi:10.1152/ajplung.00256.2009
Jiang Y, Wang X, Li Y, Mu S, Zhou S, Liu Y, Zhang B (2016) GGsTOP increases migration of human periodontal ligament cells in vitro via reactive oxygen species pathway. Mol Med Rep 13:3813–3820. doi:10.3892/mmr.2016.5038
Stupack DG, Cheresh DA (2002) Get a ligand, get a life: integrins, signaling and cell survival. J Cell Sci 115:3729–3738
Wang HJ, He WQ, Chen L, Liu WW, Xu Q, Xia MY, Hayashi T, Fujisaki H, Hattori S, Tashiro S, Onodera S, Ikejima T (2015) Type I collagen gel protects murine fibrosarcoma L929 cells from TNFalpha-induced cell death. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 457:693–699. doi:10.1016/j.bbrc.2015.01.051
Nishiyama T, Akutsu N, Horii I, Nakayama Y, Ozawa T, Hayashi T (1991) Response to growth factors of human dermal fibroblasts in a quiescent state owing to cell-matrix contact inhibition. Matrix 11:71–75
Anguiano M, Castilla C, Maska M, Ederra C, Pelaez R, Morales X, Munoz-Arrieta G, Mujika M, Kozubek M, Munoz-Barrutia A, Rouzaut A, Arana S, Garcia-Aznar JM, Ortiz-de-Solorzano C (2017) Characterization of three-dimensional cancer cell migration in mixed collagen-Matrigel scaffolds using microfluidics and image analysis. PLoS ONE 12:e0171417. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0171417
Wang HJ, Li MQ, Liu WW, Hayashi T, Fujisaki H, Hattori S, Tashiro SI, Onodera S and Ikejima T (2016) Collagen gel protects L929 cells from TNFalpha-induced death by activating NF-kappaB. Connect Tissue Res 1–8. doi:10.1080/03008207.2016.1248287
Xu J, Zutter MM, Santoro SA, Clark RA (1998) A three-dimensional collagen lattice activates NF-kappaB in human fibroblasts: role in integrin alpha2 gene expression and tissue remodeling. J Cell Biol 140:709–719
Wang HZ, Wang HH, Huang SS, Zhao H, Cao YG, Wang GZ, Wang D, Wang ZG, Liu YH (2014) Inhibitory effect of baicalin on collagen-induced arthritis in rats through the nuclear factor-kappaB pathway. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 350:435–443. doi:10.1124/jpet.114.215145
Millerot-Serrurot E, Guilbert M, Fourre N, Witkowski W, Said G, Van Gulick L, Terryn C, Zahm JM, Garnotel R, Jeannesson P (2010) 3D collagen type I matrix inhibits the antimigratory effect of doxorubicin. Cancer Cell Int 10:26. doi:10.1186/1475-2867-10-26
Xie P, Kondeti VK, Lin S, Haruna Y, Raparia K, Kanwar YS (2011) Role of extracellular matrix renal tubulo-interstitial nephritis antigen (TINag) in cell survival utilizing integrin (alpha)vbeta3/focal adhesion kinase (FAK)/phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase (PI3 K)/protein kinase B-serine/threonine kinase (AKT) signaling pathway. J Biol Chem 286:34131–34146. doi:10.1074/jbc.M111.241778
Tian B, Lessan K, Kahm J, Kleidon J, Henke C (2002) beta 1 integrin regulates fibroblast viability during collagen matrix contraction through a phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase/Akt/protein kinase B signaling pathway. J Biol Chem 277:24667–24675. doi:10.1074/jbc.M203565200
Frye RA (2000) Phylogenetic classification of prokaryotic and eukaryotic Sir2-like proteins. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 273:793–798. doi:10.1006/bbrc.2000.3000
Haigis MC, Sinclair DA (2010) Mammalian sirtuins: biological insights and disease relevance. Annu Rev Pathol 5:253–295. doi:10.1146/annurev.pathol.4.110807.092250
Cheng HL, Mostoslavsky R, Saito S, Manis JP, Gu Y, Patel P, Bronson R, Appella E, Alt FW, Chua KF (2003) Developmental defects and p53 hyperacetylation in Sir2 homolog (SIRT1)-deficient mice. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 100:10794–10799. doi:10.1073/pnas.1934713100
Yeung F, Hoberg JE, Ramsey CS, Keller MD, Jones DR, Frye RA, Mayo MW (2004) Modulation of NF-kappaB-dependent transcription and cell survival by the SIRT1 deacetylase. EMBO J 23:2369–2380. doi:10.1038/sj.emboj.7600244
Coly PM, Gandolfo P, Castel H, Morin F (2017) The autophagy machinery: a new player in chemotactic cell migration. Front Neurosci 11:78. doi:10.3389/fnins.2017.00078
Goldstone JV, Jonsson ME, Behrendt L, Woodin BR, Jenny MJ, Nelson DR, Stegeman JJ (2009) Cytochrome P450 1D1: a novel CYP1A-related gene that is not transcriptionally activated by PCB126 or TCDD. Arch Biochem Biophys 482:7–16. doi:10.1016/j.abb.2008.12.002
Hung HS, Chang CH, Chang CJ, Tang CM, Kao WC, Lin SZ, Hsieh HH, Chu MY, Sun WS, Hsu SH (2014) In vitro study of a novel nanogold-collagen composite to enhance the mesenchymal stem cell behavior for vascular regeneration. PLoS ONE 9:e104019. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0104019
Ho MT, Kang HS, Huh JS, Kim YM, Lim Y, Cho M (2014) Effects of the novel compound DK223 ([1E,2E − 1,2-Bis(6-methoxy-2H-chromen-3-yl)methylene]hydrazine) on migration and proliferation of human keratinocytes and primary dermal fibroblasts. Int J Mol Sci 15:13091–13110. doi:10.3390/ijms150713091
Taniguchi M, Arai N, Kohno K, Ushio S, Fukuda S (2012) Anti-oxidative and anti-aging activities of 2-O-alpha-glucopyranosyl-l-ascorbic acid on human dermal fibroblasts. Eur J Pharmacol 674:126–131. doi:10.1016/j.ejphar.2011.11.013
Salamone F, Galvano F, Marino Gammazza A, Paternostro C, Tibullo D, Bucchieri F, Mangiameli A, Parola M, Bugianesi E, Li Volti G (2012) Silibinin improves hepatic and myocardial injury in mice with nonalcoholic steatohepatitis. Dig Liver Dis 44:334–342. doi:10.1016/j.dld.2011.11.010
Flora K, Hahn M, Rosen H, Benner K (1998) Milk thistle (Silybum marianum) for the therapy of liver disease. Am J Gastroenterol 93:139–143. doi:10.1111/j.1572-0241.1998.00139.x
Abd El-Moneim ES, Fuerste HO, Krueger M, Elmagd AA, Brandis M, Schulte-Moenting J, Hentschel R (2005) Pressure support ventilation combined with volume guarantee versus synchronized intermittent mandatory ventilation: a pilot crossover trial in premature infants in their weaning phase. Pediatr Crit Care Med 6:286–292. doi:10.1097/01.PCC.0000161071.47031.61
Onat D, Boscoboinik D, Azzi A, Basaga H (1999) Effect of alpha-tocopherol and silibin dihemisuccinate on the proliferation of human skin fibroblasts. Biotechnol Appl Biochem 29(Pt 3):213–215
Kim BR, Seo HS, Ku JM, Kim GJ, Jeon CY, Park JH, Jang BH, Park SJ, Shin YC, Ko SG (2013) Silibinin inhibits the production of pro-inflammatory cytokines through inhibition of NF-kappaB signaling pathway in HMC-1 human mast cells. Inflamm Res 62:941–950. doi:10.1007/s00011-013-0640-1
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict and interest
The authors declare that they have no competing interest.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Liu, X., Xu, Q., Liu, W. et al. Enhanced migration of murine fibroblast-like 3T3-L1 preadipocytes on type I collagen-coated dish is reversed by silibinin treatment. Mol Cell Biochem 441, 35–62 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11010-017-3173-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11010-017-3173-z