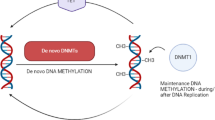
Abstract
The intestinal epithelium cells (IECs) in diabetes mellitus (DM) patients have been proven to be abnormally differentiated. During the differentiation of IECs, epigenetic modification acts as an important regulator. In this study, we aimed to examine the epigenetic alteration of Transducin-like Enhancer of Split 1 (TLE1), a multitask transcriptional co-repressor, contributing to the differentiation homeostasis in IECs of DM mice. The IECs of type 2 diabetic mice model were isolated and collected. Methylation states of whole genomic DNA promoter regions were investigated by microarray. Methylated-specific PCR was used to detect the methylation state of TLE1 promoter in DM mice IECs. The expression of TLE1, Hes1, and differentiated cell markers were measured through real-time PCR, Western blots, and immunohistochemistry; by transfection assay, TLE1 or Hes1 was independently down-regulated in intestinal epithelium cell line, IEC-6. Subsequent modulation on TLE1, Hes1, and differentiated intestinal cell markers were detected. Global gene promoter regions in DM intestinal epithelium were less methylated comparing to normal control. The expression of TLE1 was significantly increased via hypomethylated activation in DM mice IECs. Hes1 was significantly suppressed and the terminal cell markers abnormally expressed in DM mice IECs (P < 0.05). Inhibition or induction on the abundance of TLE1 in IEC-6 cell line resulted in the corresponding dysregulation of Hes1 and intestinal epithelium differentiation (P < 0.05). Demethylation of TLE1 promoter region activates the self-expression in diabetic mice IECs. Subsequently, TLE1, through the transcriptional suppression on expression of Hes1, contributes to the aberrant differentiation of IECs in DM mice.







Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- DM:
-
Diabetes mellitus
- DE:
-
Diabetic enteropathy
- IESCs:
-
Intestinal epithelium stem cells
- CBC stem cells:
-
Crypt-based columnar stem cells
- TA cells:
-
Transit-amplifying cells
- IECs:
-
Intestinal epithelial cells
- Hes1:
-
Hairy and enhancer of split 1
- Dnmt:
-
DNA methyltransferase
- CRC:
-
Colorectal cancer
- Gro/TLE:
-
Groucho homologue/transducin-like enhancer of split
- Dpp/BMP:
-
Decapentaplegic/bone morphogenetic proteins
- TLE1:
-
Transducin-like enhancer of split 1
- EDTA:
-
Ethylenediaminetetraacetic acid
- PBS:
-
Phosphate-buffered saline
- DTT:
-
DL-dithiothreitol
- ATCC:
-
American type culture collection
- DMEM:
-
Dulbecco’s modified eagle medium
- FBS:
-
Fetal bovine serum
- 5AZA:
-
5-aza-2’-deoxycytidine
- 5mC:
-
5-Methylcytidine
- TSS:
-
Transcription start site
- DEP:
-
Differential enrichment peaks
- MSP:
-
Methylation-specific PCR
- siRNA:
-
Small interfering RNA
- mRNA:
-
Messenger RNA
- RT-PCR:
-
Real-time polymerase chain reaction
- PVDF:
-
Polyvinylidene difluoride membranes
- BSA:
-
Bovine serum albumin
- Lyz1:
-
Lysozyme 1
- Tff3:
-
Trefoil factor 3
- SI:
-
Sucrase-isomaltase
- ChgA:
-
Chromogranin A
- ECL:
-
Chemiluminescence
- DAB:
-
3,3′-Diaminobenzidine tetrahydrochloride
- SE:
-
Standard error
References
Chamberlain JJ, Rhinehart AS, Shaefer CF Jr, Neuman A (2016) Diagnosis and management of diabetes: synopsis of the 2016 American Diabetes Association Standards of Medical Care in Diabetes. Ann Intern Med 164(8):542–552
Tack J, Carbone F, Rotondo A (2015) Gastroparesis. Curr Opin Gastroenterol 31(6):499–505
Horváth VJ, Putz Z, Izbéki F, Körei AE, Gerő L, Lengyel C et al (2015) Diabetes-related dysfunction of the small intestine and the colon: focus on motility. Curr Diab Rep 15(11):94
D’Addio F, Fiorina P (2016) Type 1 Diabetes and dysfunctional intestinal homeostasis. Trends Endocrinol Metab 27(7):493–503
Min XH, Yu T, Qing Q, Yuan YH, Zhong W, Chen GC et al (2015) Abnormal differentiation of intestinal epithelium and intestinal barrier dysfunction in diabetic mice associated with depressed Notch/NICD transduction in Notch/Hes1 signal pathway. Cell Biol Int 38(10):1194–1204
Tan S, Barker N (2015) Epithelial stem cells and intestinal cancer. Semin Cancer Biol 32:40–53
Sheaffer KL, Kim R, Aoki R, Elliott EN, Schug J, Burger L et al (2014) DNA methylation is required for the control of stem cell differentiation in the small intestine. Genes Dev 28(6):652–664
Okugawa Y, Grady WM, Goel A (2015) Epigenetic alterations in colorectal cancer: emerging biomarkers. Gastroenterology 149(5):1204–1225, e12
Carethers JM, Jung BH (2015) Genetics and genetic biomarkers in sporadic colorectal cancer. Gastroenterology 149(5):1177–1190, e3
Chen T, Hevi S, Gay F, Tsujimoto N, He T, Zhang B et al (2007) Complete inactivation of DNMT1 leads to mitotic catastrophe in human cancer cells. Nat Genet 39(3):391–396
Spada F, Haemmer A, Kuch D, Rothbauer U, Schermelleh L, Kremmer E et al (2007) DNMT1 but not its interaction with the replication machinery is required for maintenance of DNA methylation in human cells. J Cell Biol 176(5):565–571
Jennings BH, Ish-Horowicz D (2008) The Groucho/TLE/Grg family of transcriptional co-repressors. Genome Biol 9(1):205
Liu Y, Dehni G, Purcell KJ, Sokolow J, Carcangiu ML, Artavanis-Tsakonas S et al (1996) Epithelial expression and chromosomal location of human TLE genes: implications for notch signaling and neoplasia. Genomics 31:58–64
Fraga MF, Berdasco M, Ballestar E, Ropero S, Lopez-Nieva P, Lopez-Serra L et al (2008) Epigenetic inactivation of the Groucho homologue gene TLE1 in hematologic malignancies. Cancer Res 68(11):4116–4122
Crosnier C, Stamataki D, Lewis J (2006) Organizing cell renewal in the intestine: stem cells, signals and combinatorial control. Nat Rev Genet 7(5):349–359
Liu ZH, Dai XM, Du B (2015) Hes1: a key role in stemness, metastasis and multidrug resistance. Cancer Biol Ther 16(3):353–359
Ciarapica R, Methot L, Tang Y, Lo R, Dali R, Buscarlet M et al (2014) Prolyl isomerase Pin1 and protein kinase HIPK2 cooperate to promote cortical neurogenesis by suppressing Groucho/TLE:Hes1-mediated inhibition of neuronal differentiation. Cell Death Differ 21(2):321–332
Larabee JL, Shakir SM, Barua S, Ballard JD (2013) Increased cAMP in monocytes augments Notch signaling mechanisms by elevating RBP-J and transducin-like enhancer of Split (TLE). J Biol Chem 288(30):21526–21536
Sato T, Clevers H (2013) Primary mouse small intestinal epithelial cell cultures. Methods Mol Biol 945:319–328
Li LC, Dahiya R (2002) MethPrimer: designing primers for methylation PCRs. Bioinformatics 18(11):1427–1431
Demidenko R, Razanauskas D, Daniunaite K, Lazutka JR, Jankevicius F, Jarmalaite S (2015) Frequent down-regulation of ABC transporter genes in prostate cancer. BMC Cancer 15:683
Lo Nigro C, Wang H, McHugh A, Lattanzio L, Matin R, Harwood C et al (2013) Methylated tissue factor pathway inhibitor 2 (TFPI2) DNA in serum is a biomarker of metastatic melanoma. J Invest Dermatol 133(5):1278–1285
Ye D, Ma TY (2008) Cellular and molecular mechanisms that mediate basal and tumour necrosis factor-alpha-induced regulation of myosin light chain kinase gene activity. J Cell Mol Med 12(4):1331–1346
Huang CZ, Xu JH, Zhong W, Xia ZS, Wang SY, Cheng D et al (2017) Sox9 transcriptionally regulates Wnt signaling in intestinal epithelial stem cells in hypomethylated crypts in the diabetic state. Stem Cell Res Ther 8(1):60
Yu T, Lu XJ, Li JY, Shan TD, Huang CZ, Ouyang H et al (2016) Overexpression of miR-429 impairs intestinal barrier function in diabetic mice by down-regulating occludin expression. Cell Tissue Res 366(2):341–352
Shan TD, Ouyang H, Yu T, Li JY, Huang CZ, Yang HS et al (2016) miRNA-30e regulates abnormal differentiation of small intestinal epithelial cells in diabetic mice by downregulating Dll4 expression. Cell Prolif 49(1):102–114
Elliott EN, Kaestner KH (2015) Epigenetic regulation of the intestinal epithelium. Cell Mol Life Sci 72(21):4139–4156
Xu Y, Wang Y, Liu H, Kang X, Li W, Wei Q (2016) Genetic variants of genes in the Notch signaling pathway predict overall survival of non-small cell lung cancer patients in the PLCO study. Oncotarget 7(38):61716–61727
Morris AP, Voight BF, Teslovich TM, Ferreira T, Segrè AV, Steinthorsdottir V et al (2012) Large-scale association analysis provides insights into the genetic architecture and pathophysiology of type 2 diabetes. Nat Genet 44(9):981–990
Ouyang H, Yang HS, Yu T, Shan TD, Li JY, Huang CZ et al (2016) MEK/ERK pathway activation by insulin receptor isoform alteration is associated with the abnormal proliferation and differentiation of intestinal epithelial cells in diabetic mice. Mol Cell Biochem 413(1–2):165–178
Demitrack ES, Samuelson LC (2016) Notch regulation of gastrointestinal stem cells. J Physiol 594(17):4791–4803
Weng AP, Aster JC (2004) Multiple niches for Notch in cancer: context is everything. Curr Opin Genet Dev 14:48–54
Roy M, Pear WS, Aster JC (2007) The multifaceted role of Notch in cancer. Curr Opin Genet Dev 17:52–59
Ueo T, Imayoshi I, Kobayashi T (2012) The role of Hes genes in intestinal development, homeostasis and tumor formation. Development 139(6):1071–1082
Sang L, Coller HA, Roberts JM (2008) Control of the reversibility of cellular quiescence by the transcriptional repressor HES1. Science 321(5892):1095–1100
Jensen J, Pedersen EE, Galante P, Hald J, Heller RS, Ishibashi M et al (2000) Control of endodermal endocrine development by Hes-1. Nat Genet 24(1):36–44
Fre S, Huyghe M, Mourikis P, Robine S, Louvard D, Artavanis-Tsakonas S (2005) Notch signals control the fate of immature progenitor cells in the intestine. Nature 435(7044):964–968
Chen J, Imanaka N, Chen J, Griffin JD (2010) Hypoxia potentiates Notch signaling in breast cancer leading to decreased E-cadherin expression and increased cell migration and invasion. Br J Cancer 102(2):351–360
Danza G, Di Serio C, Rosati F, Lonetto G, Sturli N, Kacer D et al (2012) Notch signaling modulates hypoxiainduced neuroendocrine differentiation of human prostate cancer cells. Mol Cancer Res 10(2):230–238
Ju BG, Solum D, Song EJ, Lee KJ, Rose DW, Glass CK et al (2004) Activating the PARP-1 sensor component of the groucho/TLE1 corepressor complex mediates a CaMKinase IIdelta-dependent neurogenic gene activation pathway. Cell 119(6):815–829
Nuthall HN, Joachim K, Stifani S (2004) Phosphorylation of serine 239 of Groucho/TLE1 by protein kinase CK2 is important for inhibition of neuronal differentiation. Mol Cell Biol 24(19):8395–8407
Acknowledgements
All authors read and approved the final manuscript. This study was supported by National Natural Science Foundation of China (Nos. 81270442, 81370475).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Author contributions
JX and GC undertook the manuscript preparation and methylation analysis. CH carried out the microarray experiment and RT-PCR. TW took part in cell culture and Western blotting. SW and JL carried out the literature research and analytic process. DC participated in cell transfection and statistical analyses. TY and QC carried out the study design and funds collection.
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
No potential conflict of interest were disclosed.
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Xu, Jh., Chen, Gc., Huang, Cz. et al. Epigenetic modification of TLE1 induce abnormal differentiation in diabetic mice intestinal epithelium. Mol Cell Biochem 438, 85–96 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11010-017-3116-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11010-017-3116-8