Abstract
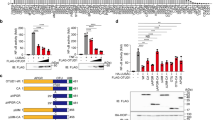
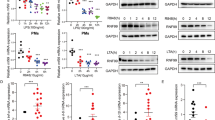
Persistent activation of nuclear factor B (NF-κB) is very important in the modulation of macrophages cellular response to microbial infections. The deubiquitinase USP14, which is critical for ubiquitin-mediated proteasomal degradation of proteins, is known to be involved in cancer, neurological diseases, and aging. However, the mechanism by which USP14 regulates inflammation remains unclear. Here, we demonstrated that decreasing the deubiquitinase activity of USP14 resulted in reduced lipopolysaccharides (LPS)-mediated tumor necrosis factor-α (TNF-α) and interleukin (IL)-6 release in THP-1 and RAW264.7 cells. Meanwhile, USP14 knockdown by siRNA showed the same effects, with no cytotoxicity in THP-1 cells. Moreover, inhibiting the deubiquitinase activity of USP14 or USP14 knockdown resulted in decreased ERK1/2 and IκBα phosphorylation, increased amounts of the NF-κB inhibitor IκBα, and reduced NF-κB p65 transport from the cytoplasm into nucleus. These findings suggested that USP14 induces NF-κB activity and ERK1/2 phosphorylation triggered by microbial infection.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Leyva-Lopez N, Gutierrez-Grijalva EP, Ambriz-Perez DL, Heredia JB (2016) Flavonoids as cytokine modulators: a possible therapy for inflammation-related diseases. Int J Mol Sci 17:921
Medzhitov R (2008) Origin and physiological roles of inflammation. Nature 454:428–435
Carmody RJ, Chen YH (2007) Nuclear factor-kappaB: activation and regulation during toll-like receptor signaling. Cell Mol Immunol 4:31–41
Hayden MS, Ghosh S (2012) NF-kappaB, the first quarter-century: remarkable progress and outstanding questions. Genes Dev 26:203–234
Solt LA, May MJ (2008) The IkappaB kinase complex: master regulator of NF-kappaB signaling. Immunol Res 42:3–18
Hayden MS, Ghosh S (2004) Signaling to NF-kappaB. Genes Dev 18:2195–2224
Arthur JS, Ley SC (2013) Mitogen-activated protein kinases in innate immunity. Nat Rev Immunol 13:679–692
Paunovic V, Harnett MM (2013) Mitogen-activated protein kinases as therapeutic targets for rheumatoid arthritis. Drugs 73:101–115
Hershko A, Ciechanover A (1992) The ubiquitin system for protein degradation. Annu Rev Biochem 61:761–807
Hochstrasser M (1995) Ubiquitin, proteasomes, and the regulation of intracellular protein degradation. Curr Opin Cell Biol 7:215–223
D’Arcy P, Brnjic S, Olofsson MH, Fryknas M, Lindsten K, De Cesare M, Perego P, Sadeghi B, Hassan M, Larsson R, Linder S (2011) Inhibition of proteasome deubiquitinating activity as a new cancer therapy. Nat Med 17:1636–1640
Liu N, Li X, Huang H, Zhao C, Liao S, Yang C, Liu S, Song W, Lu X, Lan X, Chen X, Yi S, Xu L, Jiang L, Zhao C, Dong X, Zhou P, Li S, Wang S, Shi X, Dou PQ, Wang X, Liu J (2014) Clinically used antirheumatic agent auranofin is a proteasomal deubiquitinase inhibitor and inhibits tumor growth. Oncotarget 5:5453–5471
Hanna J, Hathaway NA, Tone Y, Crosas B, Elsasser S, Kirkpatrick DS, Leggett DS, Gygi SP, King RW, Finley D (2006) Deubiquitinating enzyme Ubp6 functions noncatalytically to delay proteasomal degradation. Cell 127:99–111
Puente XS, Sanchez LM, Overall CM, Lopez-Otin C (2003) Human and mouse proteases: a comparative genomic approach. Nat Rev Genet 4:544–558
Jung H, Kim BG, Han WH, Lee JH, Cho JY, Park WS, Maurice MM, Han JK, Lee MJ, Finley D, Jho EH (2013) Deubiquitination of Dishevelled by Usp14 is required for Wnt signaling. Oncogenesis 2:e64
Nag DK, Finley D (2012) A small-molecule inhibitor of deubiquitinating enzyme USP14 inhibits dengue virus replication. Virus Res 165:103–106
Hyrskyluoto A, Bruelle C, Lundh SH, Do HT, Kivinen J, Rappou E, Reijonen S, Waltimo T, Petersen A, Lindholm D, Korhonen L (2014) Ubiquitin-specific protease-14 reduces cellular aggregates and protects against mutant huntingtin-induced cell degeneration: involvement of the proteasome and ER stress-activated kinase IRE1alpha. Hum Mol Genet 23:5928–5939
Wu N, Liu C, Bai C, Han YP, Cho WC, Li Q (2013) Over-expression of deubiquitinating enzyme USP14 in lung adenocarcinoma promotes proliferation through the accumulation of beta-catenin. Int J Mol Sci 14:10749–10760
Tian Z, D’Arcy P, Wang X, Ray A, Tai YT, Hu Y, Carrasco RD, Richardson P, Linder S, Chauhan D, Anderson KC (2014) A novel small molecule inhibitor of deubiquitylating enzyme USP14 and UCHL5 induces apoptosis in multiple myeloma and overcomes bortezomib resistance. Blood 123:706–716
Shinji S, Naito Z, Ishiwata S, Ishiwata T, Tanaka N, Furukawa K, Suzuki H, Seya T, Matsuda A, Katsuta M, Tajiri T (2006) Ubiquitin-specific protease 14 expression in colorectal cancer is associated with liver and lymph node metastases. Oncol Rep 15:539–543
Liu N, Chai R, Liu B, Zhang Z, Zhang S, Zhang J, Liao Y, Cai J, Xia X, Li A, Liu J, Huang H, Liu S (2016) Ubiquitin-specific protease 14 regulates cardiac hypertrophy progression by increasing GSK-3beta phosphorylation. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 478:1236–1241
Baeuerle PA, Henkel T (1994) Function and activation of NF-kappa B in the immune system. Annu Rev Immunol 12:141–179
Carmody RJ, Ruan Q, Palmer S, Hilliard B, Chen YH (2007) Negative regulation of toll-like receptor signaling by NF-kappaB p50 ubiquitination blockade. Science 317:675–678
Colleran A, Collins PE, O’Carroll C, Ahmed A, Mao X, McManus B, Kiely PA, Burstein E, Carmody RJ (2013) Deubiquitination of NF-kappaB by Ubiquitin-Specific Protease-7 promotes transcription. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 110:618–623
Maine GN, Mao X, Komarck CM, Burstein E (2007) COMMD1 promotes the ubiquitination of NF-kappaB subunits through a cullin-containing ubiquitin ligase. EMBO J 26:436–447
Saccani S, Marazzi I, Beg AA, Natoli G (2004) Degradation of promoter-bound p65/RelA is essential for the prompt termination of the nuclear factor kappaB response. J Exp Med 200:107–113
Brouwers H, von Hegedus J, Toes R, Kloppenburg M, Ioan-Facsinay A (2015) Lipid mediators of inflammation in rheumatoid arthritis and osteoarthritis. Best Pract Res Clin Rheumatol 29:741–755
Prabhu SD, Frangogiannis NG (2016) The biological basis for cardiac repair after myocardial infarction: from inflammation to fibrosis. Circ Res 119:91–112
Robb CT, Regan KH, Dorward DA, Rossi AG (2016) Key mechanisms governing resolution of lung inflammation. Semin Immunopathol 38:425–448
Jin YN, Chen PC, Watson JA, Walters BJ, Phillips SE, Green K, Schmidt R, Wilson JA, Johnson GV, Roberson ED, Dobrunz LE, Wilson SM (2012) Usp14 deficiency increases tau phosphorylation without altering tau degradation or causing tau-dependent deficits. PLoS ONE 7:e47884
Mialki RK, Zhao J, Wei J, Mallampalli DF, Zhao Y (2013) Overexpression of USP14 protease reduces I-kappaB protein levels and increases cytokine release in lung epithelial cells. J Biol Chem 288:15437–15441
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (81400231), Pearl River S&T Nova Program of Guangzhou (No. 201506010071) General Project (1201420465) from Guangzhou Education Commission, the Science and Technology Planning Project of Guangdong Province, China (2014A020221059), Guangzhou Medical and health science and technology project (20141A011079).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Ningning Liu, Tianyu Kong and Xiaohua Chen contributed equally to this work.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Liu, N., Kong, T., Chen, X. et al. Ubiquitin-specific protease 14 regulates LPS-induced inflammation by increasing ERK1/2 phosphorylation and NF-κB activation. Mol Cell Biochem 431, 87–96 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11010-017-2978-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11010-017-2978-0