Abstract
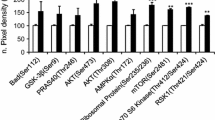
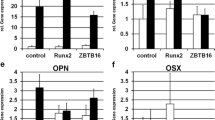
Dental follicle stem cells (DFCs) are precursor cells of alveolar osteoblasts, and previous studies have shown that the growth factor bone morphogenetic protein (BMP)2 induces the osteogenic differentiation of DFCs. However, the molecular mechanism down-stream of the induction of the osteogenic differentiation by BMP2 remains elusive. We investigated therefore the phosphoproteome of DFCs after the induction of the osteogenic differentiation with BMP2. In this study, phosphoproteins of the hedgehog “off” state were differentially expressed. Further analyses revealed that BMP2 induced the expression of repressors of the hedgehog-signaling pathway such as Patched 1 (PTCH1), Suppressor of Fused (SUFU), and Parathyroid Hormone-Related Peptide (PTHrP). Previous studies suggested that hedgehog proteins induce the osteogenic differentiation of mesenchymal stem cells via a paracrine pathway. Indian hedgehog (IHH) induced the expression of the osteogenic transcription factor RUNX2. However, a supplementation of the BMP2-based osteogenic differentiation medium with IHH did not induce the expression of RUNX2. Moreover, IHH inhibited slightly the ALP activity and the mineralization of osteogenic-differentiated DFCs. In conclusion, our results suggest that BMP2 inhibits the hedgehog signaling after the induction of the osteogenic differentiation in DFCs.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Diekwisch TG (2001) The developmental biology of cementum. Int J Dev Biol 45:695–706
Handa K, Saito M, Yamauchi M et al (2002) Cementum matrix formation in vivo by cultured dental follicle cells. Bone 31:606–611
Morsczeck C (2015) Molecular mechanisms in dental follicle precursor cells during the osteogenic differentiation. Histol Histopathol 30:1161–1169. doi:10.14670/HH-11-634
Morsczeck C, Gotz W, Schierholz J et al (2005) Isolation of precursor cells (PCs) from human dental follicle of wisdom teeth. Matrix Biol 24:155–165
Viale-Bouroncle S, Klingelhöffer C, Ettl T et al (2014) A protein kinase A (PKA)/β-catenin pathway sustains the BMP2/DLX3-induced osteogenic differentiation in dental follicle cells (DFCs). Cell Signal. doi:10.1016/j.cellsig.2014.12.008
Viale-Bouroncle S, Felthaus O, Schmalz G et al (2012) The transcription factor DLX3 regulates the osteogenic differentiation of human dental follicle precursor cells. Stem Cells Dev 21:1936–1947. doi:10.1089/scd.2011.0422
Khan M, Seppala M, Zoupa M, Cobourne MT (2007) Hedgehog pathway gene expression during early development of the molar tooth root in the mouse. Gene Expr Patterns GEP 7:239–243. doi:10.1016/j.modgep.2006.10.001
Nakatomi M, Morita I, Eto K, Ota MS (2006) Sonic hedgehog signaling is important in tooth root development. J Dent Res 85:427–431
Thesleff I (2014) Current understanding of the process of tooth formation: transfer from the laboratory to the clinic. Aust Dent J 59(Suppl 1):48–54. doi:10.1111/adj.12102
Tummers M, Thesleff I (2009) The importance of signal pathway modulation in all aspects of tooth development. J Exp Zoolog B Mol Dev Evol 312B:309–319
Koussoulakou DS, Margaritis LH, Koussoulakos SL (2009) A curriculum vitae of teeth: evolution, generation, regeneration. Int J Biol Sci 5:226–243
Ehlen HWA, Buelens LA, Vortkamp A (2006) Hedgehog signaling in skeletal development. Birth Defects Res Part C Embryo Today Rev 78:267–279. doi:10.1002/bdrc.20076
Vortkamp A (2000) The Indian hedgehog–PTHrP system in bone development. Ernst Scher Res Found Workshop 191–209
Abzhanov A, Rodda SJ, McMahon AP, Tabin CJ (2007) Regulation of skeletogenic differentiation in cranial dermal bone. Dev Camb Engl 134:3133–3144. doi:10.1242/dev.002709
Lenton K, James AW, Manu A et al (2011) Indian hedgehog positively regulates calvarial ossification and modulates bone morphogenetic protein signaling. Genesis 49:784–796. doi:10.1002/dvg.20768
Engholm-Keller K, Larsen MR (2013) Technologies and challenges in large-scale phosphoproteomics. Proteomics 13:910–931. doi:10.1002/pmic.201200484
Melo-Braga MN, Meyer M, Zeng X, Larsen MR (2015) Characterization of human neural differentiation from pluripotent stem cells using proteomics/PTMomics–current state-of-the-art and challenges. Proteomics 15:656–674. doi:10.1002/pmic.201400388
Beck HC, Gosau M, Kristensen LP, Morsczeck C (2014) A site-specific phosphorylation of the focal adhesion kinase controls the formation of spheroid cell clusters. Neurochem Res 39:1199–1205. doi:10.1007/s11064-014-1298-y
Haw R, Hermjakob H, D’Eustachio P, Stein L (2011) Reactome pathway analysis to enrich biological discovery in proteomics data sets. Proteomics 11:3598–3613. doi:10.1002/pmic.201100066
Chuang PT, McMahon AP (1999) Vertebrate Hedgehog signalling modulated by induction of a Hedgehog-binding protein. Nature 397:617–621. doi:10.1038/17611
Honda MJ, Imaizumi M, Suzuki H et al (2011) Stem cells isolated from human dental follicles have osteogenic potential. Oral Surg Oral Med Oral Pathol Oral Radiol Endod 111:700–708. doi:10.1016/j.tripleo.2010.08.004
Honda MJ, Imaizumi M, Tsuchiya S, Morsczeck C (2010) Dental follicle stem cells and tissue engineering. J Oral Sci 52:541–552
Morsczeck C, Moehl C, Gotz W et al (2005) In vitro differentiation of human dental follicle cells with dexamethasone and insulin. Cell BiolInt 29:567–575
Viale-Bouroncle S, Gosau M, Morsczeck C (2014) NOTCH1 signaling regulates the BMP2/DLX-3 directed osteogenic differentiation of dental follicle cells. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 443:500–504. doi:10.1016/j.bbrc.2013.11.120
Zhao H, Feng J, Seidel K et al (2014) Secretion of shh by a neurovascular bundle niche supports mesenchymal stem cell homeostasis in the adult mouse incisor. Cell Stem Cell 14:160–173. doi:10.1016/j.stem.2013.12.013
Viale-Bouroncle S, Gosau M, Morsczeck C (2014) Collagen I induces the expression of alkaline phosphatase and osteopontin via independent activations of FAK and ERK signalling pathways. Arch Oral Biol 59:1249–1255. doi:10.1016/j.archoralbio.2014.07.013
Plaisant M, Fontaine C, Cousin W et al (2009) Activation of hedgehog signaling inhibits osteoblast differentiation of human mesenchymal stem cells. Stem Cells Dayt Ohio 27:703–713. doi:10.1634/stemcells.2008-0888
Klingelhöffer C, Reck A, Ettl T, Morsczeck C (2016) The parathyroid hormone-related protein is secreted during the osteogenic differentiation of human dental follicle cells and inhibits the alkaline phosphatase activity and the expression of DLX3. Tissue Cell 48:334–339. doi:10.1016/j.tice.2016.05.007
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Morsczeck, C., Reck, A. & Beck, H.C. The hedgehog-signaling pathway is repressed during the osteogenic differentiation of dental follicle cells. Mol Cell Biochem 428, 79–86 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11010-016-2918-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11010-016-2918-4