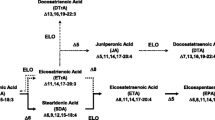
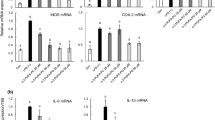
Abstract
Through studying the changes of the total phospholipid components in mouse macrophages under the inflammatory status and the drug intervention status, we found the targets of non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs on phospholipids, thus providing the basis for the targets of in vitro anti-inflammatory effects of non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs. After RAW264.7 cells were pretreated with common non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (aspirin and ibuprofen) and, respectively, stimulated with KLA for various periods (0.5, 4, 12, 16, and 24 h), the phospholipids were extracted. The dynamic changes of phospholipids in cells under various stimulations were analyzed with UPLC-Q-TOF–MS technique. Through the statistical analysis of Simca-P, we explored the potential targets of non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs on phospholipids. Through the dynamic analysis of phospholipids, we found two biomarkers (PC(17:1/18:1), PA(18:0/18:4)) which might be in vitro intervention inflammatory response targets of non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs. The analysis results show that in anti-inflammatory effects, non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs can inhibit COX, induce the cellular fatty acid desaturation and the changes of phospholipid components, stimulate free fatty acids, activate calcium ion channels of endoplasmic reticulum, and promote cell endocytosis, thus controlling inflammation and activating cells. Non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs can promote endocytosis, alter cell inflammatory response, and activate the process cells, thus realizing the anti-inflammatory effects.
Graphical Abstract







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Legrand-Poels S et al (2014) Free fatty acids as modulators of the NLRP3 inflammasome in obesity/type 2 diabetes. Biochem Pharmacol 92(1):131–141
Sethu S, Alirio J (2011) Melendez, new developments on the TNFα-mediated signalling pathways. Biosci Rep 31(1):63–76
Mojgan M, Kuda O (2015) Lipid signaling in adipose tissue: connecting inflammation & metabolism. Biochimica et Biophysica Acta (BBA) 1851(4):503–518
Poveda JA et al (2014) Lipid modulation of ion channels through specific binding sites. Biochimica et Biophysica Acta (BBA) 1838(6):1560–1567
Bates RC et al (2014) Activation of Src and release of intracellular calcium by phosphatidic acid during Xenopus laevis fertilization. Dev Biol 386(1):165–180
Cho HY, Choi EK, Lee SW (2009) Programmed death-1 receptor negatively regulates LPS-mediated IL-12 production and differentiation of murine macrophage RAW264.7 cells. Immunol Lett 127(1):39–47
Dennis EA et al (2011) Phospholipase A2 enzymes: physical structure, biological function, disease implication, chemical inhibition, and therapeutic intervention. Chem Rev 111(10):6130–6185
Bakovic M, HB Dunford (1994) Intimate relation between cyclooxygenase and peroxidase acivities of prostaglandin H synthase. peroxidase reaction of ferulic acid and its influence on the reaction of arachidonic acid. Biochemistry 33:6475–6482
Cao Y et al (2000) Intracellular unesterified arachidonic acid signals apoptosis. Proc Natl Acad Sci 97(21):11280–11285
Maurya MR, Gupta S, Li X (2013) Analysis of inflammatory and lipid metabolic networks across RAW264.7 and thioglycolate-elicited macrophages. J Lipid Res 54(9):2525–2542
Nakanishi-Matsui M et al (2012) Lipopolysaccharide induces multinuclear cell from RAW264.7 line with increased phagocytosis activity. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 425(2):144–149
Xia Wu, Zhao Lili, Peng Haibo (2015) Search for potential biomarkers by UPLC/Q-TOF–MS analysis of dynamic changes of glycerophospholipid constituents of RAW264.7 cells treated with NSAID. Chromatographia 78(3):211–220
Schwentker A, Vodovotz Y, Weller R (2002) Nitric oxide and wound repair: role of cytokines? Nitric Oxide 7:1–10
Yue R et al (2013) Rapid-resolution liquid chromatography TOF–MS for urine metabolomic analysis of collagen-induced arthritis in rats and its applications. J Ethnopharmacol 145(2):465–475
Rajalahti T et al (2009) Biomarker discovery in mass spectral profiles by means of selectivity ratio plot. Chemom Intell Lab Syst 95(1):35–48
Lin W-S, Yang C-M, Kuo B-J (2012) Classifying cultivars of rice (Oryza sativa L.) based on corrected canopy reflectance spectra data using the orthogonal projections to latent structures (O-PLS) method. Chemom Intell Lab Syst 115:25–36
Harvey KA et al (2010) Oleic acid inhibits stearic acid-induced inhibition of cell growth and pro-inflammatory responses in human aortic endothelial cells. J Lipid Res 51(12):3470–3480
Walloschke B, Fuhrmann H, Schumann J (2010) Enrichment of RAW264.7 macrophages with essential 18-carbon fatty acids affects both respiratory burst and production of immune modulating cytokines. J Nutr Biochem 21(6):556–560
Rouzer CA, Rouzer PTI (2007) Lipid profiling reveals glycerophospholipid remodeling in zymosan-stimulated macrophages. Biochemistry 46:6026–6042
Glatz JF, Luiken JJ (2015) Fatty acids in cell signaling: historical perspective and future outlook. Prostaglandins Leuk Essent Fatty Acids 92:57–62
Gómez-Fernández JC, Corbalán-García S (2007) Diacylglycerols, multivalent membrane modulators. Chem Phys Lipids 148(1):1–25
Gustavsson M, Traaseth NJ, Veglia G (2011) Activating and deactivating roles of lipid bilayers on the Ca2+-ATPase/phospholamban complex. Biochemistry 50(47):10367–10374
Pereira-Leite C, Nunes C, Reis S (2013) Interaction of nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs with membranes: in vitro assessment and relevance for their biological actions. Prog Lipid Res 52(4):571–584
Lee YN et al (2004) Phosphatidic acid positively regulates LPS-induced differentiation of RAW264.7 murine macrophage cell line into dendritic-like cells. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 318(4):839–845
Lee JG et al (2007) Phosphatidic acid as a regulator of matrix metalloproteinase-9 expression via the TNF-α signaling pathway. FEBS Lett 581(4):787–793
Olefsky JM, Glass CK (2010) Macrophages, inflammation, and insulin resistance. Ann Rev Physiol 72(1):219–246
Vihervaara T et al (2013) Modification of the lipidome in RAW264.7 macrophage subjected to stable silencing of oxysterol-binding proteins. Biochimie 95(3):538–547
Berchtold MW, Villalobo A (2014) The many faces of calmodulin in cell proliferation, programmed cell death, autophagy, and cancer. Biochimica et Biophysica Acta (BBA 1843(2):398–435
Acknowledgments
This research was supported by the Project of Guangdong Provincial National Science Foundation (Grant No. 1035102201000000).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Peng, H., Wu, X., Zhao, L. et al. Dynamic analysis of phospholipid metabolism of mouse macrophages treated with common non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs. Mol Cell Biochem 411, 161–171 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11010-015-2578-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11010-015-2578-9