Abstract
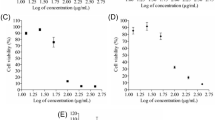
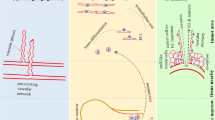
Lysophosphatidic acid (LPA) signaling via LPA receptors provides a variety of cellular functions, including angiogenesis. In this study, to assess an involvement of LPA receptors in cell motile activities of endothelial cells during chemotherapy, F-2 cells were treated with cisplatin (CDDP) and doxorubicin (DOX) at a concentration of 0.01 μM every 24 h for at least 1 month. The treatment of CDDP and DOX inhibited the expression levels of the LPA receptor-1 (Lpar1), Lpar2, and Lpar3 genes in F-2 cells. The cell motile activities of CDDP and DOX treated cells were relatively lower than those of untreated cells. Next, we investigated whether cancer cells could stimulate the cell motile activities of F-2 cells treated with CDDP and DOX. For cell motility assay, CDDP- and DOX-treated cells were co-cultured with pancreatic cancer PANC-1 cells. The cell motile activities of CDDP- and DOX-treated cells were significantly enhanced by the existence of PANC-1 cells, correlating with the LPA receptor expressions. In addition, the elevated cell motile activities were suppressed by the pretreatment of an autotaxin inhibitor S32826. These results suggest that LPA signaling via LPA receptors may regulate the cell motile activities of F-2 cells treated with anticancer drugs.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Folkman J (1971) Tumor angiogenesis: therapeutic implications. N Engl J Med 285:1182–1186
Tozer GM, Kanthou C, Baguley BC (2005) Disrupting tumor blood vessels. Nat Rev Cancer 5:423–435
Carmeliet P, Jain RK (2011) Molecular mechanisms and clinical applications of angiogenesis. Nature 473:298–307
Folkman J (2007) Angiogenesis: an organizing principle for drug discovery? Nat Rev Drug Discov 6:273–286
Bergers G, Hanahan D (2008) Modes of resistance to antiangiogenic therapy. Nat Rev Cancer 8:592–603
Jain RK (2005) Normalization of tumor vasculature: an emerging concept in antiangiogenic therapy. Science 307:58–62
Aikawa S, Hashimoto T, Kano K, Aoki J (2015) Lysophosphatidic acid as a lipid mediator with multiple biological actions. J Biochem 157:81–89
Ishii I, Fukushima N, Ye X, Chun J (2004) Lysophospholipid receptors: signaling and biology. Annu Rev Biochem 73:321–354
Lin M-E, Herr DR, Chun J (2010) Lysophosphatidic acid (LPA) receptors: signaling properties and disease relevance. Prostaglandins Other Lipid Mediat 91:130–138
Tsujiuchi T, Araki M, Hirane M, Dong Y, Fukushima N (2014) Lysophosphatidic acid receptors in cancer pathobiology. Histol Histopathol 29:313–321
Tsujiuchi T, Hirane M, Dong Y, Fukushima N (2014) Diverse effects of LPA receptors on cell motile activities of cancer cells. J Recept Signal Transduct 34:149–153
Goetzl EJ, Dolezalova H, Kong Y, Hu Y-L, Jaffe RB, Kalli KR, Conover CA (1999) Distinctive expression and functions of the type 4 endothelial differentiation gene-encoded G protein-coupled receptor for lysophosphatidic acid in ovarian cancer. Cancer Res 59:5370–5375
Hu Y-L, Tee M-K, Goetzl EJ, Auersperg N, Mills GB, Ferrara N, Jaffe RB (2001) Lysophosphatidic acid induction of vascular endothelial growth factor expression in human ovarian cancer cells. J Natl Cancer Inst 93:762–768
Fujita T, Miyamoto S, Onoyama I, Sonoda K, Mekada E, Nakano H (2003) Expression of lysophosphatidic acid receptors and vascular endothelial growth factor mediating lysophosphatidic acid in the development of human ovarian cancer. Cancer Lett 192:161–169
Yu S, Murph MM, Lu Y, Liu S, Hall HS, Liu J, Stephens C, Fang X, Mills GB (2008) Lysophosphatidic acid receptors determine tumorigenicity and aggressiveness of ovarian cancer cells. J Natl Cancer Inst 100:1630–1642
Kitayoshi M, Kato K, Tanabe E, Yoshikawa K, Fukui R, Fukushima N, Tsujiuchi T (2012) Enhancement of endothelial cell migration by constitutively active LPA1-expressing tumor cells. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 422:339–343
Okabe K, Kato K, Teranishi M, Okumura M, Fukui R, Mori T, Fukushima N, Tsujiuchi T (2011) Induction of lysophosphatidic acid receptor-3 by 12-O-tetradecanoylphorbol-13-acetate stimulates cell migration of rat liver cells. Cancer Lett 309:236–242
Inoue S, Tanabe E, Shibata A, Hirane M, Araki M, Dong Y, Fukushima N, Tsujiuchi T (2013) Ethionine regulates cell motile activity through LPA receptor-3 in liver epithelial WB-F344 cells. Mol Cell Biochem 383:173–177
Tanabe E, Shibata A, Inoue S, Kitayoshi M, Fukushima N, Tsujiuchi T (2012) Regulation of cell motile activity through the different induction of LPA receptors by estrogens in liver epithelial WB-F344 cells. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 428:105–109
Shano S, Hatanaka K, Ninose S, Moriyama R, Tsujiuchi T, Fukushima N (2008) A Lysophosphatidic acid receptor lacking the PDZ-binding domain is constitutively active and stimulates cell proliferation. Biochim Biophys Acta 1783:748–759
Barbayianni E, Magrioti V, Moutevelis-Minakakis P, Kokotos G (2013) Autotaxin inhibitors: a patent review. Expert Opin Ther Pat 23:1123–1132
Aoki J, Inoue A, Okudaira S (2008) Two pathway for lysophosphatidic acid production. Biochim Biophys Acta 1781:513–518
Hayashi M, Okabe K, Kato K, Okumura M, Fukui R, Fukushima N, Tsujiuchi T (2012) Differential function of lysophosphatidic acid receptors in cell proliferation and migration of neuroblastoma cells. Cancer Lett 316:91–96
Samadi N, Bekele R, Capatos D, Venkatraman G, Sariahmetoglu M, Brindley DN (2011) Regulation of lysophosphatidate signaling by autotaxin and lipid phosphate phosphatases with respect to tumor progression, angiogenesis, metastasis and chemo-resistance. Biochimie 93:61–70
Brindley DN, Lin F-T, Tigyi GJ (2013) Role of the autotaxin-lysophosphatidate axis in cancer resistance to chemotherapy and radiotherapy. Biochim Biophys Acta 1831:74–85
Panupinthu N, Lee HY, Mills GB (2010) Lysophosphatidic acid production and action: critical new players in breast cancer initiation and progression. Br J Cancer 102:941–946
Shida D, Kitayama J, Yanaguchi H, Okaji Y, Tsuno NH, Watanabe T, Takuwa Y, Nagawa H (2003) Lysophosphatidic acid (LPA) enhances the metastatic potential of human colon carcinoma DLD1 cells through LPA1. Cancer Res 63:1706–1711
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by JSPS KAKENHI Grant Number 24590493 and by Grants from the Faculty of Science and Engineering, Kinki University.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
None declared.
Additional information
Shiori Mori and Mutsumi Araki have contributed equally to this work.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Mori, S., Araki, M., Ishii, S. et al. LPA signaling through LPA receptors regulates cellular functions of endothelial cells treated with anticancer drugs. Mol Cell Biochem 408, 147–154 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11010-015-2490-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11010-015-2490-3