Abstract
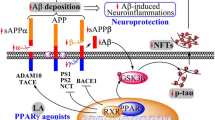
Alzheimer’s disease is a neuroinflammatory disease and is the most common cause of dementia in the elderly. Studies have shown the beneficial effects of the peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor alpha (PPAR-α) agonists on the treatment of neuroinflammatory diseases. The aim of the present study is to examine the ability of GW7647 (a PPAR-α agonist) to regulate amyloid precursor protein (APP) amyloidogenic processing in human neuroblastoma SH-SY5Y cells transfected with APPswe gene. After administration of GW7647 for 24 h, the levels of APP, soluble APPβ (sAPPβ), and presenilin 1 (PS-1) were assessed by Western blot. Cellular culture medium levels of amyloid-β 42 (Aβ42) were analyzed by ELISA, and the activity of beta-site APP cleaving enzyme 1 (BACE-1) was measured by fluorometric assay. We found that GW7647 decreased the expression of sAPPβ and the activity of BACE-1, and also reduced Aβ42 release. However, GW7647 did not modify the levels of APP and PS-1. Furthermore, LY294002, the phosphoinositide 3-kinase (PI3-K) inhibitor, reversed the effects of GW7647 on the BACE-1 activity and the levels of sAPPβ and Aβ42. Our data demonstrate that GW7647 may reduce Aβ production via inhibiting BACE-1 activity, and this may involve in PI3-K pathway.








Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- Aβ:
-
Amyloid-β
- AD:
-
Alzheimer’s disease
- APP:
-
Amyloid precursor protein
- BACE-1:
-
Beta-site amyloid precursor protein cleaving enzyme 1
- PI3-K:
-
Phosphoinositide 3-kinase
- PPAR-α:
-
Peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor alpha
- PS1:
-
Presenilin 1
- sAPPβ:
-
Soluble amyloid precursor protein beta
References
Ferri CP, Prince M, Brayne C, Brodaty H, Fratiglioni L, Ganguli M, Hall K, Hasegawa K, Hendrie H, Huang Y, Jorm A, Mathers C, Menezes PR, Rimmer E, Scazufca M, Alzheimer’s Disease International (2005) Global prevalence of dementia: a Delphi consensus study. Lancet 366:2112–2117
Kalaria RN, Maestre GE, Arizaga R, Friedland RP, Galasko D, Hall K, Luchsinger JA, Ogunniyi A, Perry EK, Potocnik F, Prince M, Stewart R, Wimo A, Zhang ZX, Antuono P, World Federation of Neurology Dementia Research Group (2008) Alzheimer’s disease and vascular dementia in developing countries: prevalence, management, and risk factors. Lancet Neurol 7:812–826
Choi SJ, Cho JH, Im I, Lee SD, Jang JY, Oh YM, Jung YK, Jeon ES, Kim YC (2010) Design and synthesis of 1,4-dihydropyridine derivatives as BACE-1 inhibitors. Eur J Med Chem 45:2578–2590
Klafki HW, Staufenbiel M, Kornhuber J, Wiltfang J (2006) Therapeutic approaches to Alzheimer’s disease. Brain 129:2840–2855
Edwards PD, Albert JS, Sylvester M, Aharony D, Andisik D, Callaghan O, Campbell JB, Carr RA, Chessari G, Congreve M, Frederickson M, Folmer RH, Geschwindner S, Koether G, Kolmodin K, Krumrine J, Mauger RC, Murray CW, Olsson LL, Patel S, Spear N, Tian G (2007) Application of fragment-based lead generation to the discovery of novel, cyclic amidine beta-secretase inhibitors with nanomolar potency, cellular activity, and high ligand efficiency. J Med Chem 50:5912–5925
Aguzzi A, O’Connor T (2010) Protein aggregation diseases: pathogenicity and therapeutic perspectives. Nat Rev Drug Discov 9:237–248
Vassar R, Bennett BD, Babu-Khan S, Kahn S, Mendiaz EA, Denis P, Teplow DB, Ross S, Amarante P, Loeloff R, Luo Y, Fisher S, Fuller J, Edenson S, Lile J, Jarosinski MA, Biere AL, Curran E, Burgess T, Louis JC, Collins F, Treanor J, Rogers G, Citron M (1999) Beta-secretase cleavage of Alzheimer’s amyloid precursor protein by the transmembrane aspartic protease BACE. Science 286:735–741
Wolfe MS, Xia W, Ostaszewski BL, Diehl TS, Kimberly WT, Selkoe DJ (1999) Two transmembrane aspartates in presenilin-1 required for presenilin endoproteolysis and gamma-secretase activity. Nature 398:513–517
Selkoe DJ (2001) Alzheimer’s disease: genes, proteins, and therapy. Physiol Rev 81:741–766
Sinha S, Anderson JP, Barbour R, Basi GS, Caccavello R, Davis D, Doan M, Dovey HF, Frigon N, Hong J, Jacobson-Croak K, Jewett N, Keim P, Knops J, Lieberburg I, Power M, Tan H, Tatsuno G, Tung J, Schenk D, Seubert P, Suomensaari SM, Wang S, Walker D, Zhao J, McConlogue L, John V (1999) Purification and cloning of amyloid precursor protein beta-secretase from human brain. Nature 402:537–540
Yan R, Bienkowski MJ, Shuck ME, Miao H, Tory MC, Pauley AM, Brashier JR, Stratman NC, Mathews WR, Buhl AE, Carter DB, Tomasselli AG, Parodi LA, Heinrikson RL, Gurney ME (1999) Membrane-anchored aspartyl protease with Alzheimer’s disease beta-secretase activity. Nature 402:533–537
Bodendorf U, Danner S, Fischer F, Stefani M, Sturchler-Pierrat C, Wiederhold KH, Staufenbiel M, Paganetti P (2002) Expression of human beta-secretase in the mouse brain increases the steady-state level of beta-amyloid. J Neurochem 80:799–806
Panahi N, Mahmoudian M, Mortazavi P, Hashjin GS (2013) Effects of berberine on beta-secretase activity in a rabbit model of Alzheimer’s disease. Arch Med Sci. 9:146–150
Lee KC, Lee Kraus W (2001) Nuclear receptors, coactivators and chromatin: new approaches, new insights. Trends Endocrinol Metab 12:191–197
Vamecq J, Latruffe N (1999) Medical significance of peroxisome proliferator-activated receptors. Lancet 354:141–148
Rosen ED, Spiegelman BM (2001) PPARgamma: a nuclear regulator of metabolism, differentiation, and cell growth. J Biol Chem 276:37731–37734
Francis GA, Fayard E, Picard F, Auwerx J (2003) Nuclear receptors and the control of metabolism. Annu Rev Physiol 2003(65):261–311
Hiukka A, Maranghi M, Matikainen N, Taskinen MR (2010) PPARalpha: an emerging therapeutic target in diabetic microvascular damage. Nat Rev Endocrinol 6:454–463
Longo FM, Massa SM (2004) Neuroprotective strategies in Alzheimer’s disease. NeuroRx 1:117–127
Khan TK, Alkon DL (2006) An internally controlled peripheral biomarker for Alzheimer’s disease: Erk1 and Erk2 responses to the inflammatory signal bradykinin. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 103:13203–13207
Murakami K, Tobe K, Ide T, Mochizuki T, Ohashi M, Akanuma Y, Yazaki Y, Kadowaki T (1998) A novel insulin sensitizer acts as a coligand for peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor-alpha (PPAR-alpha) and PPAR-gamma: effect of PPAR-alpha activation on abnormal lipid metabolism in liver of Zucker fatty rats. Diabetes 47:1841–1847
Heneka MT, Sastre M, Dumitrescu-Ozimek L, Hanke A, Dewachter I, Kuiperi C, O’Banion K, Klockgether T, Van Leuven F, Landreth GE (2005) Acute treatment with the PPARgamma agonist pioglitazone and ibuprofen reduces glial inflammation and Abeta1-42 levels in APPV717I transgenic mice. Brain 128:1442–1453
Hirohata M, Ono K, Naiki H, Yamada M (2005) Non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs have anti-amyloidogenic effects for Alzheimer’s beta-amyloid fibrils in vitro. Neuropharmacology 49:1088–1099
Combs CK, Bates P, Karlo JC, Landreth GE (2001) Regulation of beta-amyloid stimulated proinflammatory responses by peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor alpha. Neurochem Int 39:449–457
Heun R, Kölsch H, Ibrahim-Verbaas CA, Combarros O, Aulchenko YS, Breteler M, Schuur M, van Duijn CM, Hammond N, Belbin O, Cortina-Borja M, Wilcock GK, Brown K, Barber R, Kehoe PG, Coto E, Alvarez V, Lehmann MG, Deloukas P, Mateo I, Morgan K, Warden DR, Smith AD, Lehmann DJ (2012) Interactions between PPAR-alpha and inflammation-related cytokine genes on the development of Alzheimer’s disease, observed by the Epistasis Project. Int J Mol Epidemiol Genet 3:39–47
Solano DC, Sironi M, Bonfini C, Solerte SB, Govoni S, Racchi M (2000) Insulin regulates soluble amyloid precursor protein release via phosphatidyl inositol 3 kinase-dependent pathway. FASEB J 14:1015–1022
Zhao L, Yao J, Mao Z, Chen S, Wang Y, Brinton RD (2011) 17β-Estradiol regulates insulin-degrading enzyme expression via an ERβ/PI3-K pathway in hippocampus: relevance to Alzheimer’s prevention. Neurobiol Aging 32:1949–1963
Kaur P, Jodhka PK, Underwood WA, Bowles CA, de Fiebre NC, de Fiebre CM, Singh M (2007) Progesterone increases brain-derived neuroptrophic factor expression and protects against glutamate toxicity in a mitogen-activated protein kinase- and phosphoinositide-3 kinase-dependent manner in cerebral cortical explants. J Neurosci Res 85:2441–2449
Tong L, Balazs R, Soiampornkul R, Thangnipon W, Cotman CW (2008) Interleukin-1 beta impairs brain derived neurotrophic factor-induced signal transduction. Neurobiol Aging 29:1380–1393
Koo JH, Kwon IS, Kang EB, Lee CK, Lee NH, Kwon MG, Cho IH, Cho JY (2013) Neuroprotective effects of treadmill exercise on BDNF and PI3-K/Akt signaling pathway in the cortex of transgenic mice model of Alzheimer’s disease. J Exerc Nutr Biochem 17:151–160
Kummer MP, Heneka MT (2008) PPARs in Alzheimer’s disease. PPAR Res 2008:403896
Watson GS, Cholerton BA, Reger MA, Baker LD, Plymate SR, Asthana S, Fishel MA, Kulstad JJ, Green PS, Cook DG, Kahn SE, Keeling ML, Craft S (2005) Preserved cognition in patients with early Alzheimer disease and amnestic mild cognitive impairment during treatment with rosiglitazone: a preliminary study. Am J Geriatr Psychiatry 13:950–958
Inestrosa NC, Carvajal FJ, Zolezzi JM, Tapia-Rojas C, Serrano F, Karmelic D, Toledo EM, Toro A, Toro J, Santos MJ (2013) Peroxisome proliferators reduce spatial memory impairment, synaptic failure, and neurodegeneration in brains of a double transgenic mice model of Alzheimer’s disease. J Alzheimers Dis 33:941–959
Bright JJ, Kanakasabai S, Chearwae W, Chakraborty S (2008) PPAR regulation of inflammatory signaling in CNS diseases. PPAR Res 2008:658520
Edbauer D, Winkler E, Regula JT, Pesold B, Steiner H, Haass C (2003) Reconstitution of gamma-secretase activity. Nat Cell Biol 5:486–488
Harmeier A, Wozny C, Rost BR, Munter LM, Hua H, Georgiev O, Beyermann M, Hildebrand PW, Weise C, Schaffner W, Schmitz D, Multhaup G (2009) Role of amyloid-beta glycine 33 in oligomerization, toxicity, and neuronal plasticity. J Neurosci 29:7582–7590
Walsh DM, Klyubin I, Shankar GM, Townsend M, Fadeeva JV, Betts V, Podlisny MB, Cleary JP, Ashe KH, Rowan MJ, Selkoe DJ (2005) The role of cell-derived oligomers of Abeta in Alzheimer’s disease and avenues for therapeutic intervention. Biochem Soc Trans 33:1087–1090
Klyubin I, Betts V, Welzel AT, Blennow K, Zetterberg H, Wallin A, Lemere CA, Cullen WK, Peng Y, Wisniewski T, Selkoe DJ, Anwyl R, Walsh DM, Rowan MJ (2008) Amyloid beta protein dimer-containing human CSF disrupts synaptic plasticity: prevention by systemic passive immunization. J Neurosci 28:4231–4237
Shankar GM, Li S, Mehta TH, Garcia-Munoz A, Shepardson NE, Smith I, Brett FM, Farrell MA, Rowan MJ, Lemere CA, Regan CM, Walsh DM, Sabatini BL, Selkoe DJ (2008) Amyloid-beta protein dimers isolated directly from Alzheimer’s brains impair synaptic plasticity and memory. Nat Med 14:837–842
Bao XQ, Li N, Wang T, Kong XC, Tai WJ, Sun H, Zhang D (2013) FLZ alleviates the memory deficits in transgenic mouse model of Alzheimer’s disease via decreasing beta-amyloid production and tau hyperphosphorylation. PLoS One 8:e78033
Herskowitz JH, Feng Y, Mattheyses AL, Hales CM, Higginbotham LA, Duong DM, Montine TJ, Troncoso JC, Thambisetty M, Seyfried NT, Levey AI, Lah JJ (2013) Pharmacologic inhibition of ROCK2 suppresses amyloid-beta production in an Alzheimer’s disease mouse model. J Neurosci 33:19086–19098
Mecozzi VJ, Berman DE, Simoes S, Vetanovetz C, Awal MR, Patel VM, Schneider RT, Petsko GA, Ringe D, Small SA (2014) Pharmacological chaperones stabilize retromer to limit APP processing. Nat Chem Biol 10:443–449
Acknowledgments
This study was supported by the Science and Technology Research Project of Chongqing Municipal Education Commission (KJ1400227).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interests
The authors have no competing interests to declare.
Human and animal rights and informed consent
This research does not involve human participants and/or animals, and there is not informed consent.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhang, H., Gao, Y., Qiao, Pf. et al. PPAR-α agonist regulates amyloid-β generation via inhibiting BACE-1 activity in human neuroblastoma SH-SY5Y cells transfected with APPswe gene. Mol Cell Biochem 408, 37–46 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11010-015-2480-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11010-015-2480-5